NASA Wins Second Emmy Award for 2024 Total Solar Eclipse Broadcast
3 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
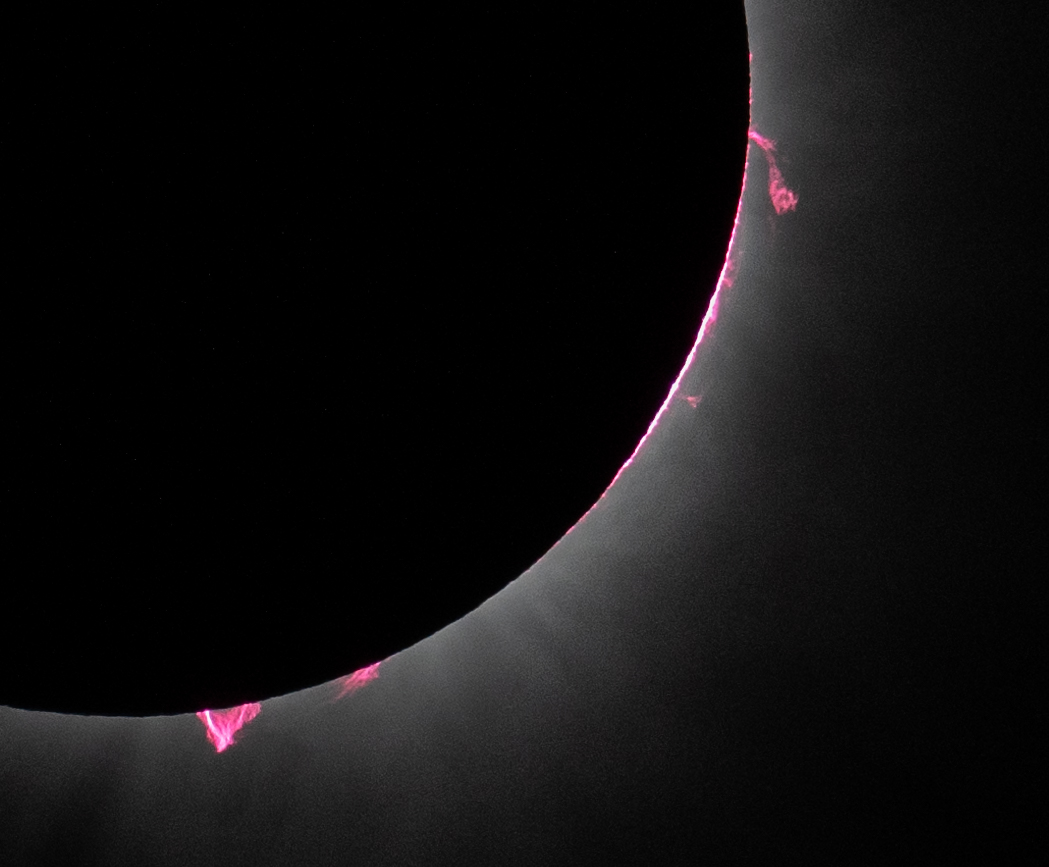
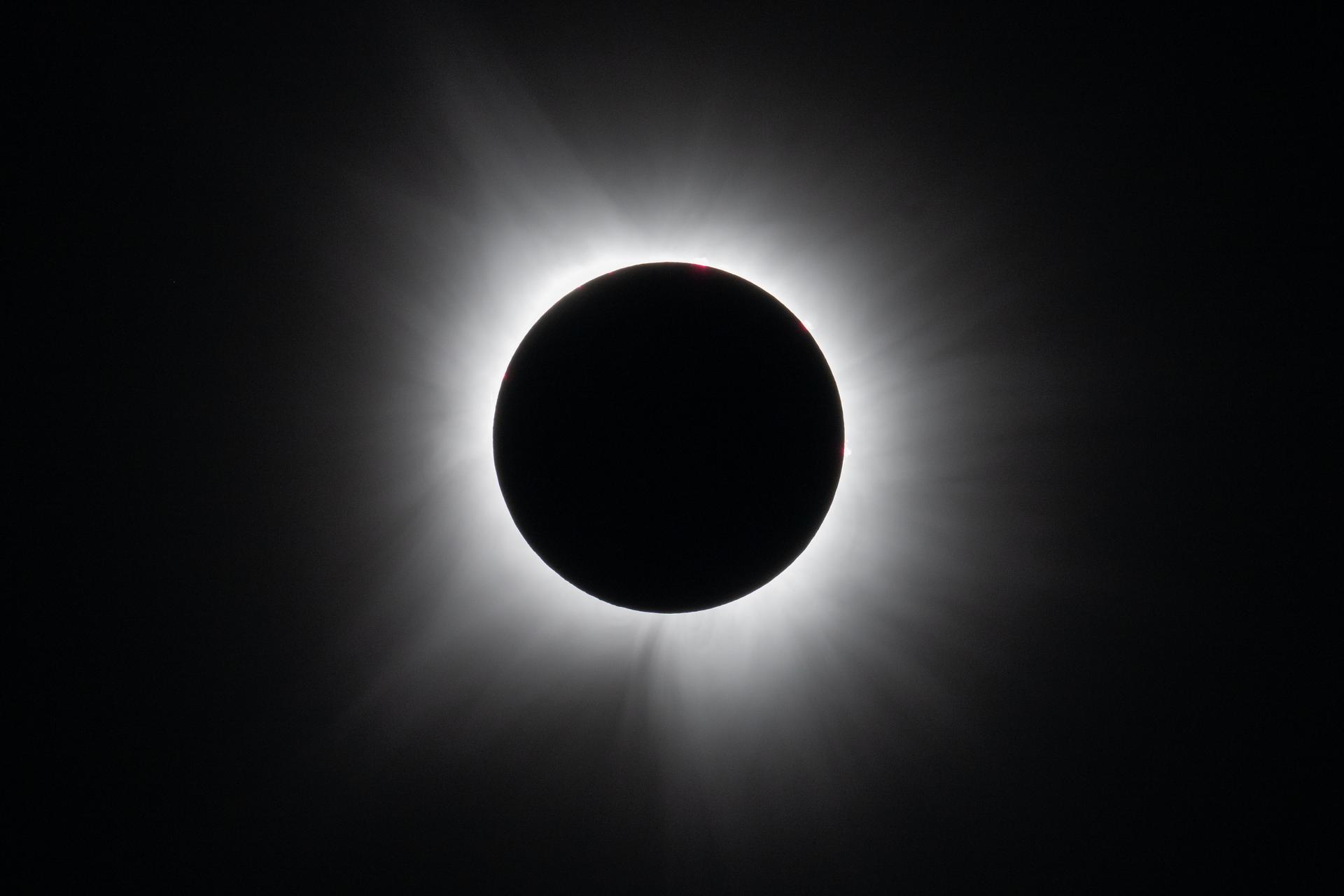
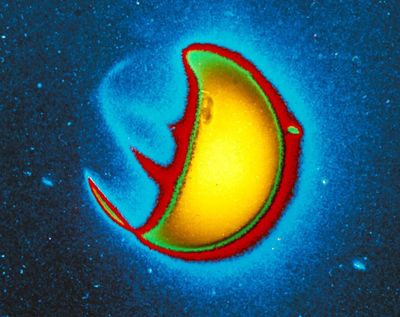
NASA’s broadcast of the April 8, 2024, total solar eclipse has won an Emmy Award for Excellence in Production Technology.
At the 76th Technology & Engineering Emmy Awards on Dec. 4, in New York City, the Academy of Television Arts & Sciences announced the win. Walt Lindblom and Sami Aziz accepted the award on behalf of the agency. For the broadcast, Lindblom served as the coordinating producer and Aziz served as the executive producer.
“By broadcasting the total solar eclipse, this team brought joy and wonder for our Sun, Moon, and Earth to viewers across America and the world,” said Will Boyington, associate administrator for the Office of Communications at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Congratulations to the production team, whose efforts demonstrate the hard work and dedication to the sharing the marvel that makes our solar system something we strive to understand.”
NASA’s live broadcast coverage of the 2024 total solar eclipse was the most complex live project ever produced by the agency. In total, NASA’s eclipse broadcasts garnered almost 40 million live and replay views across its own distribution channels, including on NASA+, the agency’s free streaming service. Externally, the agency’s main broadcast was picked up in 2,208 hits on 568 channels in 25 countries.
“Our unique place in the solar system allows us on Earth to witness one of the most spectacular science shows nature has to offer. NASA’s production team captured the action every step of the way across the path of totality, including the rare glimpse of the Sun’s corona,” said Nicky Fox, associate administrator for science at NASA Headquarters. “Congratulations to the NASA team for successfully showing the 2024 total solar eclipse through the eyes of NASA for the whole world to experience together.”
The broadcast spanned three hours, showcasing the eclipse across seven American states and two countries. From cities, parks, and stadiums, 11 hosts and correspondents provided on air commentary, interviews, and live coverage. Viewers tuned in from all over the world, including at watch parties in nine locations, from the Austin Public Library to New York’s Times Square. An interactive “Eclipse Board” provided real time data analysis as the Moon’s shadow crossed North America.
Live feeds from astronauts aboard the International Space Station and NASA’s WB-57 high-altitude research aircraft were brought in to provide rare and unique perspectives of the solar event. To make this possible, NASA deployed and enabled 67 cameras, 6 NASA Wide Area Network control rooms, 38 encoders, and 35 decoders. The team coordinated 20 live telescope feeds which represented 12 locations across the path of totality.
NASA’s eclipse broadcast won another Emmy award earlier this year at the 46th Annual News & Documentary Emmy Awards for Outstanding Live News Special. Additionally, the show received an Emmy nomination for Outstanding Show Open or Title Sequence – News. NASA’s eclipse communication and broadcast efforts also won two Webby Awards and two Webby People’s Voice Awards.
For more information about NASA, visit:
Abbey Interrante / Karen Fox
Headquarters, Washington
301-201-0124 / 202-358-1600
abbey.a.interrante@nasa.gov / karen.c.fox@nasa.gov
Details
Explore More
Discover Related Topics