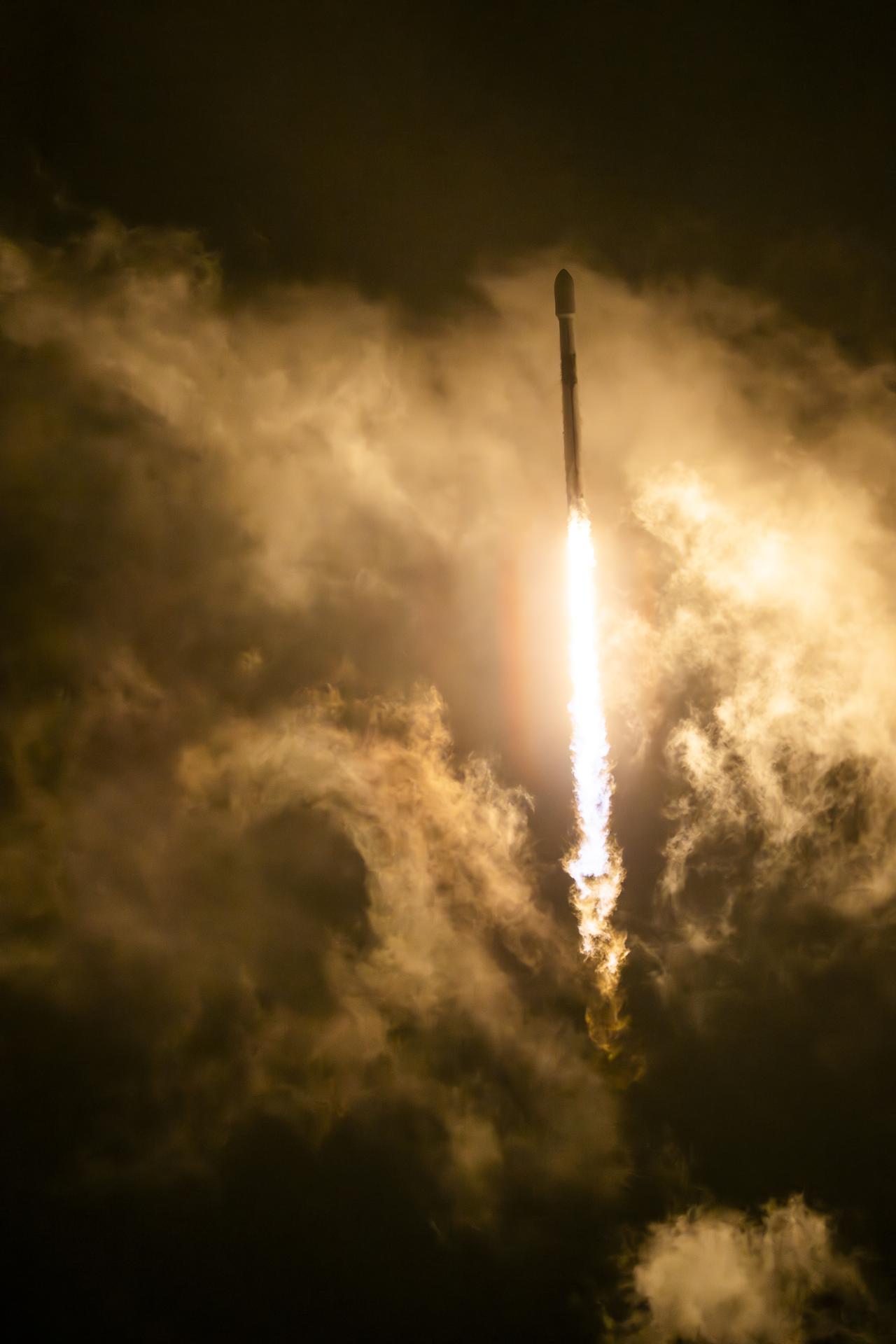
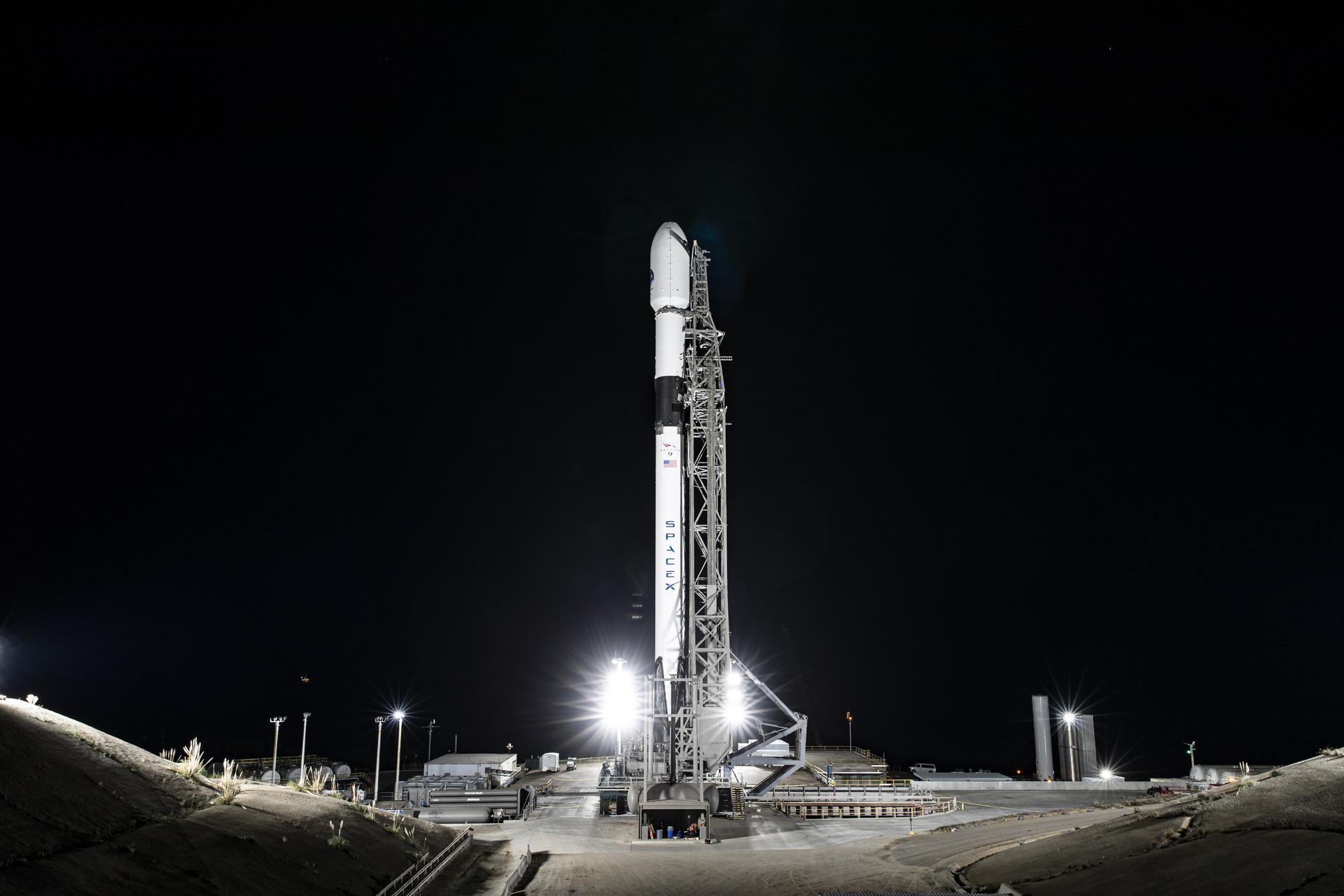
NASA, SpaceX Launch US-European Satellite to Monitor Earth’s Oceans
About the size of a full-size pickup truck, a newly launched satellite by NASA and its partners will provide ocean and atmospheric information to improve hurricane forecasts, help protect infrastructure, and benefit commercial activities, such as shipping.
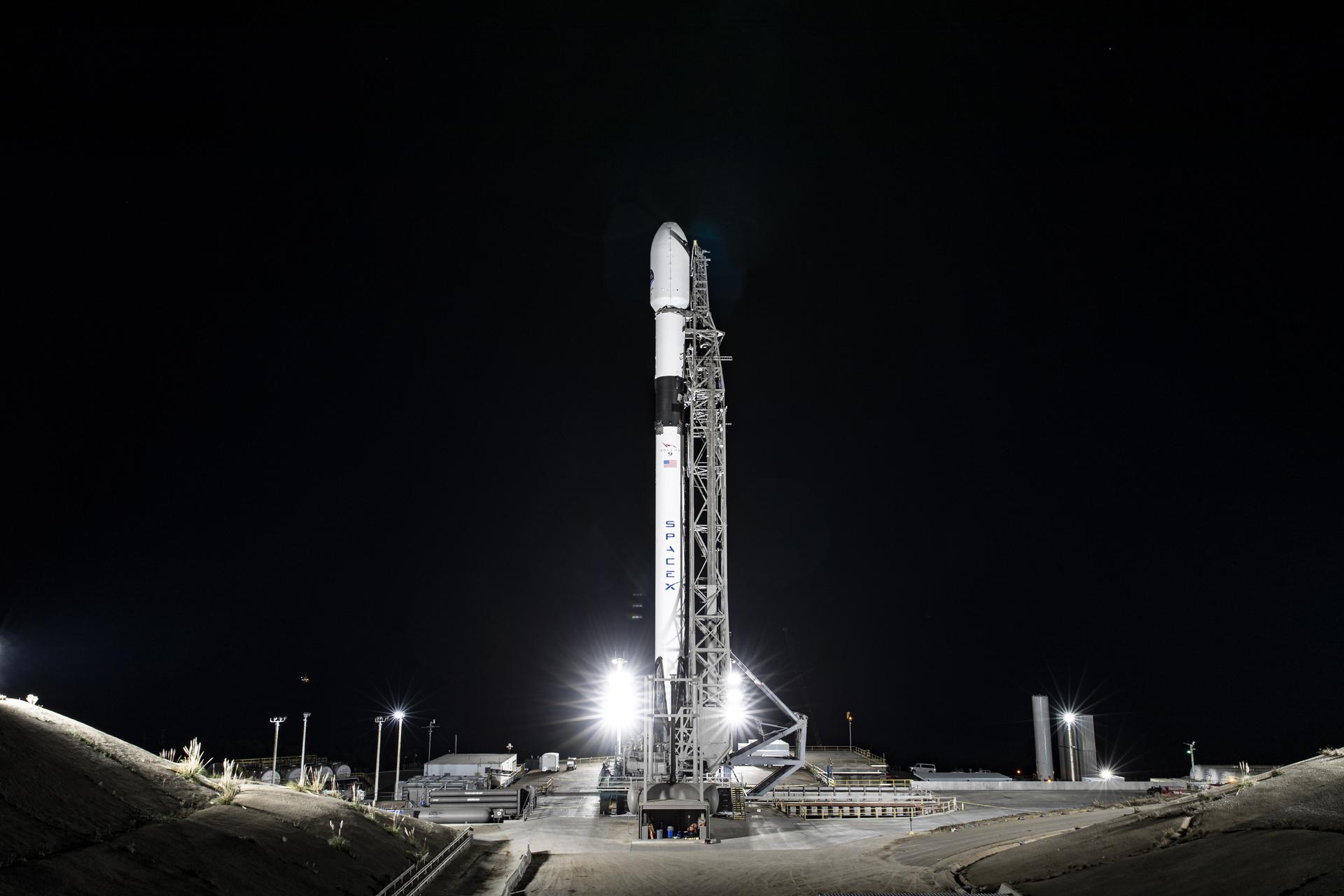
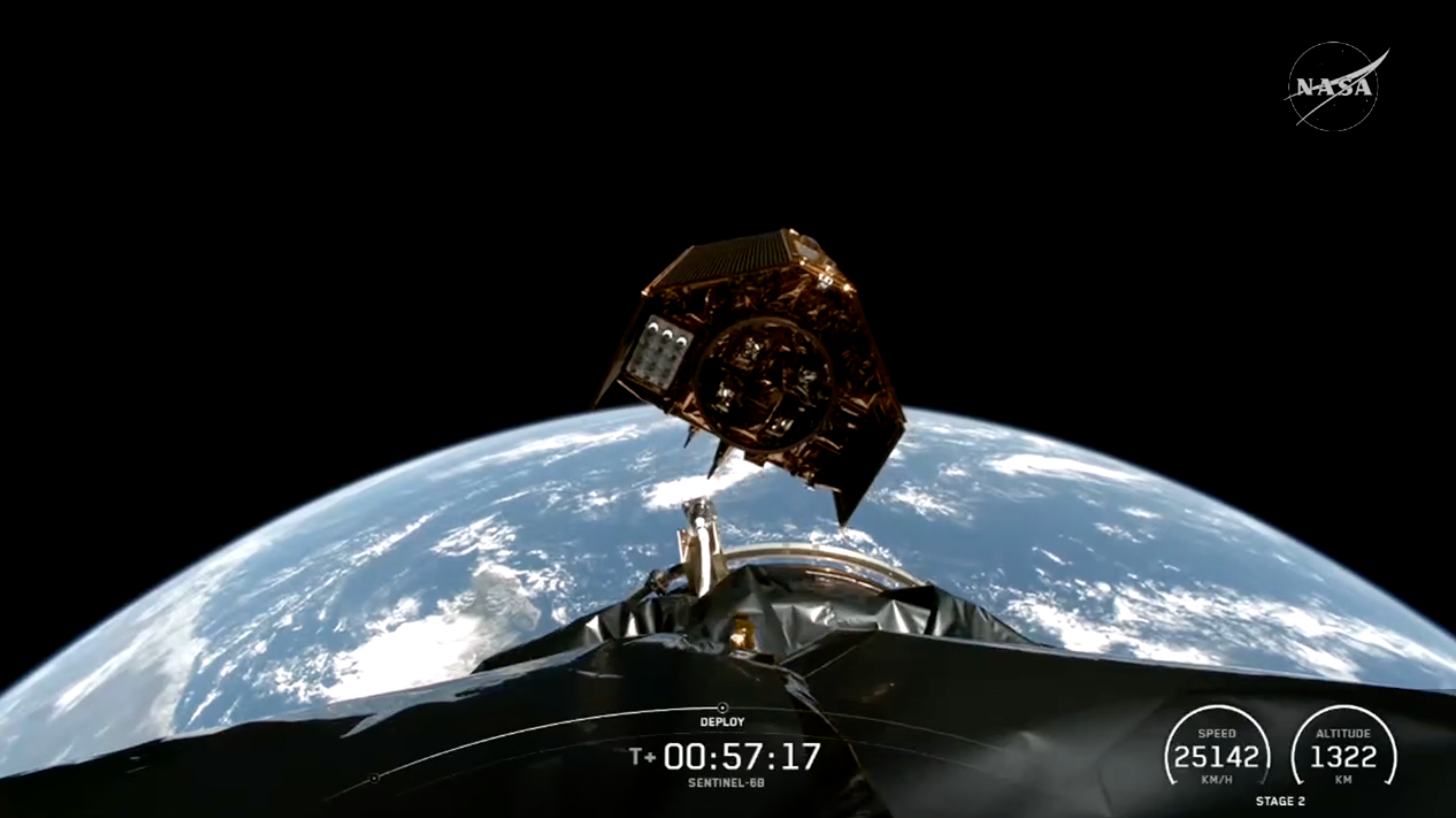
The Sentinel-6B satellite lifted off aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California at 9:21 p.m. PST on Nov. 16. Contact between the satellite and a ground station in northern Canada occurred about 1 hour and 30 minutes later at 10:54 p.m. All systems are functioning normally.
“Understanding tidal patterns down to the inch is critical in protecting how we use our oceans every day on Earth,” said Nicky Fox, associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Sentinel-6B will build upon the legacy of Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich by making sea level measurements that improve forecasts used by communities, businesses, and operations across the country. It also will support a safer reentry for our astronauts returning home, including crew from Artemis Moon missions.”
Sea levels vary from place to place, and the satellite will provide accurate measurements at both local and global scales — all from hundreds of miles above in low Earth orbit. Those observations form the basis for U.S. flood predictions, which are crucial for safeguarding coastal infrastructure, real estate, energy storage sites, and other coastal assets. Sentinel-6B will take over for Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, which launched in 2020 and later became the official reference satellite for global sea level measurements, providing sea surface height measurements against which those from other satellites are compared for accuracy.
The satellite comes from a collaboration between multiple partners, including NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). It also is part of the European Union’s family of Copernicus missions.
“Collaboration between partners is key to a mission such as Sentinel-6, and my thanks go to everyone involved in developing, launching, and operating this exceptional satellite, which follows in the footsteps of the first Sentinel-6, Michael Freilich,” said Simonetta Cheli, director, ESA’s Earth Observation Programmes. “This achievement demonstrates what can be accomplished when international agencies and industries work together toward a shared goal. Sentinel-6B will ensure we continue to collect the high-precision data needed to understand our changing climate, safeguard our oceans and support decisions that protect coastal communities around the world.”
The two satellites make up the Copernicus Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, the latest in a series of ocean-observing radar altimetry missions that have monitored Earth’s changing seas since the early 1990s.
As with its predecessor, Sentinel-6B satellite also will provide key information about wind speeds, wave heights, atmospheric temperature, and humidity. Moreover, because water expands as its temperature increases, researchers can tell which parts of the ocean are warmer than others based on where the sea surface height is greater.
Combined with data from other instruments, that knowledge can help in forecasting marine weather, including the development of hurricanes, which intensify with warmer water. Also, because large currents are taller than surrounding waters due to their higher temperatures, sea surface measurements can shed light on interactions between the Gulf Stream, for example, and nearby waves. Where they meet, seas can become rougher, presenting a hazard to even the largest ships.
“Sentinel-6B is a testament to the value of NASA’s partnership missions to put actionable satellite information and science into the hands of decision-makers on the ground,” said Karen St. Germain, director, NASA Earth Science Division at the agency’s headquarters. “Sentinel-6B will collect ocean surface observations that will inform decisions critical to coastal communities, commercial shipping and fishing, national defense, and emergency preparedness and response. This is what NASA does — puts advanced technology and science into action for the benefit of the nation.”
When Sentinel-6B reaches its operating elevation, the satellite will fly about 30 seconds behind Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, which carries identical science instruments. Once the mission finishes cross-calibrating the data collected by the two, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich will move into a different orbit, and Sentinel-6B will take over the role of official reference satellite, orbiting Earth about 13 times a day at 830 miles (1,336 kilometers) above the surface.
“Sentinel-6B demonstrates the versatile Earth science applications made possible by expertly engineered, space-based technology. The satellite’s powerful suite of instruments will measure about 90% of Earth’s oceans down to fractions of an inch — continuing to add to a vital dataset that America and a growing global community depend on,” said Dave Gallagher, director, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California.
More about Sentinel-6B
Copernicus Sentinel-6/Jason-CS is a collaboration between ESA, the European Union, EUMETSAT, NASA, and NOAA. French space agency CNES (Centre National d’Études Spatiales) contributed technical support. Copernicus, which includes the Sentinel missions, is the European Union’s Earth observation program led by the European Commission.
A division of Caltech in Pasadena, JPL contributed three science instruments for each Sentinel-6 satellite: the Advanced Microwave Radiometer, the Global Navigation Satellite System – Radio Occultation, and the laser retroreflector array. NASA also is contributing launch services, ground systems supporting operation of the NASA science instruments, the science data processors for two of these instruments, and support for the U.S. members of the international Ocean Surface Topography Science Team, and Sentinel-6 science teams.
To learn more about Sentinel-6B, visit:
https://science.nasa.gov/mission/sentinel-6B/
-end-
Elizabeth Vlock
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
elizabeth.a.vlock@nasa.gov
Andrew Wang / Andrew Good
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-379-6874 / 626-840-4291
andrew.wang@jpl.nasa.gov / andrew.c.good@jpl.nasa.gov













/Ocean%20Surface%20Topography%20Mission%20(OSTM%20Jason-2).png)


