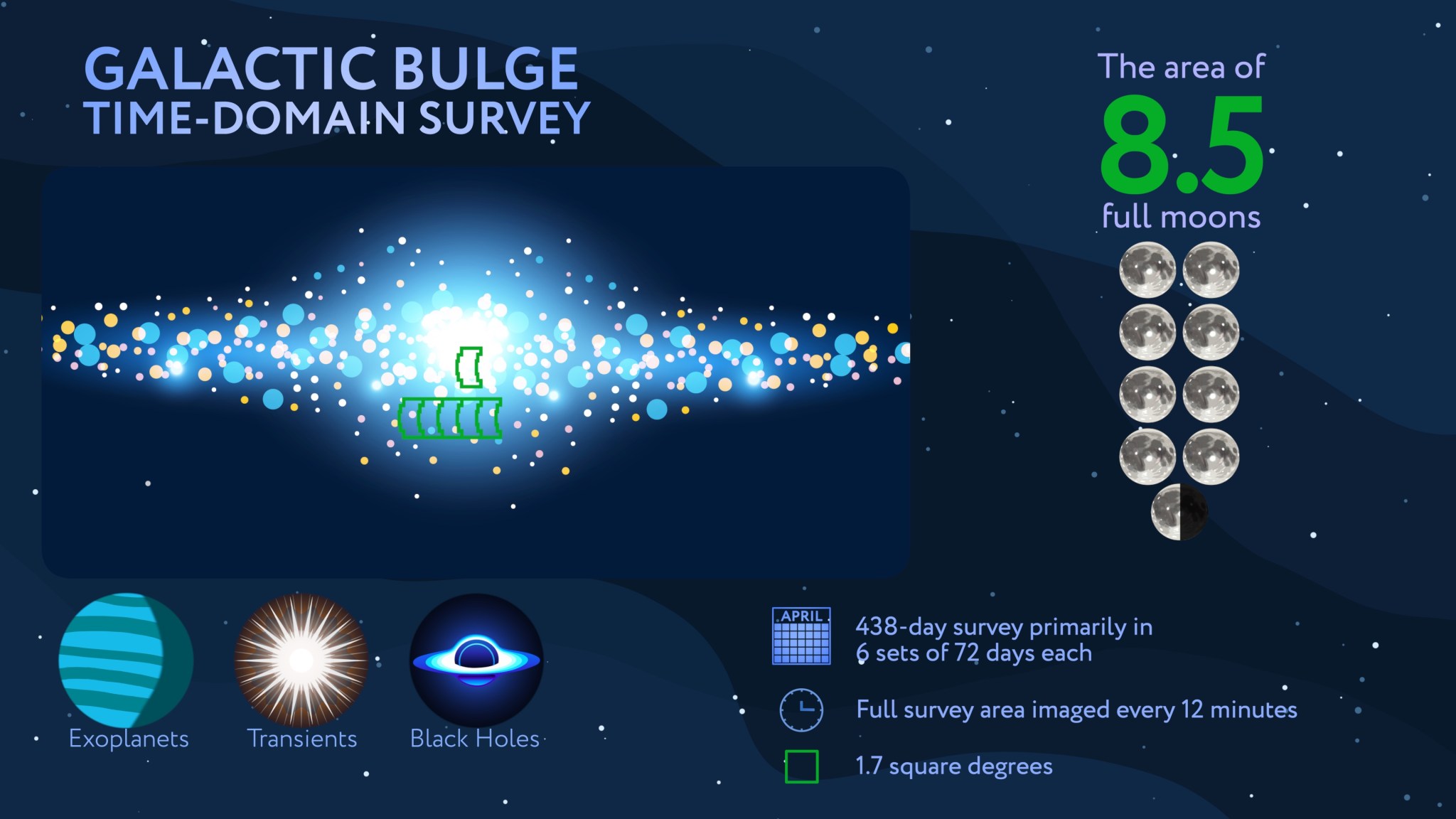
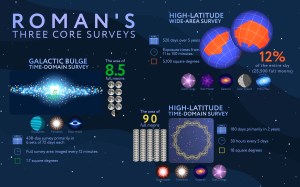
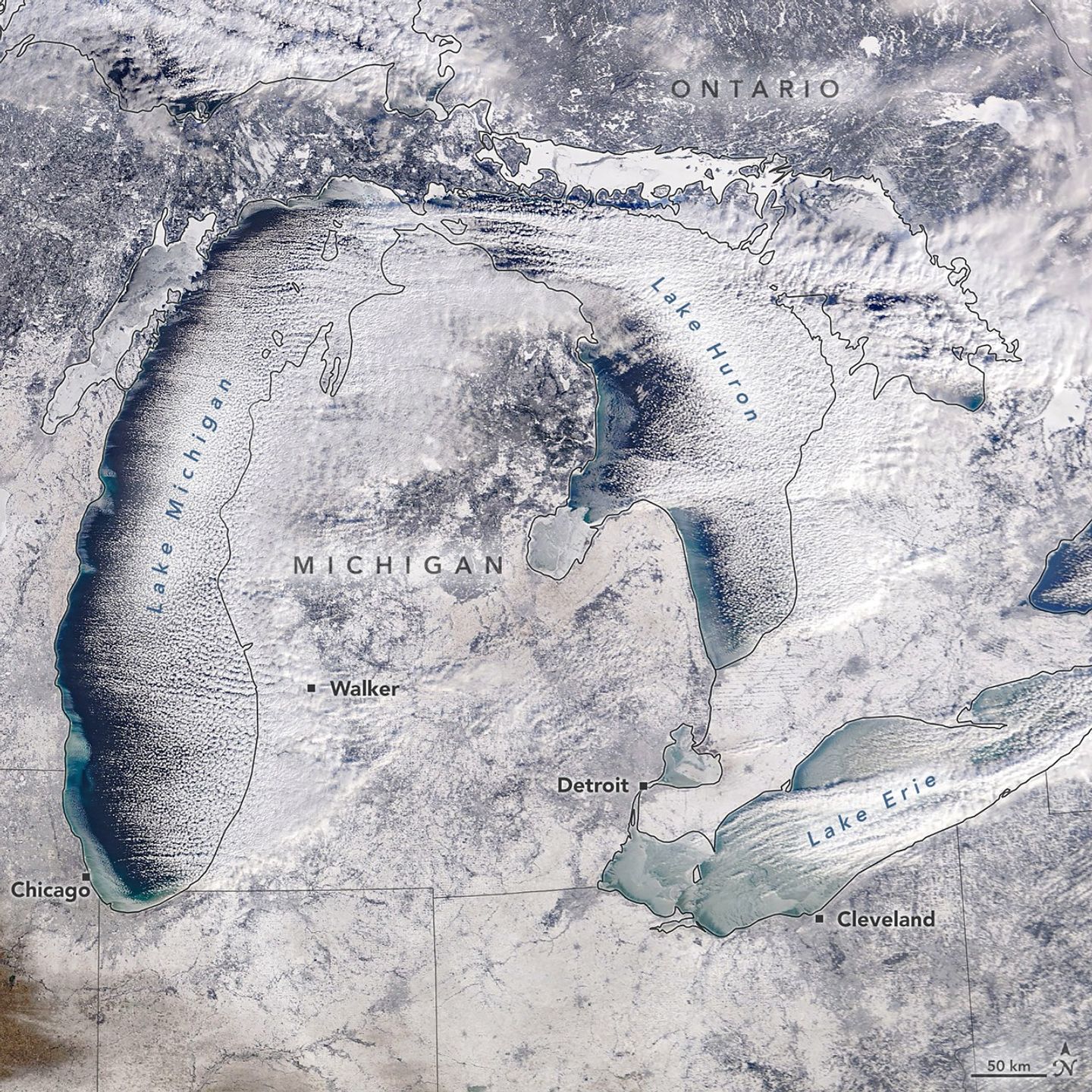
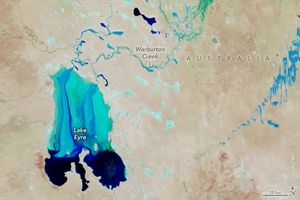
NASA Sets Briefings for SpaceX Crew-12 Mission to Space Station
NASA and its partners will discuss the upcoming crew rotation to the International Space Station during a pair of news conferences on Friday, Jan. 30, from the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
At 11 a.m. EST, mission leadership will discuss final launch and mission preparations in a news conference that will stream on the agency’s YouTube channel.
Next, the crew of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-12 mission will participate in a virtual news conference from NASA Johnson crew quarters at 1 p.m., also on the agency’s YouTube channel. Individual streams for each of the events will be available on that page. This is the final media opportunity with Crew-12 before they travel to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for launch.
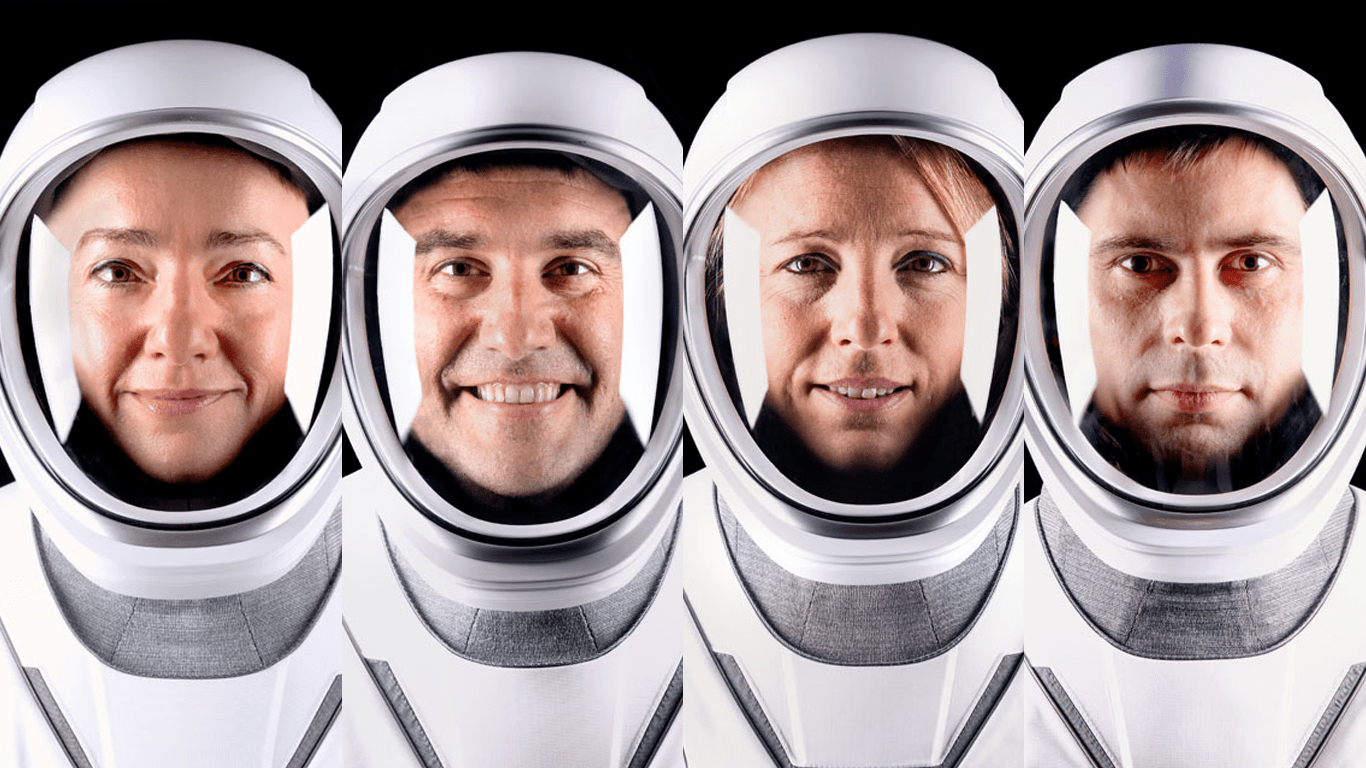
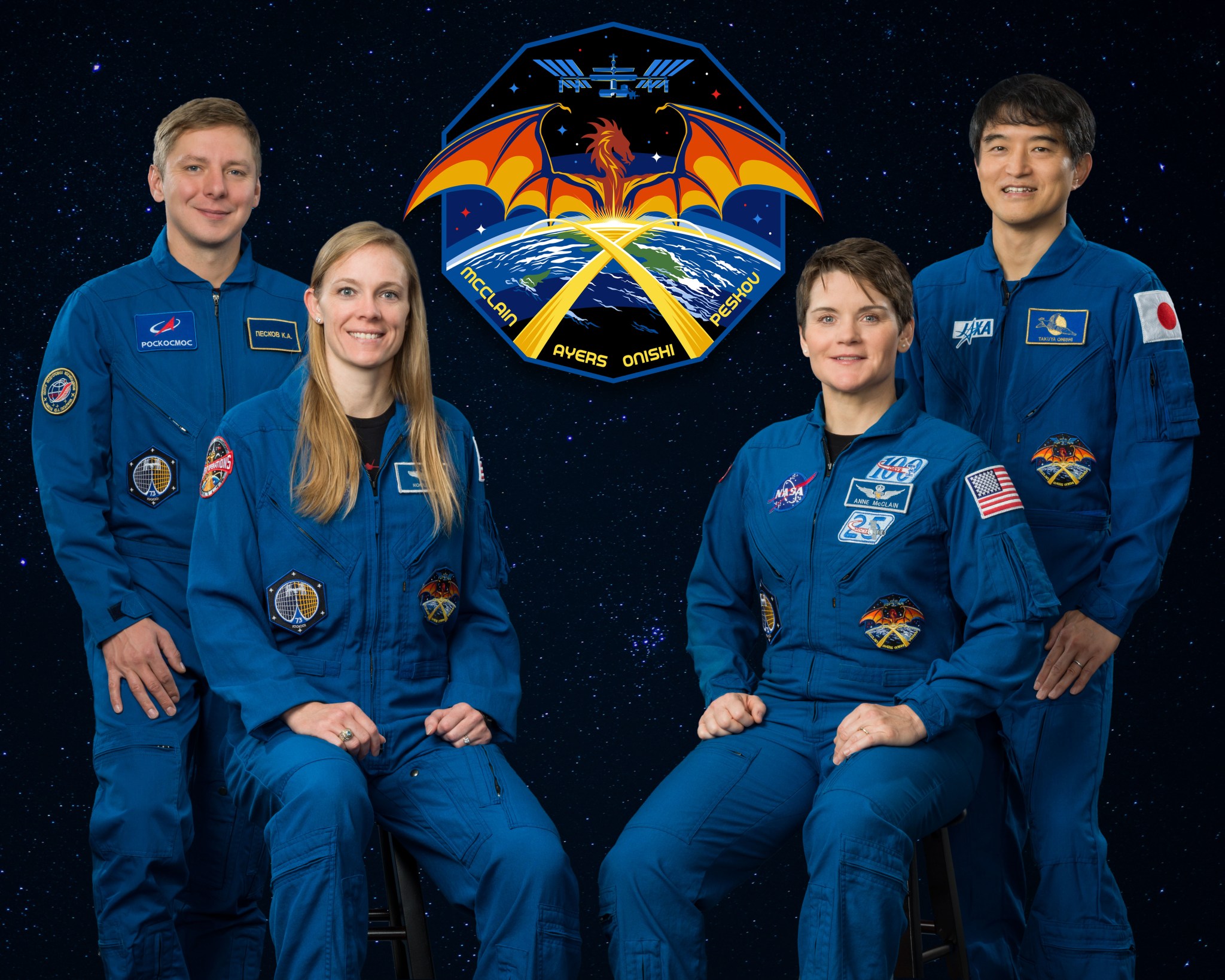
Crew-12 will carry NASA astronauts Jessica Meir and Jack Hathaway, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Sophie Adenot, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Andrey Fedyaev to the orbiting laboratory. The crew will launch aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft on the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The agency is working with SpaceX and its international partners to review options to advance the launch of Crew-12 from its original target date of Sunday, Feb. 15.
United States-based media interested in attending in person must contact the NASA Johnson newsroom no later than 5 p.m. CST on Thursday, Jan. 29, at 281-483-5111 or jsccommu@mail.nasa.gov.
Media wishing to join the news conferences by phone must contact the Johnson newsroom by 9:45 a.m. on the day of the event. A copy of NASA’s media accreditation policy is available online.
Briefing participants are as follows (all times Eastern and subject to change based on real-time operations):
11 a.m.: Mission Overview News Conference
- Ken Bowersox, associate administrator, NASA’s Space Operations Mission Directorate
- Steve Stich, manager, Commercial Crew Program, NASA Kennedy
- Dana Weigel, manager, International Space Station Program, NASA Johnson
- Andreas Mogensen, Human Exploration Group Leader, ESA
- SpaceX representative
1 p.m.: Crew News Conference
- Jessica Meir, Crew-12 commander, NASA
- Jack Hathaway, Crew-12 pilot, NASA
- Sophie Adenot, Crew-12 mission specialist, ESA
- Andrey Fedyaev, Crew-12 mission specialist, Roscosmos
This will be the second flight to the space station for Meir, who was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2013. The Caribou, Maine, native earned a bachelor’s degree in biology from Brown University, a master’s degree in space studies from the International Space University, and a doctorate in marine biology from Scripps Institution of Oceanography in San Diego. On her first spaceflight, Meir spent 205 days as a flight engineer during Expedition 61/62, and she completed the first three all-woman spacewalks with fellow NASA astronaut Christina Koch, totaling 21 hours and 44 minutes outside of the station. Since then, she has served in various roles, including assistant to the chief astronaut for commercial crew (SpaceX), deputy for the Flight Integration Division, and assistant to the chief astronaut for the human landing system.
A commander in the United States Navy, Hathaway was selected as part of the 2021 astronaut candidate class. This will be Hathaway’s first spaceflight. The South Windsor, Connecticut, native holds a bachelor’s degree in physics and history from the U.S. Naval Academy and master’s degrees in flight dynamics from Cranfield University and national security and strategic studies from the U.S. Naval War College, respectively. Hathaway also is a graduate of the Empire Test Pilot’s School, Fixed Wing Class 70 in 2011. At the time of his selection, Hathaway was deployed aboard the USS Truman, serving as Strike Fighter Squadron 81’s prospective executive officer. He has accumulated more than 2,500 flight hours in 30 different aircraft, including more than 500 carrier arrested landings and 39 combat missions.
The Crew-12 mission will be Adenot’s first spaceflight. Before her selection as an ESA astronaut in 2022, Adenot earned a degree in engineering from ISAE-SUPAERO in Toulouse, France, specializing in spacecraft and aircraft flight dynamics. She also earned a master’s degree in human factors engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. After earning her master’s degree, she became a helicopter cockpit design engineer at Airbus Helicopters and later served as a search and rescue pilot at Cazaux Air Base from 2008 to 2012. She then joined the High Authority Transport Squadron in Villacoublay, France, and served as a formation flight leader and mission captain from 2012 to 2017. Between 2019 and 2022, Adenot worked as a helicopter experimental test pilot in Cazaux Flight Test Center with DGA (Direction Générale de l’Armement – the French Defence Procurement Agency). She has logged more than 3,000 hours flying 22 different helicopters.
This will be Fedyaev’s second long-duration stay aboard the orbiting laboratory. He graduated from the Krasnodar Military Aviation Institute in 2004, specializing in aircraft operations and air traffic organization, and earned qualifications as a pilot engineer. Prior to his selection as a cosmonaut, he served as deputy commander of an Ilyushin-38 aircraft unit in the Kamchatka Region, logging more than 600 flight hours and achieving the rank of second-class military pilot. Fedyaev was selected for the Gagarin Research and Test Cosmonaut Training Center Cosmonaut Corps in 2012 and has served as a test cosmonaut since 2014. In 2023, he flew to the space station as a mission specialist during NASA’s SpaceX Crew-6 mission, spending 186 days in orbit, as an Expedition 69 flight engineer. For his achievements, Fedyaev was awarded the title Hero of the Russian Federation and received the Yuri Gagarin Medal.
For more information about the mission, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew
-end-
Joshua Finch / Jimi Russell
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1100
joshua.a.finch@nasa.gov / james.j.russell@nasa.gov
Sandra Jones / Joseph Zakrzewski
Johnson Space Center, Houston
281-483-5111
sandra.p.jones@nasa.gov / joseph.a.zakrzewski@nasa.gov