Blackest Fabric Ever Made Absorbs 99.87% of All Light That Hits It
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
The Black Death ravaged medieval Western Europe, ultimately wiping out roughly one-third of the population. Scientists have identified the bacterium responsible and its likely origins, but certain specifics of how and why it spread to Europe are less clear. According to a new paper published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment, either one large volcanic eruption or a cluster of eruptions might have been the triggering factor, setting off a chain of events that brought the plague to the Mediterranean region in the 1340s.
Technically, we’re talking about the second plague pandemic. The first, known as the Justinian Plague, broke out about 541 CE and quickly spread across Asia, North Africa, the Middle East, and Europe. (The Eastern Roman Emperor Justinian I, for whom the pandemic is named, actually survived the disease.) There continued to be outbreaks of the plague over the next 300 years, although the disease gradually became less virulent and died out. Or so it seemed.
In the Middle Ages, the Black Death burst onto the scene, with the first historically documented outbreak occurring in 1346 in the Lower Volga and Black Sea regions. That was just the beginning of the second pandemic. During the 1630s, fresh outbreaks of plague killed half the populations of affected cities. Another bout of the plague significantly culled the population of France during an outbreak between 1647 and 1649, followed by an epidemic in London in the summer of 1665. The latter was so virulent that, by October, one in 10 Londoners had succumbed to the disease—over 60,000 people. Similar numbers perished in an outbreak in Holland in the 1660s. The pandemic had run its course by the early 19th century, but a third plague pandemic hit China and India in the 1890s. There are still occasional outbreaks today.
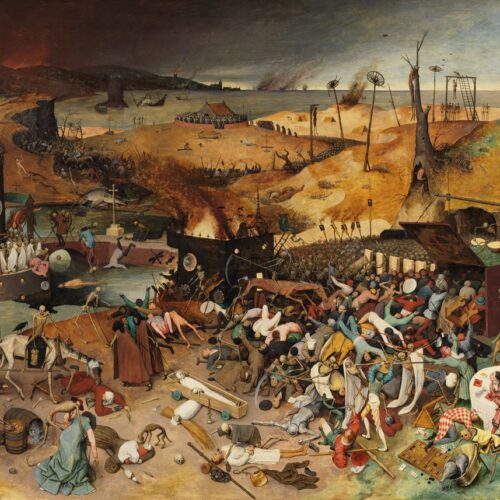
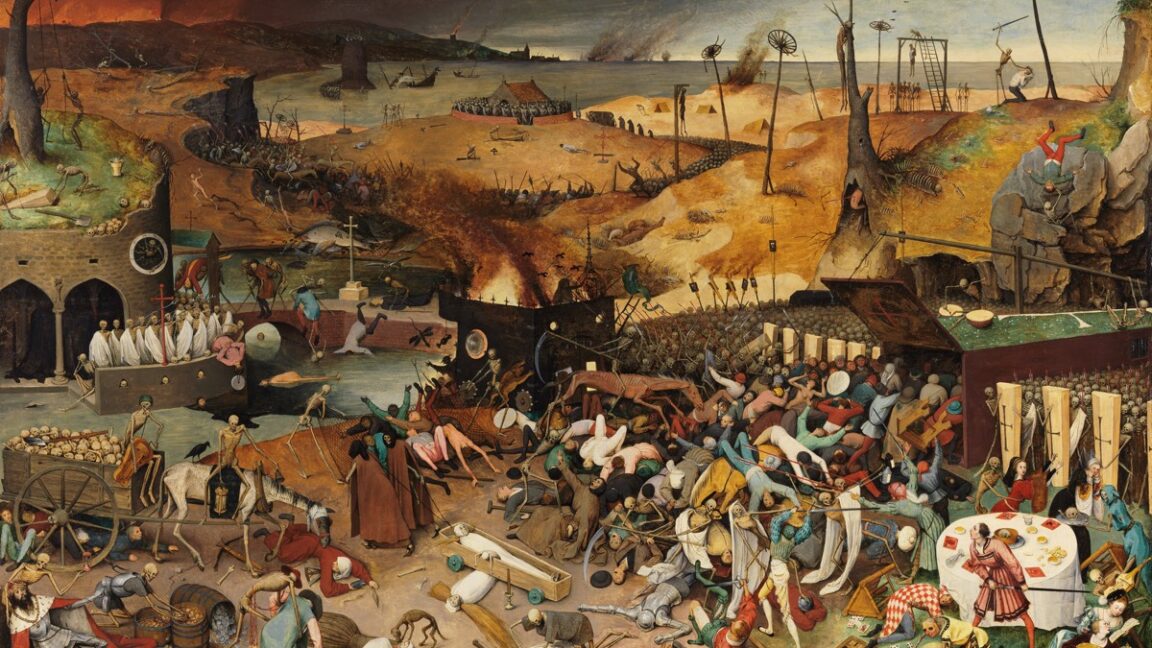


© Public domain
4 min read
NASA has selected two science instruments designed for astronauts to deploy on the surface of the Moon during the Artemis IV mission to the lunar south polar region. The instruments will improve our knowledge of the lunar environment to support NASA’s further exploration of the Moon and beyond to Mars.
“The Apollo Era taught us that the further humanity is from Earth, the more dependent we are on science to protect and sustain human life on other planets,” said Nicky Fox, associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “By deploying these two science instruments on the lunar surface, our proving ground, NASA is leading the world in the creation of humanity’s interplanetary survival guide to ensure the health and safety of our spacecraft and human explorers as we begin our epic journey back to the Moon and onward to Mars.”
After his voyage to the Moon’s surface during Apollo 17, astronaut Gene Cernan acknowledged the challenge that lunar dust presents to long-term lunar exploration. Moon dust sticks to everything it touches and is very abrasive. The knowledge gained from the DUSTER (DUst and plaSma environmenT survEyoR) investigation will help mitigate hazards to human health and exploration. Consisting of a set of instruments mounted on a small autonomous rover, DUSTER will characterize dust and plasma around the landing site. These measurements will advance understanding of the Moon’s natural dust and plasma environment and how that environment responds to the human presence, including any disturbance during crew exploration activities and lander liftoff. The DUSTER instrument suite is led by Xu Wang of the University of Colorado Boulder. The contract is for $24.8 million over a period of three years.

Data from the SPSS (South Pole Seismic Station) will enable scientists to characterize the lunar interior structure to better understand the geologic processes that affect planetary bodies. The seismometer will help determine the current rate at which the Moon is struck by meteorite impacts, monitor the real-time seismic environment and how it can affect operations for astronauts, and determine properties of the Moon’s deep interior. The crew will additionally perform an active-source experiment using a “thumper” that creates seismic energy to survey the shallow structure around the landing site. The SPSS instrument is led by Mark Panning of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The award is for $25 million over a period of three years.
“These two scientific investigations will be emplaced by human explorers on the Moon to achieve science goals that have been identified as strategically important by both NASA and the larger scientific community”, said Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for exploration, Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. “We are excited to integrate these instrument teams into the Artemis IV Science Team.”
The two payloads were selected for further development to fly on Artemis IV; however, final manifesting decisions about the mission will be determined at a later date.
Through Artemis, NASA will address high priority science questions, focusing on those that are best accomplished by on-site human explorers on and around the Moon and by using the unique attributes of the lunar environment, aided by robotic surface and orbiting systems. The Artemis missions will send astronauts to explore the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and build the foundation for the first crewed missions to Mars.
For more information on Artemis, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/humans-in-space/artemis
Karen Fox / Molly Wasser
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / molly.l.wasser@nasa.gov


As global warming accelerates, about 480 million people in North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula face intensifying and in some places unsurvivable heat, as well as drought, famine, and the risk of mass displacement, the World Meteorological Organization warned Thursday.
The 22 Arab region countries covered in the WMO’s new State of the Climate report produce about a quarter of the world’s oil, yet directly account for only 5 to 7 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions from their own territories. The climate paradox positions the region as both a linchpin of the global fossil-fuel economy and one of the most vulnerable geographic areas.
WMO Secretary-General Celeste Saulo said extreme heat is pushing communities in the region to their physical limits. Droughts show no sign of letting up in one of the world’s most water-stressed regions, but at the same time, parts of it have been devastated by record rains and flooding, she added.
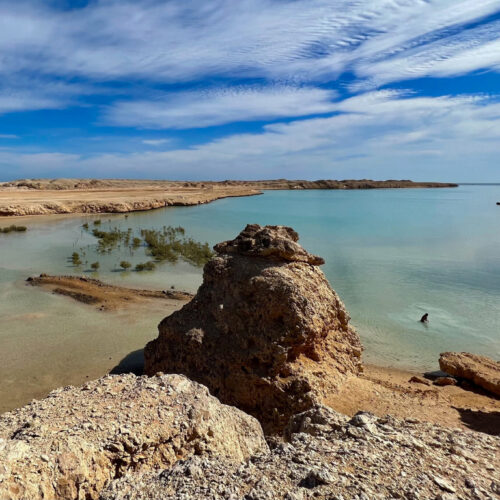


© Bob Berwyn/Inside Climate News
Welcome to Edition 8.21 of the Rocket Report! We’re back after the Thanksgiving holiday with more launch news. Most of the big stories over the last couple of weeks came from abroad. Russian rockets and launch pads didn’t fare so well. China’s launch industry celebrated several key missions. SpaceX was busy, too, with seven launches over the last two weeks, six of them carrying more Starlink Internet satellites into orbit. We expect between 15 and 20 more orbital launch attempts worldwide before the end of the year.
As always, we welcome reader submissions. If you don’t want to miss an issue, please subscribe using the box below (the form will not appear on AMP-enabled versions of the site). Each report will include information on small-, medium-, and heavy-lift rockets, as well as a quick look ahead at the next three launches on the calendar.

Another Sarmat failure. A Russian intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) fired from an underground silo on the country’s southern steppe on November 28 on a scheduled test to deliver a dummy warhead to a remote impact zone nearly 4,000 miles away. The missile didn’t even make it 4,000 feet, Ars reports. Russia’s military has been silent on the accident, but the missile’s crash was seen and heard for miles around the Dombarovsky air base in Orenburg Oblast near the Russian-Kazakh border. A video posted by the Russian blog site MilitaryRussia.ru on Telegram and widely shared on other social media platforms showed the missile veering off course immediately after launch before cartwheeling upside down, losing power, and then crashing a short distance from the launch site.
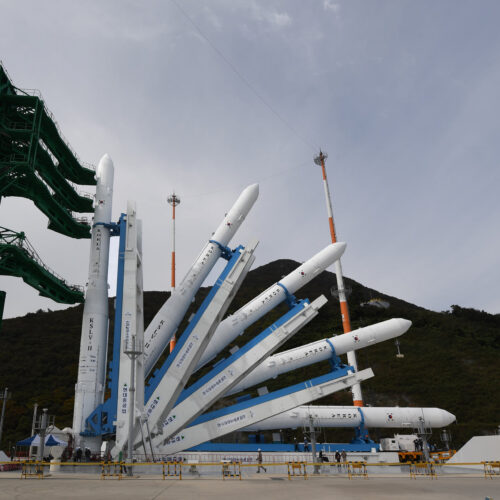
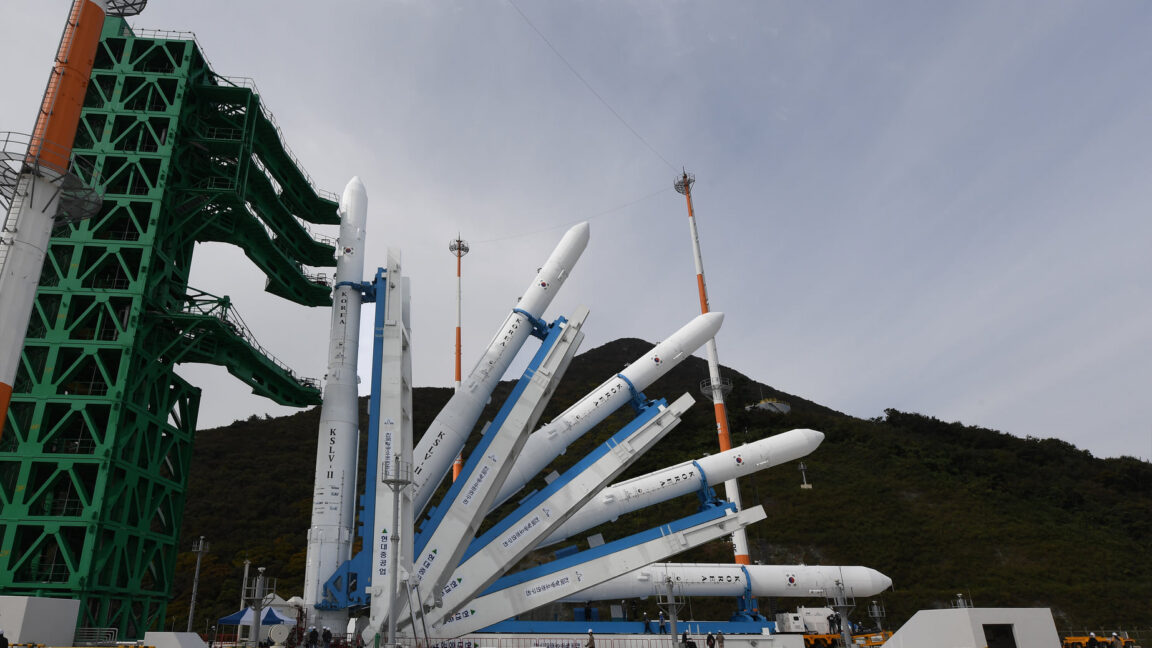


© Korea Aerospace Research Institute



It’s relatively easy to understand how optical microscopes work at low magnifications: one lens magnifies an image, the next magnifies the already-magnified image, and so on until it reaches the eye or sensor. At high magnifications, however, that model starts to fail when the feature size of the specimen nears the optical system’s diffraction limit. In a recent video, [xoreaxeax] built a simple microscope, then designed another microscope to overcome the diffraction limit without lenses or mirrors (the video is in German, but with automatic English subtitles).
The first part of the video goes over how lenses work and how they can be combined to magnify images. The first microscope was made out of camera lenses, and could resolve onion cells. The shorter the focal length of the objective lens, the stronger the magnification is, and a spherical lens gives the shortest focal length. [xoreaxeax] therefore made one by melting a bit of soda-lime glass with a torch. The picture it gave was indistinct, but highly magnified.

Besides the dodgy lens quality given by melting a shard of glass, at such high magnification some of the indistinctness was caused by the specimen acting as a diffraction grating and directing some light away from the objective lens. [xoreaxeax] visualized this by taking a series of pictures of a laser shining through a pinhole at different focal lengths, thus getting cross sections of the light field emanating from the pinhole. When repeating the procedure with a section of onion skin, it became apparent that diffraction was strongly scattering the light, which meant that some light was being diffracted out of the lens’s field of view, causing detail to be lost.
To recover the lost details, [xoreaxeax] eliminated the lenses and simply captured the interference pattern produced by passing light through the sample, then wrote a ptychography algorithm to reconstruct the original structure from the interference pattern. This required many images of the subject under different lighting conditions, which a rotating illumination stage provided. The algorithm was eventually able to recover a sort of image of the onion cells, but it was less than distinct. The fact that the lens-free setup was able to produce any image at all is nonetheless impressive.
To see another approach to ptychography, check out [Ben Krasnow’s] approach to increasing microscope resolution. With an electron microscope, ptychography can even image individual atoms.


Roughly two years ago, Sam Altman tweeted that AI systems would be capable of superhuman persuasion well before achieving general intelligence—a prediction that raised concerns about the influence AI could have over democratic elections.
To see if conversational large language models can really sway political views of the public, scientists at the UK AI Security Institute, MIT, Stanford, Carnegie Mellon, and many other institutions performed by far the largest study on AI persuasiveness to date, involving nearly 80,000 participants in the UK. It turned out political AI chatbots fell far short of superhuman persuasiveness, but the study raises some more nuanced issues about our interactions with AI.
The public debate about the impact AI has on politics has largely revolved around notions drawn from dystopian sci-fi. Large language models have access to essentially every fact and story ever published about any issue or candidate. They have processed information from books on psychology, negotiations, and human manipulation. They can rely on absurdly high computing power in huge data centers worldwide. On top of that, they can often access tons of personal information about individual users thanks to hundreds upon hundreds of online interactions at their disposal.


© Carol Yepes via Getty


Necrobotics is a field of engineering that builds robots out of a mix of synthetic materials and animal body parts. It has produced micro-grippers with pneumatically operated legs taken from dead spiders and walking robots based on deceased cockroaches. “These necrobotics papers inspired us to build something different,” said Changhong Cao, a mechanical engineering professor at the McGill University in Montreal, Canada.
Cao’s team didn’t go for a robot—instead, it adapted a female mosquito proboscis to work as a nozzle in a super-precise 3D printer. And it worked surprisingly well.
To find the right nozzle for their 3D necroprinting system, Cao’s team began with a broad survey of natural micro-dispensing tips. The researchers examined stingers of bees, wasps, and scorpions; the fangs of venomous snakes; and the claws of centipedes. All of those evolved to deliver a fluid to the target, which is roughly what a 3D printer’s nozzle does. But they all had issues. “Some were too curved and curved for high-precision 3D printing,” Cao explained. “Also, they were optimized for delivering pulses of venom, not for a steady, continuous flow, which is what you need for printing.”


© Walter Ferrari / 500px

The past few months, we’ve been giving you a quick rundown of the various ways ores form underground; now the time has come to bring that surface-level understanding to surface-level processes.
Strictly speaking, we’ve already seen one: sulfide melt deposits are associated with flood basalts and meteorite impacts, which absolutely are happening on-surface. They’re totally an igneous process, though, and so were presented in the article on magmatic ore processes.
For the most part, you can think of the various hydrothermal ore formation processes as being metamorphic in nature. That is, the fluids are causing alteration to existing rock formations; this is especially true of skarns.
There’s a third leg to that rock tripod, though: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary. Are there sedimentary rocks that happen to be ores? You betcha! In fact, one sedimentary process holds the most valuable ores on Earth– and as usual, it’s not likely to be restricted to this planet alone.
We’re talking about placer deposits, which means we’re talking about gold. In dollar value, gold’s great expense means that these deposits are amongst the most valuable on Earth– and nearly half of the world’s gold has come out of just one of them. Gold isn’t the only mineral that can be concentrated in placer deposits, to be clear; it’s just the one everyone cares about these days, because, well, have you seen the spot price lately?
Since we’re talking about sediments, as you might guess, this is a secondary process: the gold has to already be emplaced by one of the hydrothermal ore processes. Then the usual erosion happens: wind and water breaks down the rock, and gold gets swept downhill along with all the other little bits of rock on their way to becoming sediments. Gold, however, is much denser than silicate rocks. That’s the key here: any denser material is naturally going to be sorted out in a flow of grains. To be specific, empirical data shows that anything denser than 2.87 g/cm3 can be concentrated in a placer deposit. That would qualify a lot of the sulfide minerals the hydrothermal processes like to throw up, but unfortunately sulfides tend to be both too soft and too chemically unstable to hold up to the weathering to form placer deposits, at least on Earth since cyanobacteria polluted the atmosphere with O2.

Image: “MSL Sunset Dunes Mosaic“, NASA/JPL and Olivier de Goursac
One form of erosion is from wind, which tends to be important in dry regions – particularly the deserts of Australia and the Western USA. Wind erosion can also create placer deposits, which get called “aeolian placers”. The mechanism is fairly straightforward: lighter grains of sand are going to blow further, concentrating the heavy stuff on one side of a dune or closer to the original source rock. Given the annual global dust storms, aeolian placers may come up quite often on Mars, but the thin atmosphere might make this process less likely than you’d think.
We’ve also seen rockslides on Mars, and material moving in this matter is subject to the same physics. In a flow of grains, you’re going to have buoyancy and the heavy stuff is going to fall to the bottom and stop sooner. If the lighter material is further carried away by wind or water, we call the resulting pile of useful, heavy rock an effluvial placer deposit.
Still, on this planet at least it’s usually water doing the moving of sediments, and it’s water that’s doing the sortition. Heavy grains fall out of suspension in water more easily. This tends to happen wherever flow is disrupted: at the base of a waterfall, at a river bend, or where a river empties into a lake or the ocean. Any old Klondike or California prospector would know that that’s where you’re going to go panning for gold, but you probably wouldn’t catch a 49er calling it an “Alluvial placer deposit”. Panning itself is using the exact same physics– that’s why it, along with the fancy modern sluices people use with powered pumps, are called “placer mining”. Mars’s dry river beds may be replete with alluvial placers; so might the deltas on Titan, though on a world where water is part of the bedrock, the cryo-mineralogy would be very unfamiliar to Earthly geologists.
Back here on earth, wave action, with the repeated reversal of flow, is great at sorting grains. There aren’t any gold deposits on beaches these days because wherever they’ve been found, they were mined out very quickly. But there are many beaches where black magnetite sand has been concentrated due to its higher density to quartz. If your beach does not have magnetite, look at the grain size: even quartz grains can often get sorted by size on wavy beaches. Apparently this idea came after scientists lost their fascination with latin, as this type of deposit is referred to simply as a “beach placer” rather than a “littoral placer”.

While we in North America might think of the Klondike or California gold rushes– both of which were sparked by placer deposits– the largest gold field in the world was actually in South Africa: the Witwatersrand Basin. Said basin is actually an ancient lake bed, Archean in origin– about three billion years old. For 260 million years or thereabouts, sediments accumulated in this lake, slowly filling it up. Those sediments were being washed out from nearby mountains that housed orogenic gold deposits. The lake bed has served to concentrate that ancient gold even further, and it’s produced a substantial fraction of the gold metal ever extracted– depending on the source, you’ll see numbers from as high as 50% to as low as 22%. Either way, that’s a lot of gold.
Witwatersrand is a bit of an anomaly; most placer deposits are much smaller than that. Indeed, that’s in part why you’ll find placer deposits only mined for truly valuable minerals like gold and gems, particularly diamonds. Sure, the process can concentrate magnetite, but it’s not usually worth the effort of stripping a beach for iron-rich sand.
The most common non-precious exception is uraninite, UO2, a uranium ore found in Archean-age placer deposits. As you might imagine, the high proportion of heavy uranium makes it a dense enough mineral to form placer deposits. I must specify Archean-age, however, because an oxygen atmosphere tends to further oxidize the uraninite into more water-soluble forms, and it gets washed to sea instead of forming deposits. On Earth, it seems there are no uraninite placers dated to after the Great Oxygenation; you wouldn’t have that problem on Mars, and the dry river beds of the red planet may well have pitchblende reserves enough for a Martian rendition of “Uranium Fever”.

Image: Nandes Valles valley system, ESA/DLR/FU Berlin
While uranium is produced at Witwatersrand as a byproduct of the gold mines, uranium ore can be deposited exclusively of gold. You can see that with the alluvial deposits in Canada, around Elliot Lake in Ontario, which produced millions of pounds of the uranium without a single fleck of gold, thanks to a bend in a three-billion-year-old riverbed. From a dollar-value perspective, a gold mine might be worth more, but the uranium probably did more for civilization.
Speaking of useful for civilization, there’s another type of process acting on the surface to give us ores of less noble metals than gold. It is not mechanical, but chemical, and given that it requires hot, humid conditions with lots of water, it’s almost certainly restricted to Sol 3. As the subtitle gives it away, this process is called “lateritization” and is responsible for the only economical aluminum deposits out there, along with a significant amount of the world’s nickel reserves.
The process is fairly simple: in the hot tropics, ample rainfall will slowly leech any mobile ions out of clay soils. Ions like sodium and potassium are first to go, followed by calcium and magnesium but if the material is left on the surface long enough, and the climate stays hot and wet, chemical weathering will eventually strip away even the silica. The resulting “Laterite” rock (or clay) is rich in iron, aluminum, and sometimes nickel and/or copper. Nickel laterites are particularly prevalent in New Caledonia, where they form the basis of that island’s mining industry. Aluminum-rich laterites are called bauxite, and are the source of all Earth’s aluminum, found worldwide. More ancient laterites are likely to be found in solid form, compressed over time into sedimentary rock, but recent deposits may still have the consistency of dirt. For obvious reasons, those recent deposits tend to be preferred as cheaper to mine.

When we talk about a “warm and wet” period in Martian history, we’re talking about the existence of liquid water on the surface of the planet– we are notably not talking about tropical conditions. Mars was likely never the kind of place you’d see lateritization, so it’s highly unlikely we will ever find bauxite on the surface of Mars. Thus future Martians will have to make due without Aluminum pop cans. Of course, iron is available in abundance there and weighs about the same as the equivalent volume of aluminum does here on Earth, so they’ll probably do just fine without it.
Most nickel has historically come from sulfide melt deposits rather than lateralization, even on Earth, so the Martians should be able to make their steel stainless. Given the ambitions some have for a certain stainless-steel rocket, that’s perhaps comforting to hear.
It’s important to emphasize, as this series comes to a close, that I’m only providing a very surface-level understanding of these surface level processes– and, indeed, of all the ore formation processes we’ve discussed in these posts. Entire monographs could be, and indeed have been written about each one. That shouldn’t be surprising, considering the depths of knowledge modern science generates. You could do an entire doctorate studying just one aspect of one of the processes we’ve talked about in this series; people have in the past, and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future. So if you’ve found these articles interesting, and are sad to see the series end– don’t worry! There’s a lot left to learn; you just have to go after it yourself.
Plus, I’m not going anywhere. At some point there are going to be more rock-related words published on this site. If you haven’t seen it before, check out Hackaday’s long-running Mining and Refining series. It’s not focused on the ores– more on what we humans do with them–but if you’ve read this far, it’s likely to appeal to you as well.


Just a tiny amount of fentanyl, the equivalent of a few grains of sand, is enough to stop a person’s breathing. The synthetic opioid is tasteless, odorless, and invisible when mixed with other substances, and drug users are often unaware of its presence.
It’s why biotech entrepreneur Collin Gage is aiming to protect people against the drug’s lethal effects. In 2023, he became the cofounder and CEO of ARMR Sciences to develop a vaccine against fentanyl. Now, the company is launching a trial to test its vaccine in people for the first time. The goal: prevent deaths from overdose.
“It became very apparent to me that as I assessed the treatment landscape, everything that exists is reactionary,” Gage says. “I thought, why are we not preventing this?”

© Douglas Sacha via Getty Images
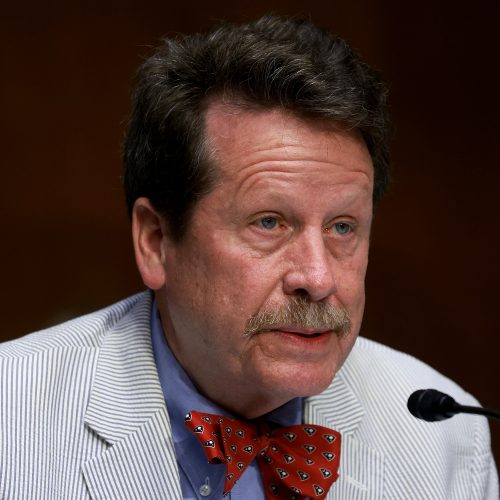
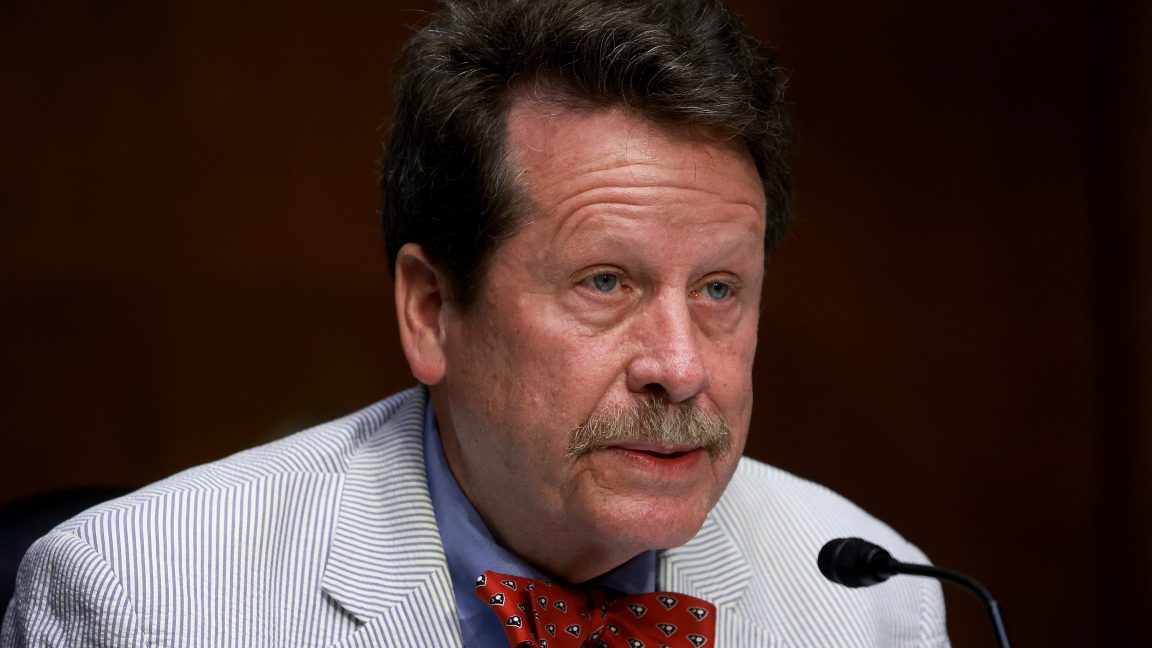
On Friday, Vinay Prasad—the Food and Drug Administration’s chief medical and scientific officer and its top vaccine regulator—emailed a stunning memo to staff that quickly leaked to the press. Without evidence, Prasad claimed COVID-19 vaccines have killed 10 children in the US, and, as such, he announced unilateral, sweeping changes to the way the agency regulates and approves vaccines, including seasonal flu shots.
On Wednesday evening, a dozen former FDA commissioners, who collectively oversaw the agency for more than 35 years, responded to the memo with a scathing rebuke. Uniting to publish their response in the New England Journal of Medicine, the former commissioners said they were “deeply concerned” by Prasad’s memo, which they framed as a “threat” to the FDA’s work and a danger to Americans’ health.
In his memo, Prasad called for abandoning the FDA’s current framework for updating seasonal flu shots and other vaccines, such as those for COVID-19. Those updates currently involve studies that measure well-characterized immune responses (called immunobridging studies). Prasad dismissed this approach as insufficient and, instead, plans to require expensive randomized trials, which can take months to years for each vaccine update.


© Getty | Joe Raedle
The fossil and genetic evidence agree that modern humans originated in Africa. The most genetically diverse human populations—the groups that have had the longest time to pick up novel mutations—live there today. But the history of what went on within Africa between our origins and the present day is a bit murky.
That’s partly because DNA doesn’t survive long in the conditions typical of most of the continent, which has largely limited us to trying to reconstruct the past using data from present-day populations. The other part is that many of those present-day populations have been impacted by the vast genetic churn caused by the Bantu expansion, which left its traces across most of the populations south of the Sahara.
But a new study has managed to extract genomes from ancient samples in southern Africa. While all of these are relatively recent, dating from after the end of the most recent glacial period, they reveal a distinct southern African population that was relatively large, outside of the range of previously described human variation, and it remained isolated until only about 1,000 years ago.
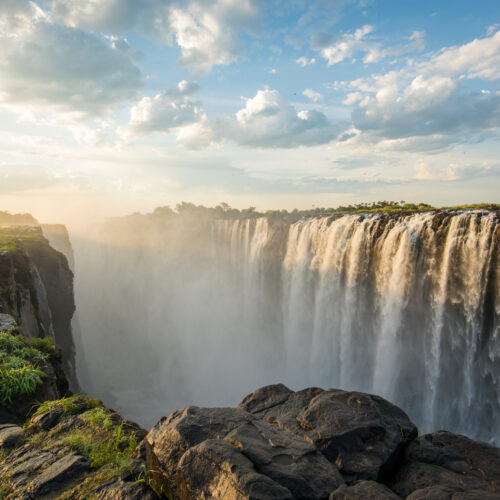
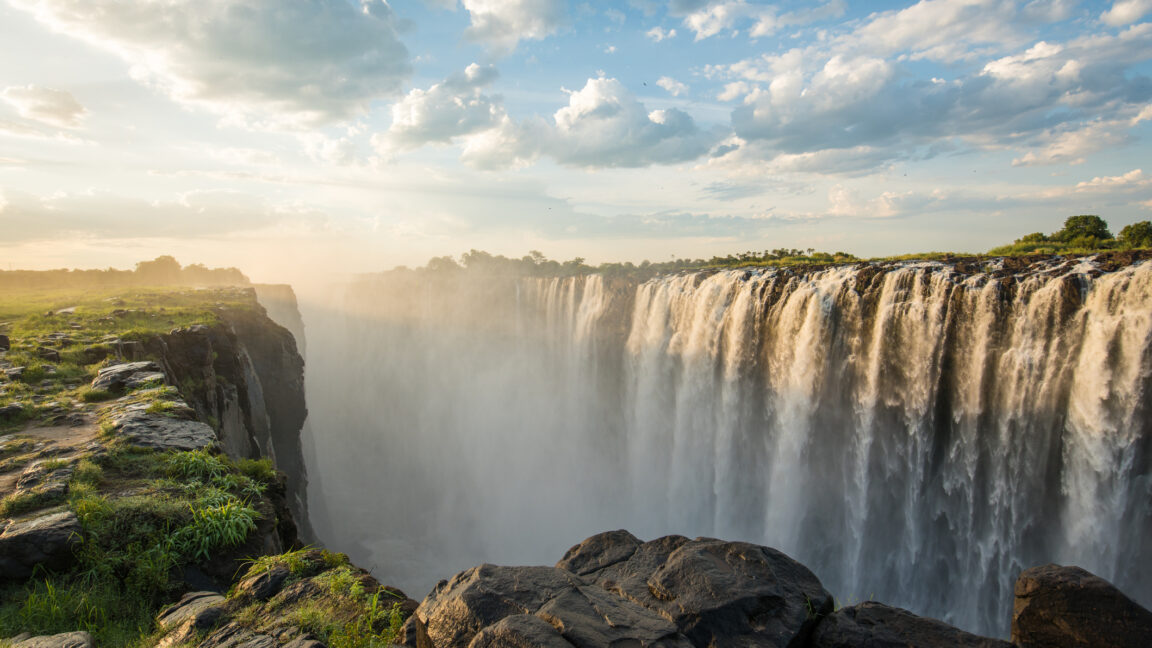


© Edwin Remsberg
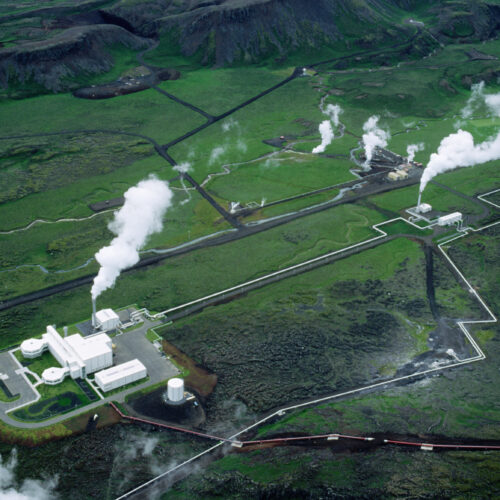
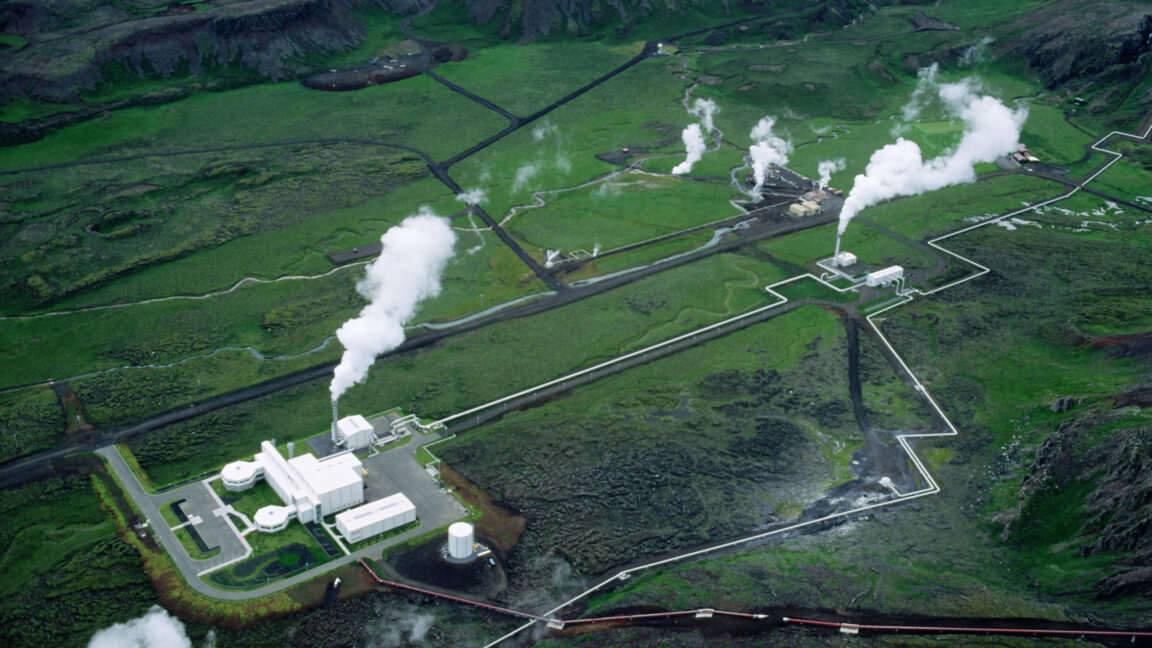
The US Department of Energy has approved an $8.6 million grant that will allow the nation’s first utility-led geothermal heating and cooling network to double in size.
Gas and electric utility Eversource Energy completed the first phase of its geothermal network in Framingham, Massachusetts, in 2024. Eversource is a co-recipient of the award along with the city of Framingham and HEET, a Boston-based nonprofit that focuses on geothermal energy and is the lead recipient of the funding.
Geothermal networks are widely considered among the most energy-efficient ways to heat and cool buildings. The federal money will allow Eversource to add approximately 140 new customers to the Framingham network and fund research to monitor the system’s performance.


© Kevin Schafer via Getty Images