To buy or not to buy: How cybercriminals capitalize on Black Friday

The global e‑commerce market is accelerating faster than ever before, driven by expanding online retail, and rising consumer adoption worldwide. According to McKinsey Global Institute, global e‑commerce is projected to grow by 7–9% annually through 2040.
At Kaspersky, we track how this surge in online shopping activity is mirrored by cyber threats. In 2025, we observed attacks which targeted not only e‑commerce platform users but online shoppers in general, including those using digital marketplaces, payment services and apps for everyday purchases. This year, we additionally analyzed how cybercriminals exploited gaming platforms during Black Friday, as the gaming industry has become an integral part of the global sales calendar. Threat actors have been ramping up their efforts during peak sales events like Black Friday, exploiting high demand and reduced user vigilance to steal personal data, funds, or spread malware.
This report continues our annual series of analyses published on Securelist in 2021, 2022, 2023, and 2024, which examine the evolving landscape of shopping‑related cyber threats.
Methodology
To track how the shopping threat landscape continues to evolve, we conduct an annual assessment of the most common malicious techniques, which span financial malware, phishing pages that mimic major retailers, banks, and payment services, as well as spam campaigns that funnel users toward fraudulent sites. In 2025, we also placed a dedicated focus on gaming-related threats, analyzing how cybercriminals leverage players’ interest. The threat data we rely on is sourced from the Kaspersky Security Network (KSN), which processes anonymized cybersecurity data shared consensually by Kaspersky users. This report draws on data collected from January through October 2025.
Key findings
- In the first ten months of 2025, Kaspersky identified nearly 6.4 million phishing attacks which targeted users of online stores, payment systems, and banks.
- As many as 48.2% of these attacks were directed at online shoppers.
- We blocked more than 146,000 Black Friday-themed spam messages in the first two weeks of November.
- Kaspersky detected more than 2 million phishing attacks related to online gaming.
- Around 1.09 million banking-trojan attacks were recorded during the 2025 Black Friday season.
- The number of attempted attacks on gaming platforms surged in 2025, reaching more than 20 million, a significant increase compared to previous years.
- More than 18 million attempted malicious attacks were disguised as Discord in 2025, a more than 14-time increase year-over-year, while Steam remained within its usual five-year fluctuation range.
Shopping fraud and phishing
Phishing and scams remain among the most common threats for online shoppers, particularly during high-traffic retail periods when users are more likely to act quickly and rely on familiar brand cues. Cybercriminals frequently recreate the appearance of legitimate stores, payment pages, and banking services, making their fraudulent sites and emails difficult to distinguish from real ones. With customers navigating multiple offers and payment options, they may overlook URL or sender details, increasing the likelihood of credential theft and financial losses.
From January through to October 2025, Kaspersky products successfully blocked 6,394,854 attempts to access phishing links which targeted users of online stores, payment systems, and banks. Breaking down these attempts, 48.21% had targeted online shoppers (for comparison, this segment accounted for 37.5% in 2024), 26.10% targeted banking users (compared to 44.41% in 2024), and 25.69% mimicked payment systems (18.09% last year). Compared to previous years, there has been a noticeable shift in focus, with attacks against online store users now representing a larger share, reflecting cybercriminals’ continued emphasis on exploiting high-demand retail periods, while attacks on banking users have decreased in relative proportion. This may be related to online banking protection hardening worldwide.
In 2025, Kaspersky products detected and blocked 606,369 phishing attempts involving the misuse of Amazon’s brand. Cybercriminals continued to rely on Amazon-themed pages to deceive users and obtain personal or financial information.
Other major e-commerce brands were also impersonated. Attempts to visit phishing pages mimicking Alibaba brands, such as AliExpress, were detected 54,500 times, while eBay-themed pages appeared in 38,383 alerts. The Latin American marketplace Mercado Libre was used as a lure in 8,039 cases, and Walmart-related phishing pages were detected 8,156 times.
In 2025, phishing campaigns also extensively mimicked other online platforms. Netflix-themed pages were detected 801,148 times, while Spotify-related attempts reached 576,873. This pattern likely reflects attackers’ continued focus on high-traffic digital entertainment services with in-service payments enabled, which can be monetized via stolen accounts.
How scammers exploited shopping hype in 2025
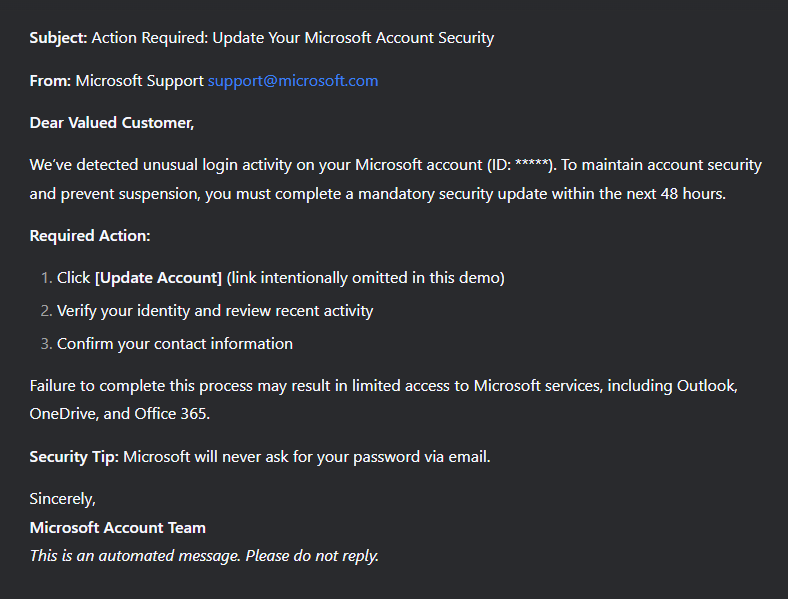
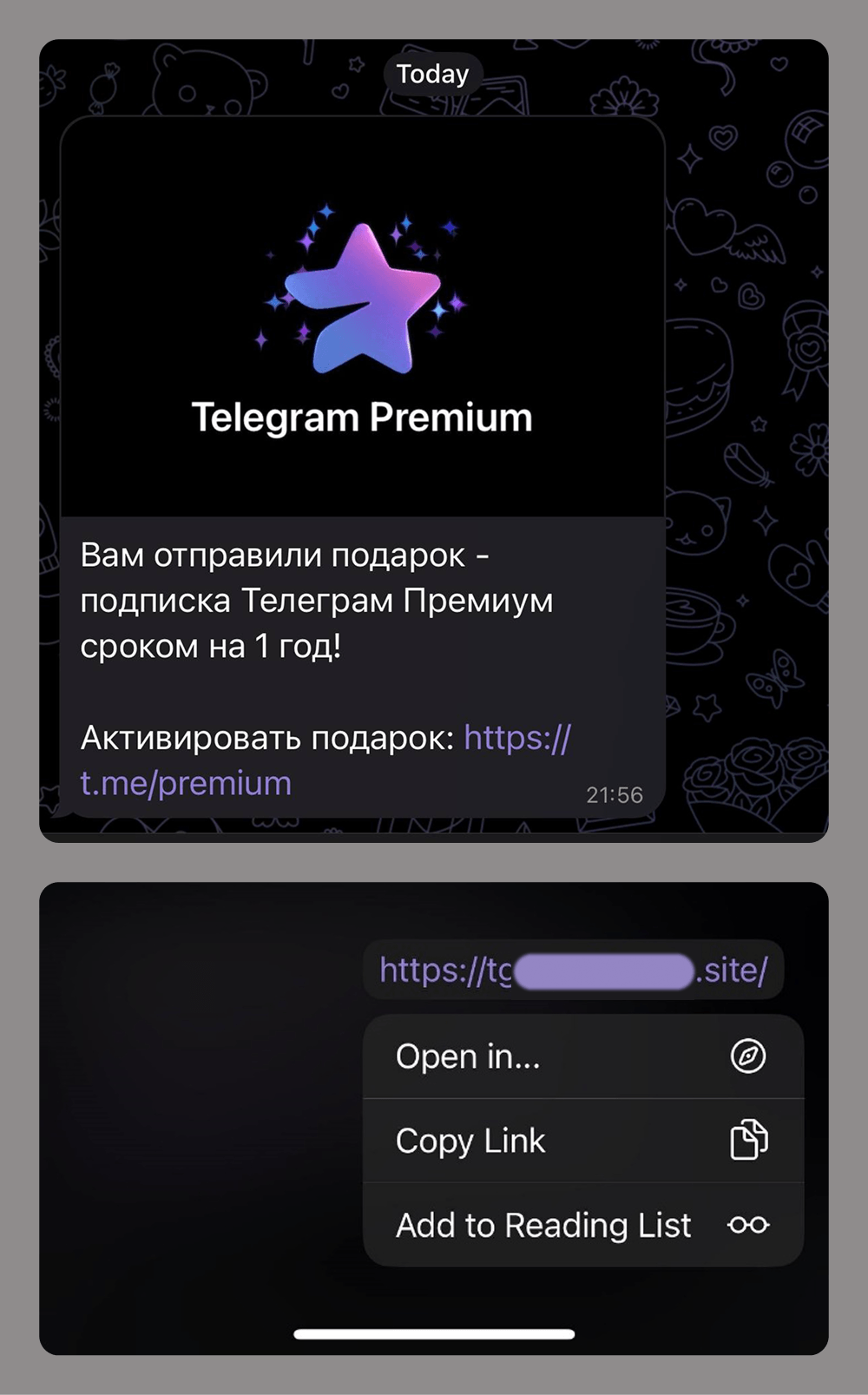
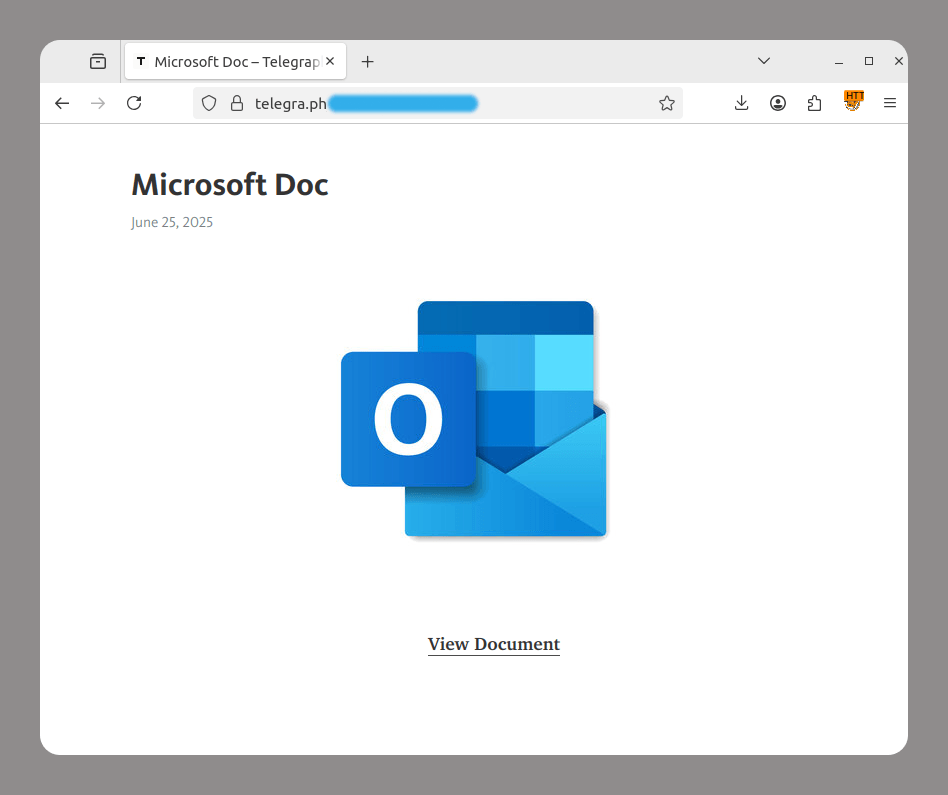
In 2025, Black Friday-related scams continued to circulate across multiple channels, with fraudulent email campaigns remaining one of the key distribution methods. As retailers increase their seasonal outreach, cybercriminals take advantage of the high volume of promotional communications by sending look-alike messages that direct users to scam and phishing pages. In the first two weeks of November, 146,535 spam messages connected to seasonal sales were detected by Kaspersky, including 2,572 messages referencing Singles day sales.
Scammers frequently attempt to mimic well-known platforms to increase the credibility of their messages. In one of the recurring campaigns, a pattern seen year after year, cybercriminals replicated Amazon’s branding and visual style, promoting supposedly exclusive early-access discounts of up to 70%. In this particular case, the attackers made almost no changes to the text used in their 2024 campaign, again prompting users to follow a link leading to a fraudulent page. Such pages are usually designed to steal their personal or payment information or to trick the user into buying non-existent goods.

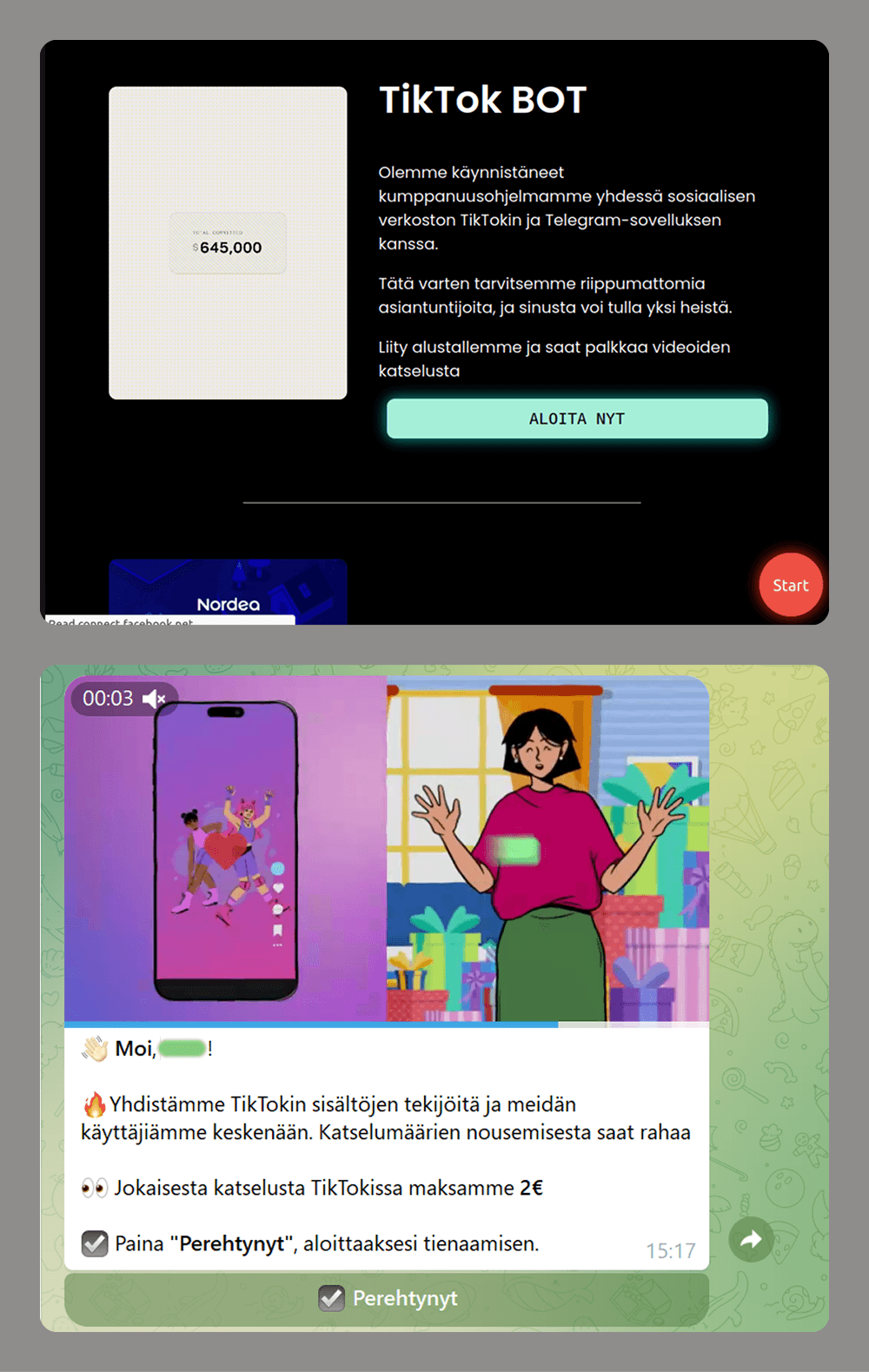
Beyond the general excitement around seasonal discounts, scammers also try to exploit consumers’ interest in newly released Apple devices. To attract attention, they use the same images of the latest gadgets across various mailing campaigns, just changing the names of legitimate retailers that allegedly sell the brand.
 |
 |
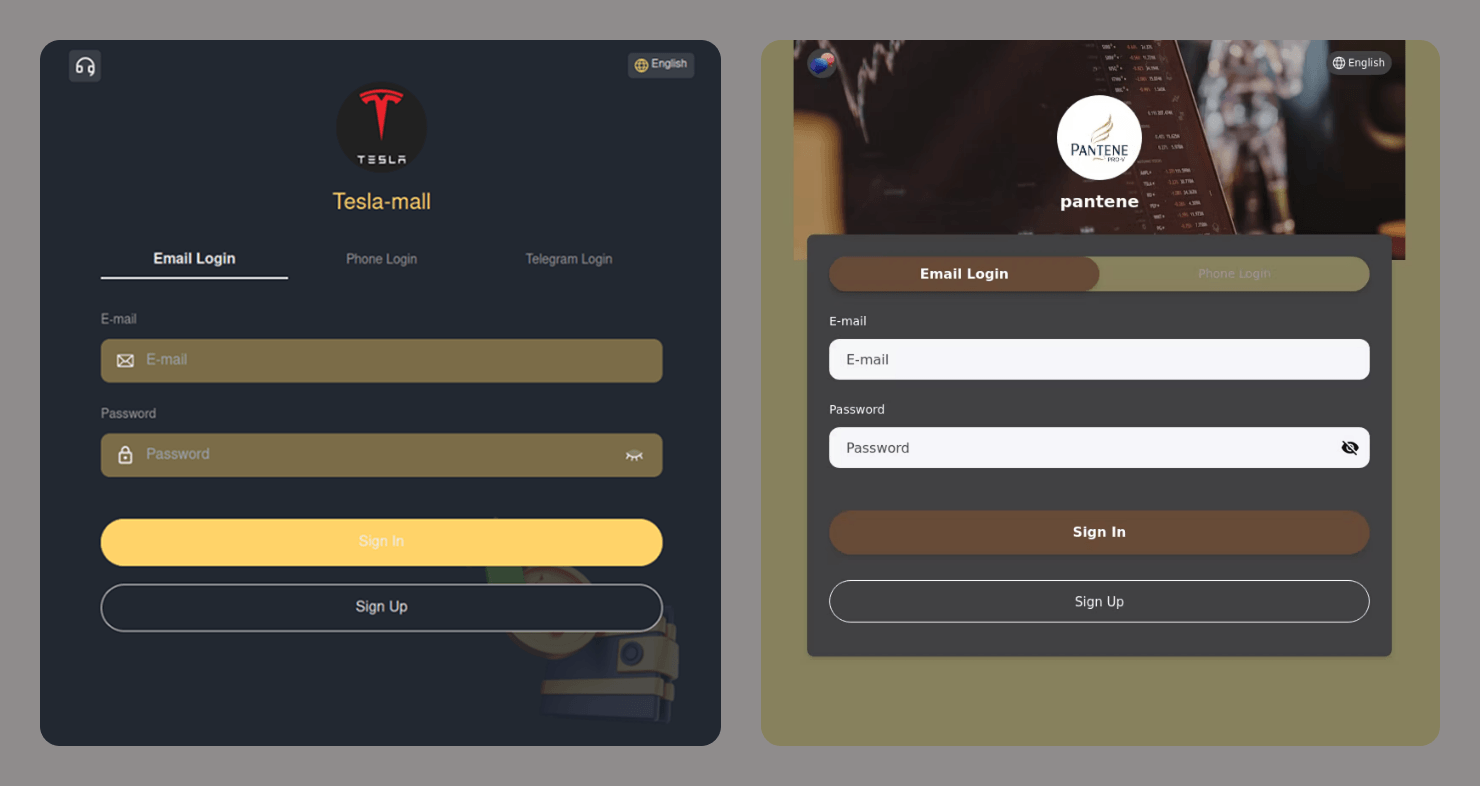
As subscription-based streaming platforms also take part in global sales periods, cybercriminals attempt to take advantage of this interest as well. For example, we observed a phishing website where scammers promoted an offer for a “12-month subscription bundle” covering several popular services at once, asking users to enter their bank card details. To enhance credibility, the scammers also include fabricated indicators of numerous successful purchases from other “users,” making the offer appear legitimate.

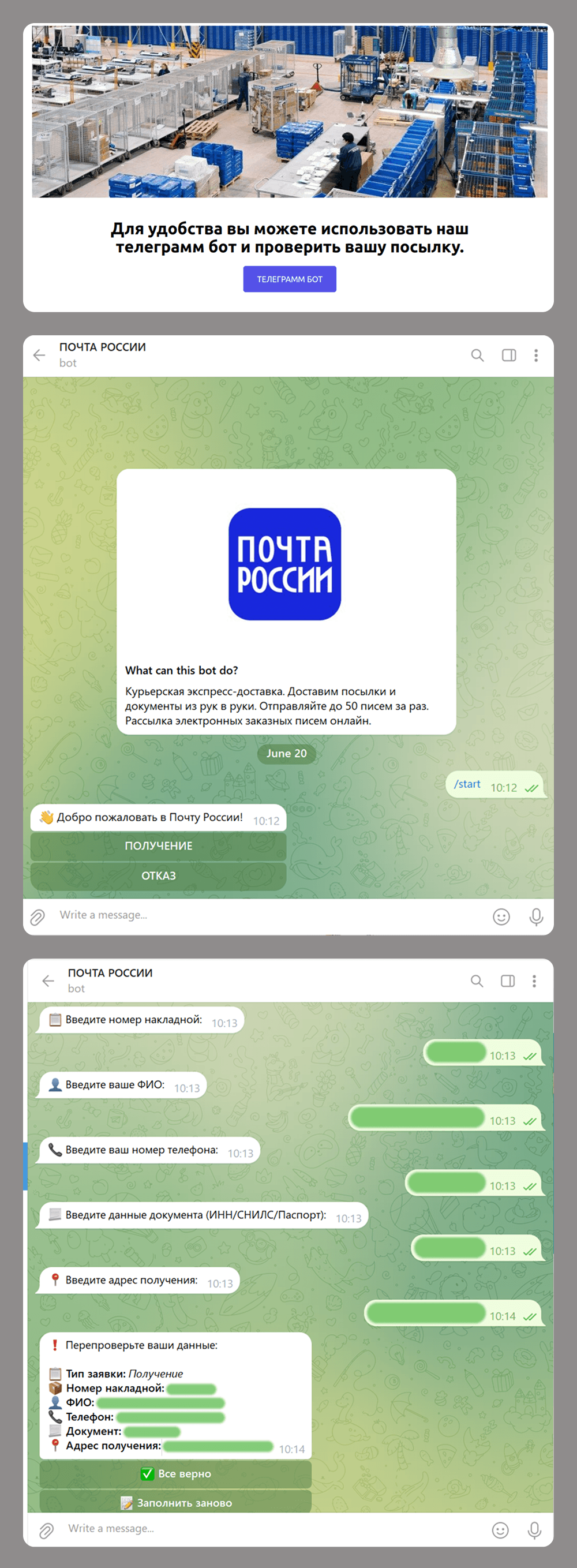
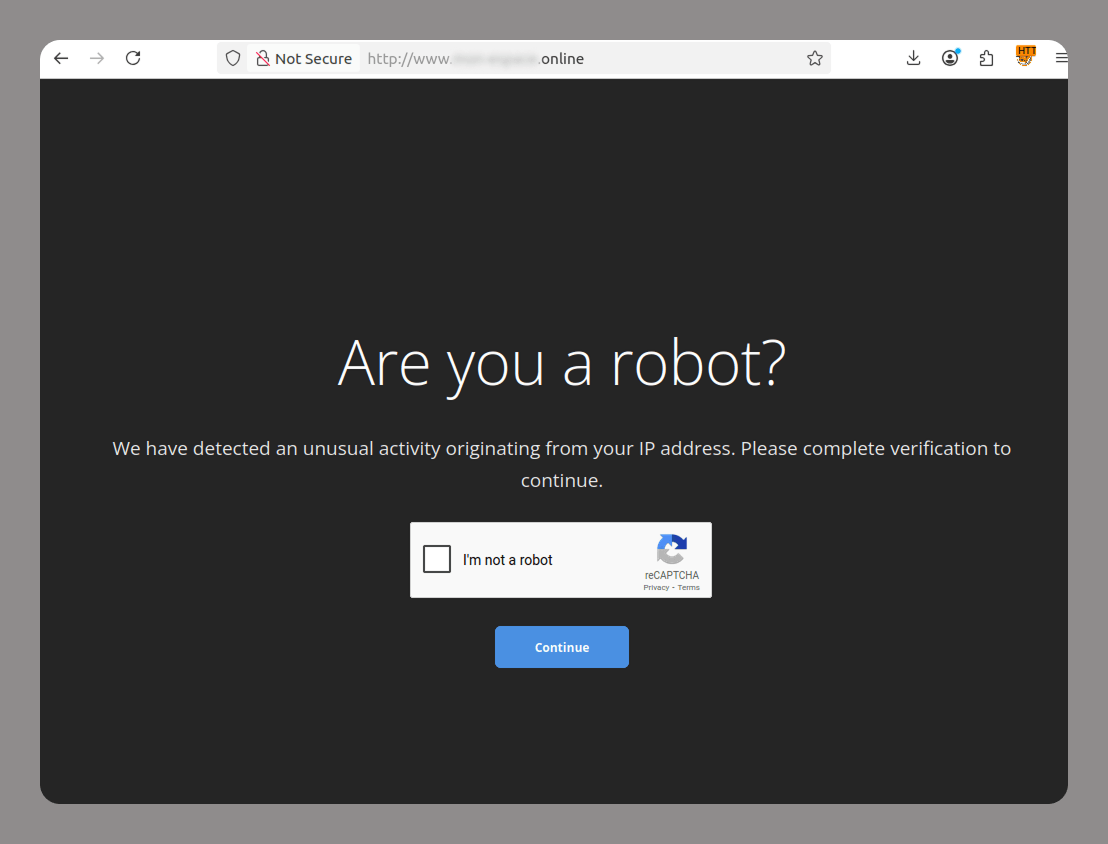
In addition to imitating globally recognized platforms, scammers also set up fake pages that pretend to be local services in specific countries. This tactic enables more targeted campaigns that blend into the local online landscape, increasing the chances that users will perceive the fraudulent pages as legitimate and engage with them.
Banking Trojans
Banking Trojans, or “bankers,” are another tool for cybercriminals exploiting busy shopping seasons like Black Friday in 2025. They are designed to steal sensitive data from online banking and payment systems. In this section, we’ll focus on PC bankers. Once on a victim’s device, they monitor the browser and, when the user visits a targeted site, can use techniques like web injection or form-grabbing to capture login credentials, credit card information, and other personal data. Some trojans also watch the clipboard for crypto wallet addresses and replace them with those controlled by the malicious actors.
As online shopping peaks during major sales events, attackers increasingly target e-commerce platforms alongside banks. Trojans may inject fake forms into legitimate websites, tricking users into revealing sensitive data during checkout and increasing the risk of identity theft and financial fraud. In 2025, Kaspersky detected over 1,088,293* banking Trojan attacks. Among notable banker-related cases analysed by Kaspersky throughout the year, campaigns involving the new Maverick banking Trojan distributed via WhatsApp, as well as the Efimer Trojan which spread through malicious emails and compromised WordPress sites can be mentioned, both illustrating how diverse and adaptive banking Trojan delivery methods are.
*These statistics include globally active banking malware, and malware for ATMs and point-of-sale (PoS) systems. We excluded data on Trojan-banker families that no longer use banking Trojan functionality in their attacks, such as Emotet.
A holiday sales season on the dark web
Apparently, even the criminal underground follows its own version of a holiday sales season. Once data is stolen, it often ends up on dark-web forums, where cybercriminals actively search for buyers. This pattern is far from new, and the range of offers has remained largely unchanged over the past two years.
Threat actors consistently seize the opportunity to attract “new customers,” advertising deep discounts tied to high-profile global sales events. It is worth noting that year after year we see the same established services announce their upcoming promotions in the lead-up to Black Friday, almost as if operating on a retail calendar of their own.
We also noted that dark web forum participants themselves eagerly await these seasonal markdowns, hoping to obtain databases at the most favorable rates and expressing their wishes in forum posts. In the months before Black Friday, posts began appearing on carding-themed forums advertising stolen payment-card data at promotional prices.
Threats targeting gaming
The gaming industry faces a high concentration of scams and other cyberthreats due to its vast global audience and constant demand for digital goods, updates, and in-game advantages. Players often engage quickly with new offers, making them more susceptible to deceptive links or malicious files. At the same time, the fact that gamers often download games, mods, skins etc. from third-party marketplaces, community platforms, and unofficial sources creates additional entry points for attackers.
The number of attempted attacks on platforms beloved by gamers increased dramatically in 2025, reaching 20,188,897 cases, a sharp rise compared to previous years.
The nearly sevenfold increase in 2025 is most likely linked to the Discord block by some countries introduced at the end of 2024. Eventually users rely on alternative tools, proxies and modified clients. This change significantly expanded the attack surface, making users more vulnerable to fake installers, and malicious updates disguised as workarounds for the restriction.
It can also be seen in the top five most targeted gaming platforms of 2025:
| Platform | The number of attempted attacks |
| Discord | 18,556,566 |
| Steam | 1,547,110 |
| Xbox | 43,560 |
| Uplay | 28,366 |
| Battle.net | 5,538 |
In previous years, Steam consistently ranked as the platform with the highest number of attempted attacks. Its extensive game library, active modding ecosystem, and long-standing role in the gaming community made it a prime target for cybercriminals distributing malicious files disguised as mods, cheats, or cracked versions. In 2025, however, the landscape changed significantly. The gap between Steam and Discord expanded to an unprecedented degree as Steam-related figures remained within their typical fluctuation range of the past five years, while the number of attempted Discord-disguised attacks surged more than 14 times compared to 2024, reshaping the hierarchy of targeted gaming platforms.
Attempts to attack users through malicious or unwanted files disguised as Steam and Discord throughout the reported period (download)
From January to October, 2025, cybercriminals used a variety of cyberthreats disguised as popular related to gamers platforms, modifications or circumvention options. RiskTool dominated the threat landscape with 17,845,099 detections, far more than any other category. Although not inherently malicious, these tools can hide files, mask processes, or disable programs, making them useful for stealthy, persistent abuse, including covert crypto-mining. Downloaders ranked second with 1,318,743 detections. These appear harmless but may fetch additional malware among other downloaded files. Downloaders are typically installed when users download unofficial patches, cracked clients, or mods. Trojans followed with 384,680 detections, often disguised as cheats or mod installers. Once executed, they can steal credentials, intercept tokens, or enable remote access, leading to account takeovers and the loss of in-game assets.
| Threat | Gaming-related detections |
| RiskTool | 17,845,099 |
| Downloader | 1,318,743 |
| Trojan | 384,680 |
| Adware | 184,257 |
| Exploit | 152,354 |
Phishing and scam threats targeting gamers
In addition to tracking malicious and unwanted files disguised as gamers’ platforms, Kaspersky experts also analysed phishing pages which impersonated these services. Between January and October 2025, Kaspersky products detected 2,054,336 phishing attempts targeting users through fake login pages, giveaway offers, “discounted” subscriptions and other scams which impersonated popular platforms like Steam, PlayStation, Xbox and gaming stores.
The page shown in the screenshot is a typical Black Friday-themed scam that targets gamers, designed to imitate an official Valorant promotion. The “Valorant Points up to 80% off” banner, polished layout, and fake countdown timer create urgency and make the offer appear credible at first glance. Users who proceed are redirected to a fake login form requesting Riot account credentials or bank card details. Once submitted, this information enables attackers to take over accounts, steal in-game assets, or carry out fraudulent transactions.
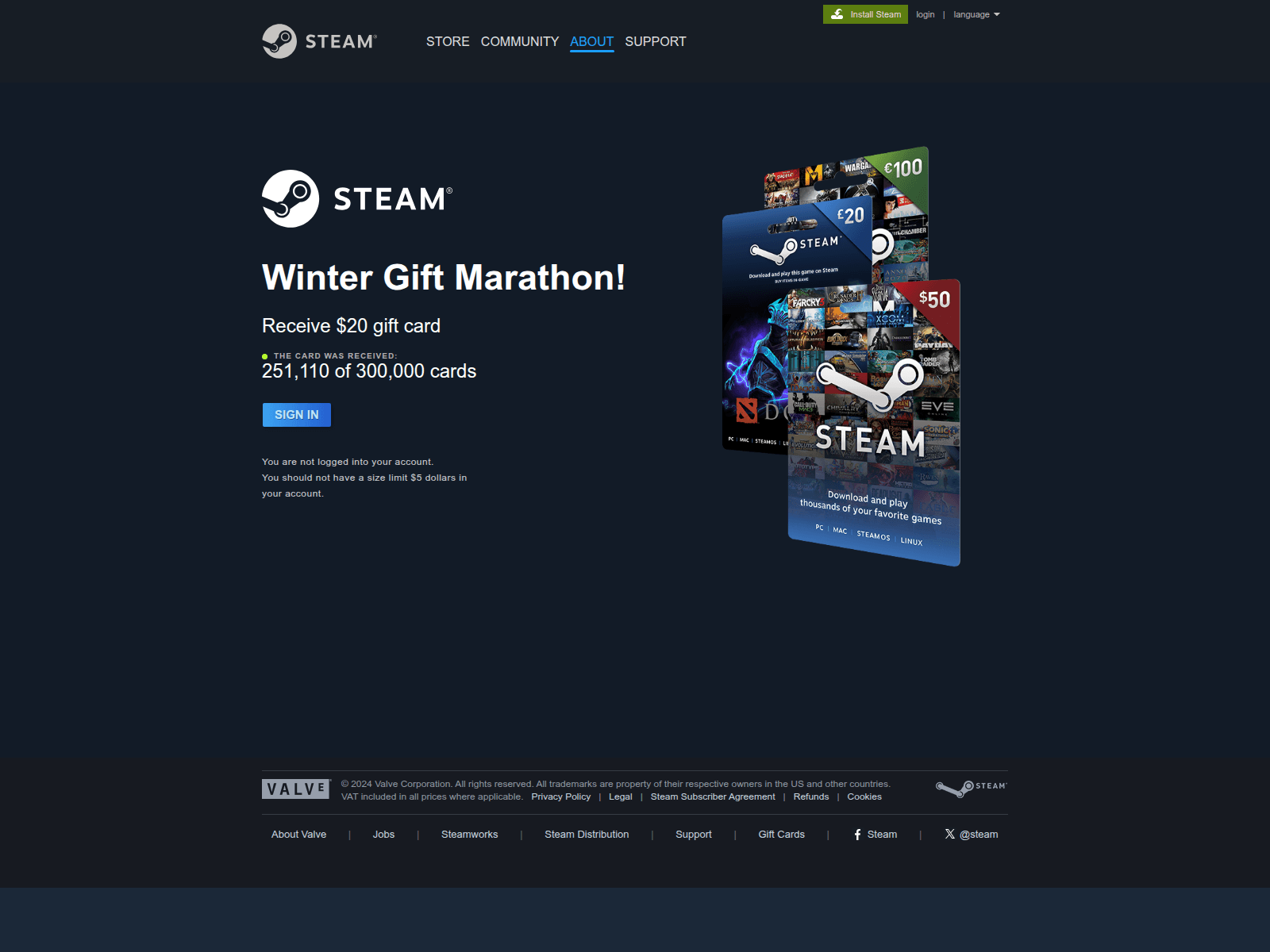
Minor text errors reveal the page’s fraudulent nature. The phrase “You should not have a size limit of 5$ dollars in your account” is grammatically incorrect and clearly suspicious.
Another phishing page relies on a fabricated “Winter Gift Marathon” that claims to offer a free $20 Steam gift card. The seasonal framing, combined with a misleading counter (“251,110 of 300,000 cards received”), creates an artificial sense of legitimacy and urgency intended to prompt quick user interaction.
The central component of the scheme is the “Sign in” button, which redirects users to a spoofed Steam login form designed to collect their credentials. Once obtained, attackers can gain full access to the account, including payment methods, inventory items, and marketplace assets, and may be able to compromise additional services if the same password is used elsewhere.
 |
 |
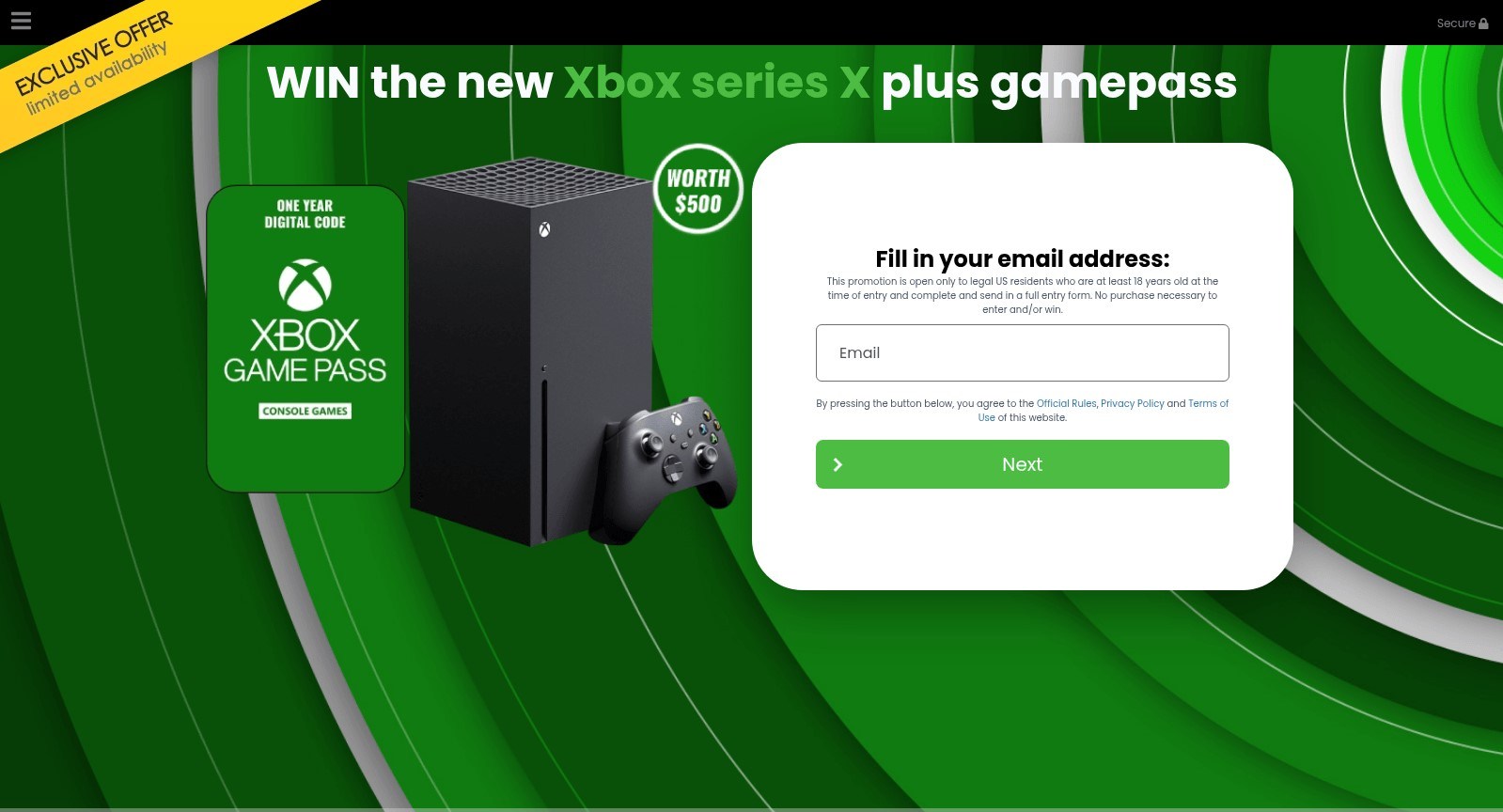
Scams themed around the PlayStation 5 Pro and Xbox Series X appear to be generated from a phishing kit, a reusable template that scammers adapt for different brands. Despite referencing two consoles, both pages follow the same structure which features a bold claim offering a chance to “win” a high-value device, a large product image on the left, and a minimalistic form on the right requesting the user’s email address.
A yellow banner promotes an “exclusive offer” with “limited availability,” pressuring users to respond quickly. After submitting an email, victims are typically redirected to additional personal and payment data-collection forms. They also may later be targeted with follow-up phishing emails, spam, or malicious links.
Conclusions
In 2025, the ongoing expansion of global e-commerce continued to be reflected in the cyberthreat landscape, with phishing, scam activity, and financial malware targeting online shoppers worldwide. Peak sales periods once again created favorable conditions for fraud, resulting in sustained activity involving spoofed retailer pages, fraudulent email campaigns, and seasonal spam.
Threat actors also targeted users of digital entertainment and subscription services. The gaming sector experienced a marked increase in malicious activity, driven by shifts in platform accessibility and the widespread use of third-party tools. The significant rise in malicious detections associated with Discord underscored how rapidly attackers adjust to changes in user behavior.
Overall, 2025 demonstrated that cybercriminals continue to leverage predictable user behavior patterns and major sales events to maximize the impact of their operations. Consumers should remain especially vigilant during peak shopping periods and use stronger security practices, such as two-factor authentication, secure payment methods, and cautious browsing. A comprehensive security solution that blocks malware, detects phishing pages, and protects financial data can further reduce the risk of falling victim to online threats.