From React to Remote Code – Protecting Against the Critical React2Shell RCE Exposure
A critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, dubbed ‘React2Shell’, affecting React Server Components (RSC) and Next.js, is allowing unauthenticated attackers to perform server-side code attacks via malicious HTTP requests.
Discovered by Lachlan Davidson, the flaw stems from insecure deserialization in the RSC ‘Flight’ protocol and impacts packages including react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel, and react-server-dom-turbopack. Exploitation is highly reliable, even in default deployments, and a single request can compromise the full Node.js process. The flaw is being tracked as CVE-2025-55182. Originally tagged as a CVE for Next.js, NIST subsequently rejected CVE-2025-66478, as it is a duplicate of CVE-2025-55182.
This blog post includes the critical, immediate actions recommended to secure your environment, new and existing Platform Detection Rules designed to defend against this vulnerability, and information on how SentinelOne Offensive Security Engine, a core component of the Singularity Cloud Security solution, allows our customers to quickly identify potentially vulnerable workloads.
Cloud Security solution, allows our customers to quickly identify potentially vulnerable workloads.
What is React2Shell? Background & Impact
On December 3, 2025, the React and Next.js teams disclosed two related vulnerabilities in the React Server Components (RSC) Flight protocol: CVE-2025-55182 (React) and CVE-2025-66478 (Next.js), with the latter CVE now marked by NIST as a duplicate.
Both enable unauthenticated RCE, impacting applications that use RSC directly or through popular frameworks such as Next.js. These vulnerabilities are rated critical (CVSS 10.0) because exploitation requires only a crafted HTTP request. No authentication, user action, or developer-added server code is needed for an attacker to gain control of the underlying Node.js process.
The vulnerability exists because RSC payloads are deserialized without proper validation, exposing server functions to attacker-controlled inputs. Since many modern frameworks enable RSC as part of their default build, some teams may be exposed without being aware that server-side RSC logic is active in their environment.
Security testing currently shows:
- Exploitation can succeed with near 100% reliability
- Default configurations are exploitable, including a standard
Next.jsapp created with create-next-app and deployed with no code changes - Applications may expose RSC endpoints even without custom server functions
- A single malicious request can escalate to full
Node.jsprocess compromise
Security researchers warn that cloud environments and server-side applications using default React or Next.js builds are particularly at risk. Exploitation could allow attackers to gain full control over servers, access sensitive data, and compromise application functionality. Reports have already emerged of China-nexus threat groups “racing to weaponize” the flaw.
Available Vendor Mitigations & Immediate Actions
Fixes are available in React 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0, and Next.js 5.x, Next.js 16.x, Next.js 14.3.0-canary.77 and later canary releases. Administrators are urged to audit environments and update affected packages immediately.
Companies are advised to review deployments, restrict unnecessary server-side exposure, and monitor logs for anomalous RSC requests. Securing default configurations, validating deserialized input, and maintaining a regular patch management schedule can prevent attackers from exploiting framework-level vulnerabilities in production applications.
- Update React by installing the patched versions of React as listed above.
- Update
Next.jsand other RSC-enabled frameworks as listed above. Ensure the latest framework and bundler releases are installed so they ship the patched React server bundles. - Review deployment behavior by checking whether your organization’s workloads expose RSC server function endpoints. These may exist regardless of whether developers added custom server functions.
How SentinelOne Protects Our Customers
Cloud Native Security – Offensive Security Engine
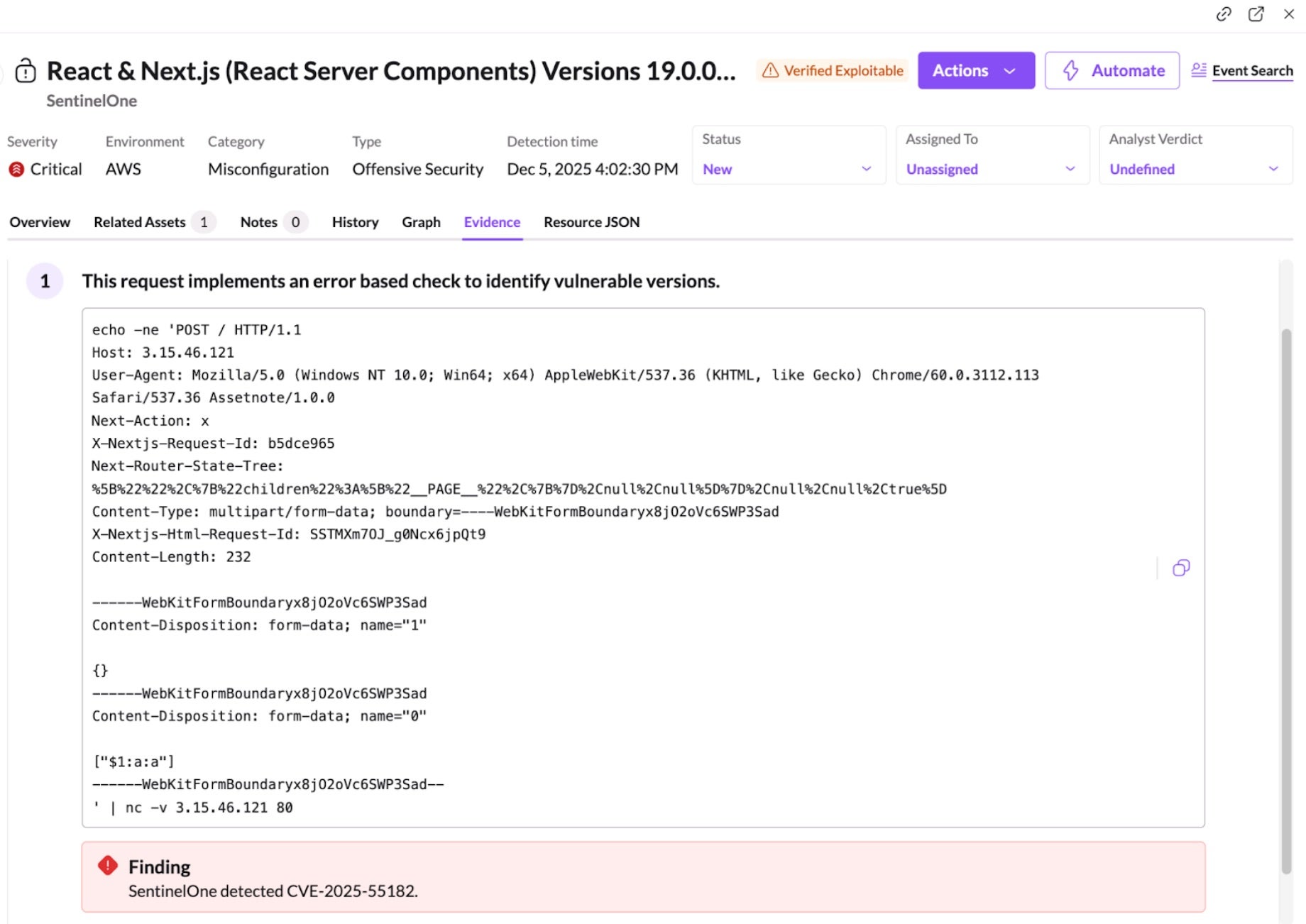
SentinelOne’s Offensive Security Engine (OSE), core component of its Singularity Cloud Security solution, proactively distinguishes between theoretical risks and actual threats by simulating an attacker’s methodology. Rather than relying solely on static scans that flag every potential misconfiguration or vulnerability, this engine automatically conducts safe, harmless simulations against your cloud infrastructure to validate exploitability.
This approach delivers differentiated outcomes by radically reducing alert fatigue and focusing security teams on immediate, confirmed dangers. By providing concrete evidence of exploitability—such as screenshots or code snippets of the successful simulation—it eliminates the need for manual validation and “red teaming” of every alert. Shift from chasing hypothetical vulnerabilities to remediating verified attack vectors, ensuring resources are always deployed against the risks that pose a genuine threat to their environment.
In response to this vulnerability, SentinelOne released a new OSE plugin which can verify exploitability of these vulnerabilities for publicly accessible workloads using a defanged (i.e., harmless) HTTP payload.
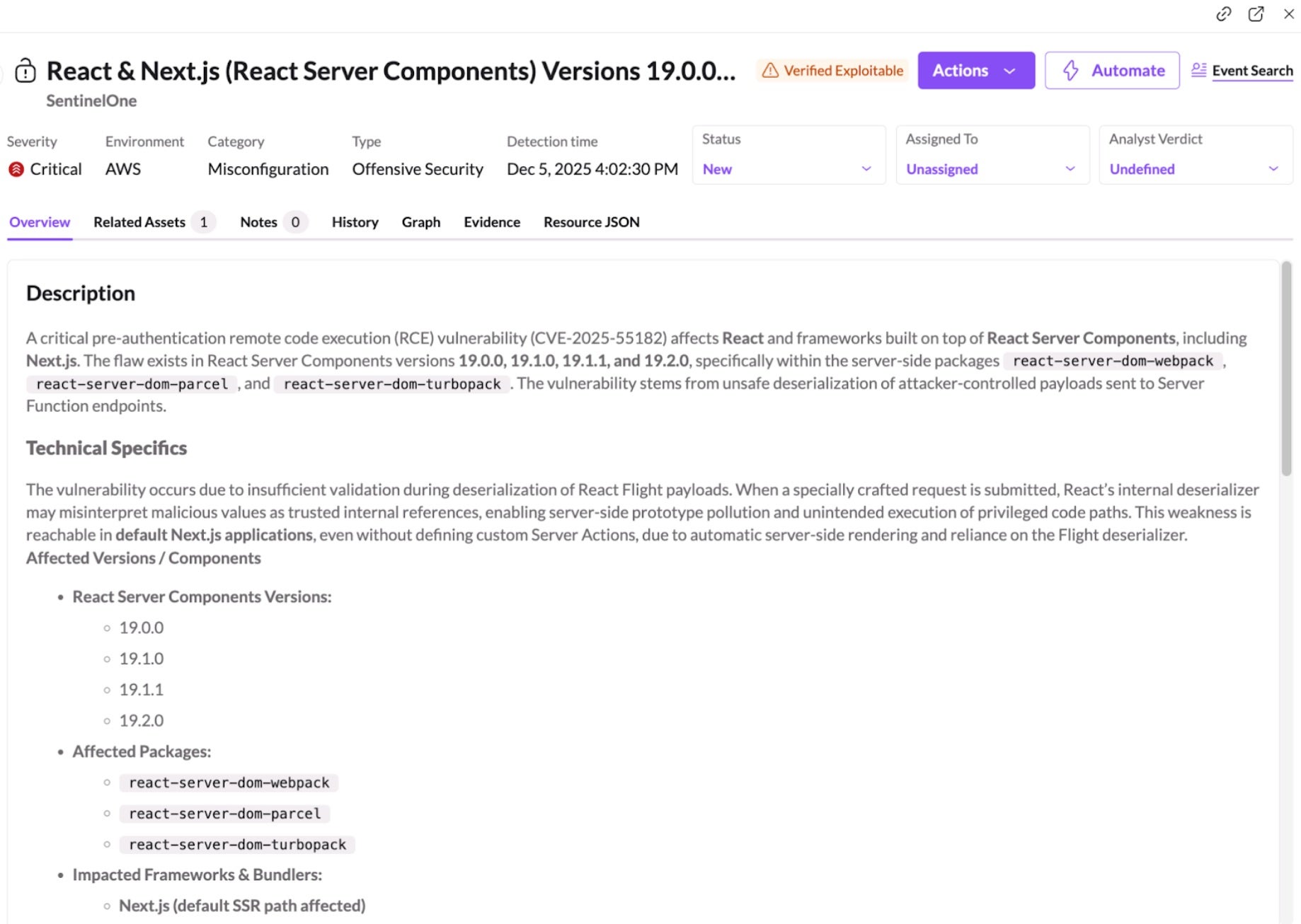
Viewing Misconfigurations in the SentinelOne Console
SentinelOne customers can quickly identify potentially vulnerable workloads using the Misconfigurations page in the SentinelOne Console.
Search for:
React & Next.js (React Server Components) Versions 19.0.0–19.2.0 Vulnerable to Pre-Authentication Remote Code Execution via Unsafe Deserialization (CVE-2025-55182)
This highlights Node.js workloads that are exposing RSC-related server function endpoints. Once identified, affected assets can be patched or temporarily isolated. SentinelOne CNS also detects suspicious Node.js behavior associated with exploitation attempts, providing protection while updates are deployed.
It identifies verified exploitable paths on your publicly exposed assets, confirming which systems are truly at risk. By validating exploitability rather than simply flagging theoretical vulnerabilities, Singularity Cloud Security minimizes noise and provides concrete evidence so security teams can focus on what matters.
Wayfinder Threat Hunting
The Wayfinder Threat Hunting team is proactively hunting for this emerging threat by leveraging comprehensive threat intelligence. This includes, but is not limited to, indicators and tradecraft associated with known active groups such as Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda.
Our current operational coverage includes:
- Atomic IOC Hunting: We have updated our atomic IOC library to include known infrastructure and indicators from these threat actors, as well as broader intelligence regarding this campaign.
- Behavioral Hunting: We are actively building and executing hunts designed to detect behavioral TTP matches that identify suspicious activity beyond static indicators.
Notification & Response All identified true positive findings will generate alerts within the console for the affected sites. For clients with MDR, the MDR team will actively review these alerts and manage further escalation as required.
Platform Detection Rules
SentinelOne’s products provide a variety of detections for potential malicious follow-on reverse shell behaviors and other actions which may follow this exploit. As of December 5, 2025, SentinelOne released new Platform Detection Rules specifically to detect observed in-the-wild exploit activity. We recommend customers apply the latest detection rule, Potential Exploitation via Insecure Deserialization of React Server Components (RSC), urgently to ensure maximum protection.
Additionally, SentinelOne recommends customers verify the following existing rules have also been enabled:
- Potential Reverse Shell via Shell Processes
- Potential Reverse Shell via Node
- Potential Reverse Shell via Python
- Reverse Shell via Perl Utility
- Potential Reverse Shell via AWK Utility
- Potential Reverse Shell via GDB Utility
- Potential Reverse Shell via Lua Utility
- Potential Reverse Shell via Netcat
- Potential Reverse Shell using Ruby Utility
- Potential Reverse Shell via Socat Utility
Conclusion
CVE-2025-55182 and CVE-2025-66478 represent critical risks within the React Server Components Flight protocol. Because frameworks like Next.js enable RSC by default, many environments may be exposed even without intentional server-side configuration. Updating React, updating dependent frameworks, and verifying whether RSC endpoints exist in your organization’s workloads are essential steps.
Singularity Cloud Security helps organizations reduce risk by identifying vulnerable workloads, flagging misconfigurations, and detecting malicious Node.js behavior linked to RCE exploitation. This provides immediate visibility and defense while patches are applied.
Learn more about SentinelOne’s Cloud Security portfolio here or book a demo with our expert team today.
Third-Party Trademark Disclaimer:
All third-party product names, logos, and brands mentioned in this publication are the property of their respective owners and are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, logos, and brands does not imply affiliation, endorsement, sponsorship, or association with the third-party.