Rare set of varied factors triggered Black Death
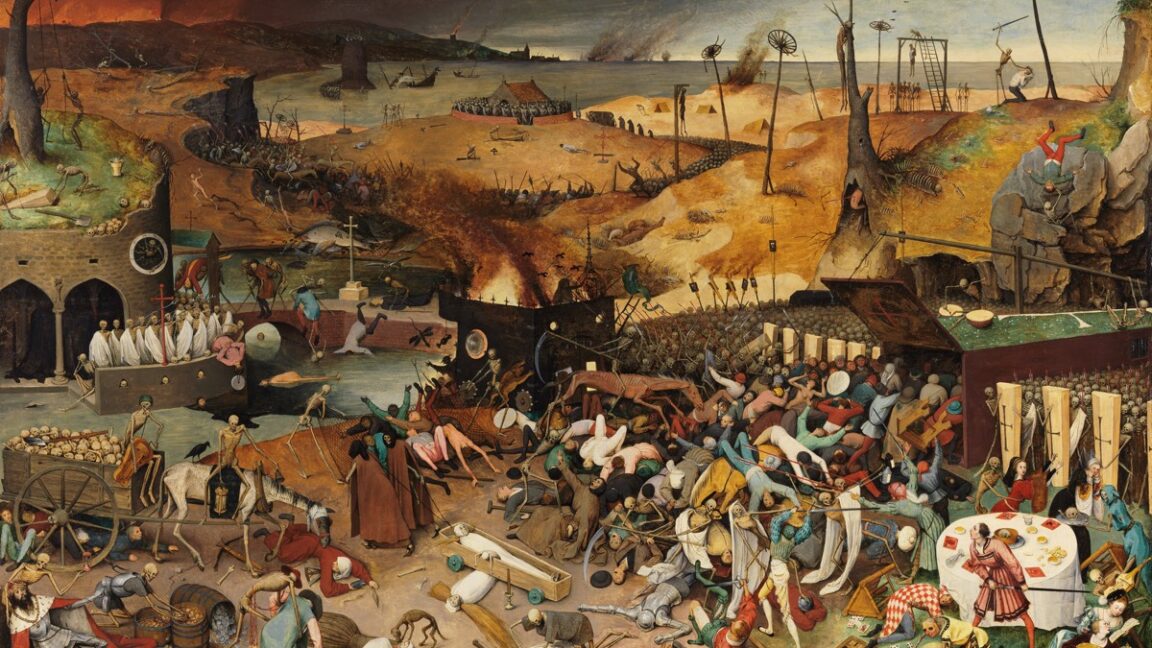
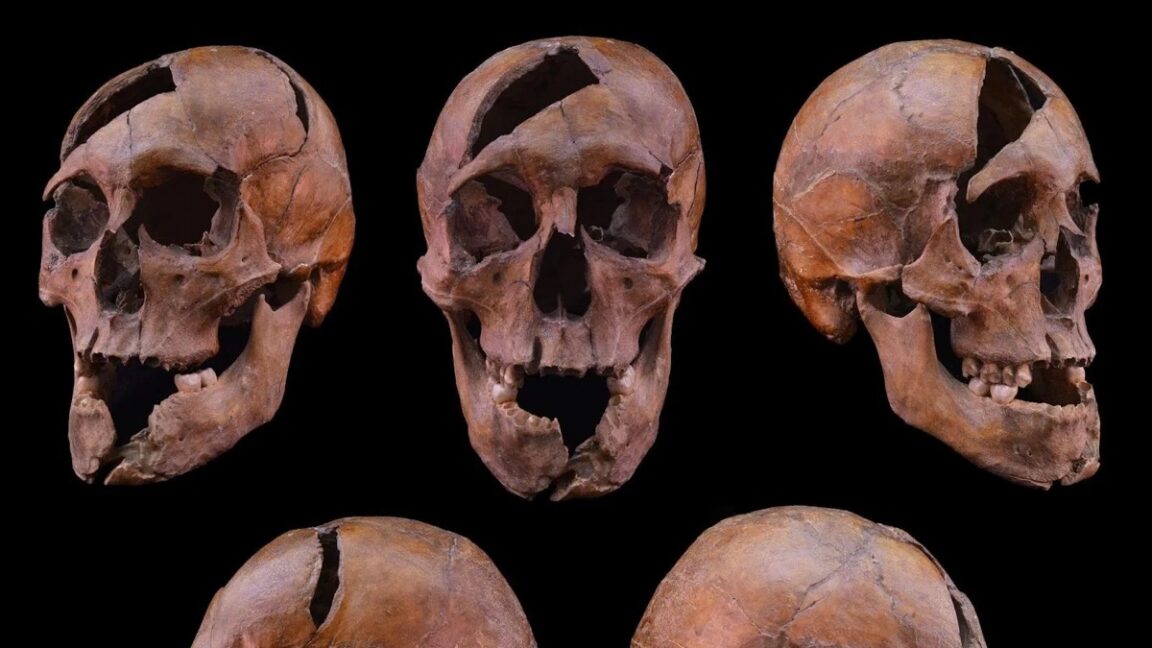
The Black Death ravaged medieval Western Europe, ultimately wiping out roughly one-third of the population. Scientists have identified the bacterium responsible and its likely origins, but certain specifics of how and why it spread to Europe are less clear. According to a new paper published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment, either one large volcanic eruption or a cluster of eruptions might have been the triggering factor, setting off a chain of events that brought the plague to the Mediterranean region in the 1340s.
Technically, we’re talking about the second plague pandemic. The first, known as the Justinian Plague, broke out about 541 CE and quickly spread across Asia, North Africa, the Middle East, and Europe. (The Eastern Roman Emperor Justinian I, for whom the pandemic is named, actually survived the disease.) There continued to be outbreaks of the plague over the next 300 years, although the disease gradually became less virulent and died out. Or so it seemed.
In the Middle Ages, the Black Death burst onto the scene, with the first historically documented outbreak occurring in 1346 in the Lower Volga and Black Sea regions. That was just the beginning of the second pandemic. During the 1630s, fresh outbreaks of plague killed half the populations of affected cities. Another bout of the plague significantly culled the population of France during an outbreak between 1647 and 1649, followed by an epidemic in London in the summer of 1665. The latter was so virulent that, by October, one in 10 Londoners had succumbed to the disease—over 60,000 people. Similar numbers perished in an outbreak in Holland in the 1660s. The pandemic had run its course by the early 19th century, but a third plague pandemic hit China and India in the 1890s. There are still occasional outbreaks today.
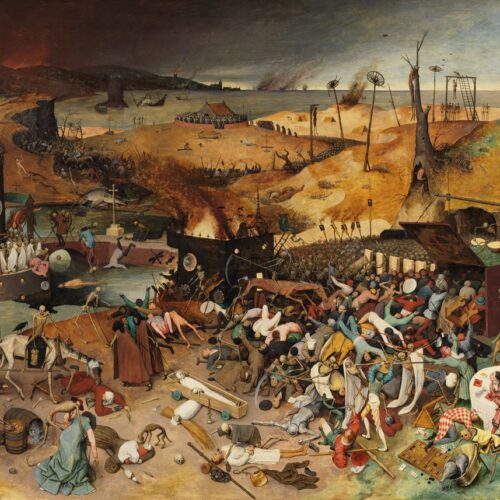


© Public domain








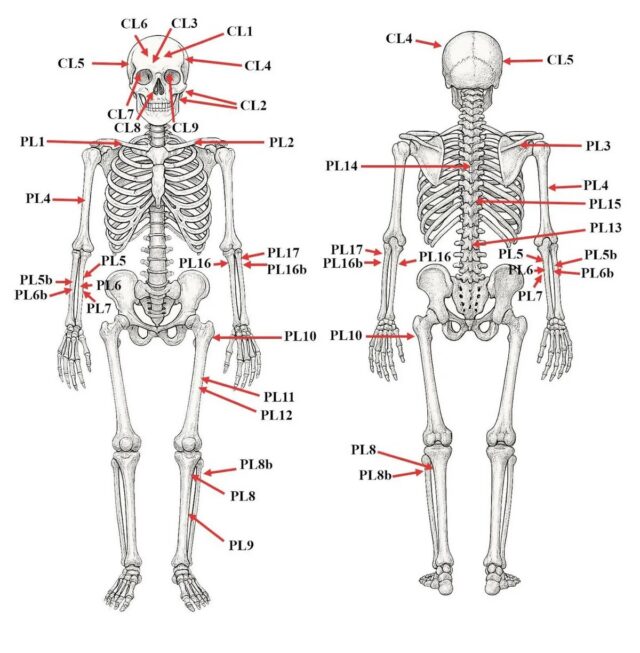 Credit:
Tamás Hajdu et al., 2026
Credit:
Tamás Hajdu et al., 2026
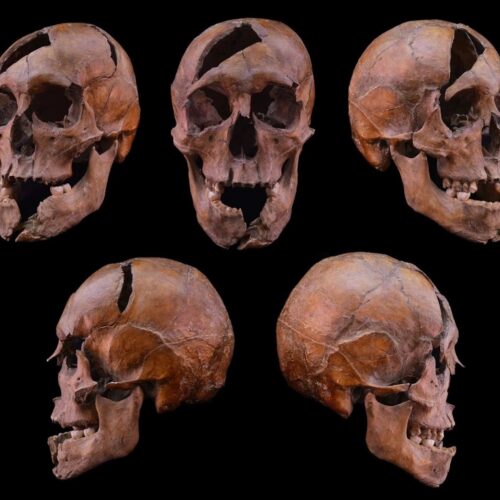

 Credit:
Warner Bros.
Credit:
Warner Bros.



















