Japanese nuclear plant operator fabricated seismic risk data
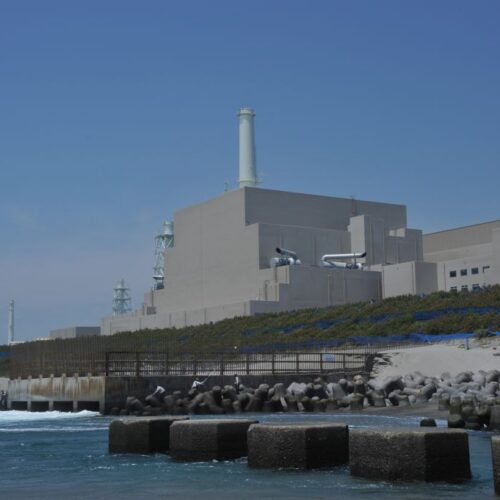
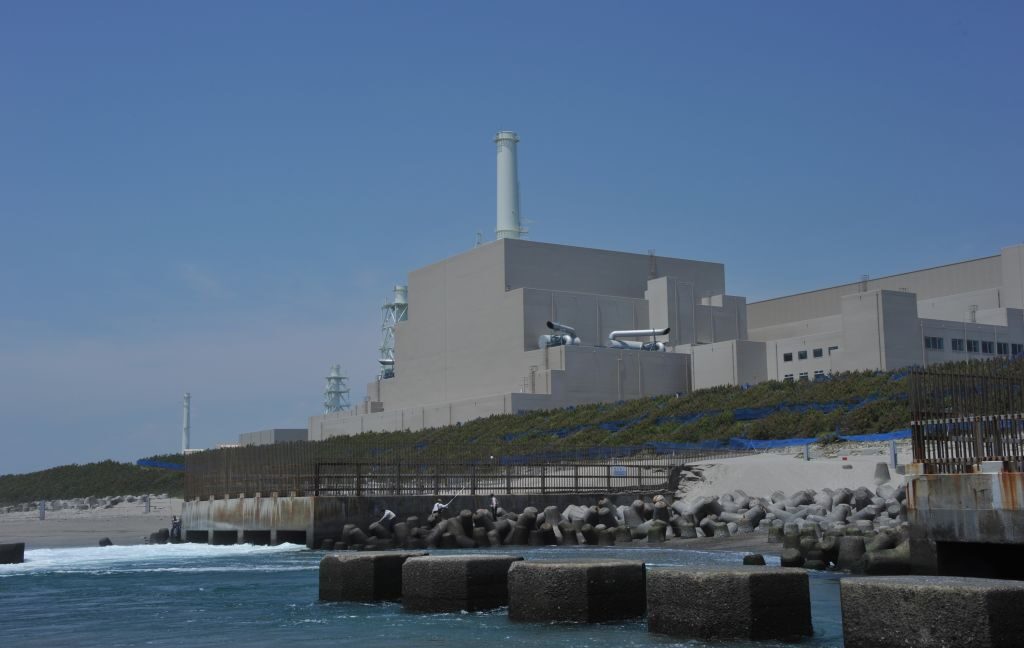
On Wednesday, Japan's Nuclear Regulation Authority announced that it is halting the relicensing process for two reactors at the Hamaoka plant after revelations that the plant's chosen operator fabricated seismic hazard data. Japan has been slowly reactivating its extensive nuclear power plant collection after it was shut down following the Fukushima Daiichi disaster. The latest scandal is especially shocking, given that the Hamaoka plant is located on the coast near an active subduction fault—just as Fukushima Daiichi is.
A whistleblower reportedly alerted the Nuclear Regulation Authority in February of last year, but the issue became public this week when the regulators halted an evaluation process that could have led to a reactor restart at Hamaoka. This prompted the company that operates the plants, the Chubu Electric Power Co., to issue a press release describing in detail how the company manipulated the seismic safety data.
Based on an English translation, it appears that seismic risks were evaluated at least in part by scaling up the ground motion using data from smaller earthquakes. This is an inexact process, so the standard approach is to create a group of 20 different upscaled earthquake motions and find the one that best represents the average among the 20.


© Kasahara KATSUMI