Controlled water stress in cannabis: a technique to increase resin
In cannabis cultivation, achieving truly exceptional harvests doesn’t depend only on large buds or high THC percentages. True quality comes from understanding how the plant responds to its environment and applying techniques that enhance its natural physiology. Among these practices, one stands out for its simplicity and effectiveness: controlled water stress. Far from being a trend, it is a science-backed strategy that allows growers to increase resin production, intensify aromas and enhance the metabolite profile without adding extra products or complicating the grow. In this article, we explore what it is, how it works and how to apply it correctly to take your flowers to the next level.

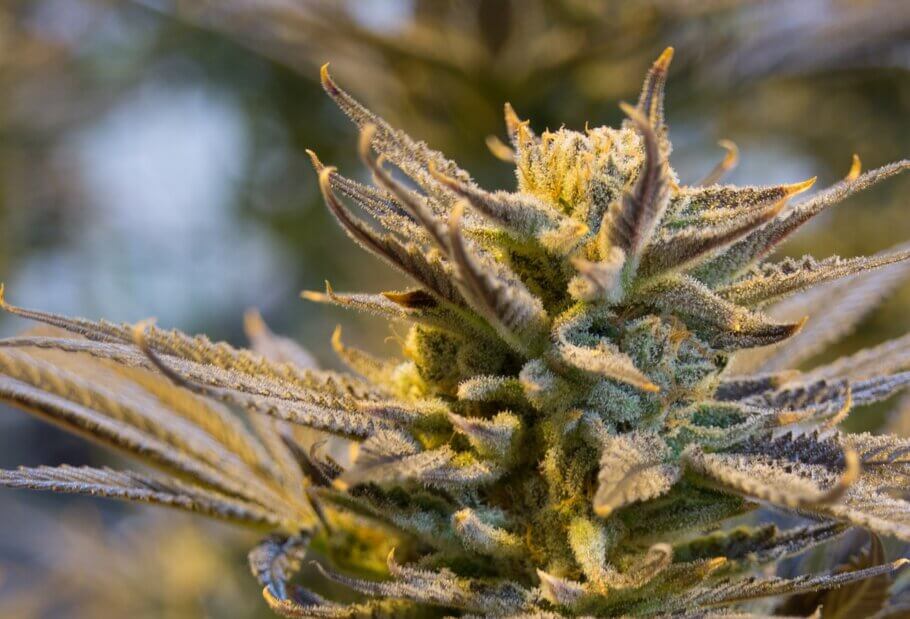
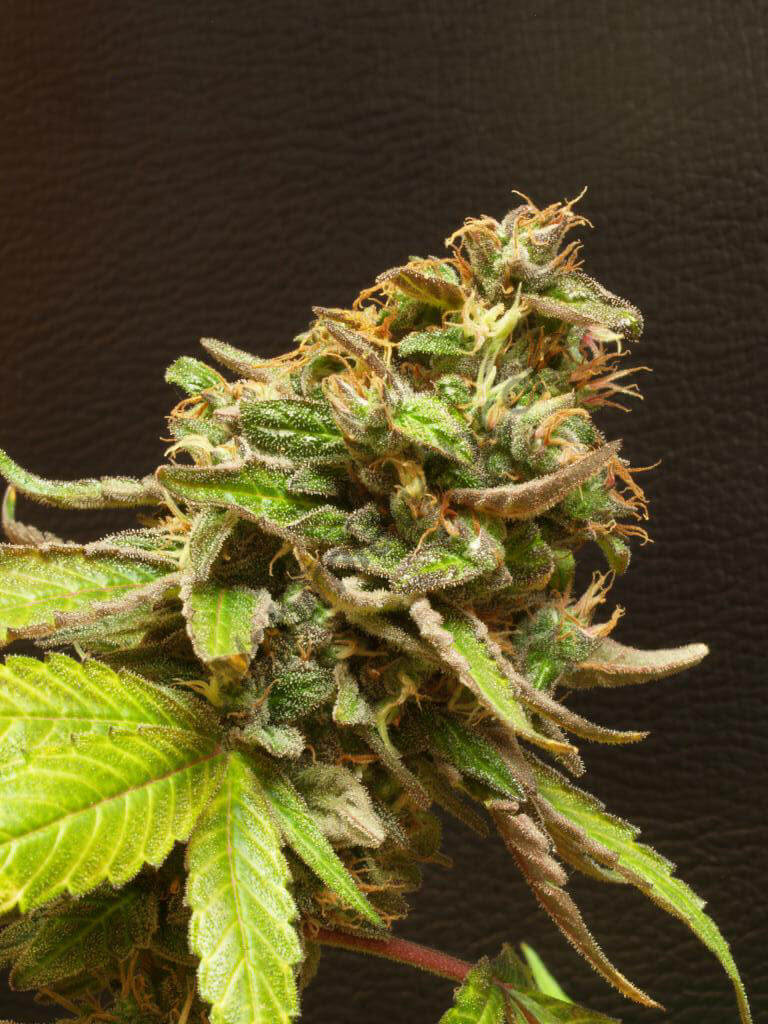
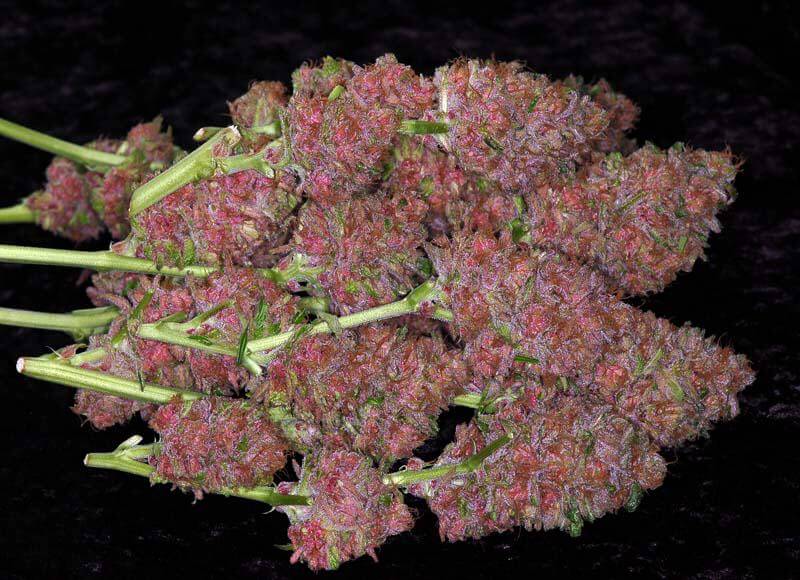
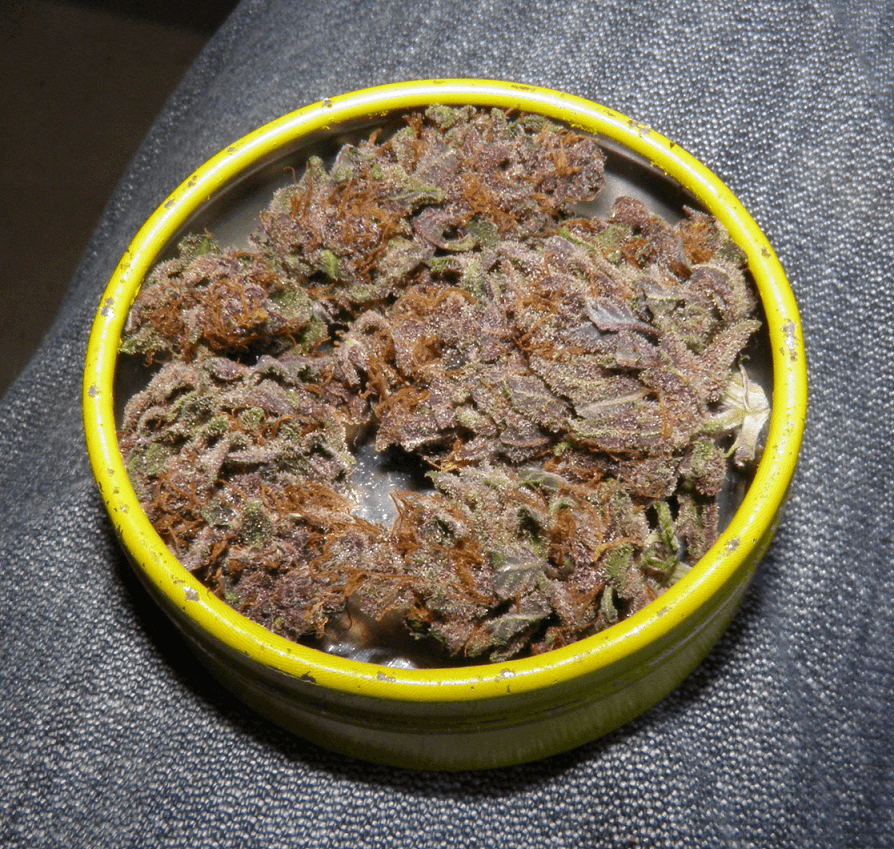
Healthy bud of Purple Punch x Do-Si-Dos by Philosopher Seeds
Although its name may sound harsh, its mechanism is based on a simple principle: when the plant senses that water is scarce, it activates defence mechanisms that increase the production of trichomes and secondary metabolites. This reaction is not exclusive to cannabis. Many aromatic and medicinal crops, such as lavender, rosemary, thyme, sage or even grapevine, respond in a similar way. In all of them, a moderate water deficit enhances aroma, essential oil concentration and, in the case of grapes, sugar levels (alcohol).
[productes tipus=”fitxa” cat=”143″ nfitxes=”3″]
What is controlled water stress?
Controlled water stress is a method applied during the final stage of flowering and consists essentially of temporarily reducing irrigation frequency. The goal is to trigger a mild physiological discomfort that activates metabolic pathways associated with defence. When roots detect reduced water availability, the plant produces abscisic acid (ABA), a hormone that instructs stomata to partially close to prevent moisture loss. This small shift alters the plant’s internal dynamics: photosynthesis decreases slightly, primary processes slow down and activity in secondary pathways increases, including the synthesis of terpenes, flavonoids and cannabinoids.
The result is often visible: greater resin density, more defined aromas and more uniform ripening. But to reach that point, the process must be applied in a controlled way, without pushing the plant into extreme drought.
The science behind water deficit
We now know that this mechanism is supported by scientific research. A study by Caplan et al. (University of Guelph, 2019) applied a water deficit during late flowering and recorded a 12–13% increase in THCA and CBDA, together with a 67% increase in total cannabinoids per cultivated area. These results were especially notable because there was no loss of biomass.
Recent reviews, such as the one published in Horticulturae by Sharma et al. (2025), compile multiple trials showing a clear pattern: mild, late water deficit stimulates secondary metabolite production as long as it is kept within safe limits. However, when stress is excessive or applied too early, the effects can be negative: reduced trichomes, oxidative stress, loss of vigour or greater susceptibility to pathogens. In other words, water stress works — but it requires precision and constant observation.
How to apply water stress without harming your plants
Choose the right timing
Water stress should only be applied when the flowers are already formed and beginning their ripening phase. For most photoperiod strains, this occurs between the 6th and 8th week of flowering. Applying it earlier may stress the root system, reduce final bud size and make plants more vulnerable to pests like mites, which quickly take advantage of weakened tissues.
Reduce watering progressively
You shouldn’t stop watering abruptly. The correct approach is to slowly space out irrigation: if you water every two days, switch to every three or four; if you water twice a week, reduce to once or one and a half, depending on pot size. What matters is allowing the substrate to dry more than usual, while never letting it dry out completely.
The plant will give clear signs: slightly drooping leaves during the warmest part of the day indicate the right stress level. In contrast, general wilting, soft stems or burnt tips mean the stress is too strong. After watering, the plant should recover within a few hours — this rebound signals proper management.
Apply repeated cycles
Controlled water stress works best when applied in gentle cycles: a period of mild dryness followed by recovery. Typically, this pattern is repeated two or three times during the last weeks of flowering. In fully controlled indoor environments (stable climate, good airflow), some advanced growers leave 10–12 days without watering right before root flushing.
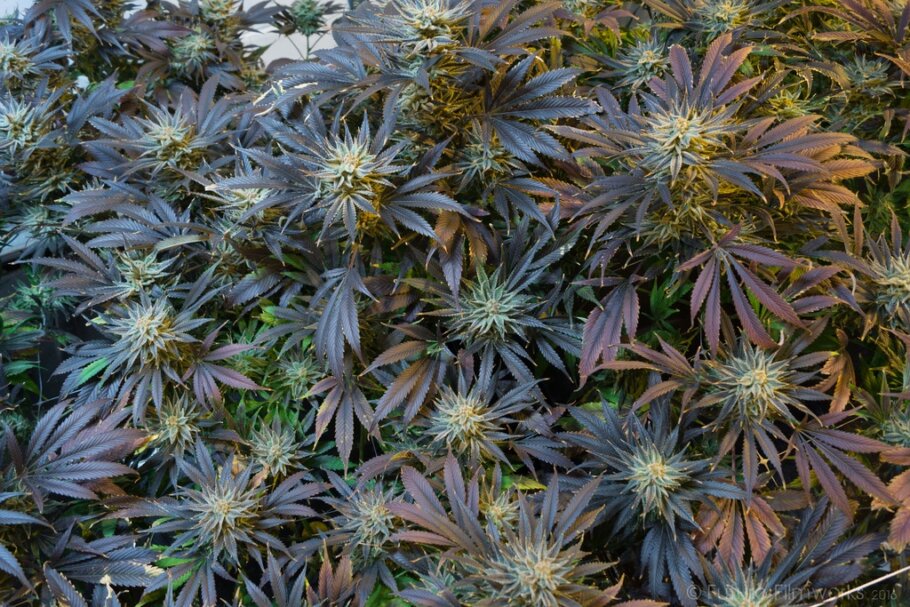
When done correctly, this method produces denser flowers, with less internal moisture and higher trichome concentration.
Expected results
When the process is executed correctly, the changes are noticeable. The increase in trichome production is often the most obvious effect. This increase is not only visual but chemical: greater concentration of essential oils and cannabinoids. The aromatic profile also changes. Volatile terpenes such as myrcene, limonene, pinene or linalool express themselves more intensely. This results in a more pronounced fragrance at harvest and a stronger flavour after curing.
Another clear benefit is the reduced risk of Botrytis. Flowers with lower internal moisture are less likely to develop mould, especially in dense-bud varieties or humid climates.
It’s important to highlight that water stress does not always increase the final yield. That is not its purpose. What it consistently improves is overall quality: more density, more resin, stronger aroma and a much more professional finish.
Precautions and common mistakes
Although the technique is simple, it is not risk-free. The most common mistake is taking drought too far. When the substrate dries out completely, roots can be damaged, leaves may show necrosis and the plant may enter a stress cycle that provides no benefit.

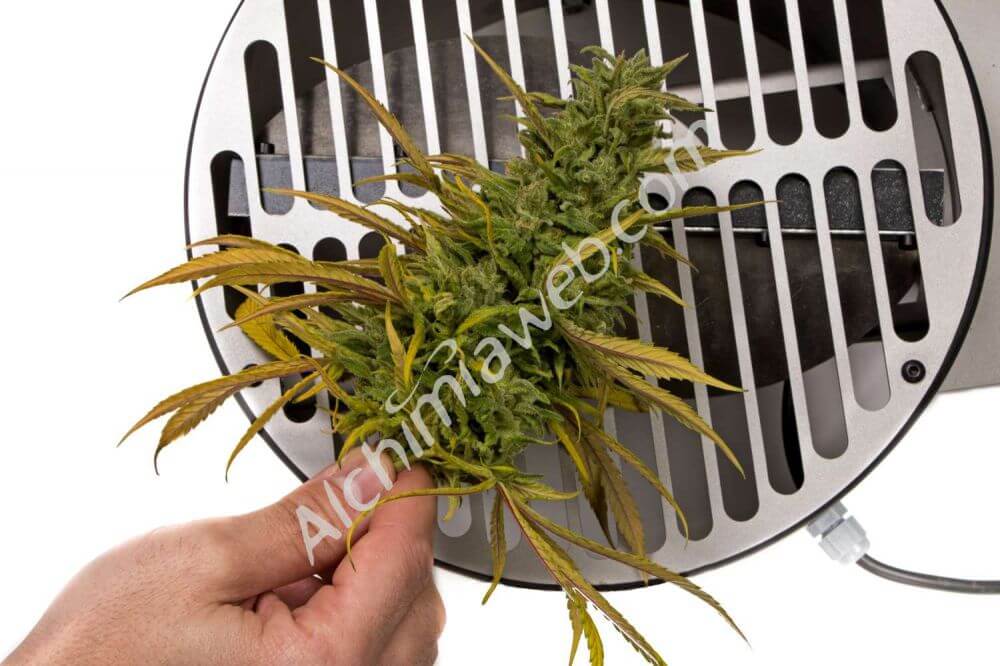
Dried cannabis plant
Another mistake is applying it at the wrong moment: during growth, preflowering or when flowers are still small. In these phases, the plant prioritizes basic structures: roots, stems, leaves and calyx formation. Interrupting that process can reduce final yield.
High temperatures can also amplify the damage caused by water deficit. With less water, the plant has a reduced ability to regulate its internal temperature. In warm environments, maintaining correct VPD and strong ventilation is essential.
An interesting ally in these situations is silicon. This element strengthens cell walls, improves tolerance to abiotic stress and reduces vulnerability to pests. At Alchimia, we recommend products such as Biotabs Silicium Flash or Atami B’Cuzz Silic Boost to support this type of technique.
A technique for growers who seek real quality
Controlled water stress is part of precision cultivation, where the goal is not to harvest more but to harvest better. It resembles what happens in viticulture: before harvest, winegrowers prefer dry weather, since excess water dilutes grape aromas and reduces sugar concentration (alcohol). In the same way, a cannabis plant with limited water availability concentrates more resin and terpenes.
Moreover, when combined with complementary techniques such as night-time temperature drop, use of natural biostimulants, VPD control or strategic pruning, water stress acts as a final enhancer that allows the plant to express its full genetic potential. Among the most widely used natural biostimulants are Aptus All-in-One Pellet and C02 Effect Led Nano, valued for supporting metabolic processes without saturating the substrate.
Scientific sources and recommended reading
Caplan, D., Dixon, M., & Zheng, Y. (2019). Increasing inflorescence dry weight and cannabinoid content in medical cannabis using controlled drought stress. HortScience, 54(5), 964–969.
Sharma, A., Singh, R., & Kumar, V. (2025). The effects of water-deficit stress on Cannabis sativa L. development and production of secondary metabolites: A review. Horticulturae, 11(6), 646.
Tanney, C. A. S., Backer, R. G. M., & Smith, D. L. (2021). Cannabis glandular trichomes: A cellular metabolite factory. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 721986.
Kurek, K., et al. (2024). Effects of water and wind stress on phytochemical diversity and insect communities in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Plants, 13(3), 474.
Burke, I. C., et al. (2024). Severe drought significantly reduces floral hemp yield, CBD, and THC concentrations. Scientia Horticulturae, 322, 112015.
Ahmad, P., et al. (2024). Interaction of water deficit and nanosilicon on Cannabis sativa L.: Growth and cannabinoid response. Physiologia Plantarum, 176(4), e14238.
The post Controlled water stress in cannabis: a technique to increase resin appeared first on Alchimia blog.