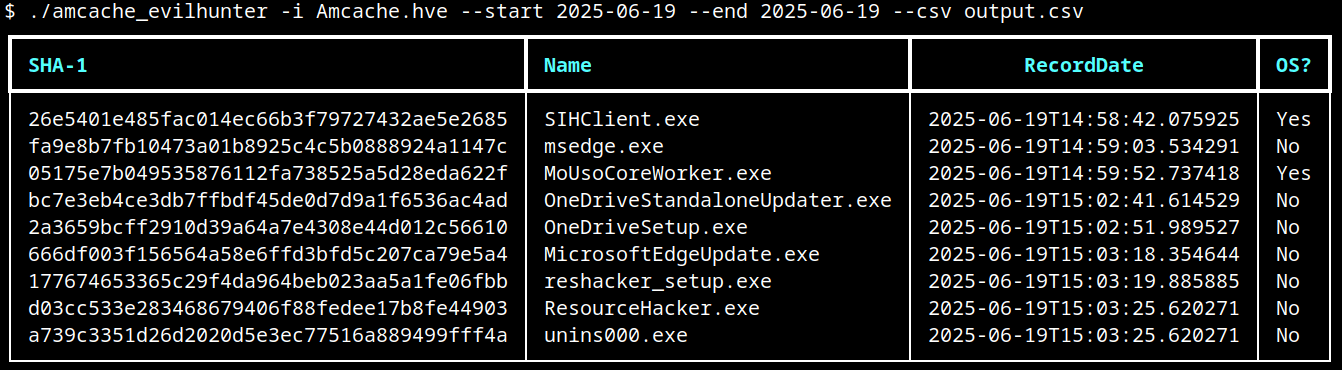
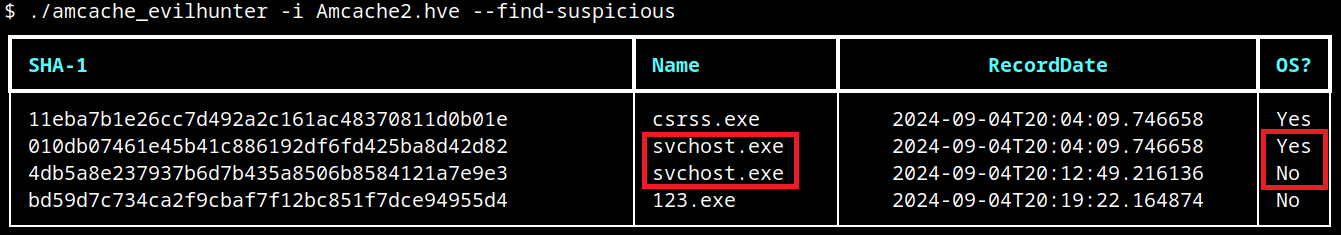
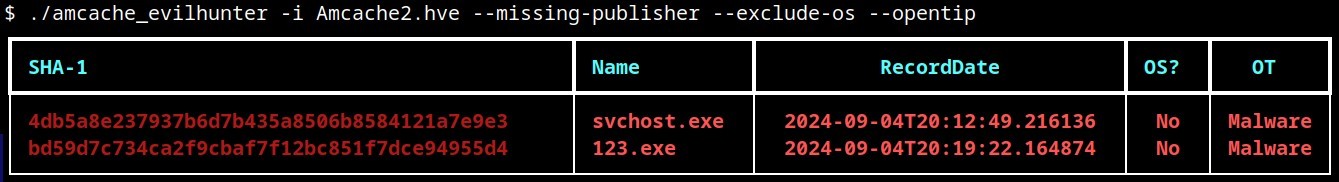
The king is dead, long live the king! Windows 10 EOL and Windows 11 forensic artifacts

Introduction
Windows 11 was released a few years ago, yet it has seen relatively weak enterprise adoption. According to statistics from our Global Emergency Response Team (GERT) investigations, as recently as early 2025, we found that Windows 7, which reached end of support in 2020, was encountered only slightly less often than the newest operating system. Most systems still run Windows 10.
Distribution of Windows versions in organizations’ infrastructure. The statistics are based on the Global Emergency Response Team (GERT) data (download)
The most widely used operating system was released more than a decade ago, and Microsoft discontinues its support on October 14, 2025. This means we are certainly going to see an increase in the number of Windows 11 systems in organizations where we provide incident response services. This is why we decided to offer a brief overview of changes to forensic artifacts in this operating system. The information should be helpful to our colleagues in the field. The artifacts described here are relevant for Windows 11 24H2, which is the latest OS version at the time of writing this.
What is new in Windows 11
Recall
The Recall feature was first introduced in May 2024. It allows the computer to remember everything a user has done on the device over the past few months. It works by taking screenshots of the entire display every few seconds. A local AI engine then analyzes these screenshots in the background, extracting all useful information, which is subsequently saved to a database. This database is then used for intelligent searching. Since May 2025, Recall has been broadly available on computers equipped with an NPU, a dedicated chip for AI computations, which is currently compatible only with ARM CPUs.
Microsoft Recall is certainly one of the most highly publicized and controversial features announced for Windows 11. Since its initial reveal, it has been the subject of criticism within the cybersecurity community because of the potential threat it poses to data privacy. Microsoft refined Recall before its release, yet certain concerns remain. Because of its controversial nature, the option is disabled by default in corporate builds of Windows 11. However, examining the artifacts it creates is worthwhile, just in case an attacker or malicious software activates it. In theory, an organization’s IT department could enable Recall using Group Policies, but we consider that scenario unlikely.
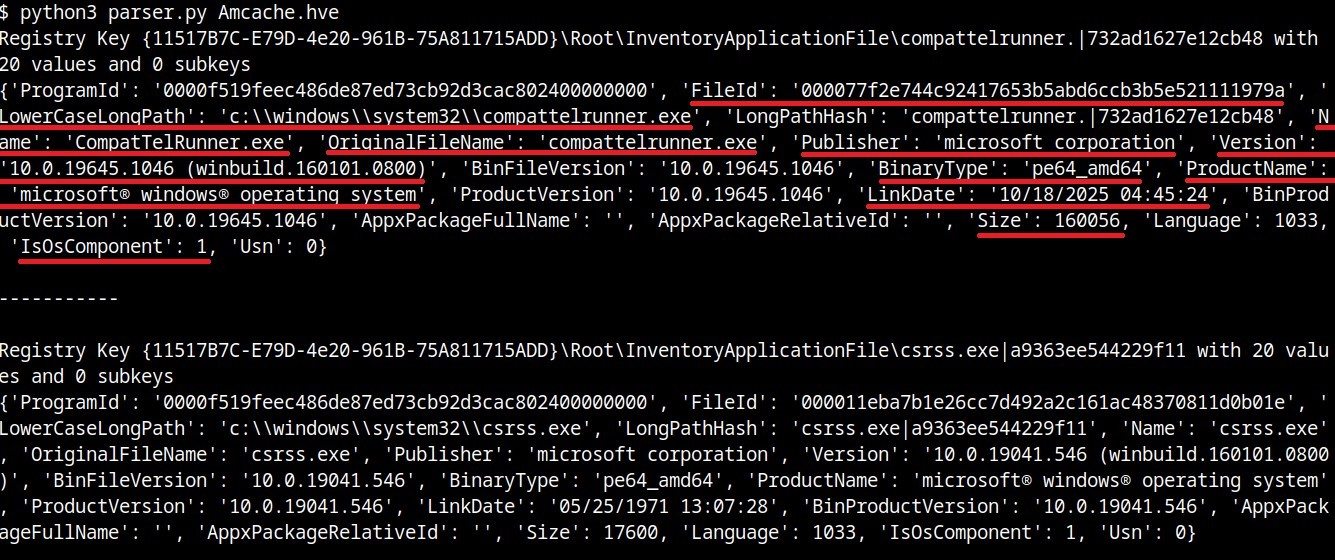
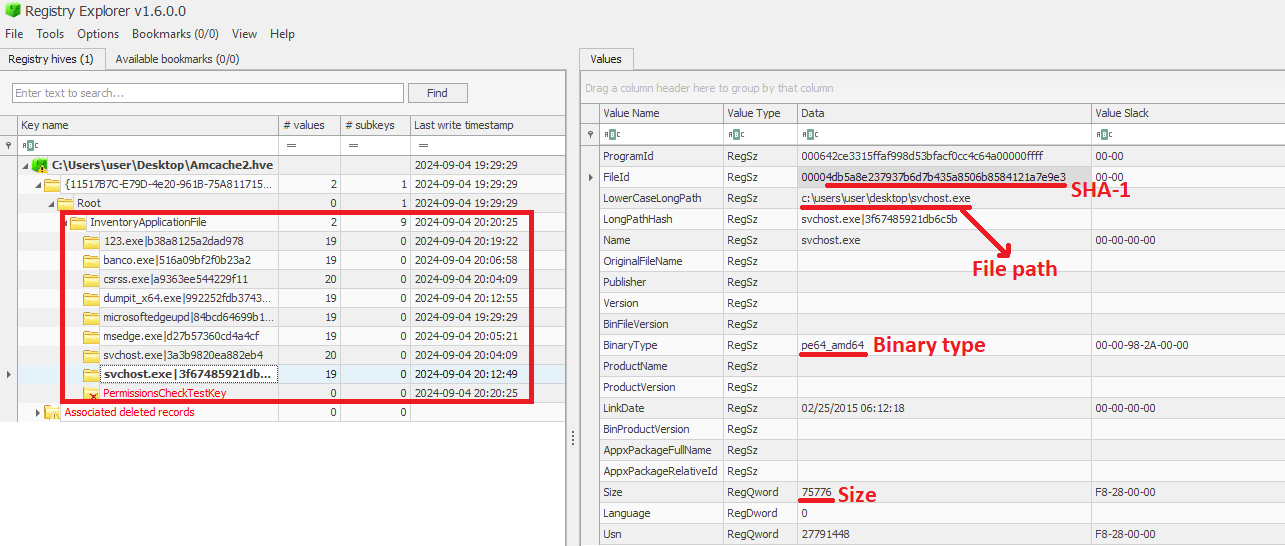
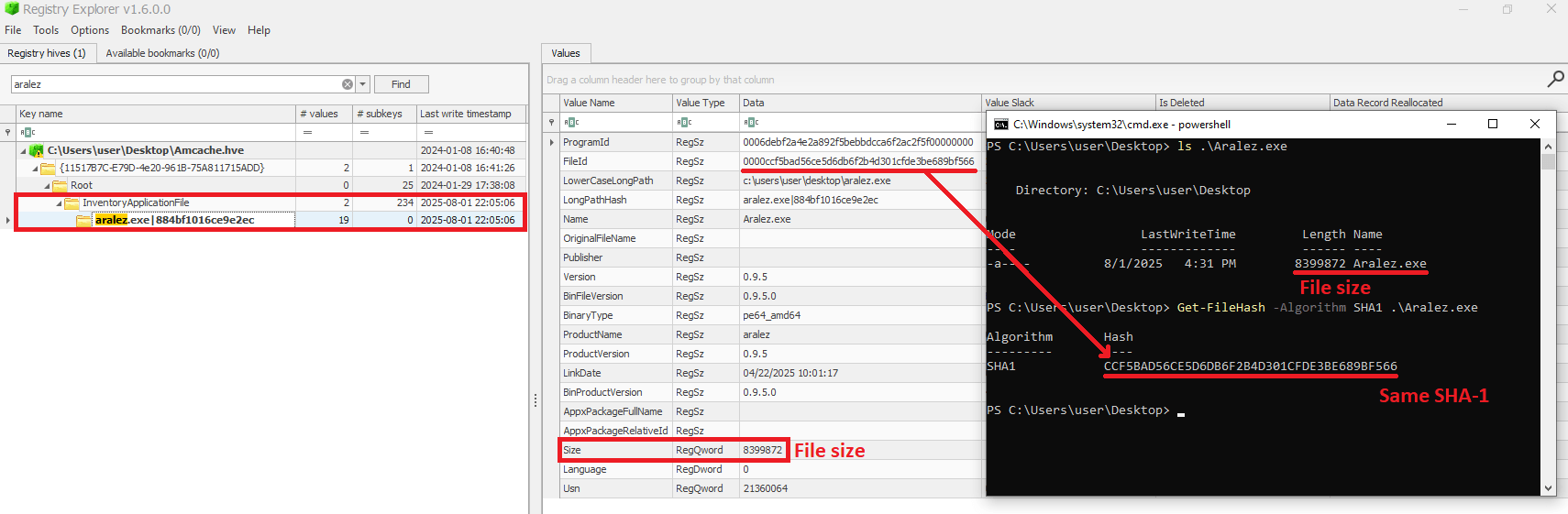
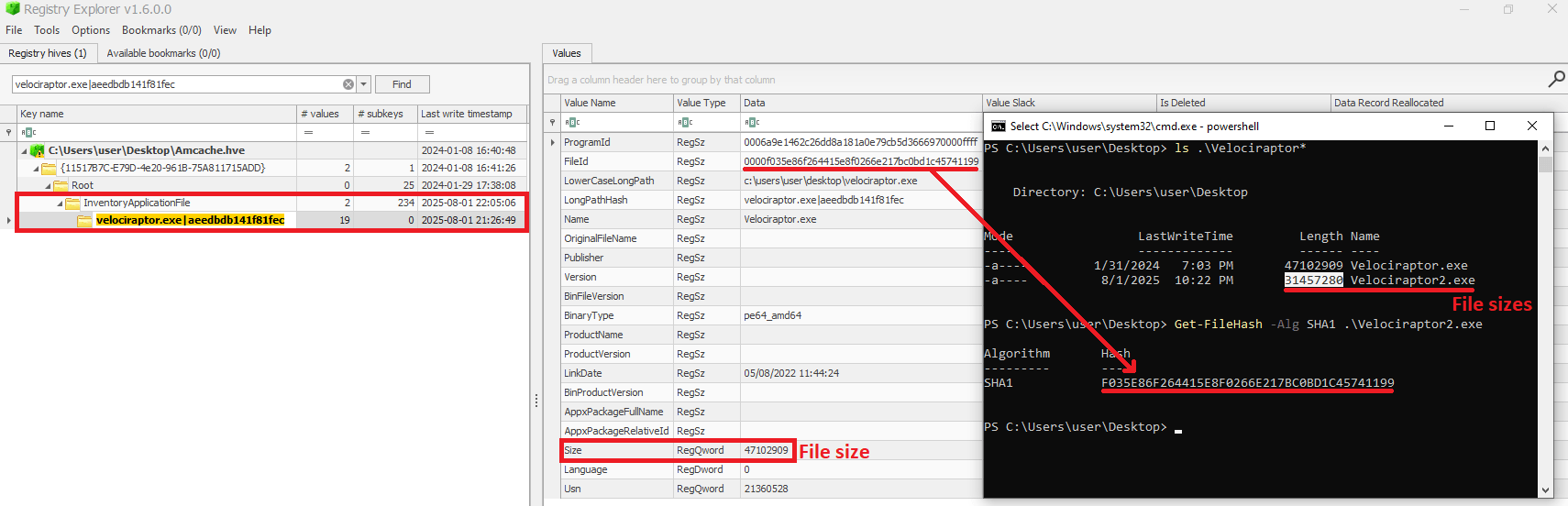
As previously mentioned, Recall takes screenshots, which naturally requires temporary storage before analysis. The raw JPEG images can be found at %AppData%\Local\CoreAIPlatform.00\UKP\{GUID}\ImageStore\*. The filenames themselves are the screenshot identifiers (more on those later).
Along with the screenshots, their metadata is stored within the standard Exif.Photo.MakerNote (0x927c) tag. This tag holds a significant amount of interesting data, such as the boundaries of the foreground window, the capture timestamp, the window title, the window identifier, and the full path of the process that launched the window. Furthermore, if a browser is in use during the screenshot capture, the URI and domain may be preserved, among other details.
Recall is activated on a per-user basis. A key in the user’s registry hive, specifically Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsAI\, is responsible for enabling and disabling the saving of these screenshots. Microsoft has also introduced several new registry keys associated with Recall management in the latest Windows 11 builds.
It is important to note that the version of the feature refined following public controversy includes a specific filter intended to prevent the saving of screenshots and text when potentially sensitive information is on the screen. This includes, for example, an incognito browser window, a payment data input field, or a password manager. However, researchers have indicated that this filter may not always engage reliably.
To enable fast searches across all data captured from screenshots, the system uses two DiskANN vector databases (SemanticTextStore.sidb and SemanticImageStore.sidb). However, the standard SQLite database is the most interesting one for investigation: %AppData%\Local\CoreAIPlatform.00\UKP\{GUID}\ukg.db, which consists of 20 tables. In the latest release, it is accessible without administrative privileges, yet it is encrypted. At the time of writing this post, there are no publicly known methods to decrypt the database directly. Therefore, we will examine the most relevant tables from the 2024 Windows 11 beta release with Recall.
- The
Apptable holds data about the process that launched the application’s graphical user interface window. - The
AppDwellTimetable contains information such as the full path of the process that initiated the application GUI window (WindowsAppId column), the date and time it was launched (HourOfDay, DayOfWeek, HourStartTimestamp), and the duration the window’s display (DwellTime). - The
WindowCapturetable records the type of event (Name column):- WindowCreatedEvent indicates the creation of the first instance of the application window. It can be correlated with the process that created the window.
- WindowChangedEvent tracks changes to the window instance. It allows monitoring movements or size changes of the window instance with the help of the WindowId column, which contains the window’s identifier.
- WindowCaptureEvent signifies the creation of a screen snapshot that includes the application window. Besides the window identifier, it contains an image identifier (ImageToken). The value of this token can later be used to retrieve the JPEG snapshot file from the aforementioned ImageStore directory, as the filename corresponds to the image identifier.
- WindowDestroyedEvent signals the closing of the application window.
- ForegroundChangedEvent does not contain useful data from a forensics perspective.
The
WindowCapturetable also includes a flag indicating whether the application window was in the foreground (IsForeground column), the window boundaries as screen coordinates (WindowBounds), the window title (WindowTitle), a service field for properties (Properties), and the event timestamp (TimeStamp).
WindowCaptureTextIndex_contentcontains the text extracted with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) from the snapshot (c2 column), the window title (WindowTitle), the application path (App.Path), the snapshot timestamp (TimeStamp), and the name (Name). This table can be used in conjunction with the WindowCapture (the c0 and Id columns hold identical data, which can be used for joining the tables) and App tables (identical data resides in the AppId and Id columns).
Recall artifacts (if the feature was enabled on the system prior to the incident) represent a “goldmine” for the incident responder. They allow for a detailed reconstruction of the attacker’s activity within the compromised system. Conversely, this same functionality can be weaponized: as mentioned previously, the private information filter in Recall does not work flawlessly. Consequently, attackers and malware can exploit it to locate credentials and other sensitive information.
Updated standard applications
Standard applications in Windows 11 have also undergone updates, and for some, this involved changes to both the interface and functionality. Specifically, applications such as Notepad, File Explorer, and the Command Prompt in this version of the OS now support multi-tab mode. Notably, Notepad retains the state of these tabs even after the process terminates. Therefore, Windows 11 now has new artifacts associated with the usage of this application. Our colleague, AbdulRhman Alfaifi, researched these in detail; his work is available here.
The main directory for Notepad artifacts in Windows 11 is located at %LOCALAPPDATA%\Packages\Microsoft.WindowsNotepad_8wekyb3d8bbwe\LocalState\.
This directory contains two subdirectories:
- TabState stores a {GUID}.bin state file for each Notepad tab. This file contains the tab’s contents if the user did not save it to a file. For saved tabs, the file contains the full path to the saved content, the SHA-256 hash of the content, the content itself, the last write time to the file, and other details.
- WindowsState stores information about the application window state. This includes the total number of tabs, their order, the currently active tab, and the size and position of the application window on the screen. The state file is named either *.0.bin or *.1.bin.
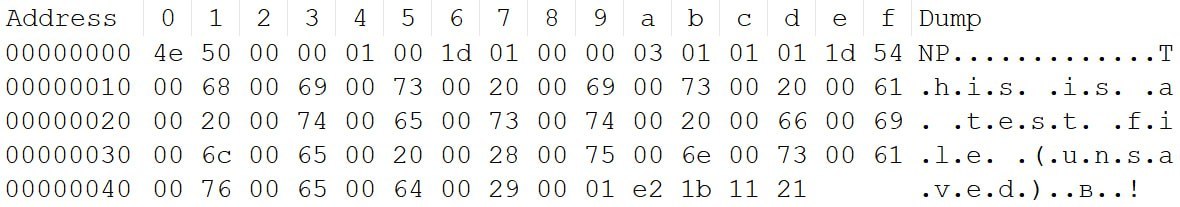
The structure of {GUID}.bin for saved tabs is as follows:
| Field | Type | Value and explanation |
| signature | [u8;2] | NP |
| ? | u8 | 00 |
| file_saved_to_path | bool | 00 = the file was not saved at the specified path 01 = the file was saved |
| path_length | uLEB128 | Length of the full path (in characters) to the file where the tab content was written |
| file_path | UTF-16LE | The full path to the file where the tab content was written |
| file_size | uLEB128 | The size of the file on disk where the tab content was written |
| encoding | u8 | File encoding: 0x01 – ANSI 0x02 – UTF-16LE 0x03 – UTF-16BE 0x04 – UTF-8BOM 0x05 – UTF-8 |
| cr_type | u8 | Type of carriage return: 0x01 — CRLF 0x02 — CR 0x03 — LF |
| last_write_time | uLEB128 | The time of the last write (tab save) to the file, formatted as FILETIME |
| sha256_hash | [u8;32] | The SHA-256 hash of the tab content |
| ? | [u8;2] | 00 01 |
| selection_start | uLEB128 | The offset of the section start from the beginning of the file |
| selection_end | uLEB128 | The offset of the section end from the beginning of the file |
| config_block | ConfigBlock | ConfigBlock structure configuration |
| content_length | uLEB128 | The length of the text in the file |
| content | UTF-16LE | The file content before it was modified by the new data. This field is absent if the tab was saved to disk with no subsequent modifications. |
| contain_unsaved_data | bool | 00 = the tab content in the {GUID}.bin file matches the tab content in the file on disk 01 = changes to the tab have not been saved to disk |
| checksum | [u8;4] | The CRC32 checksum of the {GUID}.bin file content, offset by 0x03 from the start of the file |
| unsaved_chunks | [UnsavedChunk] | A list of UnsavedChunk structures. This is absent if the tab was saved to disk with no subsequent modifications |
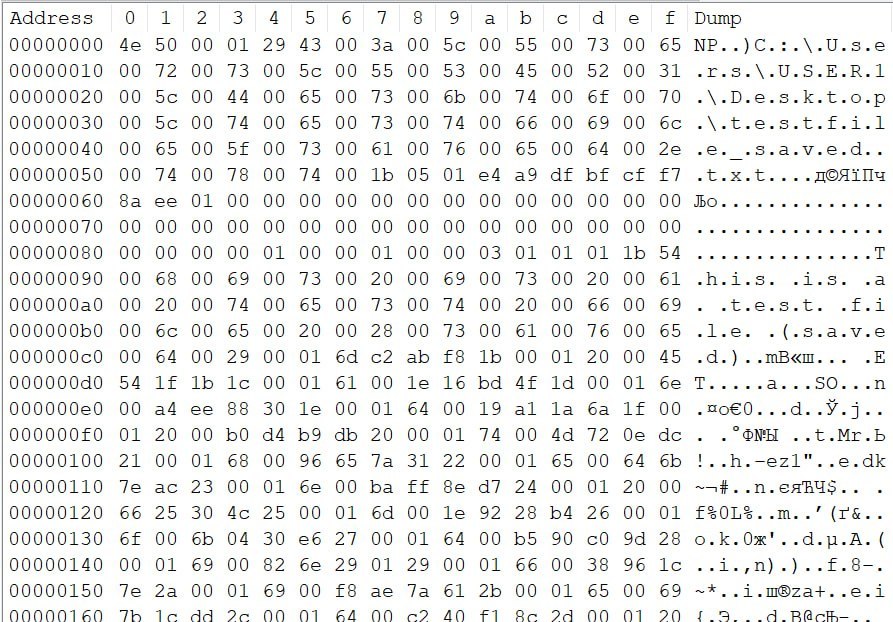
Example content of the {GUID.bin} file for a Notepad tab that was saved to a file and then modified with new data which was not written to the file
For tabs that were never saved, the {GUID}.bin file structure in the TabState directory is shorter:
| Field | Type | Value and explanation |
| signature | [u8;2] | NP |
| ? | u8 | 00 |
| file_saved_to_path | bool | 00 = the file was not saved at the specified path (always) |
| selection_start | uLEB128 | The offset of the section start from the beginning of the file |
| selection_end | uLEB128 | The offset of the section end from the beginning of the file |
| config_block | ConfigBlock | ConfigBlock structure configuration |
| content_length | uLEB128 | The length of the text in the file |
| content | UTF-16LE | File content |
| contain_unsaved_data | bool | 01 = changes to the tab have not been saved to disk (always) |
| checksum | [u8;4] | The CRC32 checksum of the {GUID}.bin file content, offset by 0x03 from the start of the file |
| unsaved_chunks | [UnsavedChunk] | List of UnsavedChunk structures |
Note that the saving of tabs may be disabled in the Notepad settings. If this is the case, the TabState and WindowState artifacts will be unavailable for analysis.
If these artifacts are available, however, you can use the notepad_parser tool, developed by our colleague Abdulrhman Alfaifi, to automate working with them.
This particular artifact may assist in recovering the contents of malicious scripts and batch files. Furthermore, it may contain the results and logs from network scanners, credential extraction utilities, and other executables used by threat actors, assuming any unsaved modifications were inadvertently made to them.
Changes to familiar artifacts in Windows 11
In addition to the new artifacts, Windows 11 introduced several noteworthy changes to existing ones that investigators should be aware of when analyzing incidents.
Changes to NTFS attribute behavior
The behavior of NTFS attributes was changed between Windows 10 and Windows 11 in two $MFT structures: $STANDARD_INFORMATION and $FILE_NAME.
The changes to the behavior of the $STANDARD_INFORMATION attributes are presented in the table below:
| Event | Access file | Rename file | Copy file to new folder | Move file within one volume | Move file between volumes |
| Win 10 1903 |
The File Access timestamp is updated. However, it remains unchanged if the system volume is larger than 128 GB | The File Access timestamp remains unchanged | The copy metadata is updated | The File Access timestamp remains unchanged | The metadata is inherited from the original file |
| Win 11 24H2 | The File Access timestamp is updated | The File Access timestamp is updated to match the modification time | The copy metadata is inherited from the original file | The File Access timestamp is updated to match the moving time | The metadata is updated |
Behavior of the $FILENAME attributes was changed as follows:
| Event | Rename file | Move file via Explorer within one volume | Move file to Recycle Bin |
| Win 10 1903 |
The timestamps and metadata remain unchanged | The timestamps and metadata remain unchanged | The timestamps and metadata remain unchanged |
| Win 11 24H2 | The File Access and File Modify timestamps along with the metadata are inherited from the previous version of $STANDARD_INFORMATION | The File Access and File Modify timestamps along with the metadata are inherited from the previous version of $STANDARD_INFORMATION | The File Access and File Modify timestamps along with the metadata are inherited from the previous version of $STANDARD_INFORMATION |
Analysts should consider these changes when examining the service files of the NTFS file system.
Program Compatibility Assistant
Program Compatibility Assistant (PCA) first appeared way back in 2006 with the release of Windows Vista. Its purpose is to run applications designed for older operating system versions, thus being a relevant artifact for identifying evidence of program execution.
Windows 11 introduced new files associated with this feature that are relevant for forensic analysis of application executions. These files are located in the directory C:\Windows\appcompat\pca\:
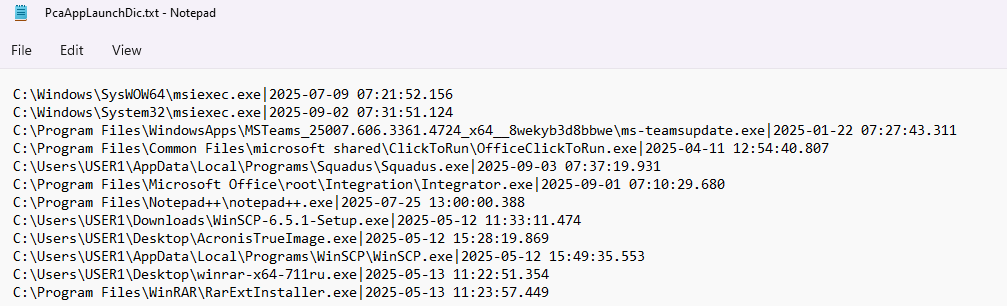
PcaAppLaunchDic.txt: each line in this file contains data on the most recent launch of a specific executable file. This information includes the time of the last launch formatted as YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.f (UTC) and the full path to the file. A pipe character (|) separates the data elements. When the file is run again, the information in the corresponding line is updated. The file uses ANSI (CP-1252) encoding, so executing files with Unicode in their names “breaks” it: new entries (including the entry for running a file with Unicode) stop appearing, only old ones get updated.
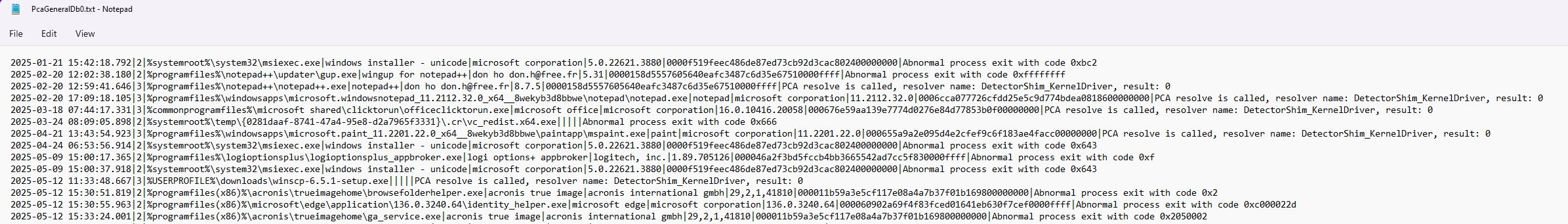
PcaGeneralDb0.txtandPcaGeneralDb1.txtalternate during data logging: new records are saved to the primary file until its size reaches two megabytes. Once that limit is reached, the secondary file is cleared and becomes the new primary file, and the full primary file is then designated as the secondary. This cycle repeats indefinitely. The data fields are delimited with a pipe (|). The file uses UTF-16LE encoding and contains the following fields:- Executable launch time (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.f (UTC))
- Record type (0–4):
- 0 = installation error
- 1 = driver blocked
- 2 = abnormal process exit
- 3 = PCA Resolve call (component responsible for fixing compatibility issues when running older programs)
- 4 = value not set
- Path to executable file. This path omits the volume letter and frequently uses environment variables (%USERPROFILE%, %systemroot%, %programfiles%, and others).
- Product name (from the PE header, lowercase)
- Company name (from the PE header, lowercase)
- Product version (from the PE header)
- Windows application ID (format matches that used in AmCache)
- Message
Note that these text files only record data related to program launches executed through Windows File Explorer. They do not log launches of executable files initiated from the console.
Windows Search
Windows Search is the built-in indexing and file search mechanism within Windows. Initially, it combed through files directly, resulting in sluggish and inefficient searches. Later, a separate application emerged that created a fast file index. It was not until 2006’s Windows Vista that a search feature was fully integrated into the operating system, with file indexing moved to a background process.
From Windows Vista up to and including Windows 10, the file index was stored in an Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) database:
%PROGRAMDATA%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.edb.
Windows 11 breaks this storage down into three SQLite databases:
%PROGRAMDATA%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows-gather.dbcontains general information about indexed files and folders. The most interesting element is the SystemIndex_Gthr table, which stores data such as the name of the indexed file or directory (FileName column), the last modification of the indexed file or directory (LastModified), an identifier used to link to the parent object (ScopeID), and a unique identifier for the file or directory itself (DocumentID). Using the ScopeID and the SystemIndex_GthrPth table, investigators can reconstruct the full path to a file on the system. The SystemIndex_GthrPth table contains the folder name (Name column), the directory identifier (Scope), and the parent directory identifier (Parent). By matching the file’s ScopeID with the directory’s Scope, one can determine the parent directory of the file.%PROGRAMDATA%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.dbstores information about the metadata of indexed files. The SystemIndex_1_PropertyStore table is of interest for analysis; it holds the unique identifier of the indexed object (WorkId column), the metadata type (ColumnId), and the metadata itself. Metadata types are described in the SystemIndex_1_PropertyStore_Metadata table (where the content of the Id column corresponds to the ColumnId content from SystemIndex_1_PropertyStore) and are specified in the UniqueKey column.%PROGRAMDATA%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows-usn.dbdoes not contain useful information for forensic analysis.
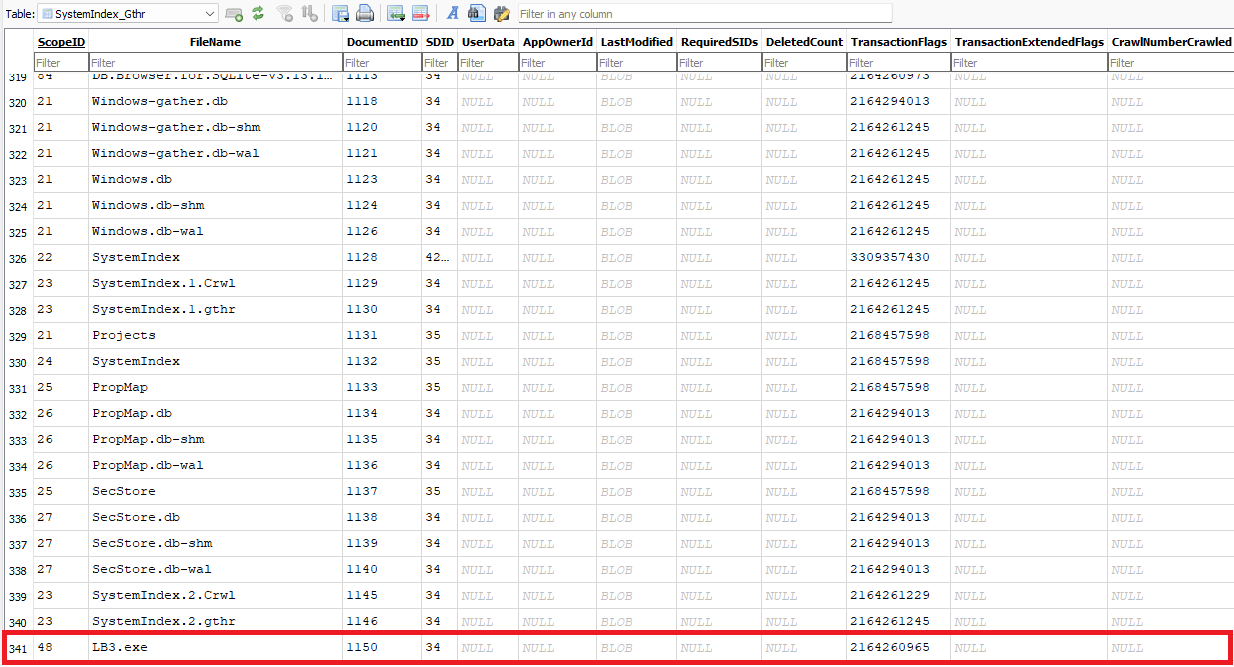
As depicted in the image below, analyzing the Windows-gather.db file using DB Browser for SQLite can provide us evidence of the presence of certain files (e.g., malware files, configuration files, files created and left by attackers, and others).
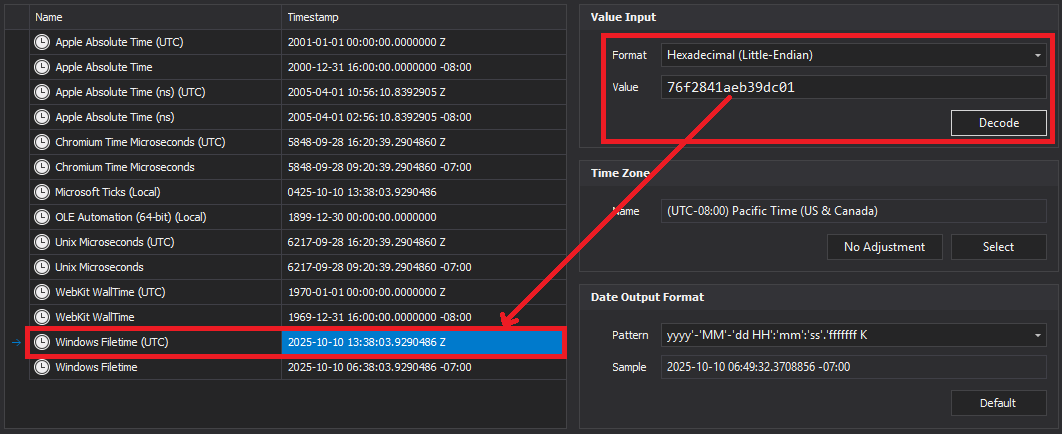
It is worth noting that the LastModified column is stored in the Windows FILETIME format, which holds an unsigned 64-bit date and time value, representing the number of 100-nanosecond units since the start of January 1, 1601. Using a utility such as DCode, we can see this value in UTC, as shown in the image below.
Other minor changes in Windows 11
It is also worth mentioning a few small but important changes in Windows 11 that do not require a detailed analysis:
- A complete discontinuation of NTLMv1 means that pass-the-hash attacks are gradually becoming a thing of the past.
- Removal of the well-known Windows 10 Timeline activity artifact. Although it is no longer being actively maintained, its database remains for now in the files containing user activity information, located at:
%userprofile%\AppData\Local\ConnectedDevicesPlatform\ActivitiesCache.db. - Similarly, Windows 11 removed Cortana and Internet Explorer, but the artifacts of these can still be found in the operating system. This may be useful for investigations conducted in machines that were updated from Windows 10 to the newer version.
- Previous research also showed that Event ID 4624, which logs successful logon attempts in Windows, remained largely consistent across versions until a notable update appeared in Windows 11 Pro (22H2). This version introduces a new field, called Remote Credential Guard, marking a subtle but potentially important change in forensic analysis. While its real-world use and forensic significance remain to be observed, its presence suggests Microsoft’s ongoing efforts to enhance authentication-related telemetry.
- Expanded support for the ReFS file system. The latest Windows 11 update preview made it possible to install the operating system directly onto a ReFS volume, and BitLocker support was also introduced. This file system has several key differences from the familiar NTFS:
- ReFS does not have the $MFT (Master File Table) that forensics specialists rely on, which contains all current file records on the disk.
- It does not generate short file names, as NTFS does for DOS compatibility.
- It does not support hard links or extended object attributes.
- It offers increased maximum volume and single-file sizes (35 PB compared to 256 TB in NTFS).
Conclusion
This post provided a brief overview of key changes to Windows 11 artifacts that are relevant to forensic analysis – most notably, the changes of PCA and modifications to Windows Search mechanism. The ultimate utility of these artifacts in investigations remains to be seen. Nevertheless, we recommend you immediately incorporate the aforementioned files into the scope of your triage collection tool.