Flight Radiation Reached 20-Year High During Recent Solar Outburst, Scientists Confirm

And as Airbus reminded us last week, we're not ready.



The first multi-spacecraft science mission to launch to Mars is now on its way, and catching a ride on the twin probes are the first kiwis to fly to the red planet.
NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) mission lifted off on a 22-month trip to Mars on Thursday aboard a New Glenn rocket. Once there, the identical satellites will enter Martian orbit to study in real time how space weather affects the planet’s hybrid magnetosphere and how the interaction drove Mars to lose its once-dense atmosphere.
Led by the Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California, Berkeley—the two spacecraft are named “Blue” and “Gold” after the school’s colors—the ESCAPADE probes are the first Mars-bound vehicles to be designed, built, and tested by Rocket Lab, the end-to-end space company headquartered in California but founded in New Zealand.
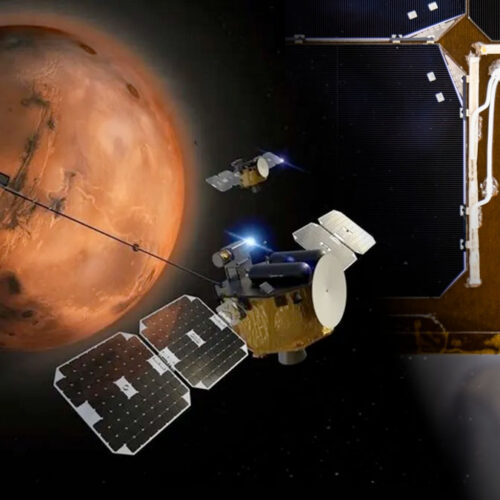
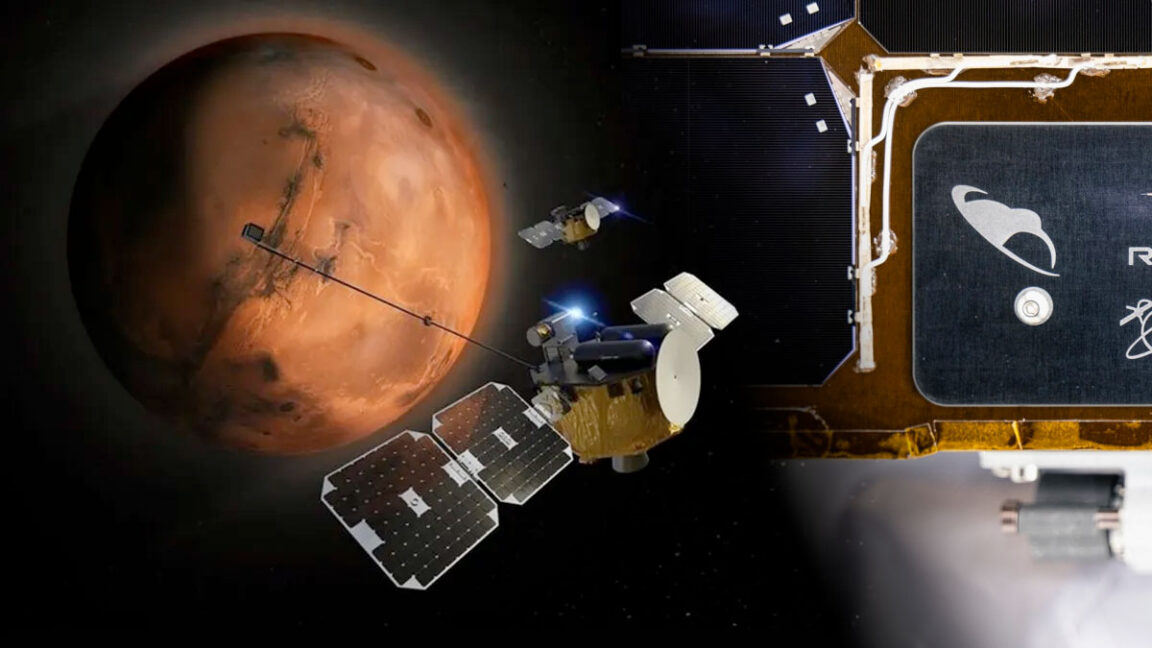
© UCB-SSL/Rocket Lab/collectSPACE.com
CAPE CANAVERAL, Florida—The second flight of Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket was postponed again Wednesday as a supercharged wave of magnetized plasma from the Sun enveloped the Earth, triggering colorful auroral displays and concerns over possible impacts to communications, navigation, and power grids.
Solar storms like the one this week can also affect satellite operations. That is the worry that caused NASA to hold off on launching a pair of science probes from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida, on Wednesday aboard Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket.
In a statement, Blue Origin said NASA, its customer on the upcoming launch, decided to postpone the mission to send the agency’s two ESCAPADE spacecraft on a journey to Mars.
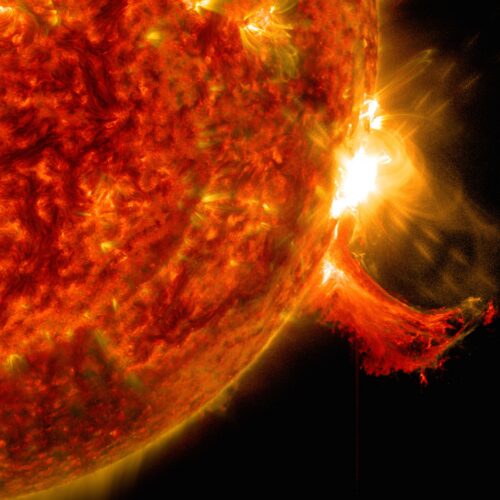
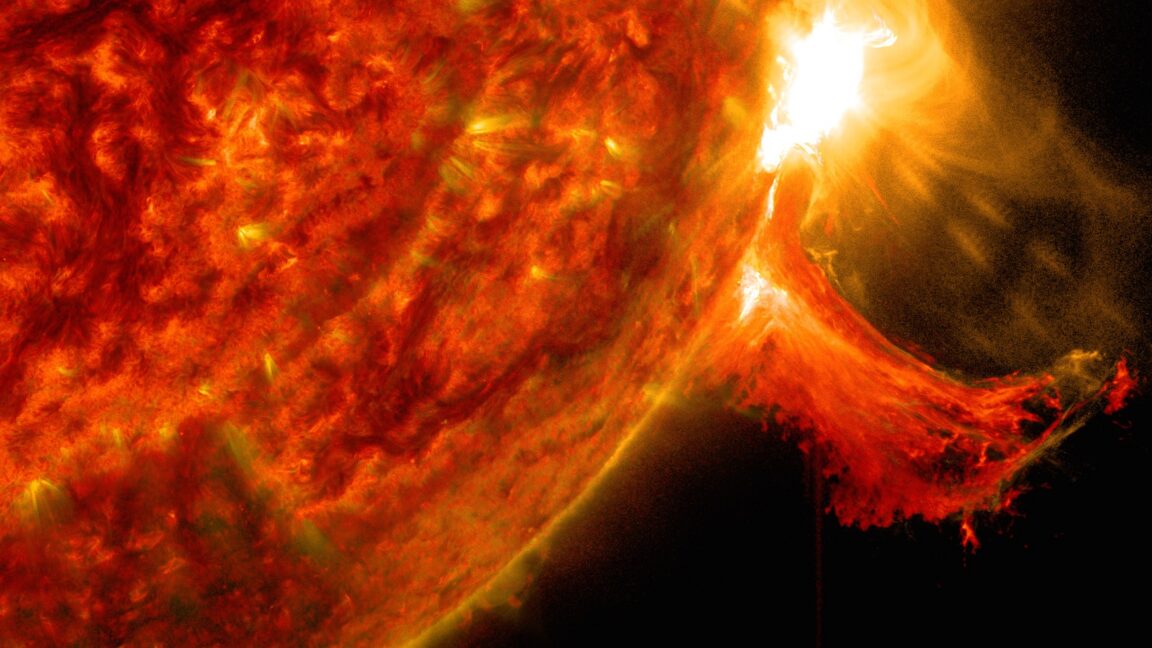
© NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center
4 min read
Recent airborne science flights to Greenland are improving NASA’s understanding of space weather by measuring radiation exposure to air travelers and validating global radiation maps used in flight path planning. This unique data also has value beyond the Earth as a celestial roadmap for using the same instrumentation to monitor radiation levels for travelers entering Mars’ atmosphere and for upcoming lunar exploration.
NASA’s Space Weather Aviation Radiation (SWXRAD) aircraft flight campaign took place August 25-28 and conducted two five-hour flights in Nuuk, Greenland. Based out of NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, the mission gathered dosimetry measurements, or the radiation dose level, to air travelers from cosmic radiation. Cosmic radiation is caused by high-energy particles from outer space that originate from our Sun during eruptive events like solar flares and from events farther away, like supernovae in our Milky Way galaxy and beyond.
“With NASA spacecraft and astronauts exploring the Moon, Mars, and beyond, we support critical research to understand – and ultimately predict – the impacts of space weather across the solar system,” said Jamie Favors, director of NASA’s Space Weather Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Though this project is focused on aviation applications on Earth, NAIRAS could be part of the next generation of tools supporting Artemis missions to the Moon and eventually human missions to Mars.”
NASA’s Nowcast of Aerospace Ionizing Radiation System, or NAIRAS, is the modeling system being enhanced by the SWXRAD airborne science flights. The model features real-time global maps of the hazardous radiation in the atmosphere and creates exposure predictions for aircraft and spacecraft.
“The radiation exposure is maximum at the poles and minimum at the equator because of the effect of Earth’s magnetic field. In the polar regions, the magnetic field lines are directed into or out of the Earth, so there’s no deflection or shielding by the fields of the radiation environment that you see everywhere else.” explained Chris Mertens, principal investigator of SWXRAD at NASA Langley. “Greenland is a region where the shielding of cosmic radiation by Earth’s magnetic field is zero.”
That means flight crews and travelers on polar flights from the U.S. to Asia or from the U.S. to Europe are exposed to higher levels of radiation.
The data gathered in Greenland will be compared to the NAIRAS modeling, which bases its computation on sources around the globe that include neutron monitors and instruments that measure solar wind parameters and the magnetic field along with spaceborne data from instruments like the NOAA GOES series of satellites.
“If the new data doesn’t agree, we have to go back and look at why that is,” said Mertens. “In the radiation environment, one of the biggest uncertainties is the effect of Earth’s magnetic field. So, this mission eliminates that variable in the model and enables us to concentrate on other areas, like characterizing the particles that are coming in from space into the atmosphere, and then the transport and interactions with the atmosphere.”
The SWXRAD science team flew aboard NASA’s B200 King Air with five researchers and crew members. In the coming months, the team will focus on measurement data quality checks, quantitative modeling comparisons, and a validation study between current NAIRAS data and the new aircraft dosimeter measurements.
All of this information is endeavoring to protect pilots and passengers on Earth from the health risks associated with radiation exposure while using NASA’s existing science capabilities to safely bring astronauts to the Moon and Mars.
“Once you get to Mars and even the transit out to Mars, there would be times where we don’t have any data sets to really understand what the environment is out there,” said Favors. “So we’re starting to think about not only how do we get ready for those humans on Mars, but also what data do we need to bring with them? So we’re feeding this data into models exactly like NAIRAS. This model is thinking about Mars in the same way it’s thinking about Earth.”
The SWXRAD flight mission is funded through NASA’s Science Mission Directorate Heliophysics Division. NASA’s Space Weather Program Office is hosted at NASA Langley and facilitates researchers in the creation of new tools to predict space weather and to understand space weather effects on Earth’s infrastructure, technology, and society.
For more information on NASA Heliophysics and NAIRAS modeling visit:
NASA’s Nowcast of Aerospace Ionizing Radiation System

Read this press release in English here.
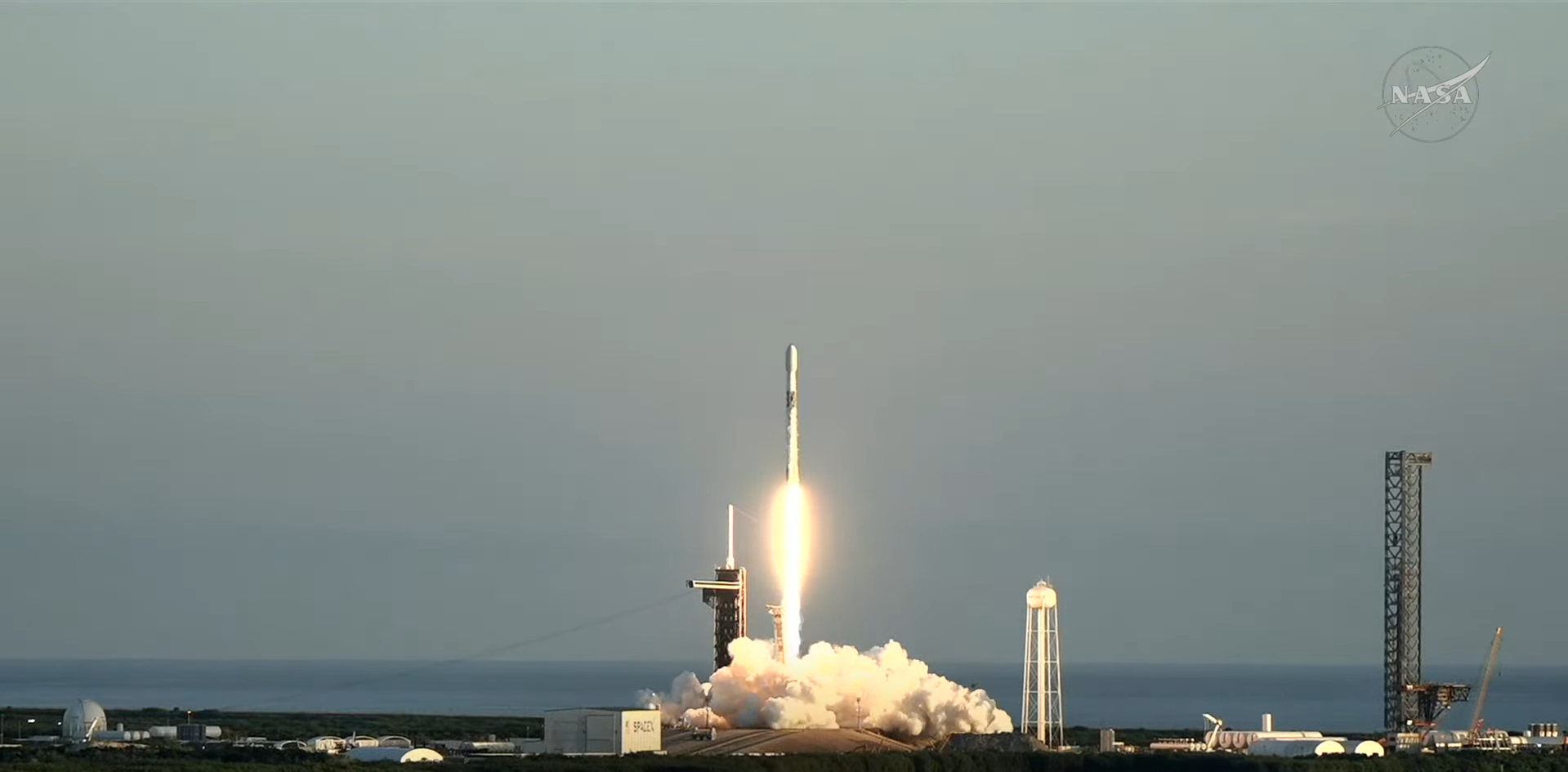
La NASA y la Administración Nacional Oceánica y Atmosférica (NOAA, por sus siglas en inglés) lanzaron el miércoles tres nuevas misiones para investigar la influencia del Sol en todo el sistema solar.
A las 7:30 a. m. EDT, un cohete Falcon 9 de SpaceX despegó del Complejo de Lanzamiento 39A del Centro Espacial Kennedy de la NASA en Florida, llevando a bordo las misiones Sonda de Cartografía y Aceleración Interestelar (IMAP, por su acrónimo en inglés) y el Observatorio Carruthers de la Geocorona, ambos de la NASA, y la nave espacial de Seguimiento de la Meteorología Espacial en el Punto de Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1, por sus siglas en inglés) de la NOAA.
“Este exitoso lanzamiento mejora la preparación de nuestro país ante las condiciones meteorológicas espaciales para proteger mejor nuestros satélites, misiones interplanetarias y astronautas que viajan al espacio de los peligros de la meteorología espacial en todo el sistema solar”, afirmó el administrador interino de la NASA, Sean Duffy. “Esta información será fundamental a medida que nos preparamos para futuras misiones a la Luna y Marte con la intención de mantener a Estados Unidos a la vanguardia en el espacio”.
Estas misiones ayudarán a proteger de las duras condiciones de la meteorología espacial tanto a nuestra tecnología basada en tierra como a nuestros exploradores espaciales humanos y robóticos.
“Mientras Estados Unidos se prepara para enviar a seres humanos de vuelta a la Luna y más adelante a Marte, la NASA y la NOAA están proporcionando la guía definitiva de supervivencia interplanetaria para dar apoyo a este épico viaje de la humanidad”, afirmó Nicola Fox, administradora asociada de la Dirección de Misiones Científicas de la sede central de la NASA en Washington. “Nuestros descubrimientos científicos e innovaciones técnicas se incorporan directamente a nuestro plan de acción know-before-you-go (infórmate antes de ir) para garantizar una presencia humana bien preparada, segura y continua en otros mundos”.
Nueva ciencia para proteger a la sociedad
Cada misión investigará los diferentes efectos de la meteorología espacial y el viento solar, el cual es un flujo continuo de partículas emitidas por el Sol, desde su origen en nuestra estrella hasta el espacio interestelar.
“Estas tres misiones únicas nos ayudarán a conocer nuestro Sol y sus efectos sobre la Tierra mejor que nunca”, afirmó Joe Westlake, director de la División de Heliofísica en la sede central de la NASA. “Este conocimiento es fundamental, ya que la actividad solar afecta directamente a nuestra vida cotidiana, desde las redes eléctricas hasta el GPS. Estas misiones nos ayudarán a garantizar la seguridad y la resiliencia de nuestro mundo interconectado”.
La misión IMAP trazará los límites de la heliosfera, una burbuja inflada por el viento solar que protege nuestro sistema solar de los rayos cósmicos galácticos. Esta es una protección clave que contribuye a que nuestro planeta sea habitable. Además, la nave espacial tomará muestras y medirá las partículas del viento solar que fluyen hacia el exterior desde el Sol, así como las partículas energéticas que fluyen hacia el interior desde los límites de nuestro sistema solar y más allá.
“IMAP nos ayudará a comprender mejor cómo el entorno espacial puede perjudicarnos a nosotros y a nuestras tecnologías, y a descubrir la ciencia de nuestro vecindario solar”, afirmó David McComas, investigador principal de la misión IMAP en la Universidad de Princeton, en Nueva Jersey.
El Observatorio Carruthers de la Geocorona es la primera misión dedicada a medir los cambios en la capa más externa de nuestra atmósfera, la exosfera, la cual juega un papel importante en cómo la Tierra responde a la meteorología espacial. Al estudiar la geocorona —el brillo ultravioleta que emite la exosfera cuando la luz del sol la ilumina— la misión Carruthers revelará cómo la exosfera responde a las tormentas solares y cómo cambia con las estaciones. La misión se basa en el legado del primer instrumento que capturó imágenes de la geocorona, el cual viajó a la Luna a bordo de Apolo 16 y fue construido y diseñado por el científico, inventor, ingeniero y educador Dr. George Carruthers.
“La misión Carruthers nos mostrará cómo funciona la exosfera y nos ayudará a mejorar nuestra capacidad para predecir los efectos de la actividad solar aquí en la Tierra”, dijo Lara Waldrop, investigadora principal de la misión en la Universidad de Illinois en Urbana-Champaign.
La nave SWFO-L1 de la NOAA, la primera de su tipo, está diseñada para ser un observatorio de meteorología espacial operativo a tiempo completo. Al vigilar la actividad solar y las condiciones espaciales cerca de la Tierra las 24 horas del día, los 7 días de la semana, sin interrupciones ni obstrucciones, SWFO-L1 proporcionará pronósticos de meteorología espacial más rápidos y precisos que nunca.
“Se trata del primero de una nueva generación de observatorios de meteorología espacial de la NOAA dedicados a operaciones ininterrumpidas, que trabajarán para evitar lagunas en la continuidad. Las observaciones en tiempo real de SWFO-L1 proporcionarán a los operadores los datos fiables necesarios para emitir alertas tempranas, de modo que los responsables de la toma de decisiones puedan actuar con antelación para proteger las infraestructuras vitales, los intereses económicos y la seguridad nacional en la Tierra y en el espacio. Se trata de proteger a la sociedad contra los peligros de la meteorología espacial”, dijo Richard Ullman, subdirector de la Oficina de Observaciones de la Meteorología Espacial de la NOAA
Siguientes pasos
En las horas posteriores al lanzamiento, las tres naves espaciales se desplegaron desde el cohete con éxito y enviaron señales a la Tierra para confirmar que están activas y funcionando correctamente.
Durante los próximos meses, los satélites se dirigirán a su destino, un lugar situado entre la Tierra y el Sol, a unos 1,6 millones de kilómetros de la Tierra, denominado punto de Lagrange 1 (L1). Se espera que lleguen en enero y, una vez completadas las comprobaciones y calibraciones de sus instrumentos, comiencen sus misiones para comprender mejor la meteorología espacial y proteger a la humanidad.
David McComas, de la Universidad de Princeton, dirige la misión IMAP con un equipo internacional formado por 27 instituciones asociadas. El Laboratorio de Física Aplicada de la Universidad Johns Hopkins, ubicado en Laurel, Maryland, construyó la nave espacial y operará la misión.
La misión del Observatorio Carruthers de la Geocorona está dirigida por Lara Waldrop, de la Universidad de Illinois Urbana-Champaign. La ejecución de la misión está a cargo del Laboratorio de Ciencias Espaciales de la Universidad de California, Berkeley, que también diseñó y construyó los dos generadores de imágenes ultravioletas. BAE Systems diseñó y construyó la nave espacial Carruthers.
La División de Proyectos de Exploradores y Heliofísica de la NASA en el Centro de Vuelo Espacial Goddard de la NASA en Greenbelt, Maryland, gestiona las misiones IMAP y Observatorio Carruthers de la Geocorona para la Dirección de Misiones Científicas de la NASA.
La misión SWFO-L1 está gestionada por la NOAA y desarrollada en colaboración con el centro Goddard de la NASA y socios comerciales. El Programa de Servicios de Lanzamiento de la NASA, con sede en el centro Kennedy de la NASA, gestiona el servicio de lanzamiento de las misiones.
Para obtener más información sobre estas misiones, visite:
-fin-
Abbey Interrante / María José Viñas
Sede central, Washington
301-201-0124
abbey.a.interrante@nasa.gov / maria-jose.vinasgarcia@nasa.gov
Sarah Frazier
Centro de Vuelo Espacial Goddard, Greenbelt, Maryland
202-853-7191
sarah.frazier@nasa.gov
Leejay Lockhart
Centro Espacial Kennedy, Florida
321-747-8310
leejay.lockhart@nasa.gov
John Jones-Bateman
Servicio de Satélites e Información de la NOAA, Silver Spring, Maryland
202-242-0929
john.jones-bateman@noaa.gov

Lee este comunicado de prensa en español aquí.
NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) launched three new missions Wednesday to investigate the Sun’s influence across the solar system.
At 7:30 a.m. EDT, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifted off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida carrying the agency’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and NOAA’s SWFO-L1 (Space Weather Follow On-Lagrange 1) spacecraft.
“This successful launch advances the space weather readiness of our nation to better protect our satellites, interplanetary missions, and space-faring astronauts from the dangers of space weather throughout the solar system,” said acting NASA Administrator Sean Duffy, “This insight will be critical as we prepare for future missions to the Moon and Mars in our endeavor to keep America first in space.”
These missions will help safeguard both our ground-based technology, as well as our human and robotic space explorers from the harsh conditions known of space weather.
“As the United States prepares to send humans back to the Moon and onward to Mars, NASA and NOAA are providing the ultimate interplanetary survival guide to support humanity’s epic journey along the way,” said Nicola Fox, associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Our scientific discoveries and technical innovations directly feed into our know-before-you-go roadmap to ensure a prepared, safe, and sustained human presence on other worlds.”
New science to protect society
Each mission will investigate different effects of space weather and the solar wind, which is a continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun, from their origins at the Sun all the way outward to interstellar space.
“These three unique missions will help us get to know our Sun and its effects on Earth better than ever before,” said Joe Westlake, Heliophysics Division director at NASA Headquarters. “This knowledge is critical because the Sun’s activity directly impacts our daily lives, from power grids to GPS. These missions will help us ensure the safety and resilience of our interconnected world.”
The IMAP mission will chart the boundary of the heliosphere, a bubble inflated by the solar wind that shields our solar system from galactic cosmic rays — a key protection that helps make our planet habitable. In addition, the spacecraft will sample and measure solar wind particles streaming outward from the Sun, as well as energetic particles streaming inward from the boundary of our solar system and beyond.
“IMAP will help us better understand how the space environment can harm us and our technologies, and discover the science of our solar neighborhood,” said David McComas, IMAP mission principal investigator at Princeton University in New Jersey.
The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is the first mission dedicated to recording changes in the outermost layer of our atmosphere, the exosphere, which plays an important role in Earth’s response to space weather. By studying the geocorona — the ultraviolet glow given off by the exosphere when sunlight shines on it — the Carruthers mission will reveal how the exosphere responds to solar storms and how it changes with the seasons. The mission builds on the legacy of the first instrument to image the geocorona, which flew to the Moon aboard Apollo 16 and was built and designed by scientist, inventor, engineer, and educator Dr. George Carruthers.
“The Carruthers mission will show us how the exosphere works and will help improve our ability to predict the impacts of solar activity here on Earth,” said Lara Waldrop, the mission’s principal investigator at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
The first of its kind, NOAA’s SWFO-L1 is designed to be a full-time operational space weather observatory. By keeping a watchful eye on the Sun’s activity and space conditions near Earth 24/7, and without interruption or obstruction, SWFO-L1 will provide quicker and more accurate space weather forecasts than ever before.
“This is the first of a new generation of NOAA space weather observatories dedicated to 24/7 operations, working to avoid gaps in continuity. Real-time observations from SWFO-L1 will give operators the trusted data necessary to issue advance warnings so that decision-makers can take early action to protect vital infrastructure, economic interests, and national security on Earth and in space. It’s about safeguarding society against space weather hazards,” said Richard Ullman, deputy director of the Office of Space Weather Observations at NOAA.
Next steps
In the hours after launch, all three spacecraft successfully deployed from the rocket and sent signals to Earth to confirm they’re active and working well.
Over the next few months, the spacecraft will make their way to their destination — a location between Earth and the Sun, about a million miles from Earth, called Lagrange point 1 (L1). They should arrive by January and, once their instrument checkouts and calibrations are complete, begin their missions to better understand space weather and protect humanity.
David McComas of Princeton University leads the IMAP mission with an international team of 27 partner institutions. The Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, built the spacecraft and will operate the mission.
The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory mission is led by Lara Waldrop from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. Mission implementation is led by the Space Sciences Laboratory at University of California, Berkeley, which also designed and built the two ultraviolet imagers. BAE Systems designed and built the Carruthers spacecraft.
The Explorers and Heliophysics Projects Division at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the IMAP and Carruthers Geocorona Observatory missions for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate.
The SWFO-L1 mission is managed by NOAA and developed with NASA Goddard, and commercial partners. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at NASA Kennedy, manages the launch service for the missions.
To learn more about these missions, visit:
-end-
Abbey Interrante
Headquarters, Washington
301-201-0124
abbey.a.interrante@nasa.gov
Sarah Frazier
Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
202-853-7191
sarah.frazier@nasa.gov
Leejay Lockhart
Kennedy Space Center, Fla.
321-747-8310
leejay.lockhart@nasa.gov
John Jones-Bateman
NOAA’s Satellite and Information Service, Silver Spring, Md.
202-242-0929
john.jones-bateman@noaa.gov