Did Edison accidentally make graphene in 1879?
Graphene is the thinnest material yet known, composed of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. That structure gives it many unusual properties that hold great promise for real-world applications: batteries, super capacitors, antennas, water filters, transistors, solar cells, and touchscreens, just to name a few. The physicists who first synthesized graphene in the lab won the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physics. But 19th century inventor Thomas Edison may have unknowingly created graphene as a byproduct of his original experiments on incandescent bulbs over a century earlier, according to a new paper published in the journal ACS Nano.
“To reproduce what Thomas Edison did, with the tools and knowledge we have now, is very exciting,” said co-author James Tour, a chemist at Rice University. “Finding that he could have produced graphene inspires curiosity about what other information lies buried in historical experiments. What questions would our scientific forefathers ask if they could join us in the lab today? What questions can we answer when we revisit their work through a modern lens?”
Edison didn't invent the concept of incandescent lamps; there were several versions predating his efforts. However, they generally had a a very short life span and required high electric current, so they weren't well suited to Edison's vision of large-scale commercialization. He experimented with different filament materials starting with carbonized cardboard and compressed lampblack. This, too, quickly burnt out, as did filaments made with various grasses and canes, like hemp and palmetto. Eventually Edison discovered that carbonized bamboo made for the best filament, with life spans over 1200 hours using a 110 volt power source.
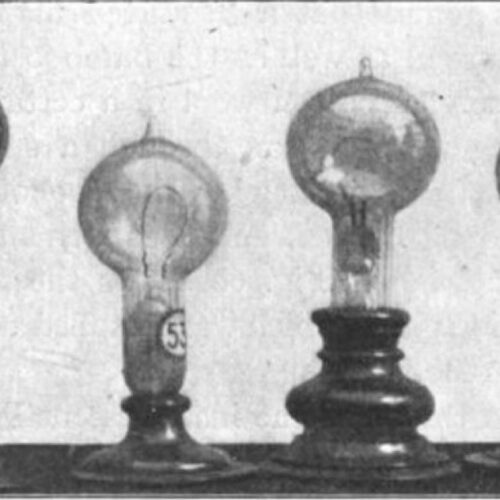
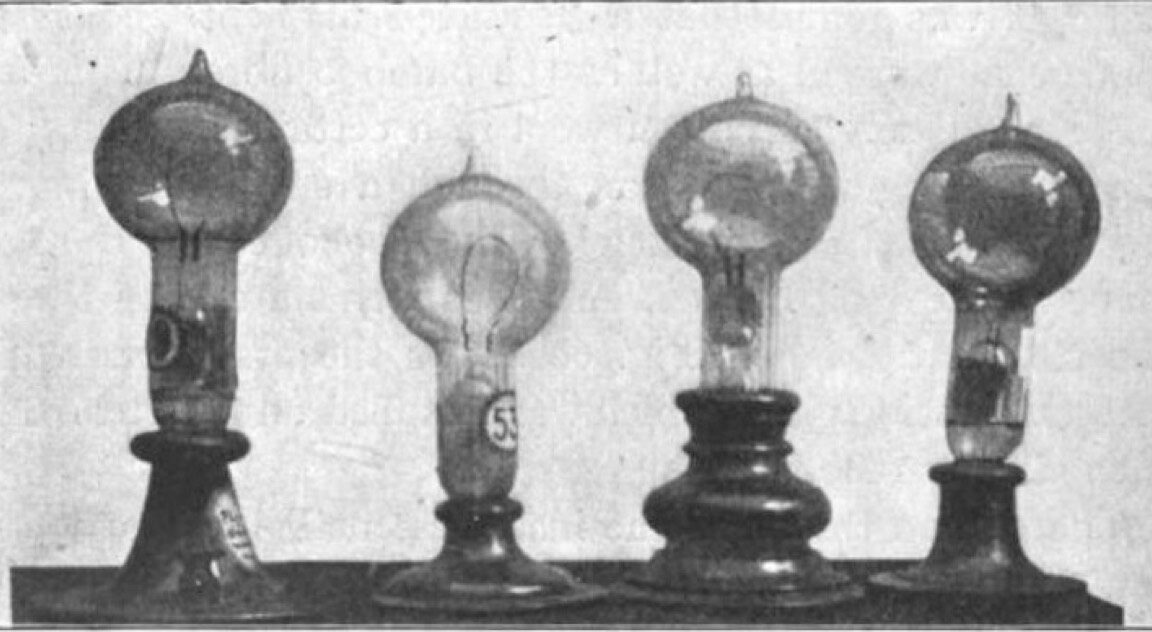


© Public domain


























 Credit:
Credit:



