NASA Sets Coverage for Astronaut Jonny Kim, Crewmates Return
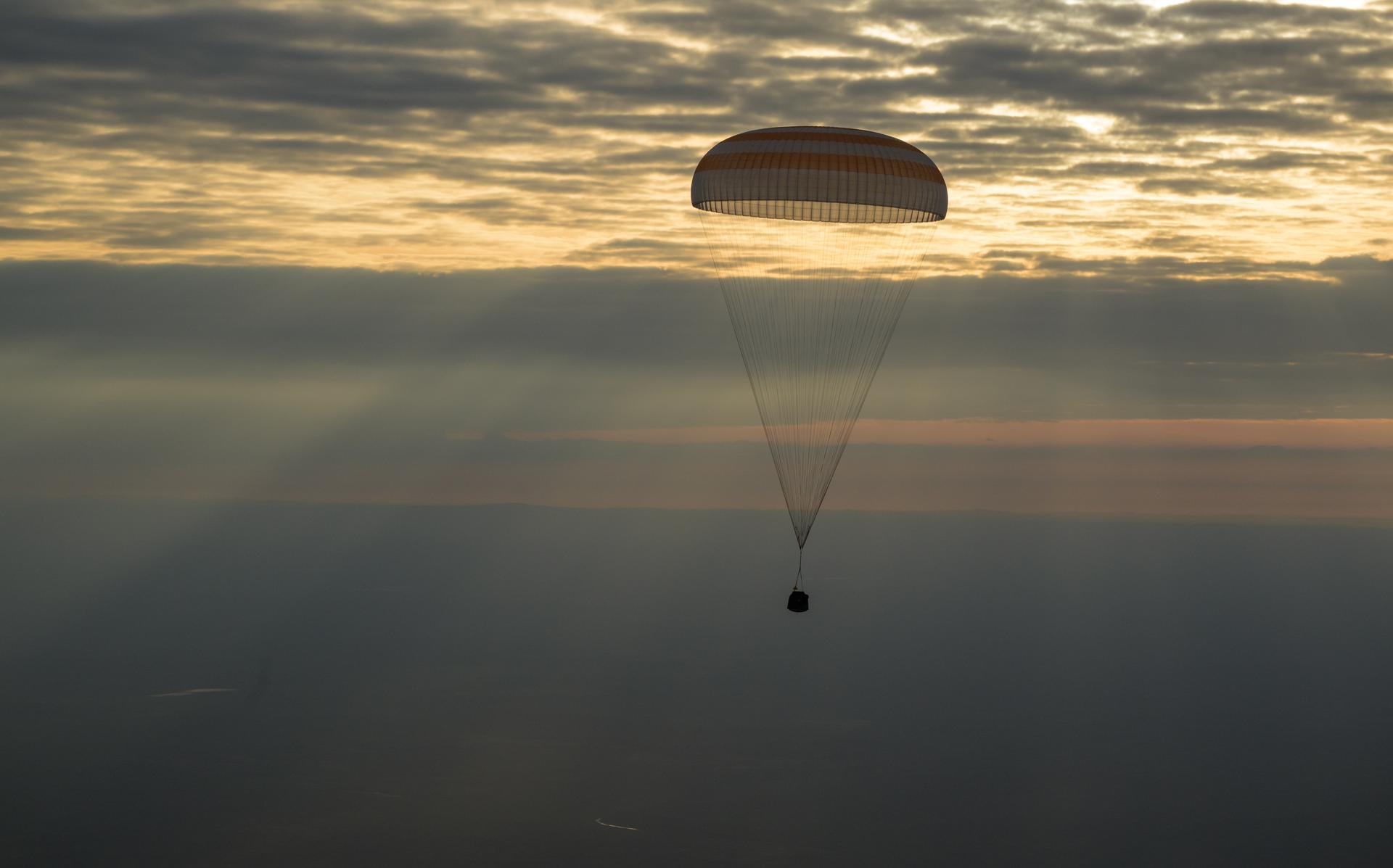
NASA astronaut Jonny Kim, accompanied by Roscosmos cosmonauts Sergey Ryzhikov and Alexey Zubritsky, is preparing to depart the International Space Station aboard the Soyuz MS-27 spacecraft and return to Earth.
Kim, Ryzhikov, and Zubritsky will undock from the station’s Prichal module at 8:41 p.m. EST on Monday, Dec. 8, headed for a parachute-assisted landing at 12:04 a.m. on Tuesday, Dec. 9 (10:04 a.m. local time in Kazakhstan), on the steppe of Kazakhstan, southeast of the city of Dzhezkazgan.
Watch NASA’s live coverage of the crew’s return on NASA+, Amazon Prime, and the agency’s YouTube channel. Learn how to stream NASA content through a variety of online platforms, including social media.
The space station change of command ceremony will begin at 10:30 a.m. Sunday, Dec. 7, on NASA+ and the agency’s YouTube channel. Rzyhikov will hand over station command to NASA astronaut Mike Fincke for Expedition 74, which begins at the time of Soyuz MS-27 undocking.
Kim and his crewmates are completing a 245-day mission aboard the station. At the conclusion of their mission, they will have orbited Earth 3,920 times and traveled nearly 104 million miles. This was the first flight for Kim and Zubritsky to the orbiting laboratory, while Ryzhikov is ending his third trip to space.
After landing, the three crew members will fly by helicopter to Karaganda, Kazakhstan, where recovery teams are based. Kim will board a NASA aircraft and return to Houston, while Ryzhikov and Zubritsky will depart for their training base in Star City, Russia.
NASA’s coverage is as follows (all times Eastern and subject to change based on real-time operations):
Sunday, Dec. 7:
10:30 a.m. – Expedition 73/74 change of command ceremony begins on NASA+ Amazon Prime, and YouTube.
Monday, Dec. 8:
4:45 p.m. – Farewells and hatch closing coverage begins on NASA+, Amazon Prime, and YouTube.
5:10 p.m. – Hatch closing
8:15 p.m. – Undocking coverage beings on NASA+, Amazon Prime, and YouTube.
8:41 p.m. – Undocking
10:30 p.m. – Deorbit and landing coverage begins on NASA+, Amazon Prime, and YouTube.
11:10 p.m. – Deorbit burn
Tuesday, Dec. 9:
12:04 a.m. – Landing
For more than 25 years, people have lived and worked continuously aboard the International Space Station, advancing scientific knowledge and making research breakthroughs that are not possible on Earth. The station is a critical testbed for NASA to understand and overcome the challenges of long-duration spaceflight and to expand commercial opportunities in low Earth orbit. As commercial companies concentrate on providing human space transportation services and destinations as part of a robust low Earth orbit economy, NASA is focusing its resources on deep space missions to the Moon as part of the Artemis campaign in preparation for future human missions to Mars.
Learn more about International Space Station research and operations at:
-end-
Josh Finch / Jimi Russell
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1100
joshua.a.finch@nasa.gov / james.j.russell@nasa.gov
Sandra Jones / Joseph Zakrzewski
Johnson Space Center, Houston
281-483-5111
sandra.p.jones@nasa.gov / joseph.a.zakrzewski@nasa.gov