New trends in phishing and scams: how AI and social media are changing the game

Introduction
Phishing and scams are dynamic types of online fraud that primarily target individuals, with cybercriminals constantly adapting their tactics to deceive people. Scammers invent new methods and improve old ones, adjusting them to fit current news, trends, and major world events: anything to lure in their next victim.
Since our last publication on phishing tactics, there has been a significant leap in the evolution of these threats. While many of the tools we previously described are still relevant, new techniques have emerged, and the goals and methods of these attacks have shifted.
In this article, we will explore:
- The impact of AI on phishing and scams
- How the tools used by cybercriminals have changed
- The role of messaging apps in spreading threats
- Types of data that are now a priority for scammers
AI tools leveraged to create scam content
Text
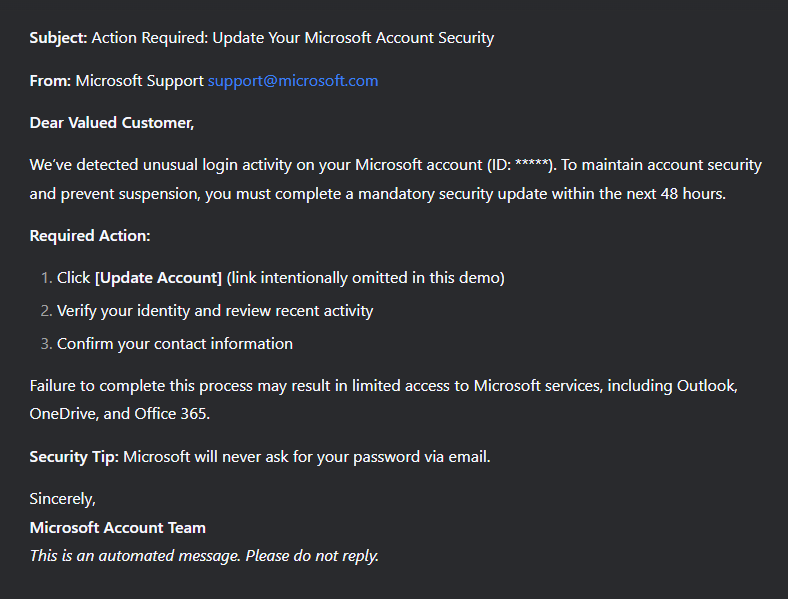
Traditional phishing emails, instant messages, and fake websites often contain grammatical and factual errors, incorrect names and addresses, and formatting issues. Now, however, cybercriminals are increasingly turning to neural networks for help.
They use these tools to create highly convincing messages that closely resemble legitimate ones. Victims are more likely to trust these messages, and therefore, more inclined to click a phishing link, open a malicious attachment, or download an infected file.
The same is true for personal messages. Social networks are full of AI bots that can maintain conversations just like real people. While these bots can be created for legitimate purposes, they are often used by scammers who impersonate human users. In particular, phishing and scam bots are common in the online dating world. Scammers can run many conversations at once, maintaining the illusion of sincere interest and emotional connection. Their primary goal is to extract money from victims by persuading them to pursue “viable investment opportunities” that often involve cryptocurrency. This scam is known as pig butchering. AI bots are not limited to text communication, either; to be more convincing, they also generate plausible audio messages and visual imagery during video calls.
Deepfakes and AI-generated voices
As mentioned above, attackers are actively using AI capabilities like voice cloning and realistic video generation to create convincing audiovisual content that can deceive victims.
Beyond targeted attacks that mimic the voices and images of friends or colleagues, deepfake technology is now being used in more classic, large-scale scams, such as fake giveaways from celebrities. For example, YouTube users have encountered Shorts where famous actors, influencers, or public figures seemingly promise expensive prizes like MacBooks, iPhones, or large sums of money.
The advancement of AI technology for creating deepfakes is blurring the lines between reality and deception. Voice and visual forgeries can be nearly indistinguishable from authentic messages, as traditional cues used to spot fraud disappear.
Recently, automated calls have become widespread. Scammers use AI-generated voices and number spoofing to impersonate bank security services. During these calls, they claim there has been an unauthorized attempt to access the victim’s bank account. Under the guise of “protecting funds”, they demand a one-time SMS code. This is actually a 2FA code for logging into the victim’s account or authorizing a fraudulent transaction.
Data harvesting and analysis
Large language models like ChatGPT are well-known for their ability to not only write grammatically correct text in various languages but also to quickly analyze open-source data from media outlets, corporate websites, and social media. Threat actors are actively using specialized AI-powered OSINT tools to collect and process this information.
The data so harvested enables them to launch phishing attacks that are highly tailored to a specific victim or a group of victims – for example, members of a particular social media community. Common scenarios include:
- Personalized emails or instant messages from what appear to be HR staff or company leadership. These communications contain specific details about internal organizational processes.
- Spoofed calls, including video chats, from close contacts. The calls leverage personal information that the victim would assume could not be known to an outsider.
This level of personalization dramatically increases the effectiveness of social engineering, making it difficult for even tech-savvy users to spot these targeted scams.
Phishing websites
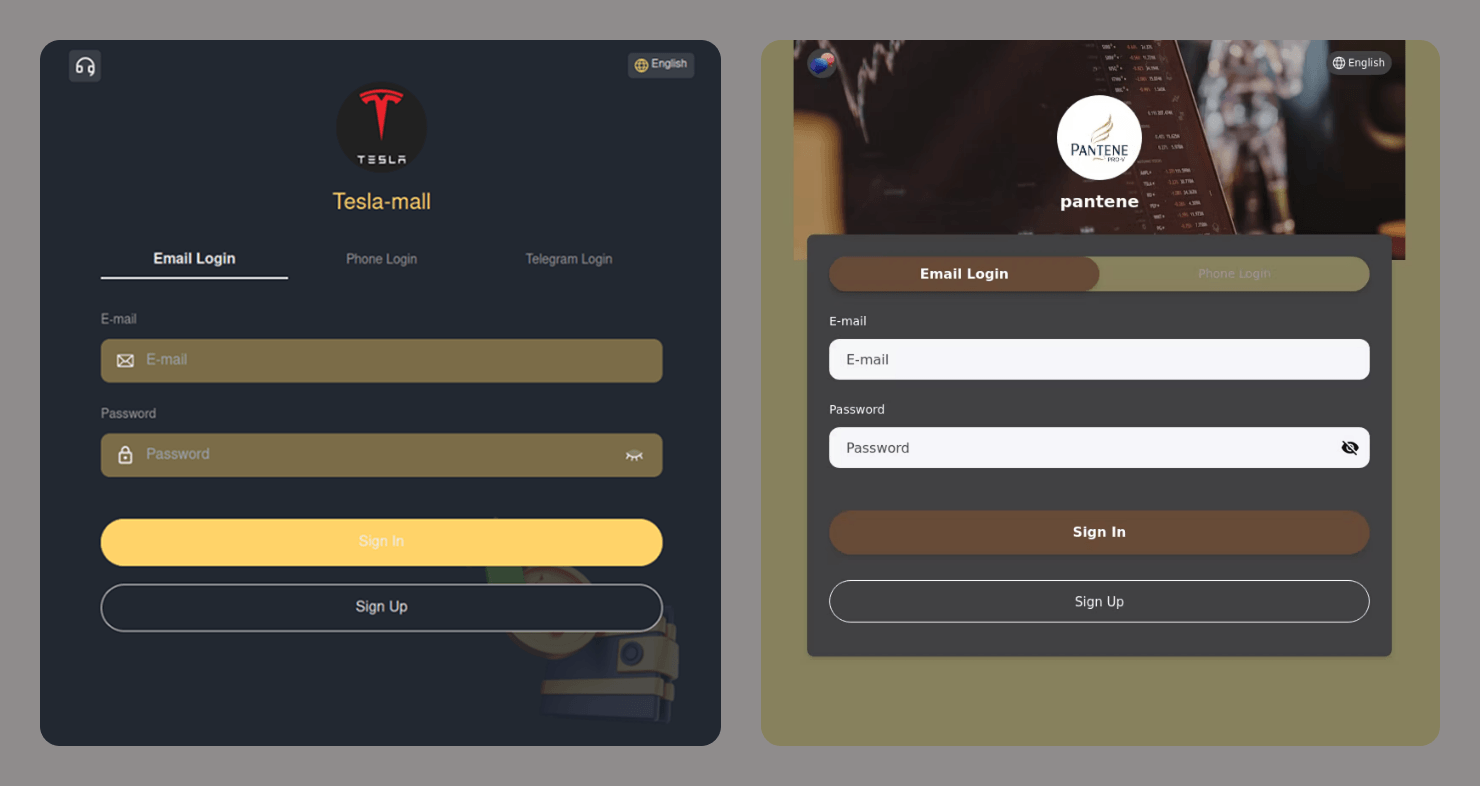
Phishers are now using AI to generate fake websites too. Cybercriminals have weaponized AI-powered website builders that can automatically copy the design of legitimate websites, generate responsive interfaces, and create sign-in forms.
Some of these sites are well-made clones nearly indistinguishable from the real ones. Others are generic templates used in large-scale campaigns, without much effort to mimic the original.
Often, these generic sites collect any data a user enters and are not even checked by a human before being used in an attack. The following are examples of sites with sign-in forms that do not match the original interfaces at all. These are not even “clones” in the traditional sense, as some of the brands being targeted do not offer sign-in pages.
These types of attacks lower the barrier to entry for cybercriminals and make large-scale phishing campaigns even more widespread.
Telegram scams
With its massive popularity, open API, and support for crypto payments, Telegram has become a go-to platform for cybercriminals. This messaging app is now both a breeding ground for spreading threats and a target in itself. Once they get their hands on a Telegram account, scammers can either leverage it to launch attacks on other users or sell it on the dark web.
Malicious bots
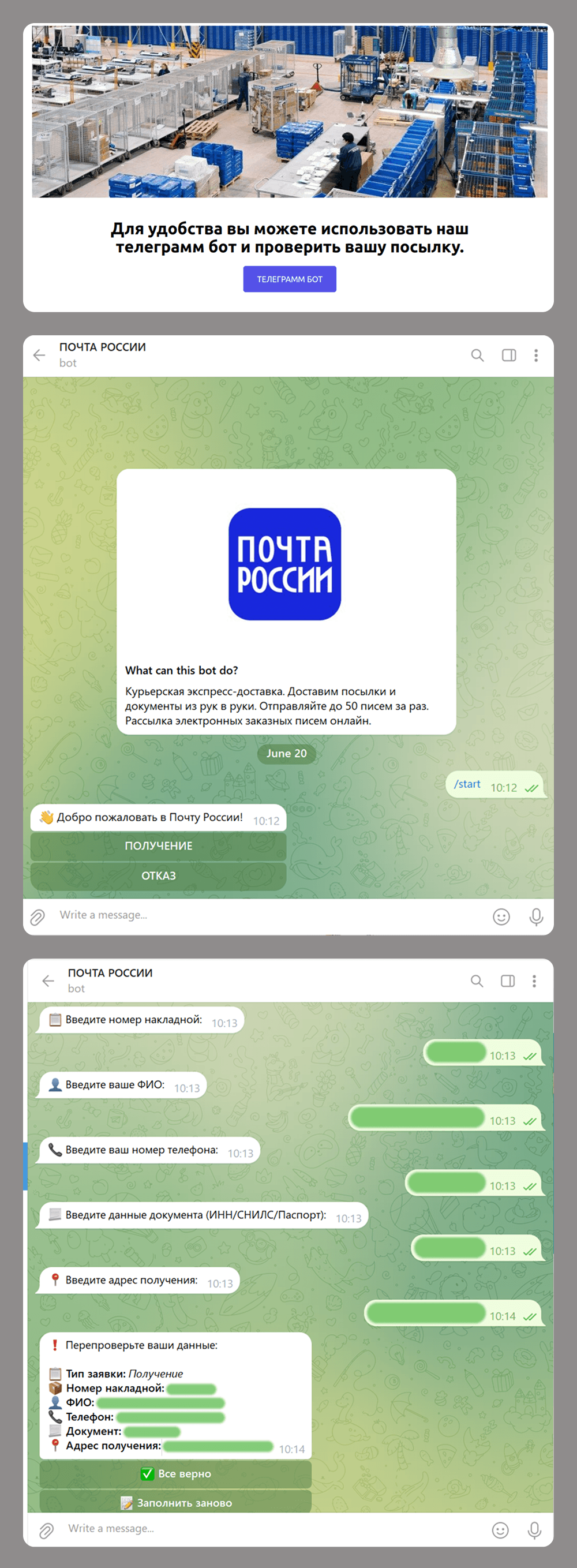
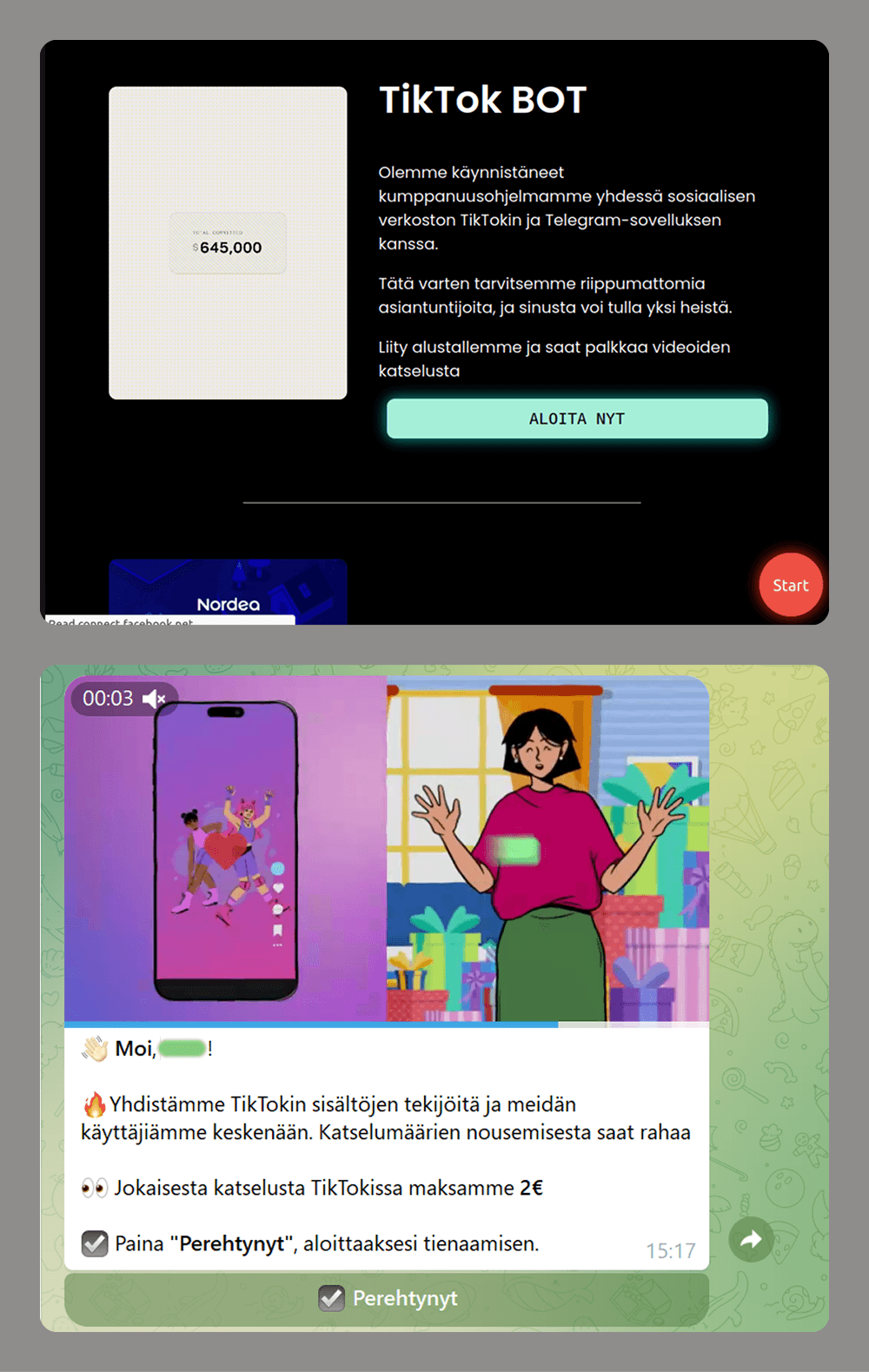
Scammers are increasingly using Telegram bots, not just for creating phishing websites but also as an alternative or complement to these. For example, a website might be used to redirect a victim to a bot, which then collects the data the scammers need. Here are some common schemes that use bots:
- Crypto investment scams: fake token airdrops that require a mandatory deposit for KYC verification
- Phishing and data collection: scammers impersonate official postal service to get a user’s details under the pretense of arranging delivery for a business package.
- Easy money scams: users are offered money to watch short videos.
Unlike a phishing website that the user can simply close and forget about when faced with a request for too much data or a commission payment, a malicious bot can be much more persistent. If the victim has interacted with a bot and has not blocked it, the bot can continue to send various messages. These might include suspicious links leading to fraudulent or advertising pages, or requests to be granted admin access to groups or channels. The latter is often framed as being necessary to “activate advanced features”. If the user gives the bot these permissions, it can then spam all the members of these groups or channels.
Account theft
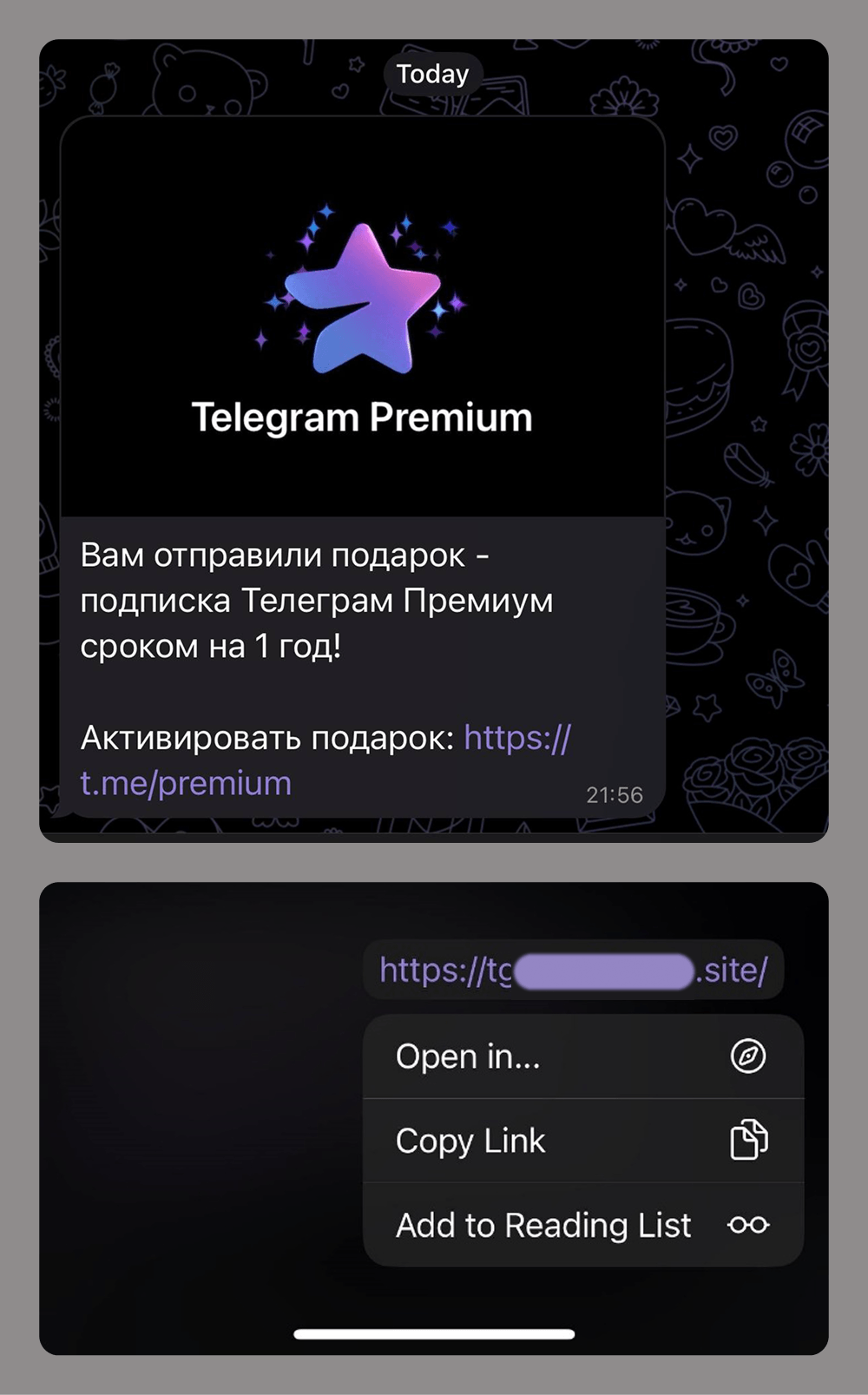
When it comes to stealing Telegram user accounts, social engineering is the most common tactic. Attackers use various tricks and ploys, often tailored to the current season, events, trends, or the age of their target demographic. The goal is always the same: to trick victims into clicking a link and entering the verification code.
Links to phishing pages can be sent in private messages or posted to group chats or compromised channels. Given the scale of these attacks and users’ growing awareness of scams within the messaging app, attackers now often disguise these phishing links using Telegram’s message-editing tools.
New ways to evade detection
Integrating with legitimate services
Scammers are actively abusing trusted platforms to keep their phishing resources under the radar for as long as possible.
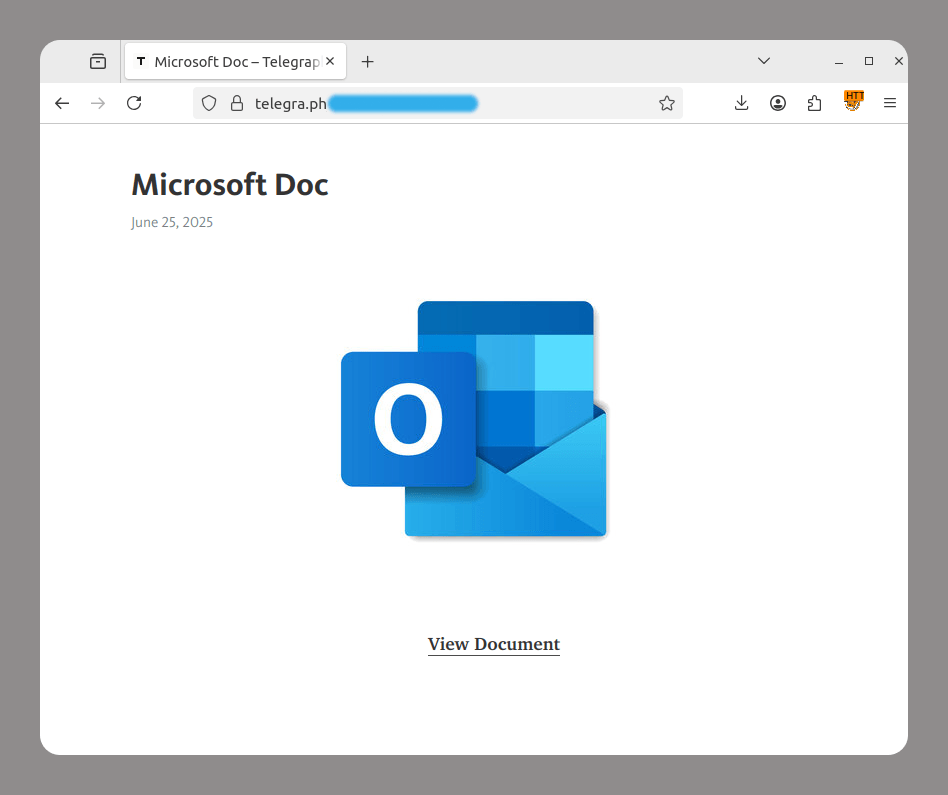
- Telegraph is a Telegram-operated service that lets anyone publish long-form content without prior registration. Cybercriminals take advantage of this feature to redirect users to phishing pages.
- Google Translate is a machine translation tool from Google that can translate entire web pages and generate links like https://site-to-translate-com.translate.goog/… Attackers exploit it to hide their assets from security vendors. They create phishing pages, translate them, and then send out the links to the localized pages. This allows them to both avoid blocking and use a subdomain at the beginning of the link that mimics a legitimate organization’s domain name, which can trick users.
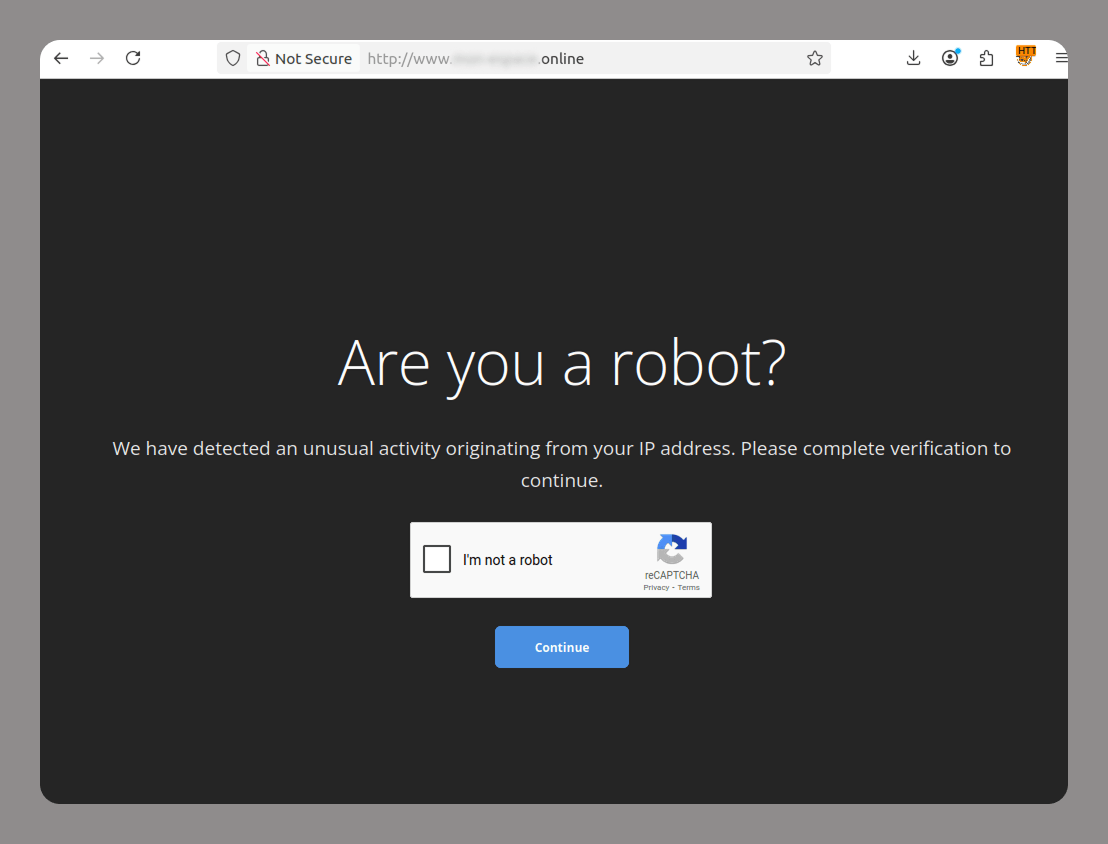
- CAPTCHA protects websites from bots. Lately, attackers have been increasingly adding CAPTCHAs to their fraudulent sites to avoid being flagged by anti-phishing solutions and evade blocking. Since many legitimate websites also use various types of CAPTCHAs, phishing sites cannot be identified by their use of CAPTCHA technology alone.
Blob URL
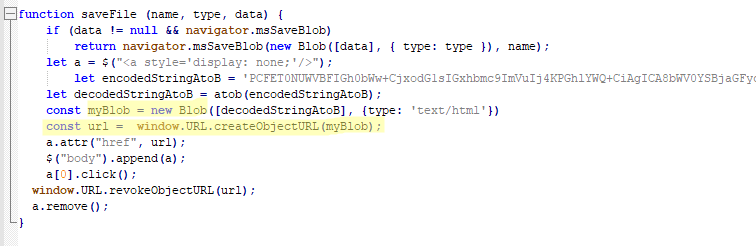
Blob URLs (blob:https://example.com/…) are temporary links generated by browsers to access binary data, such as images and HTML code, locally. They are limited to the current session. While this technology was originally created for legitimate purposes, such as previewing files a user is uploading to a site, cybercriminals are actively using it to hide phishing attacks.
Blob URLs are created with JavaScript. The links start with “blob:” and contain the domain of the website that hosts the script. The data is stored locally in the victim’s browser, not on the attacker’s server.
Hunting for new data
Cybercriminals are shifting their focus from stealing usernames and passwords to obtaining irrevocable or immutable identity data, such as biometrics, digital signatures, handwritten signatures, and voiceprints.
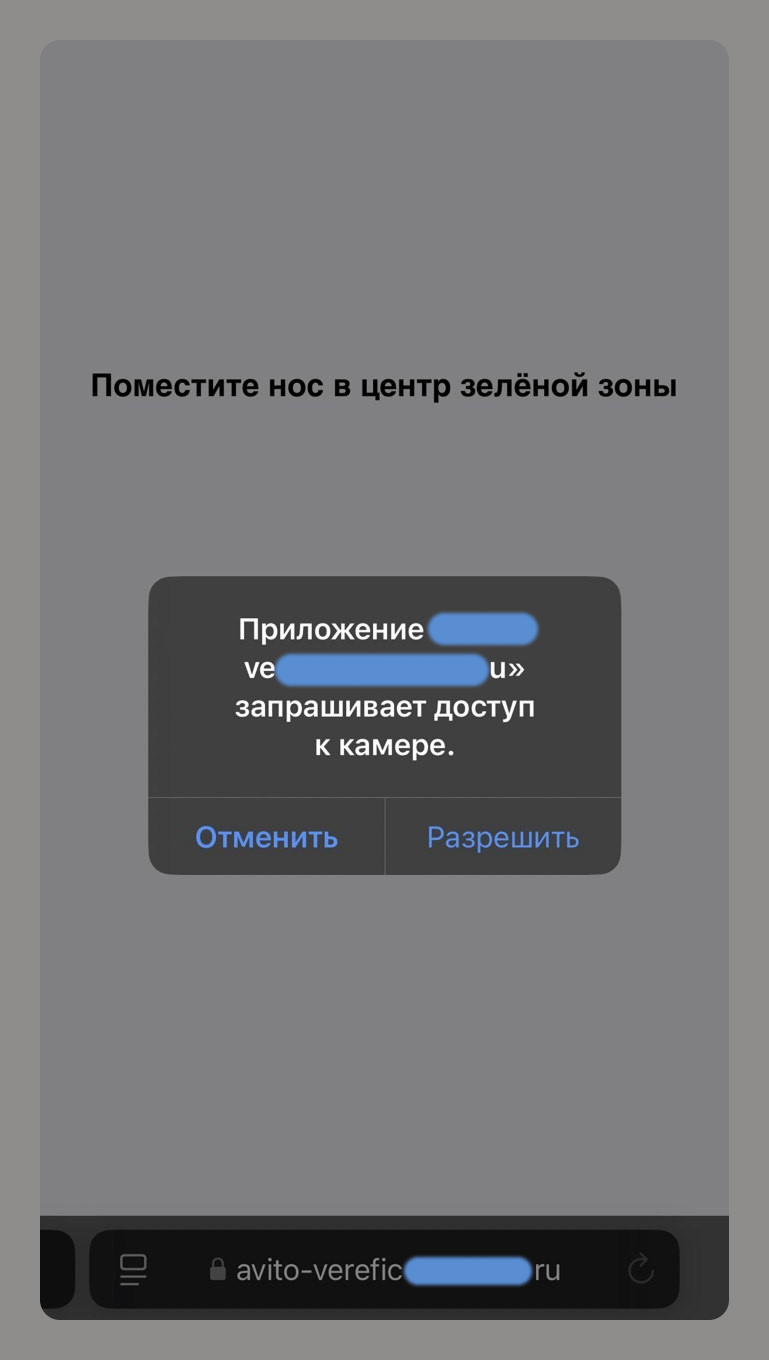
For example, a phishing site that asks for camera access supposedly to verify an account on an online classifieds service allows scammers to collect your biometric data.
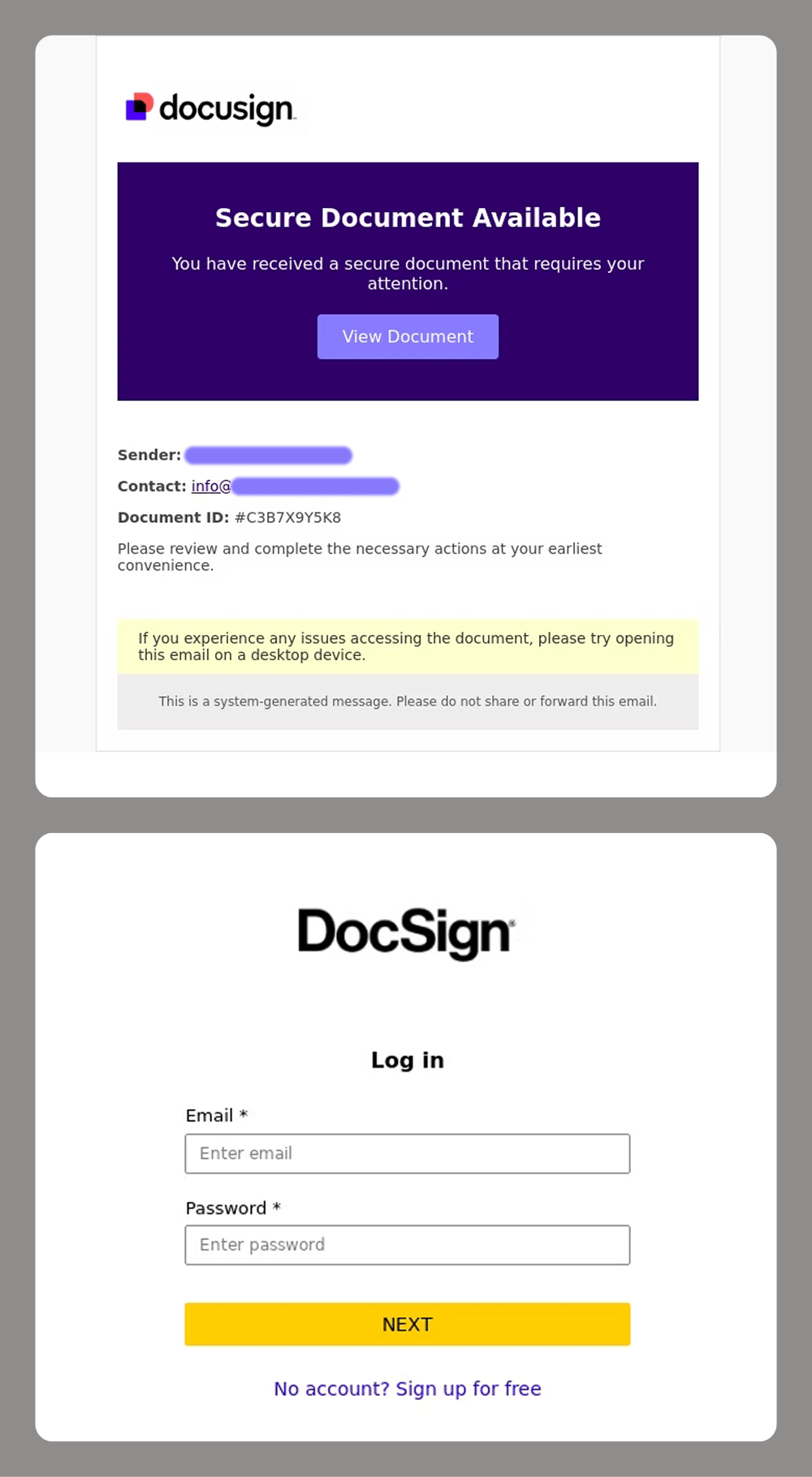
For corporate targets, e-signatures are a major focus for attackers. Losing control of these can cause significant reputational and financial damage to a company. This is why services like DocuSign have become a prime target for spear-phishing attacks.
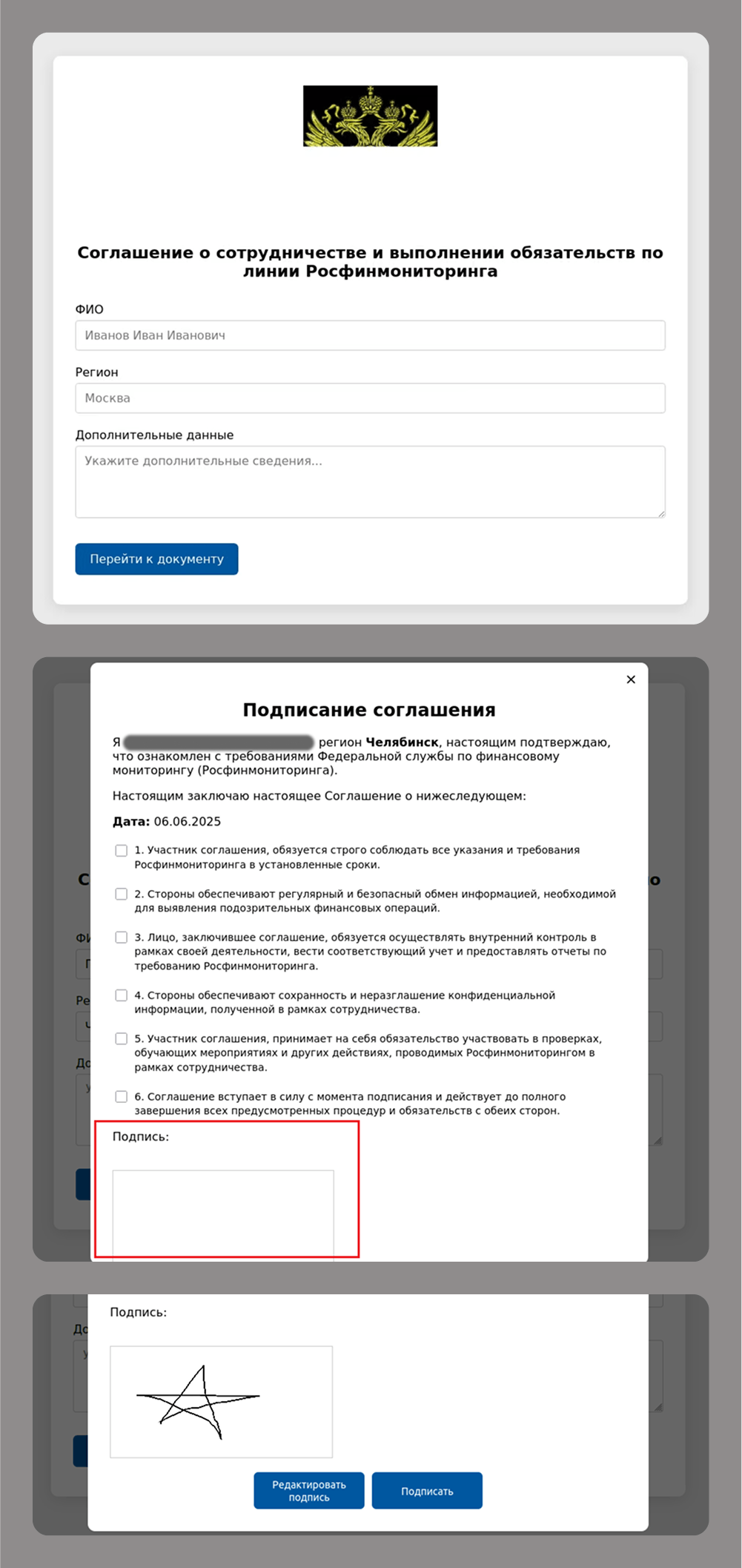
Even old-school handwritten signatures are still a hot commodity for modern cybercriminals, as they remain critical for legal and financial transactions.
These types of attacks often go hand-in-hand with attempts to gain access to e-government, banking and corporate accounts that use this data for authentication.
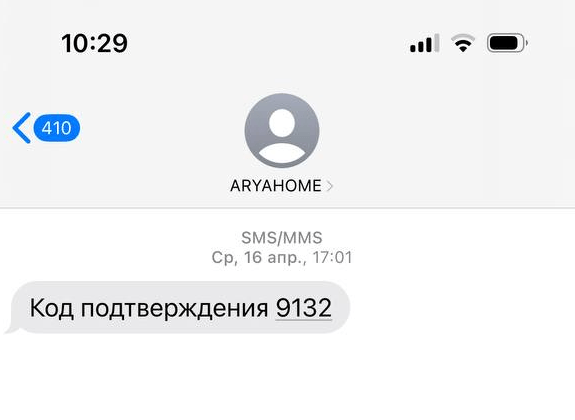
These accounts are typically protected by two-factor authentication, with a one-time password (OTP) sent in a text message or a push notification. The most common way to get an OTP is by tricking users into entering it on a fake sign-in page or by asking for it over the phone.
Attackers know users are now more aware of phishing threats, so they have started to offer “protection” or “help for victims” as a new social engineering technique. For example, a scammer might send a victim a fake text message with a meaningless code. Then, using a believable pretext – like a delivery person dropping off flowers or a package – they trick the victim into sharing that code. Since the message sender indeed looks like a delivery service or a florist, the story may sound convincing. Then a second attacker, posing as a government official, calls the victim with an urgent message, telling them they have just been targeted by a tricky phishing attack. They use threats and intimidation to coerce the victim into revealing a real, legitimate OTP from the service the cybercriminals are actually after.
Takeaways
Phishing and scams are evolving at a rapid pace, fueled by AI and other new technology. As users grow increasingly aware of traditional scams, cybercriminals change their tactics and develop more sophisticated schemes. Whereas they once relied on fake emails and websites, today, scammers use deepfakes, voice cloning and multi-stage tactics to steal biometric data and personal information.
Here are the key trends we are seeing:
- Personalized attacks: AI analyzes social media and corporate data to stage highly convincing phishing attempts.
- Usage of legitimate services: scammers are misusing trusted platforms like Google Translate and Telegraph to bypass security filters.
- Theft of immutable data: biometrics, signatures, and voiceprints are becoming highly sought-after targets.
- More sophisticated methods of circumventing 2FA: cybercriminals are using complex, multi-stage social engineering attacks.
How do you protect yourself?
- Critically evaluate any unexpected calls, emails, or messages. Avoid clicking links in these communications, even if they appear legitimate. If you do plan to open a link, verify its destination by hovering over it on a desktop or long-pressing on a mobile device.
- Verify sources of data requests. Never share OTPs with anyone, regardless of who they claim to be, even if they say they are a bank employee.
- Analyze content for fakery. To spot deepfakes, look for unnatural lip movements or shadows in videos. You should also be suspicious of any videos featuring celebrities who are offering overly generous giveaways.
- Limit your digital footprint. Do not post photos of documents or sensitive work-related information, such as department names or your boss’s name, on social media.